Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access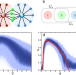 Coherence resonance in influencer networks
Coherence resonance in influencer networks
Influencer networks include a small set of highly-connected nodes and can reach synchrony only via strong node interaction. Tönjes et al. show that introducing an optimal amount of noise enhances synchronization of such networks, which may be relevant for neuroscience or opinion dynamics applications.
- Ralf Tönjes
- , Carlos E. Fiore
- & Tiago Pereira
-
Article
| Open Access Detection of eye contact with deep neural networks is as accurate as human experts
Detection of eye contact with deep neural networks is as accurate as human experts
Eye contact is a key social behavior and its measurement could facilitate the diagnosis and treatment of autism. Here the authors show that a deep neural network model can detect eye contact as accurately has human experts.
- Eunji Chong
- , Elysha Clark-Whitney
- & James M. Rehg
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying accuracy and heterogeneity in single-molecule super-resolution microscopy
Quantifying accuracy and heterogeneity in single-molecule super-resolution microscopy
Standard benchmarking of single-molecule localization microscopy cannot quantify nanoscale accuracy of arbitrary datasets. Here, the authors present Wasserstein-induced flux, a method using a chosen perturbation and knowledge of the imaging system to measure confidence of individual localizations.
- Hesam Mazidi
- , Tianben Ding
- & Matthew D. Lew
-
Article
| Open Access A social engineering model for poverty alleviation
A social engineering model for poverty alleviation
Current inequality and market consumption modelling appears to be subjective. Here the authors combined all three axes of poverty modelling - Engel-Krishnakumar’s microeconomics, Aoki-Chattopadhyay’s mathematical precept and found that multivariate construction is a key component of economic data analysis, implying all modes of income and expenditure need to be considered to arrive at a proper weighted prediction of poverty.
- Amit K. Chattopadhyay
- , T. Krishna Kumar
- & Iain Rice
-
Article
| Open Access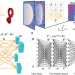 Meta-neural-network for real-time and passive deep-learning-based object recognition
Meta-neural-network for real-time and passive deep-learning-based object recognition
The authors present a passive meta-neural-network for real-time recognition of objects by analysis of acoustic scattering. It consists of unit cells termed meta-neurons, mimicking an analogous neural network for classical waves, and is shown to recognise handwritten digits and misaligned orbital-angular-momentum vortices.
- Jingkai Weng
- , Yujiang Ding
- & Jianchun Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access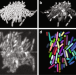 Non-invasive single-cell morphometry in living bacterial biofilms
Non-invasive single-cell morphometry in living bacterial biofilms
Accurate cell detection in dense bacterial biofilms is challenging. Here, the authors report an image analysis pipeline that is able to accurately segment and classify single bacterial cells in 3D fluorescence images: Bacterial Cell Morphometry 3D (BCM3D).
- Mingxing Zhang
- , Ji Zhang
- & Andreas Gahlmann
-
Article
| Open Access Training confounder-free deep learning models for medical applications
Training confounder-free deep learning models for medical applications
The presence of confounding effects is one of the most critical challenges in using deep learning to advance discovery in medical imaging studies. Here, the authors introduce an end-to-end approach for deriving features invariant to confounding factors as inputs to prediction models.
- Qingyu Zhao
- , Ehsan Adeli
- & Kilian M. Pohl
-
Article
| Open Access DNA synthesis for true random number generation
DNA synthesis for true random number generation
Large volumes of true random numbers are needed for increasing requirements of secure data encryption. Here the authors use the stochastic nature of DNA synthesis to obtain millions of gigabytes of unbiased randomness.
- Linda C. Meiser
- , Julian Koch
- & Robert N. Grass
-
Article
| Open Access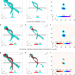 Self-attenuation of extreme events in Navier–Stokes turbulence
Self-attenuation of extreme events in Navier–Stokes turbulence
Whether a turbulent flow would inevitably develop singular behavior at the smallest length scales is an ongoing intriguing debate. Using large-scale numerical simulations, Buaria et al. find an unexpected non-linear mechanism which counteracts local vorticity growth instead of enabling it.
- Dhawal Buaria
- , Alain Pumir
- & Eberhard Bodenschatz
-
Article
| Open Access Discontinuous transition to loop formation in optimal supply networks
Discontinuous transition to loop formation in optimal supply networks
Supply networks with optimal structure do not contain loops but these can arise as a result of damages or fluctuations. Here Kaiser et al. uncover the mechanisms of loop formation, predict their location and draw analogies with loop formation in biological networks such as plants and animal vasculature.
- Franz Kaiser
- , Henrik Ronellenfitsch
- & Dirk Witthaut
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning with physicochemical relationships: solubility prediction in organic solvents and water
Machine learning with physicochemical relationships: solubility prediction in organic solvents and water
Accurate prediction of solubility represents a challenge for traditional computational approaches due to the complex nature of phenomena involved. Here the authors report a successful approach to solubility prediction in organic solvents and water using combination of machine learning and computational chemistry.
- Samuel Boobier
- , David R. J. Hose
- & Bao N. Nguyen
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-site transportability of an explainable artificial intelligence model for acute kidney injury prediction
Cross-site transportability of an explainable artificial intelligence model for acute kidney injury prediction
Artificial intelligence (AI) has demonstrated promise in predicting acutekidney injury (AKI), however, clinical adoption of these models requires interpretability and transportability across sites. Here, the authors develop an AKI prediction model and a measure for model transportability across six independent health systems.
- Xing Song
- , Alan S. L. Yu
- & Mei Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Designing accurate emulators for scientific processes using calibration-driven deep models
Designing accurate emulators for scientific processes using calibration-driven deep models
The success of machine learning for scientific discovery normally depends on how well the inherent assumptions match the problem in hand. Here, Thiagarajan et al. alleviate this constraint by allowing the change of optimization criterion in a data-driven approach to emulate complex scientific processes.
- Jayaraman J. Thiagarajan
- , Bindya Venkatesh
- & Brian Spears
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning-enabled multi-organ segmentation in whole-body mouse scans
Deep learning-enabled multi-organ segmentation in whole-body mouse scans
Organ segmentation of whole-body mouse images is essential for quantitative analysis, but is tedious and error-prone. Here the authors develop a deep learning pipeline to segment major organs and the skeleton in volumetric whole-body scans in less than a second, and present probability maps and uncertainty estimates.
- Oliver Schoppe
- , Chenchen Pan
- & Bjoern H. Menze
-
Article
| Open Access Navigating the landscape of multiplayer games
Navigating the landscape of multiplayer games
Multiplayer games can be used as testbeds for the development of learning algorithms for artificial intelligence. Omidshafiei et al. show how to characterize and compare such games using a graph-based approach, generating new games that could potentially be interesting for training in a curriculum.
- Shayegan Omidshafiei
- , Karl Tuyls
- & Rémi Munos
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid low-voltage physical unclonable function based on inkjet-printed metal-oxide transistors
Hybrid low-voltage physical unclonable function based on inkjet-printed metal-oxide transistors
Designing efficient system for digital connectivity preserving information security remains a challenge. Here, the authors present hardware-intrinsic security solutions based on physical unclonable functions incorporating an inkjet-printed core circuit as an intrinsic source of entropy, integrated into a silicon-based CMOS system environment.
- Alexander Scholz
- , Lukas Zimmermann
- & Jasmin Aghassi-Hagmann
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple imputation for analysis of incomplete data in distributed health data networks
Multiple imputation for analysis of incomplete data in distributed health data networks
Distributed health data networks (DHDNs) leverage data from multiple healthcare systems, but often face major analytical challenges in the presence of missing data. This paper develops distributed multiple imputation methods that do not require sharing subject-level data across health systems.
- Changgee Chang
- , Yi Deng
- & Qi Long
-
Article
| Open Access Mutualistic networks emerging from adaptive niche-based interactions
Mutualistic networks emerging from adaptive niche-based interactions
Nested and modular patterns are vastly observed in mutualistic networks across genres and geographic conditions. Here, the authors show a unified mechanism that underlies the assembly and evolution of such networks, based on adaptive niche interactions of the participants.
- Weiran Cai
- , Jordan Snyder
- & Raissa M. D’Souza
-
Perspective
| Open Access The misuse of colour in science communication
The misuse of colour in science communication
The accurate representation of data is essential in science communication, however, colour maps that visually distort data through uneven colour gradients or are unreadable to those with colour vision deficiency remain prevalent. Here, the authors present a simple guide for the scientific use of colour and highlight ways for the scientific community to identify and prevent the misuse of colour in science.
- Fabio Crameri
- , Grace E. Shephard
- & Philip J. Heron
-
Article
| Open Access Capturing human categorization of natural images by combining deep networks and cognitive models
Capturing human categorization of natural images by combining deep networks and cognitive models
Theories of human categorization have traditionally been evaluated in the context of simple, low-dimensional stimuli. In this work, the authors use a large dataset of human behavior over 10,000 natural images to re-evaluate these theories, revealing interesting differences from previous results.
- Ruairidh M. Battleday
- , Joshua C. Peterson
- & Thomas L. Griffiths
-
Article
| Open Access Detecting and tracking drift in quantum information processors
Detecting and tracking drift in quantum information processors
Time-dependent errors are one of the main obstacles to fully-fledged quantum information processing. Here, the authors develop a general methodology to monitor time-dependent errors, which could be used to make other characterisation protocols time-resolved, and demonstrate it on a trapped-ion qubit.
- Timothy Proctor
- , Melissa Revelle
- & Kevin Young
-
Article
| Open Access Low cost DNA data storage using photolithographic synthesis and advanced information reconstruction and error correction
Low cost DNA data storage using photolithographic synthesis and advanced information reconstruction and error correction
The current bottleneck for DNA data storage systems is the cost and speed of synthesis. Here, the authors use inexpensive, massively parallel light-directed synthesis and correct for a high error rate with a pipeline of encoding and reconstruction algorithms.
- Philipp L. Antkowiak
- , Jory Lietard
- & Robert N. Grass
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum chemical accuracy from density functional approximations via machine learning
Quantum chemical accuracy from density functional approximations via machine learning
High-level ab initio quantum chemical methods carry a high computational burden, thus limiting their applicability. Here, the authors employ machine learning to generate coupled-cluster energies and forces at chemical accuracy for geometry optimization and molecular dynamics from DFT densities.
- Mihail Bogojeski
- , Leslie Vogt-Maranto
- & Kieron Burke
-
Article
| Open Access Optical framed knots as information carriers
Optical framed knots as information carriers
Beam shaping methods can generate optical fields with nontrivial topologies, which are invariant against perturbations and thus interesting for information encoding. Here, the authors introduce the realization of framed optical knots to encode programs with the conjoined use of prime factorization.
- Hugo Larocque
- , Alessio D’Errico
- & Ebrahim Karimi
-
Article
| Open Access A network model of Italy shows that intermittent regional strategies can alleviate the COVID-19 epidemic
A network model of Italy shows that intermittent regional strategies can alleviate the COVID-19 epidemic
An ongoing global debate concerns effective and sustainable lockdown release strategies in the current pandemic. Here, the authors implement a network model at healthcare-relevant spatial scale to show that coordinated local strategies can be effective in containing further resurgence of the disease.
- Fabio Della Rossa
- , Davide Salzano
- & Mario di Bernardo
-
Article
| Open Access A deep learning approach to programmable RNA switches
A deep learning approach to programmable RNA switches
RNA can be used as a programmable tool for detection of biological analytes. Here the authors use deep neural networks to predict toehold switch functionality in synthetic biology applications.
- Nicolaas M. Angenent-Mari
- , Alexander S. Garruss
- & James J. Collins
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid vessel segmentation and reconstruction of head and neck angiograms using 3D convolutional neural network
Rapid vessel segmentation and reconstruction of head and neck angiograms using 3D convolutional neural network
Manual postprocessing of computed tomography angiography (CTA) images is extremely labor intensive and error prone. Here, the authors propose an artificial intelligence reconstruction system that can automatically achieve CTA reconstruction in healthcare services.
- Fan Fu
- , Jianyong Wei
- & Jie Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning identifies scale-free properties in disordered materials
Machine learning identifies scale-free properties in disordered materials
The performance of a trained neural network may be biased even by generic features of its architecture. Yu et al. ask for the disordered lattice of atoms producing a certain wave localization and the network prefers to answer with power-law distributed displacements.
- Sunkyu Yu
- , Xianji Piao
- & Namkyoo Park
-
Article
| Open Access Impacts of solar intermittency on future photovoltaic reliability
Impacts of solar intermittency on future photovoltaic reliability
The intermittency of solar resources is one of the primary challenges for the large-scale integration of the renewable energy. Here Yin et al. used satellite data and climate model outputs to evaluate the geographic patterns of future solar power reliability, highlighting the tradeoff between the maximum potential power and the power reliability.
- Jun Yin
- , Annalisa Molini
- & Amilcare Porporato
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting heterogeneous ice nucleation with a data-driven approach
Predicting heterogeneous ice nucleation with a data-driven approach
Heterogenous ice nucleation is a ubiquitous phenomenon, but predicting the ice nucleation ability of a substrate is challenging. Here the authors develop a machine-learning data-driven approach to predict the ice nucleation ability of substrates, which is based on four descriptors related to physical properties of the interface.
- Martin Fitzner
- , Philipp Pedevilla
- & Angelos Michaelides
-
Article
| Open Access Using synchronized oscillators to compute the maximum independent set
Using synchronized oscillators to compute the maximum independent set
Designing efficient analog dynamical systems for solving hard optimization problems remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a dynamical system of thirty oscillators with reconfigurable coupling to compute optimal/near-optimal solutions to the hard Maximum Independent Set problem with over 90% accuracy.
- Antik Mallick
- , Mohammad Khairul Bashar
- & Nikhil Shukla
-
Article
| Open Access Factor analysis of ancient population genomic samples
Factor analysis of ancient population genomic samples
Principal component analysis is often used in studies of ancient DNA, but does not account for the age of the samples. Here, the authors present a factor analysis (FA) which corrects for this by including the effect of allele frequency drift over time.
- Olivier François
- & Flora Jay
-
Article
| Open Access Arrangement and symmetry of the fungal E3BP-containing core of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
Arrangement and symmetry of the fungal E3BP-containing core of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) is a multienzyme complex connecting glycolysis to mitochondrial oxidation of pyruvate. Cryo-EM analysis of PDC from Neurospora crassa reveals localization of fungi-specific protein X (PX) and confirms that it functions like the mammalian E3BP, recruiting the E3 component of PDC.
- B. O. Forsberg
- , S. Aibara
- & E. Lindahl
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering temporal changes in Europe’s population density patterns using a data fusion approach
Uncovering temporal changes in Europe’s population density patterns using a data fusion approach
Official data on the distribution of human population often ignores the changing spatio-temporal densities resulting from mobility. Here, authors apply an approach combining official statistics and geospatial data to assess intraday and monthly population variations at continental scale at 1 km2 resolution.
- Filipe Batista e Silva
- , Sérgio Freire
- & Carlo Lavalle
-
Article
| Open Access Autoreservoir computing for multistep ahead prediction based on the spatiotemporal information transformation
Autoreservoir computing for multistep ahead prediction based on the spatiotemporal information transformation
Predicting future values of a short time series remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose an auto-reservoir computing framework, which achieved accurate and robust multistep ahead prediction by transforming high-dimensional data into temporal dynamics.
- Pei Chen
- , Rui Liu
- & Luonan Chen
-
Perspective
| Open Access Designing and understanding light-harvesting devices with machine learning
Designing and understanding light-harvesting devices with machine learning
Photon-induced charge separation phenomena are at the heart of light-harvesting applications but challenging to be described by quantum mechanical models. Here the authors illustrate the potential of machine-learning approaches towards understanding the fundamental processes governing electronic excitations.
- Florian Häse
- , Loïc M. Roch
- & Alán Aspuru-Guzik
-
Article
| Open Access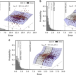 Identifying domains of applicability of machine learning models for materials science
Identifying domains of applicability of machine learning models for materials science
Machine learning models insufficient for certain screening tasks can still provide valuable predictions in specific sub-domains of the considered materials. Here, the authors introduce a diagnostic tool to detect regions of low expected model error as demonstrated for the case of transparent conducting oxides.
- Christopher Sutton
- , Mario Boley
- & Matthias Scheffler
-
Article
| Open Access Transforming machine translation: a deep learning system reaches news translation quality comparable to human professionals
Transforming machine translation: a deep learning system reaches news translation quality comparable to human professionals
The quality of human language translation has been thought to be unattainable by computer translation systems. Here the authors present CUBBITT, a deep learning system that outperforms professional human translators in retaining text meaning in English-to-Czech news translation, and validate the system on English-French and English-Polish language pairs.
- Martin Popel
- , Marketa Tomkova
- & Zdeněk Žabokrtský
-
Article
| Open Access Committee machines—a universal method to deal with non-idealities in memristor-based neural networks
Committee machines—a universal method to deal with non-idealities in memristor-based neural networks
Designing reliable and energy-efficient memristor-based artificial neural networks remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a technology-agnostic approach, committee machines, which increases the inference accuracy of memristive neural networks that suffer from device variability, faulty devices, random telegraph noise and line resistance.
- D. Joksas
- , P. Freitas
- & A. Mehonic
-
Article
| Open Access Unique universal scaling in nanoindentation pop-ins
Unique universal scaling in nanoindentation pop-ins
Although power laws are observed during nanoindentation and the power-law exponents are estimated to be approximately 1.5-1.6 for face-centered cubic metals, the origin of the exponent remains unclear. In this paper, we show the power-law statistics in pop-in magnitudes and unveil the nature of the exponent.
- Yuji Sato
- , Shuhei Shinzato
- & Shigenobu Ogata
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning enables completely automatic tuning of a quantum device faster than human experts
Machine learning enables completely automatic tuning of a quantum device faster than human experts
To optimize operating conditions of large scale semiconductor quantum devices, a large parameter space has to be explored. Here, the authors report a machine learning algorithm to navigate the entire parameter space of gate-defined quantum dot devices, showing about 180 times faster than a pure random search.
- H. Moon
- , D. T. Lennon
- & N. Ares
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial intelligence for the detection of COVID-19 pneumonia on chest CT using multinational datasets
Artificial intelligence for the detection of COVID-19 pneumonia on chest CT using multinational datasets
Chest CT is emerging as a valuable diagnostic tool for clinical management of COVID-19 associated lung disease. Here, the authors present a multinational study on the application of deep learning algorithms for COVID-19 diagnosis against multiple lung conditions as controls.
- Stephanie A. Harmon
- , Thomas H. Sanford
- & Baris Turkbey
-
Article
| Open Access Brain-inspired replay for continual learning with artificial neural networks
Brain-inspired replay for continual learning with artificial neural networks
One challenge that faces artificial intelligence is the inability of deep neural networks to continuously learn new information without catastrophically forgetting what has been learnt before. To solve this problem, here the authors propose a replay-based algorithm for deep learning without the need to store data.
- Gido M. van de Ven
- , Hava T. Siegelmann
- & Andreas S. Tolias
-
Article
| Open Access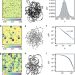 Spatiotemporal data analysis with chronological networks
Spatiotemporal data analysis with chronological networks
Extracting central information from ever-growing data generated in our lives calls for new data mining methods. Ferreira et al. show a simple model, called chronnets, that can capture frequent patterns, spatial changes, outliers, and spatiotemporal clusters.
- Leonardo N. Ferreira
- , Didier A. Vega-Oliveros
- & Elbert E. N. Macau
-
Article
| Open Access Improving the accuracy of medical diagnosis with causal machine learning
Improving the accuracy of medical diagnosis with causal machine learning
In medical diagnosis a doctor aims to explain a patient’s symptoms by determining the diseases causing them, while existing diagnostic algorithms are purely associative. Here, the authors reformulate diagnosis as a counterfactual inference task and derive new counterfactual diagnostic algorithms.
- Jonathan G. Richens
- , Ciarán M. Lee
- & Saurabh Johri
-
Article
| Open Access Clustering earthquake signals and background noises in continuous seismic data with unsupervised deep learning
Clustering earthquake signals and background noises in continuous seismic data with unsupervised deep learning
The authors here tackle the problem that too much seismic data is acquired worldwide to be evaluated in a timely fashion. Seydoux and colleagues develop a machine learning framework that can detect and cluster seismic signals in continuous seismic records.
- Léonard Seydoux
- , Randall Balestriero
- & Richard Baraniuk
-
Article
| Open Access Role of optimization algorithms based fuzzy controller in achieving induction motor performance enhancement
Role of optimization algorithms based fuzzy controller in achieving induction motor performance enhancement
Though optimization algorithms for fuzzy logic controller (FIC)-based three-phase induction motor (TIM) systems are attractive for improving efficiency, existing methods have limited search capability. Here, the authors report a quantum-inspired lightning search algorithm with enhanced performance.
- M. A. Hannan
- , Jamal Abd. Ali
- & Z. Y. Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Advancing theoretical understanding and practical performance of signal processing for nonlinear optical communications through machine learning
Advancing theoretical understanding and practical performance of signal processing for nonlinear optical communications through machine learning
Nonlinear effects provide inherent limitations in fiber optical communications. Here, the authors experimentally demonstrate improved digital back propagation with machine learning and use the results to reveal insights in the optimization of digital signal processing.
- Qirui Fan
- , Gai Zhou
- & Alan Pak Tao Lau
-
Article
| Open Access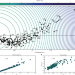 Reconciling contrasting views on economic complexity
Reconciling contrasting views on economic complexity
Both the mathematics and outcomes of the Method of Reflections (MR) and Fitness and Complexity algorithm (FC) approaches differ largely. Here the authors recast both methods in a mathematical and multidimensional framework to reconcile both and show that the conflicts between the two methodologies to measure economic complexity can be resolved by a neat mathematical method based on linear-algebra tools within a bipartite-networks framework.
- Carla Sciarra
- , Guido Chiarotti
- & Francesco Laio

 Survey data and human computation for improved flu tracking
Survey data and human computation for improved flu tracking