Featured
-
-
Letter |
 The calcium-sensing receptor regulates the NLRP3 inflammasome through Ca2+ and cAMP
The calcium-sensing receptor regulates the NLRP3 inflammasome through Ca2+ and cAMP
Evidence is presented that activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome is regulated by the calcium-sensing receptor (CASR).
- Geun-Shik Lee
- , Naeha Subramanian
- & Jae Jin Chae
-
Comment |
 The worm returns
The worm returns
Joel V. Weinstock explains why several clinical trials are deliberately infecting people with helminths to treat autoimmune diseases.
- Joel V. Weinstock
-
Article |
 Novel Foxo1-dependent transcriptional programs control Treg cell function
Novel Foxo1-dependent transcriptional programs control Treg cell function
The results of a series of genetic experiments indicate that Foxo1 has a pivotal, Foxp3-independent role controlling regulatory T-cell function.
- Weiming Ouyang
- , Will Liao
- & Ming O. Li
-
Letter |
 Host–microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease
Host–microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease
A meta-analysis of previous genome-wide association studies of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, the two most common forms of inflammatory bowel disease, with a combined total of more than 75,000 cases and controls, finds that most loci contribute to both phenotypes and other immune-mediated disorders.
- Luke Jostins
- , Stephan Ripke
- & Judy H Cho
-
Letter |
 Accelerated disassembly of IgE–receptor complexes by a disruptive macromolecular inhibitor
Accelerated disassembly of IgE–receptor complexes by a disruptive macromolecular inhibitor
The interaction between IgE and its receptor FcεRI underlies many allergic responses; here the structure and mechanism of a newly engineered DARPin inhibitor is presented, revealing that it not only blocks the receptor–ligand interaction but also dissociates already-formed complexes.
- Beomkyu Kim
- , Alexander Eggel
- & Theodore S. Jardetzky
-
Letter |
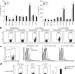 Regulatory B cells control T-cell autoimmunity through IL-21-dependent cognate interactions
Regulatory B cells control T-cell autoimmunity through IL-21-dependent cognate interactions
IL-21- and CD40-dependent cognate interactions with T cells are identified as key drivers for the generation of IL-10-producing regulatory B cells, which can protect against autoimmune disease.
- Ayumi Yoshizaki
- , Tomomitsu Miyagaki
- & Thomas F. Tedder
-
News |
 Breast-milk molecule raises risk of HIV transmission
Breast-milk molecule raises risk of HIV transmission
Although one type of sugar in breast milk from HIV-positive mothers can boost likelihood of transmission, many other sugars protect against disease.
- Anna Petherick
-
Article |
 Broad and potent neutralization of HIV-1 by a gp41-specific human antibody
Broad and potent neutralization of HIV-1 by a gp41-specific human antibody
A novel neutralizing antibody from a healthy HIV-1-infected donor that is specific for the membrane proximal region of gp41 is reported; the antibody has high potency and breadth, is not autoreactive and does not bind phospholipids.
- Jinghe Huang
- , Gilad Ofek
- & Mark Connors
-
News & Views |
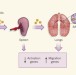 Licensed in the lungs
Licensed in the lungs
In multiple sclerosis, the body's own immune cells attack the brain and spinal cord. But how they get there from peripheral tissues has been a mystery. Surprisingly, the lungs might be a key transit point. See Letter p.675
- Richard M. Ransohoff
-
Letter |
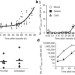 T cells become licensed in the lung to enter the central nervous system
T cells become licensed in the lung to enter the central nervous system
A Lewis rat model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is used to show that on their way to the CNS, encephalitogenic T-cell blasts are temporarily resident in the lung, where they reprogram their gene-expression profile and functional properties to enable them to transgress the blood–brain barrier into the CNS.
- Francesca Odoardi
- , Christopher Sie
- & Alexander Flügel
-
News & Views |
 Malnutrition promotes rogue bacteria
Malnutrition promotes rogue bacteria
Dietary lack of a single amino acid impairs intestinal immunity in mice, altering the guts microbial community and leaving it vulnerable to damage. The finding helps to explain how malnutrition favours gut inflammation. See Letter p.477
- Ana Izcue
- & Fiona Powrie
-
Comment |
 Towards a cure for HIV
Towards a cure for HIV
Steven G. Deeks and Françoise Barré-Sinoussi present an international research agenda to seek out a cure for AIDS.
- Steven G. Deeks
- & Françoise Barré-Sinoussi
-
News |
 Genome study highlights risk factor for multiple sclerosis
Genome study highlights risk factor for multiple sclerosis
Discovery of genetic variant could help to improve clinical trials of potential therapies.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Letter |
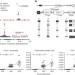 TNF receptor 1 genetic risk mirrors outcome of anti-TNF therapy in multiple sclerosis
TNF receptor 1 genetic risk mirrors outcome of anti-TNF therapy in multiple sclerosis
Genome-wide association studies in combination with functional analyses identify a genetic variant that explains why anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy, used in several autoimmune diseases, exacerbates multiple sclerosis.
- Adam P. Gregory
- , Calliope A. Dendrou
- & Lars Fugger
-
News & Views |
 Fat, bile and gut microbes
Fat, bile and gut microbes
Western-style diets could be contributing to the rapid increase in inflammatory bowel disease. New research suggests that dietary fat can alter bile composition and so favour the growth of pro-inflammatory gut microbes. See Letter p.104
- Peter J. Turnbaugh
-
Article |
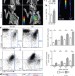 Myocardial infarction accelerates atherosclerosis
Myocardial infarction accelerates atherosclerosis
Myocardial infarction accelerates atherosclerosis through activation of the sympathetic nervous system, and the consequent release of haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.
- Partha Dutta
- , Gabriel Courties
- & Matthias Nahrendorf
-
Comment |
 Bring safe sex to China
Bring safe sex to China
China's discomfort over discussing sex, and especially homosexuality, is a major problem when it comes to HIV, says a consortium of researchers in China.
- Hong Shang
- , Junjie Xu
- & Linqi Zhang
-
Research Highlights |
Less biodiversity, more allergies
-
Outlook |
 Perspective: Rethink the immune connection
Perspective: Rethink the immune connection
Recent research suggests that the fight against type 1 diabetes is focusing too narrowly on the adaptive immune system, says Carla Greenbaum.
- Carla Greenbaum
-
Outlook |
 Immunomodulators: Cell savers
Immunomodulators: Cell savers
In type 1 diabetes, the immune system goes haywire and depletes insulin-producing cells. Drugs that interfere with this process could one day reverse the disease's course.
- Sarah DeWeerdt
-
-
News & Views Forum |
 Allergy challenged
Allergy challenged
An article suggesting that allergic responses may not be an accident of an off-target immune system, but rather a deliberate defence against potential harm, provokes the question of whether our understanding of allergy needs an overhaul. Immunologists provide their opinions. See Perspective p.465
- David Artis
- , Rick M. Maizels
- & Fred D. Finkelman
-
Perspective |
 Allergic host defences
Allergic host defences
A review of allergic host defences argues that allergic immunity has an important role in host defence against noxious environmental substances.
- Noah W. Palm
- , Rachel K. Rosenstein
- & Ruslan Medzhitov
-
-
Outlook |
Perspective: Let the sunshine in!
Population and genetic studies are confirming the link between multiple sclerosis and vitamin D, says Richard Ransohoff.
- Richard M. Ransohoff
-
Outlook |
 Progressive multiple sclerosis: The treatment gap
Progressive multiple sclerosis: The treatment gap
Most new treatments for multiple sclerosis are for patients with the relapsing–remitting form of the disease. Those with the more advanced, progressive type are being left behind.
- Courtney Humphries
-
Outlook |
 Aetiology: The X factor
Aetiology: The X factor
Researchers have plenty of theories about what might cause multiple sclerosis. But for now, the factor that triggers the disease remains elusive.
- Lauren Gravitz
-
Outlook |
 Genomics: A complex code
Genomics: A complex code
More than 100 variations in the genome have been linked to multiple sclerosis. Researchers are now trying to find the overlap with other auto-immune conditions, and understand how environmental factors interact with genes to trigger disease.
- Virginia Hughes
-
Outlook |
Perspective: Deconstructing a disease
A slew of new data suggests that it is time to rethink and reclassify autoimmune disease, says David A. Hafler.
- David A. Hafler
-
Outlook |
 Alternative therapies: Desperate measures
Alternative therapies: Desperate measures
Worms? Stents? Bee stings? Patients with multiple sclerosis who exhaust conventional therapies are turning in desperation to unproven approaches.
- Jennifer Berglund
-
Outlook |
 Stem cells: Don't believe the hype
Stem cells: Don't believe the hype
Researchers are still a long way from using stem cells to halt the decline caused by multiple sclerosis and to restore patients' health. But they are following some promising trails.
- Michael Eisenstein
-
Outlook |
 Drugs: An injection of hope
Drugs: An injection of hope
For decades, drugs have barely managed to slow the progression of multiple sclerosis. Therapies are now emerging that may even help to reverse the disease — but are they worth the risk?
- Duncan Graham-Rowe
-
Research Highlights |
Early exposure to microbes is key
-
News |
 Drug-free organ transplants without tissue matching
Drug-free organ transplants without tissue matching
Bone-marrow transfer could end the need for lifelong immunosupression.
- Elie Dolgin
-
-
News |
 Monkey vaccine hints at how to stop HIV
Monkey vaccine hints at how to stop HIV
Study could help researchers developing a human vaccine.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Research Highlights |
A boost to the brain's barrier
-
Letter |
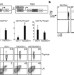 Response to self antigen imprints regulatory memory in tissues
Response to self antigen imprints regulatory memory in tissues
Thymus-derived regulatory T cells are activated by recognition of peripheral self antigen, persist in the target tissue on cessation of antigen exposure, and respond to re-exposure to self antigen with enhanced functional activity.
- Michael D. Rosenblum
- , Iris K. Gratz
- & Abul K. Abbas
-
-
Outlook |
 Treatment: In search of a booster shot
Treatment: In search of a booster shot
A plethora of therapies can keep the symptoms of allergy under control, but they can't cure. New research aims to prevent allergies from developing in the first place.
- Lauren Gravitz
-
Outlook |
 Perspective: A human touch
Perspective: A human touch
Stephen Holgate argues for a return to more human-centred studies of allergy and asthma.
- Stephen Holgate
-
Outlook |
 Atopy: Marching with allergies
Atopy: Marching with allergies
They come not single spies, but in battalions. The latest research helps explain why an individual may experience the 'atopic march' from one allergic disorder to another.
- Paige Brown
-
Outlook |
 Food: Picky eaters
Food: Picky eaters
Clinical trials are testing how careful exposure could protect people with potentially lethal allergies to everyday fare.
- Rebecca Kessler
-
Outlook |
 Perspective: Acting on the evidence
Perspective: Acting on the evidence
Allergy isn't the whole story on atopic eczema, says Hywel Williams.
- Hywel Williams
-
Outlook |
 Asthma: Breathing new life into research
Asthma: Breathing new life into research
Asthma was once thought to be a uniform disease triggered by one type of immune cell. Researchers are now revealing the complexity of the condition and hope to hasten new drugs for forms unresponsive to steroids.
- Amy Maxmen
-
Outlook |
 Genetics: Seeking a gene genie
Genetics: Seeking a gene genie
Rare gene variants could be key to unlocking the underlying genetics of allergy, now that whole genome sequencing and other technologies have sharpened the focus of epidemiology.
- Erica Westly
-
Article |
 Complement factor H binds malondialdehyde epitopes and protects from oxidative stress
Complement factor H binds malondialdehyde epitopes and protects from oxidative stress
- David Weismann
- , Karsten Hartvigsen
- & Christoph J. Binder
-
Letter |
 Broad neutralization coverage of HIV by multiple highly potent antibodies
Broad neutralization coverage of HIV by multiple highly potent antibodies
- Laura M. Walker
- , Michael Huber
- & Pascal Poignard
-
News |
 How microbes train our immune system
How microbes train our immune system
Gut bacteria coax T cells to see them as friends.
- Alla Katsnelson

 Interleukin receptor activates a MYD88–ARNO–ARF6 cascade to disrupt vascular stability
Interleukin receptor activates a MYD88–ARNO–ARF6 cascade to disrupt vascular stability Algeria to tackle HIV/AIDS
Algeria to tackle HIV/AIDS