Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access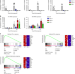 A molecular switch from STAT2-IRF9 to ISGF3 underlies interferon-induced gene transcription
A molecular switch from STAT2-IRF9 to ISGF3 underlies interferon-induced gene transcription
A rapid cellular response to interferons (IFNs) is critical for establishing antimicrobial immunity, but how cells switch from from homeostasis to IFN signaling is not fully understood. Here, the authors provide evidence that IFNs induce gene expression by alternating subunits of transcription factor ISGF3.
- Ekaterini Platanitis
- , Duygu Demiroz
- & Thomas Decker
-
Article
| Open Access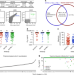 Difficult-to-neutralize global HIV-1 isolates are neutralized by antibodies targeting open envelope conformations
Difficult-to-neutralize global HIV-1 isolates are neutralized by antibodies targeting open envelope conformations
Here, the authors report that specific monoclonal antibodies isolated from vaccinated rhesus macaques can neutralize a subset of Tier 2 difficult-to-neutralize HIV-1 that express Env in an open conformation, suggesting that V3 loop-specific targeting can bias the estimation of vaccine-induced bnAbs.
- Qifeng Han
- , Julia A. Jones
- & Kevin O. Saunders
-
Article
| Open Access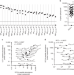 Quantification of epitope abundance reveals the effect of direct and cross-presentation on influenza CTL responses
Quantification of epitope abundance reveals the effect of direct and cross-presentation on influenza CTL responses
CTL responses are critical in protection against pathogens. Here, using mass spectrometry and flow cytometry, the authors characterize the kinetics of influenza A virus class I MHC epitopes cross-presented in professional antigen presenting cells and identify new epitopes that elicit T cell responses in infected mice.
- Ting Wu
- , Jing Guan
- & Nicole L. La Gruta
-
Article
| Open Access Tethering of vesicles to the Golgi by GMAP210 controls LAT delivery to the immune synapse
Tethering of vesicles to the Golgi by GMAP210 controls LAT delivery to the immune synapse
The immune synapse at the interface between T cells and antigen-presenting cells manifests intense vesicular trafficking, but how the vesicles are sorted is still unclear. Here the authors show that, in activated T cells, the Golgin GMAP210 specifically conveys LAT+ vesicles to immune synapse allowing proper T cell activation.
- Andres Ernesto Zucchetti
- , Laurence Bataille
- & Claire Hivroz
-
Article
| Open Access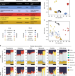 Transcriptional profiling unveils type I and II interferon networks in blood and tissues across diseases
Transcriptional profiling unveils type I and II interferon networks in blood and tissues across diseases
The authors present an extensive profile of host transcriptional respones to a diverse group of pathogens and allergens. In doing so, they identify TH1, type I IFN, TH17, and TH2 responses, that underlie each immune response in both the blood and lung, which represents a global profile of host-pathogen immune responses.
- Akul Singhania
- , Christine M. Graham
- & Anne O’Garra
-
Article
| Open Access Actomyosin-driven force patterning controls endocytosis at the immune synapse
Actomyosin-driven force patterning controls endocytosis at the immune synapse
The immune synapse promotes cellular information exchange but the role of biophysical forces in synapse function is unclear. Here, the authors show that B cells exert two types of forces, a centripetal myosin II-driven force and a central actin protrusive force at the site of antigen extraction.
- Anita Kumari
- , Judith Pineau
- & Paolo Pierobon
-
Article
| Open Access STING induces early IFN-β in the liver and constrains myeloid cell-mediated dissemination of murine cytomegalovirus
STING induces early IFN-β in the liver and constrains myeloid cell-mediated dissemination of murine cytomegalovirus
Innate immune signaling pathways sense different microbial features and can elicit distinct yet overlapping immune responses. Here the authors dissect the contribution of these pathways to the response to MCMV infection and find that STING signaling is dispensable for host survival but crucial to restrict viral replication and dissemination via myeloid cells.
- Pia-Katharina Tegtmeyer
- , Julia Spanier
- & Ulrich Kalinke
-
Article
| Open Access Targeting a therapeutic LIF transgene to muscle via the immune system ameliorates muscular dystrophy
Targeting a therapeutic LIF transgene to muscle via the immune system ameliorates muscular dystrophy
A number of therapeutic agents aimed at reducing pathology in Duchenne muscular dystrophy have been developed, but may have off-target effects when delivered systemically. Here, the authors express the therapeutic LIF transgene in leukocytes, and show this results in targeting to inflamed dystrophic muscle and reduced fibrosis by suppressing type 2 immunity.
- Steven S. Welc
- , Ivan Flores
- & James G. Tidball
-
Article
| Open Access Chromosome dynamics near the sol-gel phase transition dictate the timing of remote genomic interactions
Chromosome dynamics near the sol-gel phase transition dictate the timing of remote genomic interactions
Antibodies are generated through remote genomic interactions involving immunoglobulin variable (VH), diversity (DH) and joining (JH) gene segments. Here the authors develop a strategy to track VH-DHJH motion in B-lymphocytes and provide evidence that chromosome organisation near the sol-gel phase transition dictates the timing of genomic interactions to orchestrate gene expression and somatic recombination.
- Nimish Khanna
- , Yaojun Zhang
- & Cornelis Murre
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of HIV transmitting CD11c+ human epidermal dendritic cells
Identification of HIV transmitting CD11c+ human epidermal dendritic cells
Composition and function of immune populations at barrier surfaces is crucial for response to infection. Here, the authors identify a population of dendritic cells in human epidermis, abundant in anogenital epithelia and distinct from Langerhans cells by surface phenotype and by high capacity for HIV infection and transmission.
- Kirstie M. Bertram
- , Rachel A. Botting
- & Andrew N. Harman
-
Article
| Open Access IL-33-mediated mast cell activation promotes gastric cancer through macrophage mobilization
IL-33-mediated mast cell activation promotes gastric cancer through macrophage mobilization
Mast cells within the tumor microenvironment have controversial roles. Here, the authors show, using genetic mouse models, that in gastric cancer, mast cells at the periphery of the tumors are activated via cancer cell produced-IL33 and promote tumorigenesis by recruiting macrophages within the tumors.
- Moritz F. Eissmann
- , Christine Dijkstra
- & Matthias Ernst
-
Article
| Open Access Lugdunin amplifies innate immune responses in the skin in synergy with host- and microbiota-derived factors
Lugdunin amplifies innate immune responses in the skin in synergy with host- and microbiota-derived factors
Lugdunin is a peptide antibiotic produced by the skin commensal Staphylococcus lugdunensis. Here, the authors show that lugdunin reduces Staphylococcus aureus colonization in human keratinocytes and mouse skin by inducing the expression of human LL-37 and recruitment of monocytes and neutrophils.
- Katharina Bitschar
- , Birgit Sauer
- & Birgit Schittek
-
Article
| Open Access IL-33 drives group 2 innate lymphoid cell-mediated protection during Clostridium difficile infection
IL-33 drives group 2 innate lymphoid cell-mediated protection during Clostridium difficile infection
Here, Frisbee et al. show that hypervirulent Clostridium difficile induces IL-33 expression in the gut and IL-33 reduces mortality and morbidity via group 2 innate lymphoid cells. Furthermore, serum levels of the soluble IL-33 decoy receptor, sST2, are associated with enhanced disease severity in human C. difficile patients.
- Alyse L. Frisbee
- , Mahmoud M. Saleh
- & William A. Petri Jr.
-
Article
| Open Access P2X7 receptor induces mitochondrial failure in monocytes and compromises NLRP3 inflammasome activation during sepsis
P2X7 receptor induces mitochondrial failure in monocytes and compromises NLRP3 inflammasome activation during sepsis
Systemic sepsis is a potentially life-threatening illness and immunocompromised individuals are especially vulnerable. Here, using a cohort of patients with intra-abdominal origin sepsis, the authors show an important role for the NLRP3 inflammasome in establishing a host response, and NLRP3 dysfunction is a common feature of sepsis mortality.
- Juan José Martínez-García
- , Helios Martínez-Banaclocha
- & Pablo Pelegrin
-
Article
| Open Access Mass cytometry reveals systemic and local immune signatures that distinguish inflammatory bowel diseases
Mass cytometry reveals systemic and local immune signatures that distinguish inflammatory bowel diseases
Distinguishing clinical subtypes of IBD is critical for optimal treatments, outcome prediction, and better understanding of disease pathogenesis. Here the authors phenotype blood and intestinal immune cells by mass cytometry and identify signatures associated with distinct disease states.
- Samuel J. S. Rubin
- , Lawrence Bai
- & Aida Habtezion
-
Article
| Open Access Fcmr regulates mononuclear phagocyte control of anti-tumor immunity
Fcmr regulates mononuclear phagocyte control of anti-tumor immunity
Myeloid cells modulate the immune response within the tumour microenvironment, but the underlying mechanisms remain largely unknown. Here, the authors show that Fcmr – the putative receptor for soluble IgM – is a potent negative regulator of anti-tumour immunity.
- Shawn P. Kubli
- , Larsen Vornholz
- & Tak W. Mak
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of CAR T cell-mediated cytokine release syndrome-like toxicity using low molecular weight adapters
Regulation of CAR T cell-mediated cytokine release syndrome-like toxicity using low molecular weight adapters
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell anti-cancer therapies might result in toxic side effects. Here the authors present a strategy based on the modulation of CAR T cells via administration of a bispecific adapter that target them to cancer cells, resulting in diminished CAR-T cells toxicity and enhanced solid tumor eradication.
- Yong Gu Lee
- , Haiyan Chu
- & Philip S. Low
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of a genomic enhancer that enforces proper apoptosis induction in thymic negative selection
Identification of a genomic enhancer that enforces proper apoptosis induction in thymic negative selection
Autoreactive T cells are deleted in the thymus via thymic negative selection and Bim-mediated apoptosis. Here the authors identify a cis-acting enhancer, EBAB, that is essential for proper Bim expression and apoptosis induction, and show that EBAB deficiency specifically impairs thymic negative selection without affecting peripheral T cell homeostasis.
- Miki Arai Hojo
- , Kyoko Masuda
- & Shinpei Kawaoka
-
Article
| Open Access Two HEPN domains dictate CRISPR RNA maturation and target cleavage in Cas13d
Two HEPN domains dictate CRISPR RNA maturation and target cleavage in Cas13d
Cas13d is a class 2 type VI-D CRISPR-Cas RNA-guided RNase. Here the authors present the high-resolution crystal structure of the uncultured Ruminococcus sp. Cas13d (UrCas13d)-crRNA complex and by combining structural, mutational and biochemical studies provide mechanistic insights into the CRISPR-Cas13d system.
- Bo Zhang
- , Yangmiao Ye
- & Songying Ouyang
-
Article
| Open Access Tumor-associated reactive astrocytes aid the evolution of immunosuppressive environment in glioblastoma
Tumor-associated reactive astrocytes aid the evolution of immunosuppressive environment in glioblastoma
Astrocytes play important roles in neuroinflammatory diseases. Here the authors characterize human glioblastoma-associated astrocytes by gene expression and demonstrate their immunosuppressive role promoted by interactions with tumor and microglia cells in an organotypic model.
- Dieter Henrik Heiland
- , Vidhya M. Ravi
- & Oliver Schnell
-
Article
| Open Access Mesenchymal stem cell therapy induces FLT3L and CD1c+ dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients
Mesenchymal stem cell therapy induces FLT3L and CD1c+ dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients
Promising pilot clinical trials of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) therapy of lupus await validation in larger, controlled trials. Here the authors show that MSCs expand CD1c+ dendritic cells in cell culture by producing FLT3L, and that in lupus patients, circulating CD1c+ dendritic cells and FLT3L are increased following MSCs therapy.
- Xinran Yuan
- , Xiaodong Qin
- & Lingyun Sun
-
Article
| Open Access PRL3-zumab as an immunotherapy to inhibit tumors expressing PRL3 oncoprotein
PRL3-zumab as an immunotherapy to inhibit tumors expressing PRL3 oncoprotein
Phosphatase of regenerating liver 3 (PRL3) is usually found intracellularly, and is over-expressed in cancer cells. Here the authors show that PRL-3 is also detectable on cell surface, and can be recognized by PRL3-zumab to recruit immune cells into tumor to promote anti-tumor immunity, thereby implicating PRL-3 as a potential tumor antigen.
- Min Thura
- , Abdul Qader Al-Aidaroos
- & Qi Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access CaMKK2 in myeloid cells is a key regulator of the immune-suppressive microenvironment in breast cancer
CaMKK2 in myeloid cells is a key regulator of the immune-suppressive microenvironment in breast cancer
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase kinase 2 (CaMKK2) is highly expressed in several cancers. Here the authors investigate the role of CaMKK2 expression in the tumour microenvironment and show that CaMKK2 expression in tumour-associated macrophages promotes tumour growth by suppressing T cell anti-tumour activity.
- Luigi Racioppi
- , Erik R. Nelson
- & Donald P. McDonnell
-
Article
| Open Access Heterochronic faecal transplantation boosts gut germinal centres in aged mice
Heterochronic faecal transplantation boosts gut germinal centres in aged mice
Microbiota impacts all major aspects of physiology, but little is known about its effects on age-related changes in immune responses. Here the authors show that gut microbiota transfer between adult and old mice increases local but not systemic germinal centre responses regardless of age directionality.
- Marisa Stebegg
- , Alyssa Silva-Cayetano
- & Michelle A. Linterman
-
Article
| Open Access Extracellular vesicles from CLEC2-activated platelets enhance dengue virus-induced lethality via CLEC5A/TLR2
Extracellular vesicles from CLEC2-activated platelets enhance dengue virus-induced lethality via CLEC5A/TLR2
Dengue virus (DENV) promotes leukocyte-platelet interactions that contribute to pathogenesis. Here, the authors report a role for C-type lectins CLEC2 and CLEC5A in platelet activation and NET formation and show that blockade of CLEC5A and TLR2 attenuates inflammation and increases survival of infected mice.
- Pei-Shan Sung
- , Tur-Fu Huang
- & Shie-Liang Hsieh
-
Article
| Open Access Activated Peyer′s patch B cells sample antigen directly from M cells in the subepithelial dome
Activated Peyer′s patch B cells sample antigen directly from M cells in the subepithelial dome
Gut lumen antigens must be continuously sampled by the immune system to maintain proper immune homeostasis. Here the authors show that activated CCR6+CCR1+GL7- gut B cells retrieve lumen antigens from specialized M cells and transfer them across the subepithelial dome in the Peyer’s patch to contribute to the maintenance of gut humoral immunity.
- Rathan Joy Komban
- , Anneli Strömberg
- & Nils Lycke
-
Article
| Open Access Senescent cells evade immune clearance via HLA-E-mediated NK and CD8+ T cell inhibition
Senescent cells evade immune clearance via HLA-E-mediated NK and CD8+ T cell inhibition
Senescent cells increase with ageing and may cause inflammatory conditions, but how this accumulation is mediated is still unclear. Here the authors show that senescent cells express HLA-E to suppress NKG2A-mediated natural killer and CD8 T cell activation to avoid targeted elimination, while blocking NKG2A helps promote immunity against senescent cells.
- Branca I. Pereira
- , Oliver P. Devine
- & Arne N. Akbar
-
Article
| Open Access Targeting EZH2 histone methyltransferase activity alleviates experimental intestinal inflammation
Targeting EZH2 histone methyltransferase activity alleviates experimental intestinal inflammation
EZH2-mediated methylatation of histone 3 is essential for immune regulation. Here, the authors show that EZH2 inhibitors attenuate experimental colitis in mice by promoting the development of myeloid-derived suppressor cells, and delay the onset of colitis-associated cancer.
- Jie Zhou
- , Shuo Huang
- & Bo Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access A bioactive mammalian disaccharide associated with autoimmunity activates STING-TBK1-dependent immune response
A bioactive mammalian disaccharide associated with autoimmunity activates STING-TBK1-dependent immune response
Mammalian glycans have a role in host immunity but little is known about how they activate the host response in the context of autoimmune diseases. Here, the authors identify Manβ1-4GlcNAc as a novel innate immune modulator associated with chronic autoimmune diseases.
- Charles S. Fermaintt
- , Kanae Sano
- & Nan Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and immunogenicity of a stabilized HIV-1 envelope trimer based on a group-M consensus sequence
Structure and immunogenicity of a stabilized HIV-1 envelope trimer based on a group-M consensus sequence
Stabilized, native-like trimers of the HIV envelope protein, such as SOSIP trimers, are potential antigens for an HIV vaccine. Here, the authors generate a SOSIP trimer based on the consensus sequence of group M isolates, determine its structure and exposure of common epitopes, and show immunogenicity in rabbits and non-human primates.
- Kwinten Sliepen
- , Byung Woo Han
- & Rogier W. Sanders
-
Article
| Open Access Bcl10-controlled Malt1 paracaspase activity is key for the immune suppressive function of regulatory T cells
Bcl10-controlled Malt1 paracaspase activity is key for the immune suppressive function of regulatory T cells
The differentiation and function of regulatory T (Treg) cells are critically controlled by T cell receptor (TCR) signaling. Here the authors show that CARD11-BCL10-MALT1 (CBM) complexes are dispensable for effector Treg conversion under inflammatory conditions but are critical for mediating Treg suppressive activity in a MALT1 paracaspase-dependent manner.
- Marc Rosenbaum
- , Andreas Gewies
- & Jürgen Ruland
-
Article
| Open Access Heterogeneous GM-CSF signaling in macrophages is associated with control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Heterogeneous GM-CSF signaling in macrophages is associated with control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
GM-CSF has been implicated in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) host control. Here, the authors show that activation of GM-CSF discriminates Mtb-restrictive from -permissive macrophages while co-infection with HIV disrupts GM-CSF-mediated signaling, rendering macrophages susceptible to bacterial infection.
- Bryan D. Bryson
- , Tracy R. Rosebrock
- & Sarah M. Fortune
-
Article
| Open Access Schistosoma mansoni treatment reduces HIV entry into cervical CD4+ T cells and induces IFN-I pathways
Schistosoma mansoni treatment reduces HIV entry into cervical CD4+ T cells and induces IFN-I pathways
Schistosoma mansoniinfection has been linked with an increased risk of HIV acquisition in women. Here, the authors show that standard S. mansoniinfection treatment causes a reduction of HIV entry into cervical and blood CD4+ T cells, which is sustained for up to two months and is associated with de-repression of IFN-I signaling.
- Sergey Yegorov
- , Vineet Joag
- & Rupert Kaul
-
Article
| Open Access Candidalysin activates innate epithelial immune responses via epidermal growth factor receptor
Candidalysin activates innate epithelial immune responses via epidermal growth factor receptor
Candida albicans is an opportunistic fungus primarily affecting immunocompromised patients. Here, the authors identify a novel mechanism of host immune stimulation and highlight candidalysin and EGFR signalling components as potential targets for prophylactic and therapeutic intervention of mucosal candidiasis.
- Jemima Ho
- , Xuexin Yang
- & Julian R. Naglik
-
Article
| Open Access Contemporaneous 3D characterization of acute and chronic myocardial I/R injury and response
Contemporaneous 3D characterization of acute and chronic myocardial I/R injury and response
Detailed characterization of cardiac damage following ischemia/reperfusion injury and detection of occurring inflammatory responses is important for the development of new therapeutic concepts. Here the authors present a method for the three-dimensional investigation of acute and chronic cardiac injury responses using light sheet fluorescence microscopy.
- Simon F. Merz
- , Sebastian Korste
- & Matthias Totzeck
-
Article
| Open Access Altered respiratory virome and serum cytokine profile associated with recurrent respiratory tract infections in children
Altered respiratory virome and serum cytokine profile associated with recurrent respiratory tract infections in children
Here, the authors determine the respiratory virome and serum cytokine profile in children diagnosed with acute respiratory tract infections (ARTI) and show that relative abundance of Propionibacterium phages as well as serum levels of TIMP-1 and PDGF-BB are increased in multiple ARTIs compared with single ARTI.
- Yanpeng Li
- , Xuemin Fu
- & Chiyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Killer-like receptors and GPR56 progressive expression defines cytokine production of human CD4+ memory T cells
Killer-like receptors and GPR56 progressive expression defines cytokine production of human CD4+ memory T cells
Despite the current human CD4 memory T cell stratification by CD45RA/CCR7, functional heterogeneities still exist within the respective subsets. Here the authors show that several surface markers, including KLRB1, KLRG1, GPR56 and KLRF1, help to further refine the subsetting of human CD4 memory T cells and provide insights for their differentiation.
- Kim-Long Truong
- , Stephan Schlickeiser
- & Birgit Sawitzki
-
Article
| Open Access A toll-like receptor agonist mimicking microbial signal to generate tumor-suppressive macrophages
A toll-like receptor agonist mimicking microbial signal to generate tumor-suppressive macrophages
Turning tumour promoting macrophages into an anti-tumour phenotype is an attractive therapeutic strategy. Here, the authors develop a polysaccharide-based structure that mimicks pathogen-associated molecular patterns and, by activating the toll-like receptors on macrophage surface, promotes a safe anti-tumour immune response in mouse models.
- Yanxian Feng
- , Ruoyu Mu
- & Chunming Wang
-
Article
| Open Access CTL-mediated immunotherapy can suppress SHIV rebound in ART-free macaques
CTL-mediated immunotherapy can suppress SHIV rebound in ART-free macaques
Viral rebound following discontinuation of antiretroviral therapy (ART) is a major obstacle for HIV cure. Here, the authors show that adoptive cellular therapy using autologous Env-specific T cells augmented by therapeutic vaccination can control viral rebound after ART interruption in a SHIV macaque model.
- Jin Fan
- , Hua Liang
- & Yiming Shao
-
Article
| Open Access Diverse MR1-restricted T cells in mice and humans
Diverse MR1-restricted T cells in mice and humans
Mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells express invariant TRAV1/TRAJ33 TCR-α gene segments and detect antigens presented by MR1. Here the authors show that atypical, MR1-restricted MAIT populations that include both Trav1+ and Trav1- cells are found in both Traj33-deficient mice and human peripheral blood.
- Hui-Fern Koay
- , Nicholas A. Gherardin
- & Dale I. Godfrey
-
Article
| Open Access Development of human cGAS-specific small-molecule inhibitors for repression of dsDNA-triggered interferon expression
Development of human cGAS-specific small-molecule inhibitors for repression of dsDNA-triggered interferon expression
Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) is involved in the modulation of inflammatory responses. Here, the authors present small-molecule inhibitors of human cGAS, characterize their interaction with the protein, and show that the compounds are active in interferon-producing cells including primary human macrophages.
- Lodoe Lama
- , Carolina Adura
- & Thomas Tuschl
-
Article
| Open Access Development of an immunodeficient pig model allowing long-term accommodation of artificial human vascular tubes
Development of an immunodeficient pig model allowing long-term accommodation of artificial human vascular tubes
The development of tissue-engineered vascular grafts heavily relies on the availability of large animal models that allow long-term assessment of graft patency. Here Itoh et al. propose a novel model of immunodeficient pigs that allows long-term accommodation of human cell-derived three-dimensional bioprinted vascular tubes.
- Manabu Itoh
- , Yosuke Mukae
- & Eiji Kobayashi
-
Article
| Open Access ZFYVE21 is a complement-induced Rab5 effector that activates non-canonical NF-κB via phosphoinosotide remodeling of endosomes
ZFYVE21 is a complement-induced Rab5 effector that activates non-canonical NF-κB via phosphoinosotide remodeling of endosomes
Complement activation contributes to vascular inflammation in the contexts of allograft rejection and connective tissue disease. Here Fang et al. identify ZFYVE21 as a novel effector of Rab5 and find it regulates pro-inflammatory NF-κB signaling in endothelial cells in response to complement activation.
- Caodi Fang
- , Thomas D. Manes
- & Dan Jane-wit
-
Article
| Open Access Optimization of 4-1BB antibody for cancer immunotherapy by balancing agonistic strength with FcγR affinity
Optimization of 4-1BB antibody for cancer immunotherapy by balancing agonistic strength with FcγR affinity
Agonistic 4-1BB antibodies developed for cancer immunotherapy have suffered from either hepatotoxicity or insufficient anti-cancer activity. Here the authors determine the contribution of FcγR binding and agonistic strength to these outcomes, and engineer a 4-1BB antibody with potent anti-tumor effect and no liver toxicity in mice.
- Xinyue Qi
- , Fanlin Li
- & Xuanming Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Live-cell imaging reveals the relative contributions of antigen-presenting cell subsets to thymic central tolerance
Live-cell imaging reveals the relative contributions of antigen-presenting cell subsets to thymic central tolerance
Both thymic epithelial cells and dendritic cells present self antigens in the thymus to mediate thymic selection and T cell tolerance. Here the authors quantify, using two-photon live imaging of mouse thymic slices, the relative contribution of these two cell types, as well as the effects of antigen cross-presentation by dendritic cells, during tolerance induction.
- J. N. Lancaster
- , H. M. Thyagarajan
- & L. I. R. Ehrlich
-
Article
| Open Access Skin immunisation activates an innate lymphoid cell-monocyte axis regulating CD8+ effector recruitment to mucosal tissues
Skin immunisation activates an innate lymphoid cell-monocyte axis regulating CD8+ effector recruitment to mucosal tissues
Mucosal immunisation is important for initiating mucosal CD8+ Tcell responses but mucosal recruitment of protective CD8+ T cells can also be induced by skin immunisation. Here the authors examine the underlying mechanism and report a novel role for ILC1 recruiting CD8+ T cells to the mucosa after skin immunisation.
- Marija Zaric
- , Pablo D. Becker
- & Linda S. Klavinskis
-
Article
| Open Access Functional rare and low frequency variants in BLK and BANK1 contribute to human lupus
Functional rare and low frequency variants in BLK and BANK1 contribute to human lupus
Function-altering variants of immune-related genes cause rare autoimmune syndromes, whereas their contribution to common autoimmune diseases remains uncharacterized. Here the authors show that rare variants of lupus-associated genes are present in the majority of lupus patients and healthy controls, but only the variants found in lupus patients alter gene function.
- Simon H. Jiang
- , Vicki Athanasopoulos
- & Carola G. Vinuesa
-
Article
| Open Access Airway response to respiratory syncytial virus has incidental antibacterial effects
Airway response to respiratory syncytial virus has incidental antibacterial effects
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) can trigger secondary airway bacterial infections. Here, by proteomics and metagenomics analyses of samples from Kenyan children, the authors report that RSV associates with Streptococcus burden and a local upper airway response with direct antibacterial properties.
- Charles J. Sande
- , James M. Njunge
- & Andrew J. Pollard
-
Article
| Open Access Kappa chain maturation helps drive rapid development of an infant HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibody lineage
Kappa chain maturation helps drive rapid development of an infant HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibody lineage
Development of broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAb) against HIV-1 in infected adults is a multi-step process unachievable by current vaccine approaches. Here the authors reconstruct the ontogeny of an infant bnAb, which develops in fewer steps, and identify its unique features that may shorten the path to HIV vaccines.
- Cassandra A. Simonich
- , Laura Doepker
- & Julie Overbaugh
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Adaptive immunity
- Antigen processing and presentation
- Antimicrobial responses
- Applied immunology
- Autoimmunity
- Bone marrow transplantation
- Cell death and immune response
- Chemokines
- Coagulation system
- Complement cascade
- Cytokines
- Gene regulation in immune cells
- Haematopoiesis
- Imaging the immune system
- Immune cell death
- Immune evasion
- Immunogenetics
- Immunological disorders
- Immunotherapy
- Infection
- Infectious diseases
- Inflammation
- Innate immune cells
- Innate immunity
- Lymphatic system
- Lymphocytes
- Lymphoid tissues
- Mucosal immunology
- Neuroimmunology
- Osteoimmunology
- Plant immunology
- Signal transduction
- Translational immunology
- Transplant immunology
- Tumour immunology
- Vaccines

 Fas signaling-mediated TH9 cell differentiation favors bowel inflammation and antitumor functions
Fas signaling-mediated TH9 cell differentiation favors bowel inflammation and antitumor functions