Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access MarShie: a clearing protocol for 3D analysis of single cells throughout the bone marrow at subcellular resolution
MarShie: a clearing protocol for 3D analysis of single cells throughout the bone marrow at subcellular resolution
Three-dimensional analysis of the intact bone marrow within whole long bones remains very challenging. Here, the authors present a method that stabilizes the marrow and provides subcellular resolution of fluorescent signals throughout the murine femur.
- Till Fabian Mertens
- , Alina Tabea Liebheit
- & Anja Erika Hauser
-
Article
| Open Access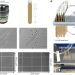 ComplexEye: a multi-lens array microscope for high-throughput embedded immune cell migration analysis
ComplexEye: a multi-lens array microscope for high-throughput embedded immune cell migration analysis
Video microscopy is key in studying cell migration, but accomplishing this in a high-throughput manner is still challenging. Here, the authors present an array microscope that can track the movements of thousands of individual cells simultaneously, and that can be used for drug screening studies.
- Zülal Cibir
- , Jacqueline Hassel
- & Matthias Gunzer
-
Article
| Open Access T cell migration requires ion and water influx to regulate actin polymerization
T cell migration requires ion and water influx to regulate actin polymerization
The ability of T cells to migrate is a central component of their functionality and is known to require WNK1 kinase that is linked to the influx of ions into the cell. Here the authors show that T cell migration requires WNK1 mediated ion and water influx to swell the membrane of the leading edge and support actin polymerisation and forward motility.
- Leonard L. de Boer
- , Lesley Vanes
- & Victor L. J. Tybulewicz
-
Article
| Open Access Dermis resident macrophages orchestrate localized ILC2 eosinophil circuitries to promote non-healing cutaneous leishmaniasis
Dermis resident macrophages orchestrate localized ILC2 eosinophil circuitries to promote non-healing cutaneous leishmaniasis
Tissue resident macrophages are intricately involved in homeostatic processes but also in tissue repair. Here Lee and colleagues show dermis-resident macrophages are a source of thymic stromal lymphopoietin and CCL24, which act on type 2 innate lymphoid cells and eosinophils respectively, to maintain their M2 properties and promote non-healing cutaneous leishmaniasis.
- Sang Hun Lee
- , Byunghyun Kang
- & David L. Sacks
-
Article
| Open Access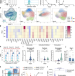 Modulation of lytic molecules restrain serial killing in γδ T lymphocytes
Modulation of lytic molecules restrain serial killing in γδ T lymphocytes
γδ T cells are unique T lymphocytes with cytotoxic functions, targeting infections and tumours. Here authors show that the target killing function of γδ T cells is tightly regulated at the level of the availability of lytic molecules granzyme B and perforin.
- Patrick A. Sandoz
- , Kyra Kuhnigk
- & Björn Önfelt
-
Article
| Open Access TIGIT can inhibit T cell activation via ligation-induced nanoclusters, independent of CD226 co-stimulation
TIGIT can inhibit T cell activation via ligation-induced nanoclusters, independent of CD226 co-stimulation
CD226 provides a co-stimulatory signal to the T cell receptor during activation, and TIGIT is believed to inhibit this process by competing for the CD226 ligand CD155. Here authors show that ligand binding induces dense nanocluster formation by TIGIT which initiates intrinsic, CD226 independent inhibitory signals, proximal to T cell receptor signalling.
- Jonathan D. Worboys
- , Katherine N. Vowell
- & Daniel M. Davis
-
Article
| Open Access Ontogenetically distinct neutrophils differ in function and transcriptional profile in zebrafish
Ontogenetically distinct neutrophils differ in function and transcriptional profile in zebrafish
Neutrophil ontogeny in zebrafish may be a continuum or consist of distinct lineages. Here the authors characterise neutrophils derived from rostral blood island and caudal haematopoietic tissue lineages and show differential gene expression and function in steady state and during wound healing.
- Juan P. García-López
- , Alexandre Grimaldi
- & Carmen G. Feijoo
-
Article
| Open Access A genetically encoded sensor for visualizing leukotriene B4 gradients in vivo
A genetically encoded sensor for visualizing leukotriene B4 gradients in vivo
Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) is a potent lipid chemoattractant driving leukocyte migration and neutrophil swarming, but methods for its real-time detection are lacking. Here, the authors develop GEM-LTB4, a genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor, and use it to visualize leukocyte-derived LTB4 gradients.
- Szimonetta Xénia Tamás
- , Benoit Thomas Roux
- & Balázs Enyedi
-
Article
| Open Access Macrophage and neutrophil heterogeneity at single-cell spatial resolution in human inflammatory bowel disease
Macrophage and neutrophil heterogeneity at single-cell spatial resolution in human inflammatory bowel disease
Chronic intestinal inflammatory diseases including ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease display extensive heterogeneity in the immunopathology, disease manifestation and response to treatment. Here the authors apply single cell transcriptomic and spatial molecular imaging, and characterise macrophage and neutrophils in samples from patients with inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Alba Garrido-Trigo
- , Ana M. Corraliza
- & Azucena Salas
-
Article
| Open Access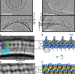 Complement is activated by elevated IgG3 hexameric platforms and deposits C4b onto distinct antibody domains
Complement is activated by elevated IgG3 hexameric platforms and deposits C4b onto distinct antibody domains
IgG3 antibodies have potent effector functions, but are not used as therapeutics and structural data are missing. Here, the authors combine cryoEM and MS to study IgG3-mediated complement activation to provide the first structural insights into IgG3.
- Leoni Abendstein
- , Douwe J. Dijkstra
- & Thomas H. Sharp
-
Article
| Open Access Antigen recognition detains CD8+ T cells at the blood-brain barrier and contributes to its breakdown
Antigen recognition detains CD8+ T cells at the blood-brain barrier and contributes to its breakdown
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) breakdown and immune cell infiltration into the central nervous system are early hallmarks of multiple sclerosis. Here, the authors demonstrate that brain endothelial cells cross-present antigen to CD8+ T cells, thereby preventing their migration and initiating BBB breakdown.
- Sidar Aydin
- , Javier Pareja
- & Britta Engelhardt
-
Article
| Open Access Inducible expression of interleukin-12 augments the efficacy of affinity-tuned chimeric antigen receptors in murine solid tumor models
Inducible expression of interleukin-12 augments the efficacy of affinity-tuned chimeric antigen receptors in murine solid tumor models
The clinical benefits of chimaeric antigen receptor (CAR) T therapy are limited by ‘on-target, off-tumour’ effects. In this study, the authors describe a strategy that promotes the recognition of antigen on tumour, but not normal, cells by combining affinity tuning with inducible interleukin-12 expression.
- Yanping Yang
- , Huan Yang
- & Moonsoo M. Jin
-
Article
| Open Access IMC-Denoise: a content aware denoising pipeline to enhance Imaging Mass Cytometry
IMC-Denoise: a content aware denoising pipeline to enhance Imaging Mass Cytometry
Multiplexed imaging technologies can reveal the complex cellular and molecular profiles of tissue. Here, the authors develop and implement a denoising pipeline to significantly enhance imaging mass cytometry quality and improve single-cell analyses.
- Peng Lu
- , Karolyn A. Oetjen
- & Daniel L. J. Thorek
-
Article
| Open Access Immune subset-committed proliferating cells populate the human foetal intestine throughout the second trimester of gestation
Immune subset-committed proliferating cells populate the human foetal intestine throughout the second trimester of gestation
The intestine is an important immunological organ in embryonic life, preparing the infant for the microbial colonization following birth. Here authors show that between gestational weeks 14 and 22, the human foetal intestine is first populated by myeloid and innate lymphoid cells, followed by the development of lymphoid cells and a wider range of proliferation-capable immune cell types.
- Nannan Guo
- , Na Li
- & Frits Koning
-
Article
| Open Access A comprehensive single-cell map of T cell exhaustion-associated immune environments in human breast cancer
A comprehensive single-cell map of T cell exhaustion-associated immune environments in human breast cancer
T cell exhaustion in breast tumours remains to be fully characterised. Here, single cell transcriptomics and imaging mass cytometry analysis of luminal breast tumours with or without exhausted T cells suggests distinct patterns of PD-1 and CXCL13 expression in T cells, and of MHC-I, but not PD-L1, expression in tumour cells.
- Sandra Tietscher
- , Johanna Wagner
- & Bernd Bodenmiller
-
Article
| Open Access Discrete LAT condensates encode antigen information from single pMHC:TCR binding events
Discrete LAT condensates encode antigen information from single pMHC:TCR binding events
The linker for activation of T cells (LAT) protein is involved in the activation of T cells. Here the authors discover micron scale LAT condensation events downstream of singly bound T-cell receptors during T cell activation and characterise how LAT condensation timing affects downstream T cell signalling.
- Darren B. McAffee
- , Mark K. O’Dair
- & Jay T. Groves
-
Article
| Open Access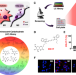 Visualizing inflammation with an M1 macrophage selective probe via GLUT1 as the gating target
Visualizing inflammation with an M1 macrophage selective probe via GLUT1 as the gating target
Studying the specific roles of macrophage subsets has been hampered by a lack of subset-specific probes. Here the authors report an M1 selective fluorescent probe named CDr17, and demonstrate the suitability of this probe for tracking M1 macrophages in vivo.
- Heewon Cho
- , Haw-Young Kwon
- & Young-Tae Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and dynamics of Toll immunoreceptor activation in the mosquito Aedes aegypti
Structure and dynamics of Toll immunoreceptor activation in the mosquito Aedes aegypti
Aedes aegypti can act as a vector for viral pathogens but the mechanism of viral resistance and evolving host-pathogen tolerance are poorly understood. Here the authors structurally characterise a duplicated pair of interacting Toll immunoreceptors and the cytokine ligand Spaetzle1C and show their dose-dependent function and mechanism of activation.
- Yoann Saucereau
- , Thomas H. Wilson
- & Monique Gangloff
-
Article
| Open Access Gata6+ resident peritoneal macrophages promote the growth of liver metastasis
Gata6+ resident peritoneal macrophages promote the growth of liver metastasis
GLPMs represent a population of fetal liver derived large peritoneal cavity Gata6+ macrophages, with the capacity to invade the tissues they surround. Here, in experimental colon cancer liver metastasis models, the authors show that GLPMs invade liver metastasis directly from the peritoneum, promoting liver metastases growth.
- Mokarram Hossain
- , Raymond Shim
- & Paul Kubes
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically active integrins target lytic secretion at the immune synapse to facilitate cellular cytotoxicity
Mechanically active integrins target lytic secretion at the immune synapse to facilitate cellular cytotoxicity
Cytotoxic response is mediated by delivery of lytic molecules at the effector cell/target cell junction site, termed the immunological synapse. Here the authors find, using single cell biophysical measurements, that the during this process the αLβ2 integrin, LFA-1, helps focus lytic granule release via talin-dependent, pulling force-mediated spatial guidance.
- Mitchell S. Wang
- , Yuesong Hu
- & Morgan Huse
-
Article
| Open Access Recycling of memory B cells between germinal center and lymph node subcapsular sinus supports affinity maturation to antigenic drift
Recycling of memory B cells between germinal center and lymph node subcapsular sinus supports affinity maturation to antigenic drift
Activated B cell enter germinal centers (GC) to become plasma cells and memory B cells. Here the authors show that some memory B cells recycle to GC via CCL-21 mediated chemotaxis to deliver antigens from the lymph node subcapsular sinus (SCS) to potentially contribute to affinity maturation and antigenic drift.
- Yang Zhang
- , Laura Garcia-Ibanez
- & Kai-Michael Toellner
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of distinct cytotoxic granules as the origin of supramolecular attack particles in T lymphocytes
Identification of distinct cytotoxic granules as the origin of supramolecular attack particles in T lymphocytes
Cytotoxic T cells have specialised granules that are important for mediating their killing function. Here the authors characterise two types of cytotoxic granules and indicate different functions and temporal release of mediators at the immunological synapse.
- Hsin-Fang Chang
- , Claudia Schirra
- & Jens Rettig
-
Article
| Open Access Postmortem high-dimensional immune profiling of severe COVID-19 patients reveals distinct patterns of immunosuppression and immunoactivation
Postmortem high-dimensional immune profiling of severe COVID-19 patients reveals distinct patterns of immunosuppression and immunoactivation
Postmortem analyses provide useful information for COVID-19 etiology. Here the authors profile 22 deceased severe COVID-19 patients with transcriptomic and histological approaches to find correlations between the presence of viral antigens with lymphocyte suppression yet myeloid activation, hinting distinct functions of these cells during pathogenesis.
- Haibo Wu
- , Peiqi He
- & Cheng Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Directly recruited GATA6 + peritoneal cavity macrophages contribute to the repair of intestinal serosal injury
Directly recruited GATA6 + peritoneal cavity macrophages contribute to the repair of intestinal serosal injury
Upon intestinal injury, bone marrow derived monocytes are recruited to the damaged site through the bloodstream. Authors here show that peritoneal cavity macrophages directly migrate to the damaged intestine in an ATP and hyaluronan dependent manner, and participate in the restoration of tissue integrity.
- Masaki Honda
- , Masashi Kadohisa
- & Taizo Hibi
-
Article
| Open Access Immune cell topography predicts response to PD-1 blockade in cutaneous T cell lymphoma
Immune cell topography predicts response to PD-1 blockade in cutaneous T cell lymphoma
PD-1 blockade is effective for only a subset of patients with cutaneous T cell lymphomas. Here, the authors report a spatial biomarker that uses immune and cancer cell topography to predict response to PD-1 blockade in this disease.
- Darci Phillips
- , Magdalena Matusiak
- & Garry P. Nolan
-
Article
| Open Access Cytotoxic T cells are able to efficiently eliminate cancer cells by additive cytotoxicity
Cytotoxic T cells are able to efficiently eliminate cancer cells by additive cytotoxicity
Cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocytes (CTL) often fail to kill tumour cells in one-to-one interactions. Here the authors show that these sublethal interactions from multiple CTL can add up over time and achieve tumour cell killing by additive cytotoxicity.
- Bettina Weigelin
- , Annemieke Th. den Boer
- & Peter Friedl
-
Article
| Open Access Integration of FRET and sequencing to engineer kinase biosensors from mammalian cell libraries
Integration of FRET and sequencing to engineer kinase biosensors from mammalian cell libraries
Existing Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) biosensors are often limited in their sensitivity. Here the authors report FRET-seq which they use to identify Fyn and ZAP70 kinase biosensors with enhanced performance, and use them to image T-cell activation and screen drugs.
- Longwei Liu
- , Praopim Limsakul
- & Yingxiao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access CD45 pre-exclusion from the tips of T cell microvilli prior to antigen recognition
CD45 pre-exclusion from the tips of T cell microvilli prior to antigen recognition
CD45 limits T cell activation, so its exclusion from the T cell immunological synapse is thought to occur as a means to enable TCR signalling. Here the authors use a variety of cellular imaging methods to show that CD45 is indeed excluded from the tips of the T cell microvilli and that this occurs prior to contact with antigen, indicating this exclusion is one of the initiating factors for antigen presentation and T cell activation.
- Yunmin Jung
- , Lai Wen
- & Klaus Ley
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic fate-mapping reveals surface accumulation but not deep organ invasion of pleural and peritoneal cavity macrophages following injury
Genetic fate-mapping reveals surface accumulation but not deep organ invasion of pleural and peritoneal cavity macrophages following injury
Body cavity macrophages reside on the serous surfaces of organs and believed to participate in organ repair following injury. Here the authors show with a fate-mapping reporter system that these cells, although accumulate at the surfaces of injured liver or lung, don’t penetrate deeply into the tissue.
- Hengwei Jin
- , Kuo Liu
- & Bin Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Temporal analysis of T-cell receptor-imposed forces via quantitative single molecule FRET measurements
Temporal analysis of T-cell receptor-imposed forces via quantitative single molecule FRET measurements
Mechanical forces acting on ligand-engaged T-cell receptors (TCRs) have previously been implicated in T-cell antigen recognition, yet their sensitivity and specificity are still poorly defined. Here, authors report a FRET-based sensor that informs directly on the magnitude and kinetics of TCR-imposed forces at the single molecule level.
- Janett Göhring
- , Florian Kellner
- & Gerhard J. Schütz
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed histology analyses for the phenotypic and spatial characterization of human innate lymphoid cells
Multiplexed histology analyses for the phenotypic and spatial characterization of human innate lymphoid cells
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are important regulators of biological processes. Here the authors combine multiplexed imaging and computational pipelines to reveal tonsillar IRF4+ ILC3s, and to identify conserved stromal landmarks for ILC localization, thereby providing a platform for future ILC studies.
- Anna Pascual-Reguant
- , Ralf Köhler
- & Anja E. Hauser
-
Article
| Open Access B cell zone reticular cell microenvironments shape CXCL13 gradient formation
B cell zone reticular cell microenvironments shape CXCL13 gradient formation
Morphogens such as chemokines form gradients to direct graded responses and modulate cell behaviors. Here the authors show, using imaging and computer simulation, that the chemokine CXCL13 originated from follicular reticular cells in the lymph nodes forms both soluble and immobilized gradients to regulate B cell recruitment and migration.
- Jason Cosgrove
- , Mario Novkovic
- & Mark C. Coles
-
Article
| Open Access Plasma membrane damage causes NLRP3 activation and pyroptosis during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
Plasma membrane damage causes NLRP3 activation and pyroptosis during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
Inflammasome activation is a response to bacterial infection but can cause damage and spread infection. Here, the authors use live single-cell imaging to show two mechanisms by which M. tuberculosis causes damage to human macrophage cell plasma membranes, resulting in activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, pyroptosis and release of infectious particles.
- Kai S. Beckwith
- , Marianne S. Beckwith
- & Trude H. Flo
-
Article
| Open Access Perivascular localization of macrophages in the intestinal mucosa is regulated by Nr4a1 and the microbiome
Perivascular localization of macrophages in the intestinal mucosa is regulated by Nr4a1 and the microbiome
Lamina propria macrophages are at the frontline of defense against intestinal pathogens. Here the authors reveal that CCR2 and NR4A1-dependent CX3CR1+ macrophages form a dense network around the vessels in the lamina propria, and implicate this anatomical structure into prevention of systemic bacterial dissemination.
- Masaki Honda
- , Bas G. J. Surewaard
- & Paul Kubes
-
Article
| Open Access Optogenetic manipulation of calcium signals in single T cells in vivo
Optogenetic manipulation of calcium signals in single T cells in vivo
The ability to manipulate and monitor calcium signaling in cells in vivo would provide insights into signaling in an endogenous context. Here the authors develop a two-photon-responsive calcium actuator and reporter combination to monitor the effect of calcium actuation on T cell migration, adhesion and chemokine release in vivo.
- Armelle Bohineust
- , Zacarias Garcia
- & Philippe Bousso
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient homing of T cells via afferent lymphatics requires mechanical arrest and integrin-supported chemokine guidance
Efficient homing of T cells via afferent lymphatics requires mechanical arrest and integrin-supported chemokine guidance
Immune cells mostly enter lymph nodes (LN) from blood circulation, but whether afferent lymphatics contributes to LN entry is unclear. Here, the authors show, using a photo-convertible reporter, that T cells in afferent lymphatics frequently enter LN and become arrested in the subcapsular sinus, with chemokines and integrins further guiding their migration in the LN.
- Rieke Martens
- , Marc Permanyer
- & Reinhold Förster
-
Article
| Open Access Brain-to-cervical lymph node signaling after stroke
Brain-to-cervical lymph node signaling after stroke
Brain damage induces systemic inflammation, but insights and implication of this induction is still unclear. Here the authors show, using rat and mouse focal cerebral ischemia models, that the damaged brain signals via the VEGF-C/VEFGR3 axis to activate inflammatory responses in the draining cervical lymph nodes to induce systemic inflammation.
- Elga Esposito
- , Bum Ju Ahn
- & Kazuhide Hayakawa
-
Article
| Open Access Chemokine receptor trafficking coordinates neutrophil clustering and dispersal at wounds in zebrafish
Chemokine receptor trafficking coordinates neutrophil clustering and dispersal at wounds in zebrafish
Inflammatory responses must be induced and resolved timely to serve protection from pathogens without inducing excessive tissue damage. Here the authors use live imaging in zebrafish to show that the intracellular trafficking of two chemokine receptors, Cxcr1 and Cxcr2, is differentially regulated on activated neutrophils to control their clustering and dispersal, respectively.
- Caroline Coombs
- , Antonios Georgantzoglou
- & Milka Sarris
-
Article
| Open Access Homogentisic acid-derived pigment as a biocompatible label for optoacoustic imaging of macrophages
Homogentisic acid-derived pigment as a biocompatible label for optoacoustic imaging of macrophages
The ability to image macrophages in vivo would provide insights into homeostasis and disease but current imaging agents have effects on viability and functionality. Here the authors develop an optoacoustic probe based on a homogentisic acid-derived pigment related to melanin, capable of visualizing macrophage migration in mice.
- Ina Weidenfeld
- , Christian Zakian
- & Andre C. Stiel
-
Article
| Open Access CXCR3 enables recruitment and site-specific bystander activation of memory CD8+ T cells
CXCR3 enables recruitment and site-specific bystander activation of memory CD8+ T cells
T cell bystander activation is induced by systemic inflammation. Here the authors show, using mouse model systems and correlating with human vaccination data, that localized inflammation elicits bystander activation, and that CXCR3 specifically recruits memory CD8+ T cells to sites of activated antigen-presenting cells for bystander activation.
- Nicholas J. Maurice
- , M. Juliana McElrath
- & Martin Prlic
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic changes in epithelial cell morphology control thymic organ size during atrophy and regeneration
Dynamic changes in epithelial cell morphology control thymic organ size during atrophy and regeneration
One aspect of ageing on immunity is attributed to accelerated thymic atrophy, but the underlying mechanism is still lacking. Here the authors show, using conditional reporter mouse models, that both atrophy and regeneration of the thymus are regulated by rate-limiting morphological changes in epithelial stroma, independent of cell death or proliferation.
- Thomas Venables
- , Ann V. Griffith
- & Howard T. Petrie
-
Article
| Open Access Tumor-reprogrammed resident T cells resist radiation to control tumors
Tumor-reprogrammed resident T cells resist radiation to control tumors
Lymphocytes are considered one of the most radiosensitive cell types in the body. Here the authors show that unlike circulating lymphocytes, tumor-infiltrating T cells survive therapeutic doses of irradiation, remaining functional and contributing to radiotherapy induced anti-tumor immunity.
- Ainhoa Arina
- , Michael Beckett
- & Ralph R. Weichselbaum
-
Article
| Open Access Oligodendrocyte precursor cells present antigen and are cytotoxic targets in inflammatory demyelination
Oligodendrocyte precursor cells present antigen and are cytotoxic targets in inflammatory demyelination
In multiple sclerosis (MS), antigen-presenting cells inducing cytotoxic T cell response against mature oligodendrocytes remain to be identified. Here the authors show that oligodendrocyte precursors cross-present antigen taken up from mature oligodendrocytes, and are targeted by cytotoxic T cells in cell culture and in an animal model of MS.
- Leslie Kirby
- , Jing Jin
- & Peter A. Calabresi
-
Article
| Open Access Tethering of vesicles to the Golgi by GMAP210 controls LAT delivery to the immune synapse
Tethering of vesicles to the Golgi by GMAP210 controls LAT delivery to the immune synapse
The immune synapse at the interface between T cells and antigen-presenting cells manifests intense vesicular trafficking, but how the vesicles are sorted is still unclear. Here the authors show that, in activated T cells, the Golgin GMAP210 specifically conveys LAT+ vesicles to immune synapse allowing proper T cell activation.
- Andres Ernesto Zucchetti
- , Laurence Bataille
- & Claire Hivroz
-
Article
| Open Access Live-cell imaging reveals the relative contributions of antigen-presenting cell subsets to thymic central tolerance
Live-cell imaging reveals the relative contributions of antigen-presenting cell subsets to thymic central tolerance
Both thymic epithelial cells and dendritic cells present self antigens in the thymus to mediate thymic selection and T cell tolerance. Here the authors quantify, using two-photon live imaging of mouse thymic slices, the relative contribution of these two cell types, as well as the effects of antigen cross-presentation by dendritic cells, during tolerance induction.
- J. N. Lancaster
- , H. M. Thyagarajan
- & L. I. R. Ehrlich
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial and temporal localization of immune transcripts defines hallmarks and diversity in the tuberculosis granuloma
Spatial and temporal localization of immune transcripts defines hallmarks and diversity in the tuberculosis granuloma
Granulomas are a hallmark and focus of infective and immunological processes during infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Here, Carow and colleagues show distinct spatial and temporal arrangement of immunological transcripts in tuberculosis granulomas.
- Berit Carow
- , Thomas Hauling
- & Martin E. Rottenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Differential organization of tonic and chronic B cell antigen receptors in the plasma membrane
Differential organization of tonic and chronic B cell antigen receptors in the plasma membrane
Signalling of the B cell receptor (BCR) is pivotal for survival and activation of naïve B cells. Here the authors show, using super-resolution microscopy techniques, that BCRs exist primarily as monomers and dimers in resting B cells, and oligomerize only on stimulation, thereby implicating a function of BCR clustering patterns on B cell biology.
- Maria Angela Gomes de Castro
- , Hanna Wildhagen
- & Felipe Opazo
-
Article
| Open Access TCR microclusters form spatially segregated domains and sequentially assemble in calcium-dependent kinetic steps
TCR microclusters form spatially segregated domains and sequentially assemble in calcium-dependent kinetic steps
Engagement of T cell receptors (TCRs) induces the formation of microclusters that mediate the downstream signalling events. Here the authors show, using high resolution TIRF-SIM and live cell imaging, that ZAP70 and LAT are recruited to TCR with distinct kinetics, with the delayed ZAP70-TCR association modulated by TCR-induced calcium flux.
- Jason Yi
- , Lakshmi Balagopalan
- & Lawrence E. Samelson
-
Article
| Open Access Perforin inhibition protects from lethal endothelial damage during fulminant viral hepatitis
Perforin inhibition protects from lethal endothelial damage during fulminant viral hepatitis
CD8 T cells can protect the liver from viral infection, but can also result in severe liver damage and organ failure. Here, the authors develop a mouse model reflecting fulminant CD8 T cell mediated viral hepatitis, which occurs in a perforin-dependent manner that is protected by the use of perforin inhibitors.
- M. Welz
- , S. Eickhoff
- & W. Kastenmüller

 Mitochondrial metabolism sustains CD8+ T cell migration for an efficient infiltration into solid tumors
Mitochondrial metabolism sustains CD8+ T cell migration for an efficient infiltration into solid tumors