Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical unclonable functions based on operable random DNA pools
Chemical unclonable functions based on operable random DNA pools
Physical unclonable functions provide algorithm-independent cryptography based on non-distributable unique tokens. Here, the authors introduce unclonable functions based on random DNA pools, enabling secure decentralized authentication.
- Anne M. Luescher
- , Andreas L. Gimpel
- & Robert N. Grass
-
Article
| Open Access Machine-learning-assisted and real-time-feedback-controlled growth of InAs/GaAs quantum dots
Machine-learning-assisted and real-time-feedback-controlled growth of InAs/GaAs quantum dots
Finding the process parameters in molecular beam epitaxy for a specific density of quantum dots is a multidimensional optimization challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate real-time feedback controlled self-assembled InAs/GaAs QDs growth based on machine learning (ML) outputs.
- Chao Shen
- , Wenkang Zhan
- & Zhanguo Wang
-
Article
| Open Access TacticAI: an AI assistant for football tactics
TacticAI: an AI assistant for football tactics
In modern football games, data-driven analysis serves as a key driver in determining tactics. Wang, Veličković, Hennes et al. develop a geometric deep learning algorithm, named TacticAI, to solve high-dimensional learning tasks over corner kicks and suggest tactics favoured over existing ones 90% of the time.
- Zhe Wang
- , Petar Veličković
- & Karl Tuyls
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic analysis of ChatGPT, Google search and Llama 2 for clinical decision support tasks
Systematic analysis of ChatGPT, Google search and Llama 2 for clinical decision support tasks
People will likely use ChatGPT to seek health advice. Here, the authors show promising performance of ChatGPT and open source models, but a lack of high accuracy considering medical question answering. Improvements are expected over time via domain-specific finetuning and integration of regulations.
- Sarah Sandmann
- , Sarah Riepenhausen
- & Julian Varghese
-
Article
| Open Access A programmable hybrid digital chemical information processor based on the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction
A programmable hybrid digital chemical information processor based on the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction
Computing platforms based on chemical processes can be an alternative to digital computers in some scenarios but have limited programmability. Here the authors demonstrate a hybrid computing platform combining digital electronics and an oscillatory chemical reaction and demonstrate its computational capabilities.
- Abhishek Sharma
- , Marcus Tze-Kiat Ng
- & Leroy Cronin
-
Article
| Open Access An actor-model framework for visual sensory encoding
An actor-model framework for visual sensory encoding
Encoding and downsampling images is key for visual prostheses. Here, the authors show that an actor-model framework using the inherent computation of the retinal network yields better performance in downsampling images compared to learning-free methods.
- Franklin Leong
- , Babak Rahmani
- & Diego Ghezzi
-
Article
| Open Access A dynamic knowledge graph approach to distributed self-driving laboratories
A dynamic knowledge graph approach to distributed self-driving laboratories
Global challenges demand global solutions. Here, the authors show a distributed self-driving lab architecture in The World Avatar, linking robots in Cambridge and Singapore for asynchronous multi-objective reaction optimisation.
- Jiaru Bai
- , Sebastian Mosbach
- & Markus Kraft
-
Article
| Open Access Encoding of multi-modal emotional information via personalized skin-integrated wireless facial interface
Encoding of multi-modal emotional information via personalized skin-integrated wireless facial interface
Technologies in human emotion recognition are challenged by their capability to accurately extract and exploit the emotional information. Lee et al. report a personalized skin-integrated facial interface to sense and combine facial and vocal expression data, enabling enhanced communication in virtual reality.
- Jin Pyo Lee
- , Hanhyeok Jang
- & Jiyun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Mosaic: in-memory computing and routing for small-world spike-based neuromorphic systems
Mosaic: in-memory computing and routing for small-world spike-based neuromorphic systems
Designing efficient artificial neural network circuit architectures for optimal information routing remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose “Mosaic", the first demonstration of on-chip in-memory spike routing using memristors, optimized for small-world graphs prevalent in mammalian brains, offering orders of magnitude reduction in routing events compared to current approaches.
- Thomas Dalgaty
- , Filippo Moro
- & Melika Payvand
-
Article
| Open Access On-chip phonon-magnon reservoir for neuromorphic computing
On-chip phonon-magnon reservoir for neuromorphic computing
Developing efficient reservoir computing hardware that combines optically excited acoustic and spin waves with high spatial density remains a challenge. In this work, the authors propose a design capable of recognizing visual shapes drawn by a laser within remarkably confined spaces, down to 10 square microns.
- Dmytro D. Yaremkevich
- , Alexey V. Scherbakov
- & Manfred Bayer
-
Article
| Open Access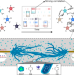 Structural plasticity for neuromorphic networks with electropolymerized dendritic PEDOT connections
Structural plasticity for neuromorphic networks with electropolymerized dendritic PEDOT connections
Neural networks are powerful tools for solving complex problems, but finding the right network topology for a given task remains an open question. Here, the authors propose a bio-inspired artificial neural network hardware able to self-adapt to solve new complex tasks, by autonomously connecting nodes using electropolymerization.
- Kamila Janzakova
- , Ismael Balafrej
- & Fabien Alibart
-
Article
| Open Access A digital twin for DNA data storage based on comprehensive quantification of errors and biases
A digital twin for DNA data storage based on comprehensive quantification of errors and biases
Archiving data in synthetic DNA offers unprecedented storage density and longevity. To understand how experimental choices affect the integrity of digital data stored in DNA, the authors study the evolution of errors and bias and with a digital twin they supply tools for experimental planning and design of error-correcing codes.
- Andreas L. Gimpel
- , Wendelin J. Stark
- & Robert N. Grass
-
Article
| Open Access Critical dynamics arise during structured information presentation within embodied in vitro neuronal networks
Critical dynamics arise during structured information presentation within embodied in vitro neuronal networks
The conditions under which networks of neurons exhibit critical dynamics remains unclear. Here, the authors investigate how simple neural cultures reorganize activity when embodied in a gameplay environment and find that network wide neural criticality arises in nuanced ways.
- Forough Habibollahi
- , Brett J. Kagan
- & Chris French
-
Article
| Open Access Retrosynthesis prediction using an end-to-end graph generative architecture for molecular graph editing
Retrosynthesis prediction using an end-to-end graph generative architecture for molecular graph editing
Retrosynthesis prediction is a fundamental problem in organic synthesis. Here, inspired by simplified arrow-pushing reaction mechanisms, the authors develop a graph-to-edits framework, Graph2Edits, based on graph neural network for retrosynthesis prediction.
- Weihe Zhong
- , Ziduo Yang
- & Calvin Yu-Chian Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Physical deep learning with biologically inspired training method: gradient-free approach for physical hardware
Physical deep learning with biologically inspired training method: gradient-free approach for physical hardware
Traditional learning procedures for artificial intelligence rely on digital methods not suitable for physical hardware. Here, Nakajima et al. demonstrate gradient-free physical deep learning by augmenting a biologically inspired algorithm, accelerating the computation speed on optoelectronic hardware.
- Mitsumasa Nakajima
- , Katsuma Inoue
- & Kohei Nakajima
-
Article
| Open Access Technology readiness levels for machine learning systems
Technology readiness levels for machine learning systems
The development of machine learning systems has to ensure their robustness and reliability. The authors introduce a framework that defines a principled process of machine learning system formation, from research to production, for various domains and data scenarios.
- Alexander Lavin
- , Ciarán M. Gilligan-Lee
- & Yarin Gal
-
Article
| Open Access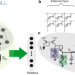 Self-organization of an inhomogeneous memristive hardware for sequence learning
Self-organization of an inhomogeneous memristive hardware for sequence learning
One gap between the neuro-inspired computing and its applications lies in the intrinsic variability of the devices. Here, Payvand et al. suggest a technologically plausible co-design of the hardware architecture which takes into account and exploits the physics behind memristors.
- Melika Payvand
- , Filippo Moro
- & Giacomo Indiveri
-
Article
| Open Access Practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution with composable security
Practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution with composable security
Continuous-variable QKD protocols are usually easier to implement than discrete-variables ones, but their security analyses are less developed. Here, the authors propose and demonstrate in the lab a CVQKD protocol that can generate composable keys secure against collective attacks.
- Nitin Jain
- , Hou-Man Chin
- & Ulrik L. Andersen
-
Article
| Open Access A framework for the general design and computation of hybrid neural networks
A framework for the general design and computation of hybrid neural networks
Hybrid neural networks combine advantages of spiking and artificial neural networks in the context of computing and biological motivation. The authors propose a design framework with hybrid units for improved flexibility and efficiency of hybrid neural networks, and modulation of hybrid information flows.
- Rong Zhao
- , Zheyu Yang
- & Luping Shi
-
Article
| Open Access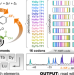 Paramagnetic encoding of molecules
Paramagnetic encoding of molecules
Molecules offer enormous capacity for information storage. Here, the authors show that information can be encoded into molecules with sequences of paramagnetic lanthanide ions, and decoded using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
- Jan Kretschmer
- , Tomáš David
- & Miloslav Polasek
-
Article
| Open Access Nanosecond optical switching and control system for data center networks
Nanosecond optical switching and control system for data center networks
Several challenges still impede the deployment of optical switches in data centers. The authors report an optical switching and control system to synergistically overcome these challenges and provide enhanced performance for data center applications.
- Xuwei Xue
- & Nicola Calabretta
-
Review Article
| Open Access Synthetic DNA applications in information technology
Synthetic DNA applications in information technology
Synthetic DNA is the basis for promising technologies in data storage, barcoding, computing 62 and sercurity. In this review, the authors provide an overview of the field and its future.
- Linda C. Meiser
- , Bichlien H. Nguyen
- & Robert N. Grass
-
Article
| Open Access Neutral bots probe political bias on social media
Neutral bots probe political bias on social media
Social media platforms moderating misinformation have been accused of political bias. Here, the authors use neutral social bots to show that, while there is no strong evidence for such a bias, the content to which Twitter users are exposed depends strongly on the political leaning of early Twitter connections.
- Wen Chen
- , Diogo Pacheco
- & Filippo Menczer
-
Article
| Open Access Deep neural networks using a single neuron: folded-in-time architecture using feedback-modulated delay loops
Deep neural networks using a single neuron: folded-in-time architecture using feedback-modulated delay loops
Development of deep neural networks benefits from new approaches and perspectives. Stelzer et al. propose to fold a deep neural network of arbitrary size into a single neuron with multiple time-delayed feedback loops which is also of relevance for new hardware implementations and applications.
- Florian Stelzer
- , André Röhm
- & Serhiy Yanchuk
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular-level similarity search brings computing to DNA data storage
Molecular-level similarity search brings computing to DNA data storage
Storage technology based on DNA is emerging as an information dense and durable medium. Here the authors use machine learning-based encoding and hybridization probes to execute similarity searches in a DNA database.
- Callista Bee
- , Yuan-Jyue Chen
- & Luis Ceze
-
Article
| Open Access Synaptic metaplasticity in binarized neural networks
Synaptic metaplasticity in binarized neural networks
Deep neural networks usually rapidly forget the previously learned tasks while training new ones. Laborieux et al. propose a method for training binarized neural networks inspired by neuronal metaplasticity that allows to avoid catastrophic forgetting and is relevant for neuromorphic applications.
- Axel Laborieux
- , Maxence Ernoult
- & Damien Querlioz
-
Article
| Open Access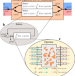 A single inverse-designed photonic structure that performs parallel computing
A single inverse-designed photonic structure that performs parallel computing
Optical analog computing has so far been mostly limited to solving a single instance of a mathematical problem at a time. Here, the authors show that the linearity of the wave equation allows to solve several problems simultaneously, and demonstrate it using an MW transmissive cavity.
- Miguel Camacho
- , Brian Edwards
- & Nader Engheta
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning in spectral domain
Machine learning in spectral domain
Theoretical aspects of automated learning from data involving deep neural networks have open questions. Here Giambagli et al. show that training the neural networks in the spectral domain of the network coupling matrices can reduce the amount of learning parameters and improve the pre-training process.
- Lorenzo Giambagli
- , Lorenzo Buffoni
- & Duccio Fanelli
-
Article
| Open Access Computing conditional entropies for quantum correlations
Computing conditional entropies for quantum correlations
Simple lower bounds on the rates of device-independent quantum information protocols can often overestimate the power of the eavesdropping party. Here, the authors use new entropic quantities defined as semidefinite programs to improve bounds in several regimes without expensive computational resources
- Peter Brown
- , Hamza Fawzi
- & Omar Fawzi
-
Article
| Open Access DNA synthesis for true random number generation
DNA synthesis for true random number generation
Large volumes of true random numbers are needed for increasing requirements of secure data encryption. Here the authors use the stochastic nature of DNA synthesis to obtain millions of gigabytes of unbiased randomness.
- Linda C. Meiser
- , Julian Koch
- & Robert N. Grass
-
Article
| Open Access Navigating the landscape of multiplayer games
Navigating the landscape of multiplayer games
Multiplayer games can be used as testbeds for the development of learning algorithms for artificial intelligence. Omidshafiei et al. show how to characterize and compare such games using a graph-based approach, generating new games that could potentially be interesting for training in a curriculum.
- Shayegan Omidshafiei
- , Karl Tuyls
- & Rémi Munos
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid low-voltage physical unclonable function based on inkjet-printed metal-oxide transistors
Hybrid low-voltage physical unclonable function based on inkjet-printed metal-oxide transistors
Designing efficient system for digital connectivity preserving information security remains a challenge. Here, the authors present hardware-intrinsic security solutions based on physical unclonable functions incorporating an inkjet-printed core circuit as an intrinsic source of entropy, integrated into a silicon-based CMOS system environment.
- Alexander Scholz
- , Lukas Zimmermann
- & Jasmin Aghassi-Hagmann
-
Article
| Open Access Low cost DNA data storage using photolithographic synthesis and advanced information reconstruction and error correction
Low cost DNA data storage using photolithographic synthesis and advanced information reconstruction and error correction
The current bottleneck for DNA data storage systems is the cost and speed of synthesis. Here, the authors use inexpensive, massively parallel light-directed synthesis and correct for a high error rate with a pipeline of encoding and reconstruction algorithms.
- Philipp L. Antkowiak
- , Jory Lietard
- & Robert N. Grass
-
Article
| Open Access Using synchronized oscillators to compute the maximum independent set
Using synchronized oscillators to compute the maximum independent set
Designing efficient analog dynamical systems for solving hard optimization problems remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a dynamical system of thirty oscillators with reconfigurable coupling to compute optimal/near-optimal solutions to the hard Maximum Independent Set problem with over 90% accuracy.
- Antik Mallick
- , Mohammad Khairul Bashar
- & Nikhil Shukla
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal data analysis with chronological networks
Spatiotemporal data analysis with chronological networks
Extracting central information from ever-growing data generated in our lives calls for new data mining methods. Ferreira et al. show a simple model, called chronnets, that can capture frequent patterns, spatial changes, outliers, and spatiotemporal clusters.
- Leonardo N. Ferreira
- , Didier A. Vega-Oliveros
- & Elbert E. N. Macau
-
Article
| Open Access Playing games with multiple access channels
Playing games with multiple access channels
Multiple access channels model communication from multiple independent senders to a common receiver. By drawing a connection to the study of classical and quantum correlations using nonlocal games, Leditzky et al. reveal remarkably complex behaviour of the entanglement-assisted and unassisted information transmission capabilities of a multiple access channel.
- Felix Leditzky
- , Mohammad A. Alhejji
- & Graeme Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Complexity control by gradient descent in deep networks
Complexity control by gradient descent in deep networks
Understanding the underlying mechanisms behind the successes of deep networks remains a challenge. Here, the author demonstrates an implicit regularization in training deep networks, showing that the control of complexity in the training is hidden within the optimization technique of gradient descent.
- Tomaso Poggio
- , Qianli Liao
- & Andrzej Banburski
-
Article
| Open Access Multicomponent molecular memory
Multicomponent molecular memory
Small non-polymeric molecules have tremendous structural diversity that can be used to represent information. Here the authors encode data in synthesized libraries of Ugi products.
- Christopher E. Arcadia
- , Eamonn Kennedy
- & Jacob K. Rosenstein
-
Article
| Open Access Implementing digital computing with DNA-based switching circuits
Implementing digital computing with DNA-based switching circuits
DNA strand displacement reactions can be difficult to scale up for computational tasks. Here the authors develop DNA switching circuits that achieve high-speed computing with fewer molecules.
- Fei Wang
- , Hui Lv
- & Chunhai Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Optimizing agent behavior over long time scales by transporting value
Optimizing agent behavior over long time scales by transporting value
People are able to mentally time travel to distant memories and reflect on the consequences of those past events. Here, the authors show how a mechanism that connects learning from delayed rewards with memory retrieval can enable AI agents to discover links between past events to help decide better courses of action in the future.
- Chia-Chun Hung
- , Timothy Lillicrap
- & Greg Wayne
-
Article
| Open Access Decoupling of brain function from structure reveals regional behavioral specialization in humans
Decoupling of brain function from structure reveals regional behavioral specialization in humans
The extent to which brain structure and function are coupled remains a complex question. Here, the authors show that coupling strength between structural connectivity and functional activity can be quantified and reveals a cortical gradient spanning from lower-level sensory areas to high-level cognitive ones.
- Maria Giulia Preti
- & Dimitri Van De Ville
-
Article
| Open Access Global labor flow network reveals the hierarchical organization and dynamics of geo-industrial clusters
Global labor flow network reveals the hierarchical organization and dynamics of geo-industrial clusters
There is a lack of systematic approaches to identify and analyze the hierarchical structure of geo-industrial clusters at the global scale. Here the authors use LinkedIn's employment history data to construct a global labor flow network from which they find that the resulting geo-industrial clusters exhibit a stronger association between the influx of educated-workers and financial performance compared to existing aggregation units.
- Jaehyuk Park
- , Ian B. Wood
- & Yong-Yeol Ahn
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstructing missing complex networks against adversarial interventions
Reconstructing missing complex networks against adversarial interventions
Recovering the properties of a network which has suffered adversarial intervention can find applications in uncovering targeted attacks on social networks. Here the authors propose a causal statistical inference framework for reconstructing a network which has suffered non-random, targeted attacks.
- Yuankun Xue
- & Paul Bogdan
-
Article
| Open Access High density DNA data storage library via dehydration with digital microfluidic retrieval
High density DNA data storage library via dehydration with digital microfluidic retrieval
DNA as a high density storage medium is receiving increasing attention, but long term physical storage is an unsolved problem. Here the authors show that up to 1 TB of data stored as dehydrated DNA spots on a glass cartridge can be retrieved in a spot of water using digital microfluidics with minimal data loss and contamination.
- Sharon Newman
- , Ashley P. Stephenson
- & Luis Ceze
-
Article
| Open Access Master clinical medical knowledge at certificated-doctor-level with deep learning model
Master clinical medical knowledge at certificated-doctor-level with deep learning model
AI is used increasingly in medical diagnostics. Here, the authors present a deep learning model that masters medical knowledge, demonstrated by it having passed the written test of the 2017 National Medical Licensing Examination in China, and can provide help with clinical diagnosis based on electronic health care records.
- Ji Wu
- , Xien Liu
- & Ping Lv
-
Article
| Open Access Multicomponent reactions provide key molecules for secret communication
Multicomponent reactions provide key molecules for secret communication
Designing molecular keys and combining advanced encryption standard cryptography with molecular steganography is a secure way for encoding messages. Here, the authors use the Ugi four-component reaction of perfluorinated acids to create a library of 500,000 molecular keys for encryption and decryption.
- Andreas C. Boukis
- , Kevin Reiter
- & Michael A. R. Meier
-
Article
| Open Access Unsupervised learning in probabilistic neural networks with multi-state metal-oxide memristive synapses
Unsupervised learning in probabilistic neural networks with multi-state metal-oxide memristive synapses
Artificial neural networks exhibit learning abilities and can perform tasks which are tricky for conventional computing systems, such as pattern recognition. Here, Serb et al. show experimentally that memristor arrays can learn reversibly from noisy data thanks to sophisticated learning rules.
- Alexander Serb
- , Johannes Bill
- & Themis Prodromakis
-
Article
| Open Access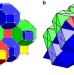 Fault-tolerant error correction with the gauge color code
Fault-tolerant error correction with the gauge color code
Construction of a scalable quantum computer requires error-correcting codes to overcome the errors introduced by noise. Here, the authors develop a decoding algorithm for the gauge color code, and obtain its threshold values when physical errors and measurement faults are included.
- Benjamin J. Brown
- , Naomi H. Nickerson
- & Dan E. Browne
-
Article
| Open Access The minimal work cost of information processing
The minimal work cost of information processing
Irreversible computation cannot be performed without a work cost, and energy dissipation imposes limitations on devices' performances. Here the authors show that the minimal work requirement of logical operations is given by the amount of discarded information, measured by entropy.
- Philippe Faist
- , Frédéric Dupuis
- & Renato Renner

 DenRAM: neuromorphic dendritic architecture with RRAM for efficient temporal processing with delays
DenRAM: neuromorphic dendritic architecture with RRAM for efficient temporal processing with delays