Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Land use change and carbon emissions of a transformation to timber cities
Land use change and carbon emissions of a transformation to timber cities
Wood used in construction stores carbon and reduces the emissions from steel and cement production. Transformation to timber cities while protecting forest and biodiversity is possible without significant increase in competition for land.
- Abhijeet Mishra
- , Florian Humpenöder
- & Alexander Popp
-
Article
| Open Access Co-benefits of CO2 emission reduction from China’s clean air actions between 2013-2020
Co-benefits of CO2 emission reduction from China’s clean air actions between 2013-2020
China’s clean air action stimulated a net accumulative reduction of 2.43 Gt CO2 emission from 2013-2020. Phase-out and upgrades of outdated, polluting, and inefficient combustion facilities have promoted the transition of the country’s energy system.
- Qinren Shi
- , Bo Zheng
- & Qiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Inequality can double the energy required to secure universal decent living
Inequality can double the energy required to secure universal decent living
In exploring the energy required to provide decent living for all, the authors find the costs of inequality to be far greater than that of population growth. Nonetheless, population growth remains important for other reasons.
- Joel Millward-Hopkins
-
Article
| Open Access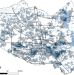 Social inequalities in climate change-attributed impacts of Hurricane Harvey
Social inequalities in climate change-attributed impacts of Hurricane Harvey
New study shows that up to 50% of properties flooded after hurricane Harvey flooded because of climate change, with low-income and Latina/x/o neighborhoods experiencing higher climate change-attributed impacts.
- Kevin T. Smiley
- , Ilan Noy
- & Oliver E. J. Wing
-
Article
| Open Access Increased energy use for adaptation significantly impacts mitigation pathways
Increased energy use for adaptation significantly impacts mitigation pathways
A new study characterizes adaptation in mitigation pathways, and shows that climate adaptation can lead to higher energy demand, power system costs and carbon prices, with mitigation’s benefits compensating decarbonization costs.
- Francesco Pietro Colelli
- , Johannes Emmerling
- & Enrica De Cian
-
Article
| Open Access Human expansion into Asian highlands in the 21st Century and its effects
Human expansion into Asian highlands in the 21st Century and its effects
Most of the intensive human activities usually occur in lowlands. Here the authors report that human activity expansions also were widely distributed in Asian highlands in the 21st century and held dual effects, which provides new insights for regional human activity expansions.
- Chao Yang
- , Huizeng Liu
- & Guofeng Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Americans experience a false social reality by underestimating popular climate policy support by nearly half
Americans experience a false social reality by underestimating popular climate policy support by nearly half
A new study finds that Americans underestimate how many are concerned about climate change as well as support for major climate policies by nearly half, with climate policy supporters significantly outnumbering non-supporters.
- Gregg Sparkman
- , Nathan Geiger
- & Elke U. Weber
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring corporate Paris Compliance using a strict science-based approach
Measuring corporate Paris Compliance using a strict science-based approach
New study defines key guidelines to accurately assess the alignment of companies with Paris goals, finding that current methods to evaluate performance are deficient with few companies assessed as Paris Compliant.
- S. Rekker
- , M. C. Ives
- & C. Greig
-
Article
| Open Access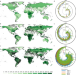 Contrasting inequality in human exposure to greenspace between cities of Global North and Global South
Contrasting inequality in human exposure to greenspace between cities of Global North and Global South
Through an analysis of global differences in human exposure to greenspace, a new study identifies a contrasting pattern of greenspace exposure between Global South and North cities and finds seasonal variations in greenspace exposure inequality.
- Bin Chen
- , Shengbiao Wu
- & Peng Gong
-
Article
| Open Access Tracing the origin of lithium in Li-ion batteries using lithium isotopes
Tracing the origin of lithium in Li-ion batteries using lithium isotopes
Rechargeable Li-ion batteries play a key role in the energy transition towards clean energy. It is challenging for end users to ensure that Li comes from environmentally and responsible sources. Here the authors show that Li isotope ‘fingerprints’ are a useful tool for determining the origin of Li in battery.
- Anne-Marie Desaulty
- , Daniel Monfort Climent
- & Catherine Guerrot
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient use of cement and concrete to reduce reliance on supply-side technologies for net-zero emissions
Efficient use of cement and concrete to reduce reliance on supply-side technologies for net-zero emissions
A new study finds supply-side efforts alone are unlikely to lead to net-zero emissions across the cement and concrete cycle by 2050, advocating for more efficient use of cement and concrete in the built environment and more strategic options for decarbonization.
- Takuma Watari
- , Zhi Cao
- & Keisuke Nansai
-
Article
| Open Access Responding to eruptive transitions during the 2020–2021 eruption of La Soufrière volcano, St. Vincent
Responding to eruptive transitions during the 2020–2021 eruption of La Soufrière volcano, St. Vincent
The 2020 – 2021 eruption of La Soufrière volcano transitioned from an effusive to explosive eruption style. Here the authors show that input from multiple monitoring datasets and an evolving conceptual model were key to anticipating and responding to the eruptive transition at the La Soufrière volcano, St. Vincent, in a resource-constrained setting.
- E. P. Joseph
- , M. Camejo-Harry
- & R. S. J. Sparks
-
Article
| Open Access Contrasting suitability and ambition in regional carbon mitigation
Contrasting suitability and ambition in regional carbon mitigation
New study finds geographical mismatch in cross-regional ranking between cost and benefit of carbon mitigation, as well as spatial mismatch between relative suitability of mitigation and mitigation ambition of emitters.
- Yu Liu
- , Mingxi Du
- & Klaus Hubacek
-
Article
| Open Access Shallow subsurface heat recycling is a sustainable global space heating alternative
Shallow subsurface heat recycling is a sustainable global space heating alternative
Using shallow geothermal energy systems to recycle the heat accumulating in the subsurface due to climate change and urbanization is a feasible, sustainable, and opportunistic alternative to conventional space heating in the face of climate change
- Susanne A. Benz
- , Kathrin Menberg
- & Barret L. Kurylyk
-
Article
| Open Access Green gentrification in European and North American cities
Green gentrification in European and North American cities
The relationship between new greenspaces and gentrification is an important one for urbanization. Here the authors show a positive relationship for at least one decade between greening in the 1990s–2000s and gentrification that occurred between 2000–2016 in 17 of 28 studied cities in North America and Europe.
- Isabelle Anguelovski
- , James J. T. Connolly
- & Joaquin Martinez Minaya
-
Comment
| Open AccessGlobal exposure to flood risk and poverty
Flooding is a pervasive natural hazard, with new research demonstrating that more than one in five people around the world live in areas directly exposed to 1-in-100 year flood risk. Exposure to such flood risk is particularly concentrated amongst lower income households worldwide.
- Thomas K. J. McDermott
-
Article
| Open Access Sharing the effort of the European Green Deal among countries
Sharing the effort of the European Green Deal among countries
An ethically-based method for allocating climate change mitigation effort among subsidiaries, applicable worldwide, is proposed. Applied to the EU Green Deal, this results in a wider range of targets than the Commission’s proposal of 2021.
- Karl W. Steininger
- , Keith Williges
- & Keywan Riahi
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-cutting scenarios and strategies for designing decarbonization pathways in the transport sector toward carbon neutrality
Cross-cutting scenarios and strategies for designing decarbonization pathways in the transport sector toward carbon neutrality
New study shows how region-specific policy under the Avoid–Shift–Improve framework may aid in realizing a deep decarbonization in the transport sector and assist in achieving China’s carbon neutrality goals.
- Runsen Zhang
- & Tatsuya Hanaoka
-
Article
| Open Access Targeting climate adaptation to safeguard and advance the Sustainable Development Goals
Targeting climate adaptation to safeguard and advance the Sustainable Development Goals
Without targeted climate adaptation, impacts of climate change threaten achievement of all 169 SDG targets. Fuldauer et al. provide an actionable framework to assess these impacts and help systematically align national adaptation plans with the SDGs.
- Lena I. Fuldauer
- , Scott Thacker
- & Jim W. Hall
-
Article
| Open Access Meeting sustainable development goals via robotics and autonomous systems
Meeting sustainable development goals via robotics and autonomous systems
A horizon scan was used to explore possible impacts of robotics and automated systems on achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Positive effects are likely. Iterative regulatory processes and continued dialogue could help avoid environmental damages and increases in inequality.
- Solène Guenat
- , Phil Purnell
- & Martin Dallimer
-
Article
| Open Access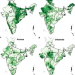 Solving groundwater depletion in India while achieving food security
Solving groundwater depletion in India while achieving food security
Using optimization models with climate, crop & economic data, the authors show that India can stop groundwater depletion, reduce energy use and meet food/nutrition targets by changing where it sources crops for its food procurement and distribution system.
- Naresh Devineni
- , Shama Perveen
- & Upmanu Lall
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring disaster impacts on adaptation actions in 549 cities worldwide
Exploring disaster impacts on adaptation actions in 549 cities worldwide
Here the authors explore the effects of disasters on adaptation actions in 549 cities, finding that the effects of disaster frequency and severity are modest and depend on action type, population size, and adaptive capacity.
- Daniel Nohrstedt
- , Jacob Hileman
- & Charles F. Parker
-
Article
| Open Access Resilience of urban public electric vehicle charging infrastructure to flooding
Resilience of urban public electric vehicle charging infrastructure to flooding
A study of how the Greater London electric vehicle charging network is affected by flooding reveals disproportionate impacts on already-stressed parts of the network, peaking as far as over 10 km away from the flooded regions.
- Gururaghav Raman
- , Gurupraanesh Raman
- & Jimmy Chih-Hsien Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Cost increase in the electricity supply to achieve carbon neutrality in China
Cost increase in the electricity supply to achieve carbon neutrality in China
This study indicates that approximately 5.8 TW of wind and solar photovoltaic capacity would be required to achieve carbon neutrality in China’s power system by 2050. The electricity supply costs would increase by 19.9% or 9.6 CNY¢/kWh.
- Zhenyu Zhuo
- , Ershun Du
- & Chongqing Kang
-
Comment
| Open Access The delusive accuracy of global irrigation water withdrawal estimates
The delusive accuracy of global irrigation water withdrawal estimates
Miscalculating the volumes of water withdrawn for irrigation, the largest consumer of freshwater in the world, jeopardizes sustainable water management. Hydrological models quantify water withdrawals, but their estimates are unduly precise. Model imperfections need to be appreciated to avoid policy misjudgements.
- Arnald Puy
- , Razi Sheikholeslami
- & Andrea Saltelli
-
Article
| Open Access Pathway to a land-neutral expansion of Brazilian renewable fuel production
Pathway to a land-neutral expansion of Brazilian renewable fuel production
Fuel output of Brazilian sugarcane ethanol facilities may be increased by over 40% without using additional land if production is combined with synthetic fuel processes. This amounts to 100TWh of fuel, sparing 27,000 km2 of land.
- Luis Ramirez Camargo
- , Gabriel Castro
- & Johannes Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access Amplification of downstream flood stage due to damming of fine-grained rivers
Amplification of downstream flood stage due to damming of fine-grained rivers
Dams constructed on fine-grained rivers cause an increase in flow resistance downstream, thereby amplifying, rather than reducing, flood stage.
- Hongbo Ma
- , Jeffrey A. Nittrouer
- & Baosheng Wu
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Marine abundance and its prehistoric past in the Baltic
Marine abundance and its prehistoric past in the Baltic
- Niklas Hausmann
- , Harry K. Robson
- & Geoff Bailey
-
Article
| Open Access Estimating global economic well-being with unlit settlements
Estimating global economic well-being with unlit settlements
Nighttime lights from satellite are combined with a map of human settlements, showing that 19% of these areas, mainly in Africa, the Middle East and Asia, have no detectable artificial light. These data were then used in models to predict well-being.
- Ian McCallum
- , Christopher Conrad Maximillian Kyba
- & Steffen Fritz
-
Article
| Open Access Contrasting influences of biogeophysical and biogeochemical impacts of historical land use on global economic inequality
Contrasting influences of biogeophysical and biogeochemical impacts of historical land use on global economic inequality
Historical land use impacts climate by biogeophysical and biogeochemical effects. Their combined effects on mean and extreme temperature may harm economically disadvantaged countries but benefit those in rich countries, raising questions of equality.
- Shu Liu
- , Yong Wang
- & Le Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Indigenous oyster fisheries persisted for millennia and should inform future management
Indigenous oyster fisheries persisted for millennia and should inform future management
‘Commercial fisheries have decimated keystone species, including oysters in the past 200 years. Here, the authors examine how Indigenous oyster harvest in North America and Australia was managed across 10,000 years, advocating for effective future stewardship of oyster reefs by centering Indigenous peoples.’
- Leslie Reeder-Myers
- , Todd J. Braje
- & Torben C. Rick
-
Article
| Open Access Unlocking bimetallic active sites via a desalination strategy for photocatalytic reduction of atmospheric carbon dioxide
Unlocking bimetallic active sites via a desalination strategy for photocatalytic reduction of atmospheric carbon dioxide
Ultrathin two-dimensional metal oxyhalides show excellent photocatalytic properties with unique electronic and interfacial structures. Here, the authors develop a top-down desalination strategy to engineer ultrathin bimetallic two-dimensional material for photocatalytic atmospheric carbon dioxide reduction.
- Xuezhen Feng
- , Renji Zheng
- & Hong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Reversible Power-to-Gas systems for energy conversion and storage
Reversible Power-to-Gas systems for energy conversion and storage
Reversible Power-to-Gas systems can convert electricity to hydrogen at times of ample and inexpensive power supply and operate in reverse to deliver electricity during times when power is relatively scarce. Here, the authors show that such systems can already be economically viable relative to current hydrogen prices in the context of the German and Texas electricity markets.
- Gunther Glenk
- & Stefan Reichelstein
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing global risks of labor abuse and illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing
Revealing global risks of labor abuse and illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing
Taking action to reduce risks of labor abuse and illegal, unreported, and unregulated (IUU) fishing in the fishing sector is hindered by a lack of spatially explicit data and an understanding of different drivers of risks. Here the authors combine expert assessments with satellite information to map and quantify risks of labor abuse and IUU fishing at port, at sea and associated with transshipment globally.
- Elizabeth R. Selig
- , Shinnosuke Nakayama
- & Jessica L. Decker Sparks
-
Article
| Open Access Adverse biobehavioral effects in infants resulting from pregnant rhesus macaques’ exposure to wildfire smoke
Adverse biobehavioral effects in infants resulting from pregnant rhesus macaques’ exposure to wildfire smoke
Little is known about the consequences of prenatal exposure to wildfire smoke on biobehavioural outcomes. Here, the authors show that infant rhesus monkeys exposed early in gestation to wildfire smoke from the 2018 Camp Fire in California show more inflammation, blunted cortisol and altered behaviour outcomes compared to non-exposed animals.
- John P. Capitanio
- , Laura A. Del Rosso
- & Bill L. Lasley
-
Article
| Open Access Global impacts of future urban expansion on terrestrial vertebrate diversity
Global impacts of future urban expansion on terrestrial vertebrate diversity
Population growth in the coming decades will lead to increasing land conversion to urban areas. Here, the authors use spatially explicit projections of global urban expansion to analyze its effects on habitat changes, and terrestrial mammals, birds and amphibians under the main shared socioeconomic pathways.
- Guangdong Li
- , Chuanglin Fang
- & Xiaoping Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Battery technology and recycling alone will not save the electric mobility transition from future cobalt shortages
Battery technology and recycling alone will not save the electric mobility transition from future cobalt shortages
New study finds cobalt-free batteries and recycling progress can significantly alleviate long-term cobalt supply risks, however a cobalt supply shortage appears inevitable in the short- to medium-term, even under the most technologically optimistic scenario.
- Anqi Zeng
- , Wu Chen
- & Gang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access COVID-19, Green Deal and recovery plan permanently change emissions and prices in EU ETS Phase IV
COVID-19, Green Deal and recovery plan permanently change emissions and prices in EU ETS Phase IV
This paper finds that the EU’s 2030 reduction target of -55% might correspond to EU ETS allowance prices between 45 and 94 e/ton CO2 today, while the invalidation rule reduces carbon emissions to 14.2 to 18.3 GtCO2 over the EU ETS’ remaining lifetime.
- Kenneth Bruninx
- & Marten Ovaere
-
Article
| Open Access Air quality and health co-benefits of China’s carbon dioxide emissions peaking before 2030
Air quality and health co-benefits of China’s carbon dioxide emissions peaking before 2030
Understanding benefits of carbon mitigation is an important impetus for governments to adopt more ambitious climate targets. Here, the authors show positive air quality and health co-benefits are possible if China’s CO2 emissions peak before 2030.
- Rong Tang
- , Jing Zhao
- & Haikun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Accounting for interactions between Sustainable Development Goals is essential for water pollution control in China
Accounting for interactions between Sustainable Development Goals is essential for water pollution control in China
The UN’s 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are highly interrelated. This study finds 319 interactions between SDGs for the case of water pollution in China. Results show that effective pollution control requires accounting for these interactions.
- Mengru Wang
- , Annette B. G. Janssen
- & Carolien Kroeze
-
Article
| Open Access Consistent cooling benefits of silvopasture in the tropics
Consistent cooling benefits of silvopasture in the tropics
A new study shows that tropical silvopasture systems can provide significant cooling services for local communities, and identifies where these silvopasture systems can most effectively counteract global climate change to help communities adapt to warming.
- Lucas R. Vargas Zeppetello
- , Susan C. Cook-Patton
- & Yuta J. Masuda
-
Comment
| Open AccessRelevance of international partnerships in the implementation of the UN Sustainable Development Goals
Sustainable Development Goal 17 focuses on partnerships that can enable the achievement of other SDGs. In this comment the authors examine the obstacles to the success of SDG 17 and suggest measures to overcome these.
- Walter Leal Filho
- , Tony Wall
- & Julianna Ramirez
-
Article
| Open Access Vegetation-based climate mitigation in a warmer and greener World
Vegetation-based climate mitigation in a warmer and greener World
Vegetation changes have been suggested as a climate mitigation option, but the numerous feedbacks between vegetation and climate are not well understood. Here, the authors show that greening leads to surface cooling in many areas, but the size of the effect depends on the background climate.
- Ramdane Alkama
- , Giovanni Forzieri
- & Alessandro Cescatti
-
Article
| Open Access Competition for water induced by transnational land acquisitions for agriculture
Competition for water induced by transnational land acquisitions for agriculture
Water scarcity associated with large-scale land acquisitions is exacerbated by adoption of water-intensive crops and expansion of irrigation, which in turn increases rival water uses.
- Davide Danilo Chiarelli
- , Paolo D’Odorico
- & Maria Cristina Rulli
-
Article
| Open Access Regional trade agreement burdens global carbon emissions mitigation
Regional trade agreement burdens global carbon emissions mitigation
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) will come into force in January 2022. Here the authors quantify ex ante economic and environmental effects following RCEP tariff reductions.
- Kailan Tian
- , Yu Zhang
- & Shouyang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A measurement strategy to address disparities across household energy burdens
A measurement strategy to address disparities across household energy burdens
Net energy metrics reveal disparities in United States household energy burdens. Here the authors find that at least five million households are excluded from current accounting methods, with race, education, and housing tenure accounting for large differences in energy burden.
- Eric Scheier
- & Noah Kittner
-
Article
| Open Access Alloy information helps prioritize material criticality lists
Alloy information helps prioritize material criticality lists
Critically lists tend to ignore the fact that most metals are largely used in alloy form. Here the authors analyze four key metrics and show that six critical metals can be singled out for enhanced concern – Dy, Sm, V, Nb, Te, and Ga.
- T. E. Graedel
- , Barbara K. Reck
- & Alessio Miatto
-
Article
| Open Access Assessing the energy transition in China towards carbon neutrality with a probabilistic framework
Assessing the energy transition in China towards carbon neutrality with a probabilistic framework
China’s transition path toward carbon neutrality remains uncertain. Here the authors combine Monte Carlo analysis with an energy-environment-economy model to present a probabilistic view of China’s energy transition across 3,000 cases.
- Shu Zhang
- & Wenying Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Global cooling induced by biophysical effects of bioenergy crop cultivation
Global cooling induced by biophysical effects of bioenergy crop cultivation
Bioenergy crops has been proposed as a climate mitigation measure, but how the biophysical effects of large-scale cultivation would influence the climate is not well known. Here, the authors use models to show that large-scale cultivation could cool the global land by 0.03 to 0.08 °C.
- Jingmeng Wang
- , Wei Li
- & Olivier Boucher

 Comparing the levelized cost of electric vehicle charging options in Europe
Comparing the levelized cost of electric vehicle charging options in Europe