Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling of cocatalysts photodeposited selectively on facets of BiVO4 to boost solar water splitting
Unraveling of cocatalysts photodeposited selectively on facets of BiVO4 to boost solar water splitting
Artificial photosynthesis offers an integrated means to convert light to fuel, but efficiencies are often low. Here, authors report a Z-scheme system utilizing Ir and FeCoOx co-catalysts to enhance charge separation on BiVO4 facets that achieves high quantum efficiencies for overall water splitting.
- Yu Qi
- , Jiangwei Zhang
- & Fuxiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Merging enzymes with chemocatalysis for amide bond synthesis
Merging enzymes with chemocatalysis for amide bond synthesis
Proteins, other metabolites and many valuable synthetic products contain amide bonds and there is a need for more sustainable amide synthesis routes. Here the authors show an integrated next generation multi-catalytic system, merging nitrile hydratase enzymes with a Cu-catalysed N-arylation reaction in a single reaction vessel, for the construction of ubiquitous amide bonds.
- Luis Bering
- , Elliott J. Craven
- & Jason Micklefield
-
Article
| Open Access Iridium-catalyzed enantioconvergent hydrogenation of trisubstituted olefins
Iridium-catalyzed enantioconvergent hydrogenation of trisubstituted olefins
Usually asymmetric hydrogenation of olefins is enantiodivergent and thus requires isomerically pure olefins, which is a considerable drawback. Here, the authors show a general iridium-catalyzed enantioconvergent hydrogenation of a broad range of functionalized trisubstituted olefins.
- Bram B. C. Peters
- , Jia Zheng
- & Pher G. Andersson
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic production of low-carbon footprint sustainable natural gas
Catalytic production of low-carbon footprint sustainable natural gas
The recalcitrance of lignocellulosic biomass is the major limitation for the production of natural gas. Here the authors develop a catalytic-drive approach with Ni2Al3 alloy catalyst to enable nearly complete conversion of various agricultural and forestry residues into natural gas.
- Xiaoqin Si
- , Rui Lu
- & Fang Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanochemical synthesis of magnesium-based carbon nucleophiles in air and their use in organic synthesis
Mechanochemical synthesis of magnesium-based carbon nucleophiles in air and their use in organic synthesis
Grignard reagents have widespread utility in organic chemistry, but their preparation is limited by several drawbacks, such as the use of dry organic solvents and long reaction times. Here, the authors report a general mechanochemical synthesis of Grignard reagents in paste form in air, using a ball milling technique.
- Rina Takahashi
- , Anqi Hu
- & Hajime Ito
-
Article
| Open Access Changing the game of time resolved X-ray diffraction on the mechanochemistry playground by downsizing
Changing the game of time resolved X-ray diffraction on the mechanochemistry playground by downsizing
Time-resolved in situ (TRIS) X-ray powder diffraction promises great potential to study mechanochemical processes. Here, the authors develop a strategy to enhance the resolution of TRIS experiments to allow deeper interpretation of mechanochemical transformations; the method is applied to a variety of model systems including inorganic, metal-organic, and organic mechanosyntheses.
- Giulio I. Lampronti
- , Adam A. L. Michalchuk
- & Franziska Emmerling
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable and functional deep eutectic solvents for lignocellulose valorization
Tunable and functional deep eutectic solvents for lignocellulose valorization
Deep eutectic solvents (DES) are intriguing green reaction media for biomass processing, however, undesired lignin condensation is a typical drawback. Here the authors develop a tunable ternary DES system that allows for stabilization of reactive intermediates for efficient lignocellulose fractionation.
- Yongzhuang Liu
- , Noemi Deak
- & Katalin Barta
-
Article
| Open Access Directed evolution of prenylated FMN-dependent Fdc supports efficient in vivo isobutene production
Directed evolution of prenylated FMN-dependent Fdc supports efficient in vivo isobutene production
Isobutene is a high value gaseous alkene that is widely used as fuel additive and a chemical building block. Here, the authors report an alternative pathway for isobutene bioproduction by directed evolution of prenylated FMN-dependent ferulic acid decarboxylase.
- Annica Saaret
- , Benoît Villiers
- & David Leys
-
Article
| Open Access Electrocatalytic upcycling of polyethylene terephthalate to commodity chemicals and H2 fuel
Electrocatalytic upcycling of polyethylene terephthalate to commodity chemicals and H2 fuel
Plastic upcycling to value-added products is of great interests. Here the authors investigate a nickel-cobalt phosphide electrocatalyst for electroreforming of polyethylene terephthalate plastic toward valuable potassium diformate, terephthalic acid, and H2 fuel.
- Hua Zhou
- , Yue Ren
- & Haohong Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Zn-Nx sites on N-doped carbon for aerobic oxidative cleavage and esterification of C(CO)-C bonds
Zn-Nx sites on N-doped carbon for aerobic oxidative cleavage and esterification of C(CO)-C bonds
Selective cleavage of C-C bonds is very important in organic chemistry, but remains challenging because of their inert chemical nature. Here, the authors report that Zn2+ coordinated with N species on N-doped carbon catalysts can catalyze the aerobic oxidative cleavage and esterification of C(CO)-C bonds with high efficiency and activity.
- Chao Xie
- , Longfei Lin
- & Buxing Han
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphorus coordinated Rh single-atom sites on nanodiamond as highly regioselective catalyst for hydroformylation of olefins
Phosphorus coordinated Rh single-atom sites on nanodiamond as highly regioselective catalyst for hydroformylation of olefins
Single-atom Rh catalysts present superior activity in olefins hydroformylation, yet with limited success in regioselectivity control. Here the authors develop a Rh1 single-atom catalyst with nanodiamond as support, with which good to excellent regioselectivities to branched aldehydes in hydroformylation of terminal olefins are achieved.
- Peng Gao
- , Guanfeng Liang
- & Fen-Er Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainable production of benzene from lignin
Sustainable production of benzene from lignin
Efficient production of benzene from lignin is attractive and of great importance, but has not been realized. Here, the authors develop a strategy to transform lignin into benzene over a RuW/zeolite catalyst in water, and the yield of benzene can be as high as 18.8% on lignin weight basis.
- Qinglei Meng
- , Jiang Yan
- & Buxing Han
-
Article
| Open Access A tool for identifying green solvents for printed electronics
A tool for identifying green solvents for printed electronics
For printed electronics to realize its potential as a sustainable ubiquitous technology, eco-friendly solvents that deliver excellent ink performance must be found. Here, the authors report a free online tool that identifies functional green solvents for solution-processed printed electronics.
- Christian Larsen
- , Petter Lundberg
- & Ludvig Edman
-
Article
| Open Access Visible-light photoredox-catalyzed umpolung carboxylation of carbonyl compounds with CO2
Visible-light photoredox-catalyzed umpolung carboxylation of carbonyl compounds with CO2
Compounds bearing a carbonyl group, such as aldehydes and ketones, are important industrial chemicals and widespread in pharmaceuticals and natural products. Here, the authors report a strategy for visible-light photoredox-catalyzed umpolung carboxylation of diverse carbonyl compounds with CO2, to generate valuable α-hydroxycarboxylic acids.
- Guang-Mei Cao
- , Xin-Long Hu
- & Da-Gang Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Unique reactivity of nanoporous cellulosic materials mediated by surface-confined water
Unique reactivity of nanoporous cellulosic materials mediated by surface-confined water
The efficiency of chemical reactions in biological systems is often connected to the properties of confined water, but the developments and applications of artificial mimicking systems are impeded by the complexity of the biological systems. Here, the authors show how surface bound water in nanoporous cellulosic fibers can increase the reaction rate of surface acetylation reactions and enable regioselectivity of the reaction
- Marco Beaumont
- , Paul Jusner
- & Thomas Rosenau
-
Article
| Open Access Raw biomass electroreforming coupled to green hydrogen generation
Raw biomass electroreforming coupled to green hydrogen generation
The scale-up of the coupling of water electroreduction (HER) with organic electrooxidation remains challenging. Here the authors address this challenge by coupling HER with electrooxidation of raw biomass chitin, cogenerating acetate and green hydrogen safely at high current density.
- Hu Zhao
- , Dan Lu
- & Hong Li
-
Article
| Open Access BioAIEgens derived from rosin: how does molecular motion affect their photophysical processes in solid state?
BioAIEgens derived from rosin: how does molecular motion affect their photophysical processes in solid state?
To date we have a myriad of luminogenes at our deposal but many of them face problems like weakened emission in the aggregated state as well as poor sustainability. Here, the authors develop a class of rosin-derived luminogens with aggregation induced emission properties providing good biocompatibility and demonstrate their application in organelle imaging.
- Xu-Min Cai
- , Yuting Lin
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Boosting photocatalytic hydrogen production from water by photothermally induced biphase systems
Boosting photocatalytic hydrogen production from water by photothermally induced biphase systems
The solar-driven H2 production from water by particulate photocatalysts is an effective approach to produce H2 fuel. Here, the authors propose an integrated photothermal–photocatalytic biphase system, which lowers the reaction barrier and the delivery resistance of the H2, boosting the catalytic H2 evolution rate.
- Shaohui Guo
- , Xuanhua Li
- & Bingqing Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Selective hydrogenation of 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural to 5-methylfurfural over single atomic metals anchored on Nb2O5
Selective hydrogenation of 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural to 5-methylfurfural over single atomic metals anchored on Nb2O5
Selective hydrogenation of 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural (HMF) to 5-Methylfurfural using H2 as reductant is very attractive, but remains challenging. Here, the authors report that isolated single atomic catalysts can catalyze the reaction efficiently with selectivity >99% at complete conversion of HMF.
- Shaopeng Li
- , Minghua Dong
- & Buxing Han
-
Article
| Open Access Ionic liquid enables highly efficient low temperature desalination by directional solvent extraction
Ionic liquid enables highly efficient low temperature desalination by directional solvent extraction
Directional Solvent Extraction is an emerging non-membrane desalination technology for sea water desalination but is limited by throughput and energy efficiency. Here, the authors demonstrate that the production rate and energy efficiency can be increased by using ionic liquids as directional solvent.
- Jiaji Guo
- , Zachary D. Tucker
- & Tengfei Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Metal-free atom transfer radical polymerization with ppm catalyst loading under sunlight
Metal-free atom transfer radical polymerization with ppm catalyst loading under sunlight
Organocatalytic atom transfer radical polymerization (O-ATRP) is attractive due to its metal-free nature but catalysts are rarely applied at a low loading. Here the authors introduce a catalyst design logic based on heteroatom-doping of polycyclic arenes, which led to the discovery of oxygen-doped anthanthrene as an organic photoredox catalysts for O-ATRP.
- Qiang Ma
- , Jinshuai Song
- & Saihu Liao
-
Article
| Open Access Selective hydrogenolysis of catechyl lignin into propenylcatechol over an atomically dispersed ruthenium catalyst
Selective hydrogenolysis of catechyl lignin into propenylcatechol over an atomically dispersed ruthenium catalyst
C-lignin represents an ideal feedstock for producing catechol derivatives. Here, the authors engineered an atomically dispersed Ru catalyst, which can cleave C−O bonds efficiently and circumvent C=C bonds hydrogenation selectively, thus leading to propenylcatechol in high yields with high TONs.
- Shuizhong Wang
- , Kaili Zhang
- & Guoyong Song
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient carbon dioxide hydrogenation to formic acid with buffering ionic liquids
Efficient carbon dioxide hydrogenation to formic acid with buffering ionic liquids
Basic ionic liquids provide a buffering effect that enables the efficient synthesis of free formic acid from CO2 hydrogenation. Here, a highly efficient catalytic system that transforms CO2 to formic acid without the need of strong bases is demonstrated, avoiding the formation of formate salts.
- Andreas Weilhard
- , Stephen P. Argent
- & Victor Sans
-
Article
| Open Access Transforming carbon dioxide into jet fuel using an organic combustion-synthesized Fe-Mn-K catalyst
Transforming carbon dioxide into jet fuel using an organic combustion-synthesized Fe-Mn-K catalyst
Design and discovery of catalysts to make clean energy and mitigate the harmful effect of greenhouse gases remains a massive challenge. Here the authors report a combustion-synthesised iron-based catalyst of high activity and selectivity for directly converting CO2 to aviation jet fuel.
- Benzhen Yao
- , Tiancun Xiao
- & Peter P. Edwards
-
Article
| Open Access Visible-light photoredox-catalyzed C–O bond cleavage of diaryl ethers by acridinium photocatalysts at room temperature
Visible-light photoredox-catalyzed C–O bond cleavage of diaryl ethers by acridinium photocatalysts at room temperature
The high bond energies of C–O bonds in biomass and its derivatives make their cleavage very challenging. Here, the authors report a photoredox-catalyzed C–O bond cleavage in diaryl ethers by acidolysis with an aryl carboxylic acid followed by hydrolysis in a one-pot manner.
- Fang-Fang Tan
- , Xiao-Ya He
- & Yang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Empowering alcohols as carbonyl surrogates for Grignard-type reactions
Empowering alcohols as carbonyl surrogates for Grignard-type reactions
Alcohols are more naturally abundant than carbonyl compounds, which in turn are well known for their reactivity in Grignard reactions. Here, the authors showcase a distinct Grignard-like reactivity by using alcohols as coupling partners with hydrazones and synthesize more complex alcohols under ruthenium catalysis.
- Chen-Chen Li
- , Haining Wang
- & Chao-Jun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Photosynthetic hydrogen production by droplet-based microbial micro-reactors under aerobic conditions
Photosynthetic hydrogen production by droplet-based microbial micro-reactors under aerobic conditions
The development of techniques capable of orchestrating the assembly of living cells into multicellular ensembles with synergistic and function is challenge. Here, the authors construct algal or algal/bacterial cells-based core shell-like structure based on aqueous two-phase system for synergic photosynthetic H2 production.
- Zhijun Xu
- , Shengliang Wang
- & Stephen Mann
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of chiral anti-1,2-diamine derivatives through copper(I)-catalyzed asymmetric α-addition of ketimines to aldimines
Synthesis of chiral anti-1,2-diamine derivatives through copper(I)-catalyzed asymmetric α-addition of ketimines to aldimines
Chiral 1,2-diamines are useful chemicals used as ligands in asymmetric catalysis. Here, the authors report a copper(I)-catalyzed asymmetric α-addition of ketimines derived from trifluoroacetophenone and 2- or 4-NO2-benzylamines to aldimines, affording a series of chiral anti-1,2-diamine derivatives.
- Xu-Cheng Gan
- , Cheng-Yuan Zhang
- & Liang Yin
-
Article
| Open Access Reductive cyanation of organic chlorides using CO2 and NH3 via Triphos–Ni(I) species
Reductive cyanation of organic chlorides using CO2 and NH3 via Triphos–Ni(I) species
Nitriles are key intermediates in production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals and organic materials. Here, the authors report a nickel-catalyzed reductive cyanation of organic chlorides with CO2/NH3 and urea as cyanation reagents to afford a broad range of organic nitriles.
- Yanan Dong
- , Peiju Yang
- & Yuehui Li
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable aesthetic transparent wood for energy efficient buildings
Scalable aesthetic transparent wood for energy efficient buildings
Transparent wood composites are promising engineered materials for green energy-efficient building. Here, authors demonstrate novel aesthetic wood with integrated functions of optical transparency, UV-blocking, thermal insulation, and mechanical strength for this sustainable application.
- Ruiyu Mi
- , Chaoji Chen
- & Liangbing Hu
-
Article
| Open Access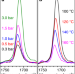 Photodegradable branched polyethylenes from carbon monoxide copolymerization under benign conditions
Photodegradable branched polyethylenes from carbon monoxide copolymerization under benign conditions
Small amounts of in-chain keto groups render polyethylene (PE) photodegradable, a desirable feature in view of environmental plastics pollution. Here the authors introduce low ketone content by copolymerization in organic solvent or under aqueous conditions at moderate pressures.
- Tobias O. Morgen
- , Maximilian Baur
- & Stefan Mecking
-
Article
| Open Access Enantiospecific electrochemical rearrangement for the synthesis of hindered triazolopyridinone derivatives
Enantiospecific electrochemical rearrangement for the synthesis of hindered triazolopyridinone derivatives
Chiral and hindered triazolopyridinone derivatives are an underexplored area of chemical space mainly due to their challenging synthesis via classical methods. Here, the authors report an electrochemical rearrangement for the synthesis of triazolopyridinones using diverse, available alkyl carboxylic acids as starting materials.
- Zenghui Ye
- , Yanqi Wu
- & Fengzhi Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling hydrocerussite as an electrochemically stable active phase for efficient carbon dioxide electroreduction to formate
Unveiling hydrocerussite as an electrochemically stable active phase for efficient carbon dioxide electroreduction to formate
While electrochemical CO2 reduction represents a renewable means to produce high-value products, catalyst transformation may compete with desirable processes. Here, authors prevent catalyst self-reduction during CO2 electroreduction and show stable, formate-selective performances of hydrocerussite.
- Yanmei Shi
- , Yan Ji
- & Bin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Reductive dearomative arylcarboxylation of indoles with CO2 via visible-light photoredox catalysis
Reductive dearomative arylcarboxylation of indoles with CO2 via visible-light photoredox catalysis
Catalytic reductive coupling of two electrophiles and one C = C bond is usually performed by two electron transfer metal catalysis. Herein, the authors show a visible light photoredox-catalyzed successive single electron transfer leading to dearomative arylcarboxylation of indoles with CO2 and generating indoline-3-carboxylic acids.
- Wen-Jun Zhou
- , Zhe-Hao Wang
- & Da-Gang Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Cobalt-catalyzed highly enantioselective hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids
Cobalt-catalyzed highly enantioselective hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids
A large number of marketed drugs contains a chiral carboxylic acid scaffold. Here, the authors report the asymmetric hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids to α-chiral carboxylic acids using a cobalt catalyst bearing an electron-donating chiral diphosphine ligand.
- Xiaoyong Du
- , Ye Xiao
- & Xumu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing oxidation resistance of Cu(I) by tailoring microenvironment in zeolites for efficient adsorptive desulfurization
Enhancing oxidation resistance of Cu(I) by tailoring microenvironment in zeolites for efficient adsorptive desulfurization
Zeolite Cu(I)Y is attractive for adsorptive removal of sulfur compounds from fuel, however practical application is limited by instability of Cu(I). Here the authors use a coating to achieve superhydrophobicity in the zeolite, leading to improved Cu(I) stability against oxidation and thiophene removal.
- Yu-Xia Li
- , Jia-Xin Shen
- & Lin-Bing Sun
-
Article
| Open Access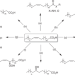 Photobiocatalytic synthesis of chiral secondary fatty alcohols from renewable unsaturated fatty acids
Photobiocatalytic synthesis of chiral secondary fatty alcohols from renewable unsaturated fatty acids
Natural fatty acids are important starting materials in bio-based chemical production. Here, the authors developed a two-enzyme cascade to produce enantiomerically pure secondary fatty alcohols from natural unsaturated fatty acids in one pot.
- Wuyuan Zhang
- , Jeong-Hoo Lee
- & Frank Hollmann
-
Article
| Open Access Photoinduced site-selective alkenylation of alkanes and aldehydes with aryl alkenes
Photoinduced site-selective alkenylation of alkanes and aldehydes with aryl alkenes
Dehydrogenative alkenylation of C-H bonds is an atom-economical approach to prepare more complex olefins. Here, the authors use a combination of decatungstate and a cobaloxime catalyst for the photocatalytic dehydrogenative alkenylation of alkanes and aliphatic aldehydes with aryl alkenes.
- Hui Cao
- , Yulong Kuang
- & Jie Wu
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance particulate matter including nanoscale particle removal by a self-powered air filter
High-performance particulate matter including nanoscale particle removal by a self-powered air filter
Particulate matter (PM) pollutants have been considered serious threats to public health but effective removal of nanoscale particles (NPs) by filter materials is challenging. Here, the authors fabricate an ionic liquid based self-powered air filter that can be used in high-efficiency removal of PM, including NPs.
- Guo-Hao Zhang
- , Qiu-Hong Zhu
- & Guo-Hong Tao
-
Article
| Open Access CO2 controls the oriented growth of metal-organic framework with highly accessible active sites
CO2 controls the oriented growth of metal-organic framework with highly accessible active sites
Producing two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with highly exposed active surfaces is important for catalysis. Here, authors prepare MOF nanosheets by using CO2 as a capping agent to control the oriented growth of MOFs.
- Fanyu Zhang
- , Jianling Zhang
- & Jing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Photo splitting of bio-polyols and sugars to methanol and syngas
Photo splitting of bio-polyols and sugars to methanol and syngas
Methanol and syngas are important fuels and chemicals, which are presently produced from fossil resources. Here, the authors report the conversion of biomass-derived polyols and sugars into methanol and syngas via UV light irradiation under room temperature.
- Min Wang
- , Meijiang Liu
- & Feng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Silica accelerates the selective hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol on cobalt catalysts
Silica accelerates the selective hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol on cobalt catalysts
The hydrogenation of CO2 into valuable chemicals is greatly demanded, but suffers from complex product distribution. Here, the authors reported that, as a support and ligand, silica boosts cobalt catalysts to selectively hydrogenate CO2 into the desired methanol product.
- Lingxiang Wang
- , Erjia Guan
- & Feng-Shou Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Single-pass transformation of syngas into ethanol with high selectivity by triple tandem catalysis
Single-pass transformation of syngas into ethanol with high selectivity by triple tandem catalysis
Direct synthesis of ethanol from non-petroleum carbon resources via syngas (CO/H2) is a highly attractive but challenging target. Here, the authors report a triple tandem catalytic system for single-pass conversion of syngas into ethanol with selectivity as high as 90%.
- Jincan Kang
- , Shun He
- & Ye Wang
-
Comment
| Open Access Is electrosynthesis always green and advantageous compared to traditional methods?
Is electrosynthesis always green and advantageous compared to traditional methods?
While electrosynthesis represents a green and advantageous alternative to traditional synthetic methods, electrochemical reactions still suffer from some drawbacks that require further efforts in order to fully express the potential of electricity-driven transformations. In this Comment, we will briefly discuss both the advantages and limitations of electrosynthesis, especially when compared with the other traditional synthetic organic methods, and share some forward-looking thoughts on the future developments of electrochemical reactions.
- Yong Yuan
- & Aiwen Lei
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon dioxide electroreduction on single-atom nickel decorated carbon membranes with industry compatible current densities
Carbon dioxide electroreduction on single-atom nickel decorated carbon membranes with industry compatible current densities
Here the authors deploy Ni single atom-decorated carbon membranes as integrated gas diffusion electrodes to construct an extremely stable three-phase interface for CO2 electroreduction, producing CO with a partial current density of 308.4 mA cm–2 and a Faradaic efficiency of 88% for up to 120 h.
- Hengpan Yang
- , Qing Lin
- & Chuanxin He
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient electrochemical production of glucaric acid and H2 via glucose electrolysis
Efficient electrochemical production of glucaric acid and H2 via glucose electrolysis
Renewable biomass conversion may afford high-value products from common materials, but catalysts usually require expensive metals and exhibit poor selectivities. Here, authors employ nickel-iron oxide and nitride electrocatalysts to produce H2 and to convert glucose to glucaric acid selectively.
- Wu-Jun Liu
- , Zhuoran Xu
- & Han-Qing Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Chemo-enzymatic cascades to produce cycloalkenes from bio-based resources
Chemo-enzymatic cascades to produce cycloalkenes from bio-based resources
Cycloalkenes are bulk petrochemicals that are currently obtained from fossil fuels. Here, the authors developed multi enzyme pathways in combination with a Ru-catalyzed metathesis reaction for the one-pot production of cyclopentene, cyclohexene, and cycloheptene from olive oil-derived intermediates.
- Shuke Wu
- , Yi Zhou
- & Thomas R. Ward
-
Article
| Open Access Green oxidation of indoles using halide catalysis
Green oxidation of indoles using halide catalysis
Indole oxidation represents a fundamental organic transformation delivering valuable nitrogen compounds. Here, the authors report a general halide catalysis protocol applied to three classes of oxidation reactions of indoles with oxone as a sustainable terminal oxidant.
- Jun Xu
- , Lixin Liang
- & Rongbiao Tong
-
Article
| Open Access Highly selective oxygen reduction to hydrogen peroxide on transition metal single atom coordination
Highly selective oxygen reduction to hydrogen peroxide on transition metal single atom coordination
Hydrogen peroxide can be produced alternatively using green inputs such as air, water, and sunlight but this requires a selective catalyst. Here the authors report an iron single atom catalyst that can convert oxygen into hydrogen peroxide with a selectivity of above 95% in both alkaline and neutral pH.
- Kun Jiang
- , Seoin Back
- & Haotian Wang

 Non-thermal plasma-assisted rapid hydrogenolysis of polystyrene to high yield ethylene
Non-thermal plasma-assisted rapid hydrogenolysis of polystyrene to high yield ethylene