Featured
-
-
In Your Element |
 The riches of uranium
The riches of uranium
Uranium is best known, and feared, for its involvement in nuclear energy. Marisa J. Monreal and Paula L. Diaconescu take a look at how its unique combination of properties is now increasingly attracting the attention of chemists.
- Marisa J. Monreal
- & Paula L. Diaconescu
-
News & Views |
 Iron opens up to high activity
Iron opens up to high activity
The iron active sites of enzymes routinely cleave strong C–H bonds, but synthetic complexes have so far been much slower and less efficient. Now, the reactivity of a biomimetic diiron complex has been dramatically enhanced by converting its oxo bridge into a terminal ligand, and its iron centre from low spin to high spin.
- Sason Shaik
-
News & Views |
 A bridge to higher ground
A bridge to higher ground
Single-molecule magnets are coordination clusters with magnetic properties that are typically reliant on the coupling between pairs of metal centres. Now, a cluster in which magnetism arises from delocalized electrons — built using an imidazolate bridge, a common linker in metal–organic architectures — shows promise for molecular memory devices.
- Annie K. Powell
-
News & Views |
 Spinning into control
Spinning into control
Spin transitions are the most common mechanism for switching molecules between two distinct energy states, for uses as diverse as memory devices and displays. How the transition is triggered is crucial, and a pentanuclear cluster has now been reported in which the spin transition is promoted by redox transfer between different metal ions.
- Roberta Sessoli
-
Review Article |
 Induction of chiral porous solids containing only achiral building blocks
Induction of chiral porous solids containing only achiral building blocks
The synthesis or separation of chiral compounds is crucial for many areas of chemistry, with chiral solids having important roles as catalysts or separating agents. This Review covers recent progress and future avenues for developing methods of preparing chiral solids from achiral starting materials.
- Russell E. Morris
- & Xianhui Bu
-
Article |
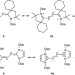 Isolation of crystalline carbene-stabilized P2-radical cations and P2-dications
Isolation of crystalline carbene-stabilized P2-radical cations and P2-dications
N-heterocyclic carbenes have been shown to be versatile ligands for metal catalysts and even catalysts in their own right. Here, bulky N-heterocyclic carbenes are shown to stabilize paramagnetic and electron-poor species sufficiently for their crystallographic characterization.
- Olivier Back
- , Bruno Donnadieu
- & Guy Bertrand
-
In Your Element |
 Green bismuth
Green bismuth
Ram Mohan looks at how bismuth — a remarkably harmless element among the toxic heavy metals in the periodic table — has sparked interest in areas varying from medicinal to industrial chemistry.
- Ram Mohan
-
Article |
 The rational design of helium bonds
The rational design of helium bonds
Helium is a reluctant participant when it comes to chemical reactions and bonding and it is one of only two stable elements for which there are currently no known crystalline derivatives. Now, based on a computational investigation, compounds containing helium atoms that form charge-shift, rather than covalent bonds have been proposed.
- Henry S. Rzepa
-
Research Highlights |
 Stable and able
Stable and able
A stable water-oxidation catalyst containing a cobalt oxide core has been made.
- Neil Withers
-
Review Article |
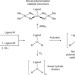 Novel polymerization catalysts and hydride clusters from rare-earth metal dialkyls
Novel polymerization catalysts and hydride clusters from rare-earth metal dialkyls
Rare-earth metal dialkyl complexes can be readily transformed into the corresponding cationic monoalkyl species — which have been shown to catalyse a range of (co)polymerization processes — as well as into polyhydride complexes that have unique structures and a rich reaction chemistry.
- Masayoshi Nishiura
- & Zhaomin Hou
-
Article |
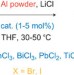 Preparation of functionalized organoaluminiums by direct insertion of aluminium to unsaturated halides
Preparation of functionalized organoaluminiums by direct insertion of aluminium to unsaturated halides
The reactivity of organoaluminium reagents makes them particularly attractive nucleophiles for a wide range of organic reactions. Here, the use of metal halide catalysts provides access to functionalized organoaluminium reagents directly from the metal. The utility of these organoaluminium reagents is then demonstrated by their reaction with a wide variety of electrophilic coupling partners.
- Tobias Blümke
- , Yi-Hung Chen
- & Paul Knochel
-
Article |
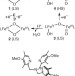 Million-fold activation of the [Fe2(µ-O)2] diamond core for C–H bond cleavage
Million-fold activation of the [Fe2(µ-O)2] diamond core for C–H bond cleavage
Although enzymes are known to use diiron centres to cleave carbon–hydrogen bonds, preparing synthetic compounds that can break these strong, stable bonds has remained notoriously difficult. Now, converting a low-spin ‘diamond core’ iron–oxo biomimetic complex into its high-spin ‘open core’ counterpart has enhanced its C–H bond cleavage ability by over a million times.
- Genqiang Xue
- , Raymond De Hont
- & Lawrence Que Jr
-
Article |
 High-spin ground states via electron delocalization in mixed-valence imidazolate-bridged divanadium complexes
High-spin ground states via electron delocalization in mixed-valence imidazolate-bridged divanadium complexes
Single-molecule magnets are clusters of metal ions linked together by organic bridges, with properties typically arising from exchange coupling of unpaired metal electrons. In mixed-valence systems, another magnetic mechanism involving itinerant electrons can also occur and induce a high-spin ground state. Now, such electron delocalization has been observed through an imidazolate bridge — a common linker in metal-organic architectures — which may enable the construction of higher spin clusters or three-dimensional magnets.
- Bettina Bechlars
- , Deanna M. D'Alessandro
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Article |
 Face-directed self-assembly of an electronically active Archimedean polyoxometalate architecture
Face-directed self-assembly of an electronically active Archimedean polyoxometalate architecture
A wide range of porous framework materials has been assembled with a modular approach that takes advantage of prefabricated structural building units (SBUs). Now, it has been shown that functional all-inorganic frameworks can be made from a macrocyclic polyoxometalate SBU — that has a built-in aperture approximately 1 nm in diameter — linked together with redox-switchable metal ions.
- Scott G. Mitchell
- , Carsten Streb
- & Leroy Cronin
-
Research Highlights |
 The krypton factor
The krypton factor
A krypton difluoride coordination compound — where it acts as a ligand to a bromine atom — has been synthesized and studied.
- Neil Withers
-
In Your Element |
 A flourish of fluorine
A flourish of fluorine
Herbert Roesky relates how the small, highly electronegative fluorine atom unveiled the chemical reactivity of noble gases and found many practical applications. but it can also render organic compounds highly toxic or pollutants.
- Herbert W. Roesky
-
News & Views |
 Seizing the caesium
Seizing the caesium
Public acceptance of the expansion of nuclear power may hinge on the safe disposal of nuclear waste. Ion exchangers that remove radioactive metals — such as caesium ions — from the waste could provide part of the answer, so a flexible-framework material that selectively grab them from solution is a step in the right direction.
- Abraham Clearfield
-
Research Highlights |
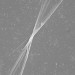 An illuminating twist
An illuminating twist
The slow oxidation of tellurium in semiconductor cadmium telluride nanoparticles, accompanied by the replacement of tellurium by sulfur, has led to CdS/CdTe nanoparticles that self-assemble under visible light into twisted nanoribbons.
- Anne Pichon
-
Article |
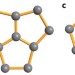 Chlorofullerenes featuring triple sequentially fused pentagons
Chlorofullerenes featuring triple sequentially fused pentagons
Fullerene cages that break the isolated pentagon rule are rare and often unstable. Now a range of fullerenes that feature three sequentially fused pentagons of carbon have been stabilized by chlorination.
- Yuan-Zhi Tan
- , Jia Li
- & Lan-Sun Zheng
-
Article |
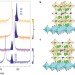 Anisotropic oxygen diffusion at low temperature in perovskite-structure iron oxides
Anisotropic oxygen diffusion at low temperature in perovskite-structure iron oxides
The movement of oxygen ions through materials is important in electrolytes and separation membranes, but is rare at lower temperatures. Two different low-temperature diffusion pathways are revealed during the reduction process of CaFeO2.5 to CaFeO2. The two pathways are significantly different, resulting in anisotropy.
- Satoru Inoue
- , Masanori Kawai
- & Yuichi Shimakawa
-
Article |
 A concentric planar doubly π-aromatic B19− cluster
A concentric planar doubly π-aromatic B19− cluster
A combined theoretical and experimental approach has been used to investigate the structure and bonding of an all-boron cluster (B19−). Calculations suggest that the minimum energy structure is a near-planar one — in which a pentagonal B6 unit is encircled by a larger B13 ring — possessing two concentric aromatic π systems.
- Wei Huang
- , Alina P. Sergeeva
- & Alexander I. Boldyrev
-
Article |
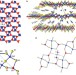 Selective incarceration of caesium ions by Venus flytrap action of a flexible framework sulfide
Selective incarceration of caesium ions by Venus flytrap action of a flexible framework sulfide
A perforated framework material of gallium antimony sulfide is able to selectively extract caesium ions from solution. After this capture, the holes close and prevent the ions leaching back out. This dynamic response could be used to remove caesium from nuclear waste.
- Nan Ding
- & Mercouri G. Kanatzidis
-
Research Highlights |
 Array of sunshine
Array of sunshine
Arrays of silicon microwires grown by a vapour–liquid–solid method point the way to more efficient photocathodes.
- Neil Withers
-
Research Highlights |
 Targeting tyrosine
Targeting tyrosine
A very mild method for the selective functionalization of tyrosine residues in proteins provides an attractive new option for bioconjugation.
- Stephen Davey
-
Article |
 Dianionic species with a bond consisting of two pentacoordinated silicon atoms
Dianionic species with a bond consisting of two pentacoordinated silicon atoms
Silicon, like carbon, favours a four-coordinate geometry and this underpins the frameworks of the wide range of inorganic and organosilicon compounds, from silicate minerals to polysilanes. Although some pentavalent silicon compounds have already been reported, this work presents the first example where two five-coordinate silicon atoms are bonded to each other.
- Naokazu Kano
- , Hideaki Miyake
- & Shigeru Nagase
-
Article |
 Solution structure of a DNA double helix with consecutive metal-mediated base pairs
Solution structure of a DNA double helix with consecutive metal-mediated base pairs
The incorporation of non-natural base pairs into double-stranded DNA, especially those mediated by metal–ligand interactions, offers new opportunities for synthetic DNA materials. The structural implications of such modifications will help guide developments in this area, and a solution structure of a B-type DNA duplex containing consecutive metal-mediated base pairs has now been elucidated.
- Silke Johannsen
- , Nicole Megger
- & Jens Müller
-
Research Highlights |
 Ephemeral templating
Ephemeral templating
The isolation of an intermediate species during the self-assembly of a giant molybdenum oxide wheel suggests that a smaller cluster templates the wheel's formation before being evicted.
- Anne Pichon
-
News & Views |
 An electric effect
An electric effect
Electrically tunable materials are used to construct switches and memory devices. Applying an electric field within a specific temperature range to cyanometallate complexes triggers their charge-transfer phase transition, altering their optical and magnetic properties.
- Osamu Sato

 Direct detection of CH/π interactions in proteins
Direct detection of CH/π interactions in proteins