Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Antigen presentation plays positive roles in the regenerative response to cardiac injury in zebrafish
Antigen presentation plays positive roles in the regenerative response to cardiac injury in zebrafish
An adequate immune response is necessary to promote heart regeneration. Here, the authors identified a link between antigen presentation, immune cells, and endocardial cells during the regenerative response to cardiac injury in the adult zebrafish.
- João Cardeira-da-Silva
- , Qianchen Wang
- & Didier Y. R. Stainier
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative transcriptomics coupled to developmental grading via transgenic zebrafish reporter strains identifies conserved features in neutrophil maturation
Comparative transcriptomics coupled to developmental grading via transgenic zebrafish reporter strains identifies conserved features in neutrophil maturation
Maturation of innate immune cells is a graded stereotypic process which is often conserved across species. Here authors label distinct neutrophil leukocyte developmental stages via generating combinations of transgenic zebrafish reporter strains, followed by transcriptome analysis of different neutrophil maturation stages and comparison to the gene expression profile of developing neutrophils from humans and mice.
- Stefanie Kirchberger
- , Mohamed R. Shoeb
- & Martin Distel
-
Article
| Open Access Hand2 delineates mesothelium progenitors and is reactivated in mesothelioma
Hand2 delineates mesothelium progenitors and is reactivated in mesothelioma
The mesothelium supports homeostasis and regeneration, yet its development origins remain unclear. Here, the authors uncovered the earliest mesothelium progenitor cells in zebrafish, linking Hand2 gene function to mesothelium formation and its re-activation to mesothelioma tumors.
- Karin D. Prummel
- , Helena L. Crowell
- & Christian Mosimann
-
Article
| Open Access Smad4 controls signaling robustness and morphogenesis by differentially contributing to the Nodal and BMP pathways
Smad4 controls signaling robustness and morphogenesis by differentially contributing to the Nodal and BMP pathways
The role of the transcriptional effector SMAD4 in vertebrate embryo development remains unresolved. Here the authors show that in the absence of Smad4, dorsal/ventral embryo patterning is disrupted due to the loss of BMP signaling, while Nodal signaling is maintained, but insufficient for optimal endoderm specification.
- Luca Guglielmi
- , Claire Heliot
- & Caroline S. Hill
-
Article
| Open Access In situ and transcriptomic identification of microglia in synapse-rich regions of the developing zebrafish brain
In situ and transcriptomic identification of microglia in synapse-rich regions of the developing zebrafish brain
Microglia remodel synapses and engulf apoptotic cells. The molecular program underlying these distinct functions are unclear. Here, the authors identify distinct microglial subsets associated with synaptic vs. neurogenic regions of the developing zebrafish brain.
- Nicholas J. Silva
- , Leah C. Dorman
- & Anna V. Molofsky
-
Article
| Open Access Analysis of gene network bifurcation during optic cup morphogenesis in zebrafish
Analysis of gene network bifurcation during optic cup morphogenesis in zebrafish
The gene regulatory network controlling the bifurcation of common progenitors into the neural retina and retinal-pigmented epithelium programs remains poorly understood. Here the authors study transcriptome dynamics and chromatin accessibility during this process in zebrafish, revealing network redundancy, as well as context-dependent and sequential transcription factor activity.
- Lorena Buono
- , Jorge Corbacho
- & Juan-Ramón Martínez-Morales
-
Article
| Open Access Spatio-temporal mRNA tracking in the early zebrafish embryo
Spatio-temporal mRNA tracking in the early zebrafish embryo
Early stages of embryogenesis are known to depend on subcellular localization and transport of maternal mRNA, but systematic analyses have been hindered by a lack of methods for tracking of RNA. Here the authors combine spatially-resolved transcriptomics and single-cell RNA labeling to perform a spatio-temporal analysis of the transcriptome during early zebrafish development, revealing insights into this process.
- Karoline Holler
- , Anika Neuschulz
- & Jan Philipp Junker
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo biomolecular imaging of zebrafish embryos using confocal Raman spectroscopy
In vivo biomolecular imaging of zebrafish embryos using confocal Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopic imaging (RSI) can provide information on the chemical composition of a sample, but application to living organisms has lacked sufficient spatial resolution and signal strength. Here the authors apply confocal RSI to whole-mount zebrafish embryos to distinguish different infectious bacteria and to living zebrafish embryos to monitor the wound healing process.
- Håkon Høgset
- , Conor C. Horgan
- & Molly M. Stevens
-
Article
| Open Access Image quality guided smart rotation improves coverage in microscopy
Image quality guided smart rotation improves coverage in microscopy
Multi-view SPIM imaging can improve coverage of large samples such as whole embryos, but the procedure increases phototoxicity and involves manual steps that can introduce inconsistencies. Here the authors develop a smart rotation workflow that performs on-the-fly image analysis and identifies optimal set of views to maximize sample coverage.
- Jiaye He
- & Jan Huisken
-
Article
| Open Access Zika virus enhances monocyte adhesion and transmigration favoring viral dissemination to neural cells
Zika virus enhances monocyte adhesion and transmigration favoring viral dissemination to neural cells
Zika virus (ZIKV) can infect the central nervous system, but it is not clear how it reaches the brain. Here, Ayala-Nunez et al. show in ex vivo and in vivo models that ZIKV can hitch a ride in monocytes in a Trojan Horse manner to cross the endothelium and disseminate the virus.
- Nilda Vanesa Ayala-Nunez
- , Gautier Follain
- & Raphael Gaudin
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of amyloid beta toxicity in zebrafish with a chaperone-gold nanoparticle dual strategy
Inhibition of amyloid beta toxicity in zebrafish with a chaperone-gold nanoparticle dual strategy
Treating Alzheimer’s disease, one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases, is of wide interest. Here, the authors report on the development of casein coated gold nanoparticles which were able to cross the blood brain barrier and protect against amyloid beta toxicity in a zebrafish model.
- Ibrahim Javed
- , Guotao Peng
- & Sijie Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Stem cell proliferation is induced by apoptotic bodies from dying cells during epithelial tissue maintenance
Stem cell proliferation is induced by apoptotic bodies from dying cells during epithelial tissue maintenance
Damaged epithelial tissues are known to compensate for cell death through compensatory cell divisions to maintain epithelial integrity. Here, the authors show in living epithelia that dying cells stimulate adjacent stem cells to divide through caspase-dependent production of Wnt8a-containing apoptotic bodies.
- Courtney K. Brock
- , Stephen T. Wallin
- & George T. Eisenhoffer
-
Article
| Open Access tmem33 is essential for VEGF-mediated endothelial calcium oscillations and angiogenesis
tmem33 is essential for VEGF-mediated endothelial calcium oscillations and angiogenesis
Calcium signalling downstream of VEGF is essential for VEGF-induced angiogenesis. Here Savage et al. show that Transmembrane Protein 33 (TMEM33) is required for angiogenesis and the endothelial calcium response to VEGF, revealing a function for TMEM33 in multicellular organisms.
- Aaron M. Savage
- , Sathishkumar Kurusamy
- & Robert N. Wilkinson
-
Article
| Open Access Heart enhancers with deeply conserved regulatory activity are established early in zebrafish development
Heart enhancers with deeply conserved regulatory activity are established early in zebrafish development
During early embryogenesis, critical cardiac specification events occur. Here the authors isolate cardiac progenitor cells from early zebrafish embryos and characterize accessible chromatin regions specific to this cell population, finding that many of these regions overlap with conserved non-coding elements that are ortholgous to accessible chromatin regions in human.
- Xuefei Yuan
- , Mengyi Song
- & Michael D. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates VE-cadherin-mediated anastomosis of brain capillaries by counteracting S1pr1 signaling
Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates VE-cadherin-mediated anastomosis of brain capillaries by counteracting S1pr1 signaling
Wnt signaling is known to regulate the formation of the blood-brain barrier. Here Hübner et al. dissect the underlying mechanisms using high resolution live imaging in zebrafish, and find that Wnt regulates anastomosis of angiogenic sprouts in the brain by counteracting sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signaling.
- Kathleen Hübner
- , Pauline Cabochette
- & Wiebke Herzog
-
Article
| Open Access Systems glycomics of adult zebrafish identifies organ-specific sialylation and glycosylation patterns
Systems glycomics of adult zebrafish identifies organ-specific sialylation and glycosylation patterns
Zebrafish is a popular system for studying the molecular basis of glycan-related human diseases. Here, the authors present glycomic profiles of eight zebrafish organs and establish the organ-specific expression patterns of related biosynthetic enzymes.
- Nao Yamakawa
- , Jorick Vanbeselaere
- & Yann Guerardel
-
Article
| Open Access Iridophores as a source of robustness in zebrafish stripes and variability in Danio patterns
Iridophores as a source of robustness in zebrafish stripes and variability in Danio patterns
Iridophores interact with other cells to give zebrafish their stripes, but what drives their form shifts is unknown. Here, modelling allows the authors to identify robust cues that may specify iridophore form and to find changes to these cues that likely account for altered patterns on related fish.
- Alexandria Volkening
- & Björn Sandstede
-
Article
| Open Access Lipoprotein lipase regulates hematopoietic stem progenitor cell maintenance through DHA supply
Lipoprotein lipase regulates hematopoietic stem progenitor cell maintenance through DHA supply
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) hydrolyzes triglycerides to supply free fatty acids (FFAs) to muscle for energy and adipocytes for storage. Here, the authors demonstrate that Lpl and its product, the FFA docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are required for haematopoietic stem progenitor cell expansion during zebrafish embryogenesis.
- Chao Liu
- , Tianxu Han
- & Yury I. Miller
-
Article
| Open Access Tbx5a lineage tracing shows cardiomyocyte plasticity during zebrafish heart regeneration
Tbx5a lineage tracing shows cardiomyocyte plasticity during zebrafish heart regeneration
It is not clear if it is the embryonic origin or anatomical location of cardiomyocytes that restrict their contribution to zebrafish heart regeneration. Here, the authors show a plasticity of embryonic precursors following tbx5a fate mapping and that trabecular cardiomyocytes help to rebuild the cortical myocardium.
- Héctor Sánchez-Iranzo
- , María Galardi-Castilla
- & Nadia Mercader
-
Article
| Open Access Small molecule screen in embryonic zebrafish using modular variations to target segmentation
Small molecule screen in embryonic zebrafish using modular variations to target segmentation
Chemical screens can identify small molecules that affect biological development, with potential therapeutic value. Here, the authors use a modular approach in a screen in zebrafish embryos, varying concentration, genotype and timing to target segmentation disorders, birth defects that affect the spinal column.
- Sandra Richter
- , Ulrike Schulze
- & Andrew C. Oates
-
Article
| Open Access Different developmental histories of beta-cells generate functional and proliferative heterogeneity during islet growth
Different developmental histories of beta-cells generate functional and proliferative heterogeneity during islet growth
Βeta-cells have recently been shown to be heterogeneous with regard to morphology and function. Here, the authors show that β-cells in zebrafish switch from proliferative to functional states with increasing time since β-cell birth, leading to functional and proliferative heterogeneity.
- Sumeet Pal Singh
- , Sharan Janjuha
- & Nikolay Ninov
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable base editing of zebrafish genome using a modified CRISPR-Cas9 system
Programmable base editing of zebrafish genome using a modified CRISPR-Cas9 system
The use of base editing enables precise genetic modifications in model animals. Here the authors show high efficient single-base editing in zebrafish using modified Cas9 and its VQR variant with an altered PAM specificity.
- Yihan Zhang
- , Wei Qin
- & Shuo Lin
-
Article
| Open Access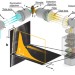 Hyperspectral light sheet microscopy
Hyperspectral light sheet microscopy
Multicolour information is required to study the complex interplay of biological tissues. Here, Jahr et al.acquire spectral information at high resolution for each pixel in a hyperspectral light sheet microscope, while maintaining its perpendicular illumination and low phototoxicity.
- Wiebke Jahr
- , Benjamin Schmid
- & Jan Huisken
-
Article
| Open Access Chamber identity programs drive early functional partitioning of the heart
Chamber identity programs drive early functional partitioning of the heart
The heart forms from combining the first with the second heart field, which in mammals creates left and right ventricle. Here transgenic zebrafish and physiology studies reveal that transcription factors controlling septation in mammals already in teleosts guide muscle coupling by controlling the relative contribution of the two fields to the heart.
- Christian Mosimann
- , Daniela Panáková
- & Leonard I. Zon
-
Article
| Open Access Effective heritable gene knockdown in zebrafish using synthetic microRNAs
Effective heritable gene knockdown in zebrafish using synthetic microRNAs
Zebrafish is a model system for which for no reliable heritable gene silencing method is available. Here the authors provide a system for heritable miRNA-mediated knockdown and demonstrate tunable silencing of the smn1gene that recapitulate different forms of spinal muscular atrophy.
- Jean Giacomotto
- , Silke Rinkwitz
- & Thomas S. Becker
-
Article
| Open Access Pigment cell movement is not required for generation of Turing patterns in zebrafish skin
Pigment cell movement is not required for generation of Turing patterns in zebrafish skin
Pigment pattern formation in zebrafish depends on the interactions between the pigment cells. Here the authors present a mathematical model based on mutual interaction of pigment cells in the absence of cell motion, revising the current model of the pattern formation that relies on reaction–diffusion Turing patterns.
- D. Bullara
- & Y. De Decker

 The miR-144/Hmgn2 regulatory axis orchestrates chromatin organization during erythropoiesis
The miR-144/Hmgn2 regulatory axis orchestrates chromatin organization during erythropoiesis