Abstract
In recent years, increasing attention has been given to the potential supply risks of critical battery materials, such as cobalt, for electric mobility transitions. While battery technology and recycling advancement are two widely acknowledged strategies for addressing such supply risks, the extent to which they will relieve global and regional cobalt demand–supply imbalance remains poorly understood. Here, we address this gap by simulating historical (1998-2019) and future (2020-2050) global cobalt cycles covering both traditional and emerging end uses with regional resolution (China, the U.S., Japan, the EU, and the rest of the world). We show that cobalt-free batteries and recycling progress can indeed significantly alleviate long-term cobalt supply risks. However, the cobalt supply shortage appears inevitable in the short- to medium-term (during 2028-2033), even under the most technologically optimistic scenario. Our results reveal varying cobalt supply security levels by region and indicate the urgency of boosting primary cobalt supply to ensure global e-mobility ambitions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
While renewable energy and low-carbon technology transitions are imperative to achieve the climate neutrality and post-COVID-19 green recovery ambitions of many countries1,2, such transitions require various types and significant amounts of critical materials (e.g., rare earth for magnets, platinum for catalysts, and lithium for batteries)3,4,5,6,7. In particular, while the decarbonization of the transport sector can benefit from sustainable fuels such as electrofuels and biomethane8, battery technology, which depends fundamentally on critical materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, is widely deemed indispensable in renewable energy storage and automobile electrification9,10. Both lithium and cobalt are deemed critical materials by major economies such as the U.S.11, China12, the EU13, Japan14, and Australia15 due to their potential geopolitical supply risks and the importance of the renewable energy transition. Therefore, understanding the demand for such critical materials and exploring mitigation strategies for potential supply risks are essential for ensuring a green and low-carbon future16,17.
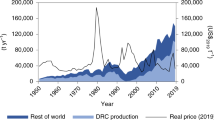
The global cobalt demand, for example, increased by more than 5 times between 1995 and 2019, and almost half of the global cobalt use in 2019 was for batteries18. Such an escalating demand is expected to continue due to the fast diffusion of electric vehicles (EVs) to combat climate and pollution challenges in the coming decades19. However, global cobalt mining and refining are very unevenly distributed (e.g., 70% of mine production came from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and 67% of refining occurred in China in 201920,21), which raises enormous concerns about future demand–supply imbalances among governmental and industry decision-makers.
The two most widely discussed strategies for addressing such supply risks are battery technology development and progress in recycling22,23,24, in addition to further mineral exploration and trade diversification25. Indeed, as the price of cobalt has fluctuated (e.g., it tripled from 2016 to 2018) and environmental and social concerns about cobalt mining in the DRC26 have increased, the prospect of battery development with less or even no cobalt has gained increasing attention in recent years27,28,29. When more EVs and batteries reach their end of life (EoL), secondary cobalt provision through recycling will be essential to supplement the primary supply30,31. There has been a growing body of literature on global and national cobalt material flows32,33,34,35,36,37,38, trade links39,40, demand forecasting41, and recycling potential (mostly of lithium-ion batteries)42,43,44,45. However, the extent to which battery and recycling technology progress will relieve the global and regional cobalt demand–supply imbalance, particularly considering the spatiotemporal variations in different world regions, remains poorly understood.
Here, we aim to answer this question by simulating historical and future global cobalt stocks and flows with regional resolution on major economies (i.e., China, the U.S., Japan, the EU, and the rest of the world (ROW)) based on dynamic material flow analysis (MFA) (see modeling framework in Fig. 1 and details under Methods). Both traditional (e.g., superalloys and magnets) and emerging (e.g., power batteries) end uses of cobalt are considered, while the latter has a higher resolution (e.g., different purposes and battery chemistries) to enable discussion on technological progress. We first characterize the global and regional cobalt cycle from 1998 (when cobalt use started to penetrate the market) to 2019 (the latest data available) and then employ a prospective stock-driven approach4,46,47 to explore cobalt demand and secondary supply potential by end use in each region up to 2050. We show that cobalt-free batteries and recycling progress can indeed significantly alleviate cobalt supply risks in the long run; however, a cobalt shortage between 2028 and 2033 appears inevitable, even under the most optimistic scenario, due to global automobile electrification ambitions. Our results reveal significant regional disparities in future cobalt demand-supply balance and supply security levels and indicate the urgency of boosting primary cobalt supply to ensure global e-mobility ambitions.
BEV battery electric vehicles, PHEV plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, NMC lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide, NCA(I) lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide, NCA(II) advanced NCA with lower cobalt content and higher energy density, LFP(I) lithium iron phosphate, LFP(II) new form of LFP (e.g., blade LFP battery developed by the company BYD), LMO lithium manganese oxide, Li-air lithium-air, Li-S lithium-sulfur, SSB solid-state battery, B-PEV battery for electric passenger vehicles, B-EB battery for electric buses, B-ESS battery for energy storage systems, B-CE&O battery for consumer electronics and other battery products, SA superalloy, CC cemented carbides, MAG magnets, CAT catalysts, PI pigments, OTH other end uses. Battery cathodes in black and red colors indicate state-of-the-art battery technologies and future battery technologies, respectively.
Results
Historical cobalt stocks and flows at global and regional scales
The global anthropogenic cobalt cycle (Fig. 1) includes five transformation processes: mining, refining, manufacturing, use, and waste management and recycling. The global cumulative cobalt apparent consumption (flows entering manufacturing processes) amounted to 1455 kt between 1998 and 2019, as shown in Fig. 2a, while owing to manufacturing losses, the global cumulative cobalt demand (inflows into in-use stocks of different end-use categories) added up to 1403 kt during the same period. This demand was mostly for B-CE&O (42%), followed by SA (14%), OTH (13%), and CC (11%). The global in-use stock of cobalt reached 471 kt in 2019, and B-CE&O contributed the largest proportion of this (47%). The cumulative cobalt demand and in-use stock for emerging end uses accounted for a small share (3% and 9%, respectively) because they were still in the early development stage in 2019. Primary production (1340 kt) was still the main source of supply, accounting for 83%. Only 279 kt of old (postconsumer) scrap cobalt was recycled (from mainly SA, CC, and B-CE&O) and reentered the refining process. New scrap that was recycled and reentered the manufacturing process from 1998 to 2019 amounted to 152 kt, but 96% of this scrap was superalloys, due to their high value and purity. The cumulative cobalt losses in the mining, refining, manufacturing, and waste management and recycling stages from 1998 to 2019 were 722, 162, 53, and 857 kt, respectively. Notably, the B-CE&O contributed to 48% of the total cumulative recycling loss due to the low collection rates for EoL consumer electronics.
a Cumulative global cobalt cycle, b cumulative cobalt apparent consumption (inflows to manufacturing) by sector by region, c cumulative net import (positive values) and net export (negative values) of cobalt-containing final products by sector by region, d cumulative demand (inflows to in-use stocks) by sector by region, and e in-use stocks by end use by region in 2019. All values are in metric kilotons as cobalt metallic equivalent.
Among all world regions, China consumed the most refined cobalt (541 kt; in terms of apparent consumption shown in Fig. 2b) from 1998 to 2019. The majority (60%) of this consumption was in B-CE&O manufacturing, which was further exported as semi-finished or final products (216 kt; Fig. 2c) to the other regions. This reflects China’s role as a ‘world factory’ for consumer electronics in this period. Similar to China, Japan also has a large cumulative apparent consumption and a high share of consumption through B-CE&O due to the country’s large electronics industry. In contrast, the U.S. and EU produce only a small amount of B-CE&O and depend mainly on imports for their supply. Instead, most of the cobalt apparent consumption in the U.S. and Europe went into superalloys due to their advanced military and aerospace industry. In terms of cumulative cobalt demand (inflows to in-use stocks from 1998 to 2019, Fig. 2d), the ROW clearly appears to be the highest. China has the highest amount of in-use stocks, reflecting its relatively later development and thus newer stock. When only emerging end-use categories are considered, China shows the largest cobalt cumulative demand (17 kt) and in-use stock (16 kt), notably accounting for 98% of the global cumulative demand and in-use stock of cobalt for B-EB during this period. Among the different types of emerging end uses, B-PEV dominates the cobalt demand, while B-EB and B-ESS have accounted for a small fraction to date.
Global prospects
In this work, we establish four battery cathode technology (BT) scenarios (state-of-the-art battery development BT1, lower cobalt evolutionary progress BT2, mature cobalt-free technology penetration BT3, and next-generation cobalt-free battery breakthrough BT4; see details in the Methods) with varying market shares based on lithium-ion battery (LIB) technology progress assumptions in terms of cobalt intensity. Based on such BT assumptions and additional key parameters (Table 1) such as battery lifetime and progress in recycling, we have selected and presented seven scenarios (as detailed in Table 2 in the Methods) to discuss global and regional cobalt demand–supply imbalance and resource security that consider varying battery technologies (S1–S4), battery lifetime technologies (S5), recycling progress (S6), and the most ambitious technology combinations (S7).
The development of emerging end uses (especially B-PEV) would significantly increase the global cobalt demand in the following decades. For example, the cobalt demand for B-PEV would reach 1258 and 591 kt in 2050 for the S1 and S2 scenarios, respectively, corresponding to 79 and 66% of their respective total demand. Compared with state-of-the-art battery cathode technologies (S1), low-cobalt battery cathode technologies (S2) would effectively decrease cobalt demand, and the diffusion of cobalt-free battery cathode technologies (S3 and S4) would totally change the picture. Under the S3 and S4 scenarios with cobalt-free battery technologies, the cobalt demand for B-PEV would peak at 175 kt in 2033 and 612 kt in 2038, respectively, and fall to 6 and 3 kt in 2050, respectively (2% and 1% of their respective totals). The battery cathode technology advancement can also reduce the cobalt demand in B-EB and B-ESS, despite much lower levels due to their smaller market shares. Doubling battery lifetimes (S5) would also reduce cobalt demand by 619 kt by 2050, which would be nearly half the total demand in S1. Cobalt demand for traditional end uses would double from 144 kt in 2020 to 273 kt in 2050 for all scenarios. Traditional end-use sectors would gradually dominate again in the total cobalt demand with the penetration of new battery technologies.
Recycling cobalt as a secondary supply would be an essential way to supplement to primary supply. It would gradually become the major source of cobalt supply as more cobalt-containing products reach their EoL. The increase in the EoL recycling rate for cobalt-containing products would improve the secondary supply by 3680 kt in total from 2020 to 2050 in the S6 scenario. Under the S4 and S7 scenarios, the secondary cobalt supply could exceed the total demand after 2044 and 2043, respectively, indicating a closure of the cobalt cycle in the long run through recycling only.
Primary supply, however, is found to be essential to achieve supply-demand balance in most scenarios. When all the announced or scheduled cobalt production in the operating mines41 is considered (primary-base supply scenario), a cobalt supply shortage is still inevitable in all scenarios. Even under the most optimistic scenario (S7), with the most advantageous battery technologies and recycling technologies are employed, a slight supply shortage would still occur from 2028 to 2033. This suggests that battery technology and recycling alone will not save the global ambitious electric mobility transition from cobalt supply shortages if global primary production increases as planned (primary-base supply scenario, the red line in Fig. 3). Only if unscheduled mining projects that have not already been announced41 are additionally considered (primary-high supply scenario, the blue line in Fig. 3; detailed in the Methods) can future cobalt supply shortages be prevented under the most technologically optimistic scenarios (S3 and S7 only).
a S1: state-of-the-art battery cathode technology scenario as the reference scenario; b S2: low-cobalt battery cathode technology scenario; c S3: LFP-dominant cobalt-free battery cathode technology scenario; d S4: next-generation cobalt-free battery cathode technology scenario; e S5: extending battery lifetime scenario; f S6: high recycling rate scenario; and g S7: the most optimistic technology scenario. The scenarios are detailed in Table 2 in the Methods section. The primary-base and primary-high indicate two primary supply scenarios, as shown in Table 1 and Methods.
In addition to the abovementioned critical influencing factors, EV market shares and vehicle ownership are the other two key parameters affecting the prospective cobalt demand of power batteries. The sensitivity analysis results of global cobalt demand in total and by end-use sector for all key parameters are shown in Supplementary Figs. 30–39.
Regional disparities
Figure 4 shows the cumulative primary demand (gross demand minus secondary supply) of cobalt in the five world regions under the seven selected scenarios (S1–S7) and their primary cobalt supply security levels (assuming cobalt reserves remain the same as in 2019) measured by different approaches. The results reveal that China has the highest cumulative cobalt primary demand under scenario S1, followed by the ROW, U.S., and EU, while Japan’s cumulative net demand is much lower than that of the other regions (in Fig. 4a). However, the domestic cobalt reserves of China, the U.S., the EU, and Japan are very small, amounting to less than 3% of the global total (7100 kt), as shown in Fig. 4b. Such large gaps between demand and supply imply enormous supply risk for the four major economies.
a The regional cumulative primary demand (gross demand minus secondary supply) under the seven scenarios from 2020 to 2050; b shares of domestic reserves by region in 2019; c shares of total reserves (domestic reserves plus overseas cobalt reserve ownership88) by region in 2019 and the primary cobalt supply security level during 2020–2050 measured by d domestic reserve divided by cumulative primary demand; e total reserve divided by cumulative primary demand; and f total reserve divided by cumulative primary apparent consumption (primary demand plus net export of cobalt final products, which are assumed the same as the 2019 levels).
In reality, of course, these major economies (China, the U.S., Japan, and the EU) have also managed to continuously expand their ownership of foreign cobalt mines through overseas mining projects. Therefore, when the total cobalt reserves (domestic reserves plus foreign cobalt reserve ownership; 2383, 1401, 70, 2732, and 415 kt, respectively, for China, the U.S., Japan, the EU, and the ROW, as shown in Fig. 4c) are considered, the cobalt demand–supply gap would be very different, as shown in Fig. 4d, e. In fact, the EU would no longer face a supply shortage under scenarios S2–S7. In addition, the U.S. and China could avoid supply shortages if the mature or upcoming cobalt-free battery technologies gradually penetrated the market (under scenarios S3, S4, and S7). However, Japan and the ROW would still face supply shortages under all scenarios, even under the most optimistic scenario (S7). The international trade of cobalt-containing products (e.g., final products and scrap) can affect the regional cobalt demand–supply imbalance to some extent. For example, if the future regional trade patterns of cobalt final products remain the same as in 2019 (Fig. 4f), China, as the main exporter of cobalt-containing products (mainly batteries), would no longer be able to secure its cobalt supply, even after the penetration of cobalt-free technologies (LFP dominant in S3 and next generation in S4), whereas the EU would be able to ensure cobalt supply security in all seven scenarios.
Discussion
Our results reveal that battery technology innovation, especially cobalt-free technologies, can significantly alleviate the cobalt supply risk. Many battery producers have already prioritized lowering the cobalt content in LIBs and producing NMC-811 instead of NMC-111 in the face of expensive cobalt and geopolitical supply risks24. However, due to the rapid expansion of the EV market and increasing battery capacity, the cobalt shortage appears inevitable in the future if the primary supply follows only the scheduled extraction plan as announced for each deposit41 (primary-base supply scenario). Low-cobalt battery cathode technology development could alleviate, but not prevent, the supply crisis. This demand–supply gap would still occur around 2028–2033, even though cobalt-free LFP technology already penetrated the market in 2020 and it is predicted that the next-generation cobalt-free battery technologies will become commercialized by 2030. Nevertheless, current (LFP) and upcoming (Li-air, Li-S, and SSB) cobalt-free technology penetration could still reduce cobalt cumulative demand by 62% and 41%, respectively (see Fig. 3c). Extending the battery lifetime with technology innovation is another effective measure to mitigate cobalt supply pressure. Our results show that doubling the battery lifetime would nearly halve the cobalt demand. Therefore, battery technology is crucial to mitigate potential cobalt shortages, and joint efforts are urgently needed to further accelerate the research and market penetration of various decobaltization battery technologies, particularly cobalt-free technologies. In view of the short- to medium-term (during 2028–2033) shortage of cobalt supply, further accelerated penetration of the new LFP battery technology might be the most effective cure. However, due to the significant barrier of the low energy density of the LFP cathode, next-generation cobalt-free technologies are still indispensable in making more powerful batteries and alleviating mileage anxiety in PEVs, which requires governmental financial and regulatory support and multistakeholder cooperation, including that between industries and research institutes.
Cobalt recycling is a vital strategy for supplementing the primary supply. The increasing secondary cobalt availability under various scenarios suggests considerable potential for recycling to relieve primary resource pressure in the future, especially in the long term. For example, secondary cobalt accounts for 66% of the accumulative cobalt demand under scenario S7, 75% of which would be generated from 2035 to 2050. Therefore, combined efforts in technology, regulatory, and economic areas should be explored to motivate cobalt recycling48 so as to ensure cobalt supply security in the future. First, further technological development for the recycling of products with currently low recycling rates would be essential to harness the increasing potential of urban mining. For example, the present recycling rate of B-CE&O is only 10% due to high cost and technological challenges, which can be mitigated by further development and the application of leaching-regeneration hydrometallurgy49. Second, an extended producer responsibility system and design for remanufacturing, reuse, and recycling should be further promoted to stimulate closed-loop recycling among manufacturers, especially for cars and battery producers, due to their significant role in future cobalt consumption. Third, a better societal collection and recycling system should be constructed to reduce the EoL losses, taking advantage of emerging information technologies such as internet Plus, integrated logistics networks, and the big data platform36 to connect consumers with qualified recyclers, logistics companies, processing companies, and producers and to promote online and offline interactions. Finally, relevant regulations and industrial standards should be established to attract more investment in the recycling industry, and policy support should be provided to enterprises, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises, to ensure sustained profitability when facing the increasing financial costs of technology advancement and equipment upgrading50.
Primary supply is necessary and important for ensuring future cobalt demand–supply balance, especially in the short- to medium-term. Our scenario results show that increasing primary supply is urgently needed to close the cobalt demand–supply gap that cannot be fully filled by battery technology and recycling progress alone. A primary supply increase could be realized via more exploration, investment, and technology development for both existing and unexplored cobalt deposits. Therefore, enhancing the exploration of cobalt deposits, deep-sea mining enabled by advanced extraction technologies, and improving the efficiency of ore extraction, smelting, and refining could all further boost the primary supply. For example, the future prevalence of high-pressure acid leaching in the EU would improve cobalt extraction from laterite deposits25, and the reopening of Mutanda would significantly increase cobalt mine production51.
Despite the significance of primary supply, a few key uncertainties and challenges in increasing primary cobalt supply remain. First, cobalt ore production is economically susceptible to short-term price fluctuations and rising production costs52. For example, the international mining giant Glencore, which is the world’s top cobalt mine producer, had to close the Mutanda copper-cobalt mine in the DRC, which provided 1/5 of the global cobalt production in 2018 due to the increasing input costs and taxes as well as the continually decreasing price52. Second, it typically takes over a decade from the discovery of undiscovered deposits to the extraction of the first ore, and such a time lag makes it difficult to address the global and regional demand–supply imbalance in the short- to medium-term. Third, 94% of cobalt production is accompanied by copper or nickel ores as byproducts53, so cobalt is closely related to the production and price fluctuations of these two metals. Fourth, given by the massive extraction of specific cobalt deposits, the decreasing ore grade of cobalt is inevitable, which would increase cobalt production costs (economically, socially, and environmentally) and affect cobalt production to some extent. Last but not least, the cobalt primary supply faces various types of geopolitical (e.g., civil wars and unstable governmental systems in producing countries) and supply chain risks, as exemplified by the on-going COVID-19 pandemic-induced lockdown in the DRC and corresponding impacts on shipping ports (e.g., Durban in South Africa) and production capacities54.
Given the regional resolution of our data, our results can shed light on regional resource security concerns and mitigation strategies. China is expected to consume much more cobalt than any other region in the future, primarily due to its enormously booming domestic EV market and expanding battery production capacity in the future. In 2019, China’s cobalt reserve was only 80 kt, but it contributed to 67% of the global cobalt refinery production55, which resulted in its strong dependence on overseas primary cobalt resources. Although we show that China could secure its cobalt demand–supply balance under the most optimistic scenario (Fig. 4f), its supply risk will still be considerably high if the country continues to expand exports of batteries or cannot accelerate the market penetration of cobalt-free technologies. Reducing the cobalt supply risk thus requires both the diversification of secured import channels of primary cobalt and system planning for industry policy, urban mining, and battery technology innovation.
The cobalt supply security levels for the EU and U.S. are relatively high. They have, on the one hand, transferred part of the supply pressure of primary cobalt to China and Japan by outsourcing battery production there and, on the other hand, controlled most of overseas cobalt mine production by their mining giants. However, this may change as they plan to build a stronger domestic battery industry to reduce supply chain risks and boost domestic industrial competition and employment (e.g., as planned in the EU’s Battery 2030 + Strategy56) and as competition for overseas mining projects becomes fiercer in the future. Targeted initiatives have already been implemented by some companies to address the vulnerable cobalt supply chain. For example, Apple now attempts to procure cobalt directly from miners57, and Tesla’s battery suppliers have been expanded from only Panasonic to multiple Japanese and Chinese battery producers58. The cooperation between manufacturers and their suppliers regarding technology development and market information should be encouraged to make the supply chain more transparent and robust. For example, Tesla has already begun to partially replace their NCA batteries with new LFP technologies in some EV models that have been put on the Chinese market by collaborating with the local battery supplier CATL59.
Although the cobalt demand for Japan is much lower than that for other regions, the limited domestic cobalt reserves and overseas reserve ownership lead to a relatively higher supply risk in Japan. In this regard, Japan’s ambition to build a ‘hydrogen society’, which signifies a preference for fuel cell vehicles (cobalt-free vehicles) in the transportation system instead of BEVs and PHEVs, could significantly reduce the country’s dependency on cobalt and mitigate potential supply shortages to some extent.
Our study primarily investigated the extent to which battery and recycling technology progress can relieve the global and regional cobalt demand–supply imbalance in the coming decades. Due to data gaps, the absolute results should be interpreted with caution and with unavoidable uncertainties in mind. First, only PEVs and EBs are included for the electric mobility transition, while HEVs, electric two-wheelers, electric bicycles, and electric trucks are not explicitly considered. Second, the battery lifetime is set as half or the same as the PEV lifetime; this indicator could be further improved by considering battery health status and real-time modeling in the future. Third, EoL management and circular economy strategies other than recycling, such as remanufacturing and reuse for grid stability or private energy storage, need to be further discussed in the future. Nevertheless, we believe our scenario results still provide robust conclusions about the characteristics of global and regional historical and future cobalt cycles and the role of technology innovations in addressing the demand–supply imbalance. The identified inevitable supply shortage in the short- to medium-term calls for multistakeholder, beyond-technology, and urgent actions and joint efforts to increase primary supply and boost technology innovations for securing a green transition in the future.
Methods
System definition
The global anthropogenic cobalt cycle (as shown in Fig. 1) includes five transformation processes: mining, refining, manufacturing, use, and waste management & recycling. Cobalt flows into the refining process can be derived from three sources: cobalt ores produced from mining (primary supply), cobalt old scrap recycled from EoL products (secondary supply), and the net import of cobalt old scrap. The cobalt-containing final products can be classified into three emerging end uses and seven traditional end uses. Emerging end uses include batteries for passenger electric vehicles (B-PEVs), batteries for electric buses (B-EBs), and batteries for energy storage systems (B-ESSs). Traditional end uses include batteries for consumer electronics and other battery products (B-CE&O), superalloys (SA), cemented carbides (CC), magnets (MAG), catalysts (CAT), pigments (PI), and other uses (OTH). Losses were considered in mining, refining, manufacturing, and waste management and recycling processes; part of the new scrap generated in manufacturing can be efficiently recycled in corresponding manufacturing sectors. The global cobalt cycle and relevant stocks and flows are disaggregated into five regions: China, the U.S., Japan, the EU, and the ROW. The international trade of cobalt-containing final products and old scrap between these five regions are also taken into consideration.
Historical cobalt cycle and stocks and flows
A dynamic MFA approach4,60 was employed to quantify the global cobalt cycle from 1998 to 2019. For example, the outflows were calculated as shown below:
where \(\left(\frac{1}{\sigma \,*\, \sqrt{2\,*\, \pi }}* {{e}^{-\frac{(\tau \,-\,\mu )}{{2\sigma }^{2}}}}^{2}\right)\) represents the lifetime distribution (assumed to be the normal distribution) of cobalt-containing end-use products, t is the actual time,τ is the age cohort (time of input), μ is the average lifetime of the products, and σ is the standard deviation.
The cobalt stocks in year t were determined by the initial stock and annual net stocks that equal inflow minus outflow over the past t year. The initial cobalt in-use stocks of each end use before 1998 were assumed to be negligible. Cobalt inflows data were compiled from a wide range of statistics and literature. Losses were determined by relative coefficients of the corresponding process. Other flows are calculated by the mass balance principle. The indirect trade of cobalt embodied in final products in international trade was also accounted for since the regional cobalt apparent consumption data by end uses did not include that part. We have detailed the quantification of historical cobalt stocks and flows from 1998 to 2019 in Supplementary Table 2.
Prospective cobalt cycle and stocks and flows
Stock-driven dynamic MFA models61,62,63 were employed to simulate prospective cobalt demand by end use by region. Seven traditional end uses and three emerging end uses were considered for all five regions and the global total, but the simulation processes varied between them.
The prospective cobalt demand for traditional end uses was determined by the lifetime distribution function and future stock patterns derived from population prospects and per capita cobalt stock assumptions. The per capita cobalt stock of each traditional end use was simulated using a logistic model64,65 that complies with the S-shaped curve based on the historical patterns4,47,62 and considers the possible impact of technological changes (as shown in Eq. (2)).
where S(t) is the stock at time t, K is the assumed stock saturation level, S0 is the initial stock, and a is a constant.
The prospective cobalt demand for emerging end uses was based on a product-specific stock-driven model that consists of the fleet module and the material module. The prospective cobalt demand for B-PEV and B-EB was determined by the cobalt intensity, battery cathode material market shares, average battery capacity per vehicle, and battery demand for EVs. The cobalt demand for B-ESS was affected by cobalt intensity, battery cathode material market shares, and future assumed ESS demand.
Battery cathode technology scenarios
We set four BT scenarios with varying market shares based on the assumed technological progress in terms of cobalt intensity: state-of-the-art battery development, cobalt-less evolutionary progress, new LFP development with zero cobalt, and next-generation cobalt-free revolutionary breakthrough, as summarized below and detailed in Supplementary Figs. 6–8.
-
BT1 assumes that the ‘state-of-the-art’ LIB technology and its foreseeable inventions in the near future (i.e., expected shift from NMC-111, NMC-433, NMC-532, and NMC-622 to NMC-811 with less cobalt intensive chemistry66,67) will remain until 2050.
-
BT2 considers evolutionary progress in LIB technology with the penetration of ‘low-cobalt batteries’, such as NMC-9.5.568,69,70 and advanced NCA71, with an average cobalt intensity of 0.05 kg/kWh30 from 2020. State-of-the-art battery cathode technology will accordingly be substituted from 2020 onward in BT2.
-
BT3 assumes that the relatively mature cobalt-free battery technology LFP with a higher energy density than the former generation (e.g., blade battery developed by BYD company) will gradually replace NMC and NCA from 2020 onward and will dominate the market completely by 205010.
-
BT4 includes a revolutionary breakthrough with ‘cobalt-free battery cathode technology’72, such as lithium-air, lithium-sulfur73, and solid-state batteries74. We assume that next-generation cobalt-free battery cathode technologies will start penetrating and substituting state-of-the-art battery technologies in 203045.
Battery lifetime scenarios
Battery lifetime is an important parameter for determining cobalt inflows and outflows. We set two scenarios for battery lifetime to explore the impact of battery lifetime extension: one as the current value (832, 775, and 1076 years, respectively, for B-PEV, B-EB, and B-ESS), and the other doubling the present level as a result of improved battery technologies (e.g., electrolyte technology)77.
Recycling scenarios
Two recycling progress scenarios were used to quantify the potential secondary cobalt supply: one assumed that the present EoL recycling rates increase by 10% in 2050 based on historical levels, and the other assumed that these recycling rates increase gradually to a high level of 95% by 2050 following an S-shaped curve (except for some end uses that cannot be recycled; see details in Supplementary Fig. 9).
Primary supply scenarios
Two primary supply scenarios (one called primary-base and the other one called primary-high) are assumed accordingly based on the literature41. The primary-base supply scenario considered only announced or scheduled cobalt mine production until 2030. The primary-high supply scenario considered both the scheduled and unscheduled cobalt mine production until 2030. The primary supply after 2030 was assumed to increase with an annual growth rate of 1% for both scenarios (see details in Supplementary Fig. 10).
Description of the seven selected scenarios
Based on the scenario set for the key parameters, we selected and presented seven scenarios (as shown in Table 2) to reveal the impact of various technologies (e.g., battery cathode technology, battery lifetime, and recycling technology) on cobalt demand and supply. S1 is the base scenario for presenting the possible situation under state-of-the-art battery cathode technology, current battery lifetime, and recycling technology. S2, S3, and S4 are scenarios in which there is a shift to BT2, BT3, and BT4 batteries. S5 considers extending the battery lifetime. S6 considers a high cobalt EoL recycling rate. S7 is the optimistic scenario with the lowest demand and highest supply under the most advantageous technology assumptions. More details regarding the parameters in Table 2 can be found in Supplementary Tables 6–8 and Supplementary Figs. 6–10.
Data availability
All data analyzed in this study are included in its Supplementary information files.
Code availability
The mathematical algorithm used in this study is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
van Vuuren, D. P. et al. Alternative pathways to the 1.5 °C target reduce the need for negative emission technologies. Nat. Clim. Change 8, 391–397 (2018).
Kitzing, L., Jensen, M. K., Telsnig, T. & Lantz, E. Multifaceted drivers for onshore wind energy repowering and their implications for energy transition. Nat. Energy 5, 1012–1021 (2020).
Li, J. et al. Critical rare-earth elements mismatch global wind-power ambitions. One Earth 3, 116–125 (2020).
Rasmussen, K. D., Wenzel, H., Bangs, C., Petavratzi, E. & Liu, G. Platinum demand and potential bottlenecks in the global green transition: a dynamic material flow analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 11541–11551 (2019).
Hao, H. et al. Impact of transport electrification on critical metal sustainability with a focus on the heavy-duty segment. Nat. Commun. 10, 5398 (2019).
Cao, Z. et al. Resourcing the fairytale country with wind power: a dynamic material flow analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 11313–11322 (2019).
International Energy Agency, (IEA). The Role of Critical Minerals in Clean Energy Transitions. https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/24d5dfbb-a77a-4647-abcc-667867207f74/TheRoleofCriticalMineralsinCleanEnergyTransitions.pdf (2021).
Melton, N., Axsen, J. & Sperling, D. Moving beyond alternative fuel hype to decarbonize transportation. Nat. Energy 1, 16013 (2016).
Kittner, N., Lill, F. & Kammen, D. M. Energy storage deployment and innovation for the clean energy transition. Nat. Energy 2, 17125 (2017).
Dunn, J., Slattery, M., Kendall, A., Ambrose, H. & Shen, S. Circularity of Lithium-Ion Battery Materials in Electric Vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 5189–5198 (2021).
Executive Office of the President of the United States Federal Government. Addressing the Threat to the Domestic Supply Chain From Reliance on Critical Minerals From Foreign Adversaries and Supporting the Domestic Mining and Processing Industries. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2020/10/05/2020-22064/addressing-the-threat-to-the-domestic-supply-chain-from-reliance-on-critical-minerals-from-foreign (2020).
Ministry of Natural Resources & National Development and Reform Commission of the People’s Republic of China. National Mineral Resources Planning 2016-2020. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/fggz/fzzlgh/gjjzxgh/201705/t20170511_1196755.html (2016).
Blengini, G. A. et al. Study on the EU’s list of Critical Raw Materials (2020) Final Report. https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/c0d5292a-ee54-11ea-991b-01aa75ed71a1/language-en (2020).
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan, (METI). New International Resource Strategy. https://www.meti.go.jp/english/press/2020/0330_005.html (2020).
Mudd, G. M. et al. Critical minerals in Australia: A review of opportunities and research needs. https://doi.org/10.11636/Record.2018.051 (2018).
Hao, H. et al. Securing platinum-group metals for transport low-carbon transition. One Earth 1, 117–125 (2019).
Fishman, T., Myers, R., Rios, O. & Graedel, T. E. Implications of emerging vehicle technologies on rare earth supply and demand in the United States. Resources 7, 9 (2018).
Roskill. Cobalt: Outlook to 2030. https://www.roskillinteractive.com/ (2021).
Alves Dias, P., Blagoeva, D., Pavel, C. & Arvanitidis, N. Cobalt: demand-supply balances in the transition to electric mobility. https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2760/97710 (2018).
U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2020. https://doi.org/10.3133/mcs2020. (2020).
Dehaine, Q., Tijsseling, L. T., Glass, H. J., Törmänen, T. & Butcher, A. R. Geometallurgy of cobalt ores: A review. Miner. Eng. 160, 106656 (2021).
Recycle spent batteries. Nat. Energy 4, 253–253 (2019).
Tran, M. K., Rodrigues, M.-T. F., Kato, K., Babu, G. & Ajayan, P. M. Deep eutectic solvents for cathode recycling of Li-ion batteries. Nat. Energy 4, 339–345 (2019).
Schmuch, R., Wagner, R., Hörpel, G., Placke, T. & Winter, M. Performance and cost of materials for lithium-based rechargeable automotive batteries. Nat. Energy 3, 267–278 (2018).
Horn, S. et al. Cobalt resources in Europe and the potential for new discoveries. Ore Geol. Rev. 130, 103915 (2021).
Banza Lubaba Nkulu, C. et al. Sustainability of artisanal mining of cobalt in DR Congo. Nat. Sustain. 1, 495–504 (2018).
Manthiram, A. & Goodenough, J. B. Layered lithium cobalt oxide cathodes. Nat. Energy 6, 323–323 (2021).
Liu, T. et al. Understanding Co roles towards developing Co-free Ni-rich cathodes for rechargeable batteries. Nat. Energy 6, 277–286 (2021).
Cutting cobalt. Nat. Energy 5, 825–825 (2020).
Baars, J., Domenech, T., Bleischwitz, R., Melin, H. E. & Heidrich, O. Circular economy strategies for electric vehicle batteries reduce reliance on raw materials. Nat. Sustain. 4, 71–79 (2021).
Zeng, X., Ali, S. H., Tian, J. & Li, J. Mapping anthropogenic mineral generation in China and its implications for a circular economy. Nat. Commun. 11, 1544 (2020).
Harper, E. M., Kavlak, G. & Graedel, T. E. Tracking the Metal of the Goblins: Cobalt’s Cycle of Use. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46, 1079–1086 (2012).
Chen, Z., Zhang, L. & Xu, Z. Analysis of cobalt flows in mainland China: Exploring the potential opportunities for improving resource efficiency and supply security. J. Clean. Prod. 275, 122841 (2020).
Chen, Z., Zhang, L. & Xu, Z. Tracking and quantifying the cobalt flows in mainland China during 1994–2016: Insights into use, trade and prospective demand. Sci. Total Environ. 672, 752–762 (2019).
Zeng, X. & Li, J. On the sustainability of cobalt utilization in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 104, 12–18 (2015).
Wang, Y. & Ge, J. Potential of urban cobalt mines in China: An estimation of dynamic material flow from 2007 to 2016. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 161, 104955 (2020).
Liu, W. et al. Dynamic material flow analysis of critical metals for lithium-ion battery system in China from 2000–2018. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 164, 105122 (2021).
Godoy León, M. F., Blengini, G. A. & Dewulf, J. Analysis of long-term statistical data of cobalt flows in the EU. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 173, 105690 (2021).
Sun, X., Hao, H., Liu, Z., Zhao, F. & Song, J. Tracing global cobalt flow: 1995–2015. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 149, 45–55 (2019).
Nansai, K. et al. Global Flows of Critical Metals Necessary for Low-Carbon Technologies: The Case of Neodymium, Cobalt, and Platinum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 1391–1400 (2014).
Fu, X. et al. Perspectives on Cobalt Supply through 2030 in the Face of Changing Demand. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 2985–2993 (2020).
Dunn, J. B., Gaines, L., Kelly, J. C., James, C. & Gallagher, K. G. The significance of Li-ion batteries in electric vehicle life-cycle energy and emissions and recycling’s role in its reduction. Energy Env. Sci. 8, 158–168 (2015).
Olivetti, E. A., Ceder, G., Gaustad, G. G. & Fu, X. Lithium-Ion Battery Supply Chain Considerations: Analysis of Potential Bottlenecks in Critical. Met. Joule 1, 229–243 (2017).
Asari, M. & Sakai, S. Li-ion battery recycling and cobalt flow analysis in Japan. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 81, 52–59 (2013).
Simon, B., Ziemann, S. & Weil, M. Potential metal requirement of active materials in lithium-ion battery cells of electric vehicles and its impact on reserves: Focus on Europe. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 104, 300–310 (2015).
Liu, J. et al. Pathways for practical high-energy long-cycling lithium metal batteries. Nat. Energy 4, 180–186 (2019).
Cao, Z. et al. The sponge effect and carbon emission mitigation potentials of the global cement cycle. Nat. Commun. 11, 3777 (2020).
Gaines, L. Profitable Recycling of Low-Cobalt Lithium-Ion Batteries Will Depend on New Process Developments. One Earth 1, 413–415 (2019).
Fan, E. et al. Sustainable Recycling Technology for Li-Ion Batteries and Beyond: Challenges and Future Prospects. Chem. Rev. 120, 7020–7063 (2020).
Woodard, R. Waste management in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)—A barrier to developing circular cities. Waste Manag 118, 369–379 (2020).
Michael, K. Glencore to Reopen One of World’s Biggest Cobalt Mines in Congo. Bloomberg.com https://www.bnnbloomberg.ca/glencore-to-reopen-one-of-world-s-biggest-cobalt-mines-in-congo-1.1619919 (2021).
Glencore. 2019 Annual Report. Glencore https://www.glencore.com/investors/reports-results/2019-annual-report (2020).
European Commission. Study on the review of the list of Critical Raw Materials: Critical Raw Materials Factsheets. https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/7345e3e8-98fc-11e7-b92d-01aa75ed71a1/language-en (2017).
Ying, L. Cobalt: The spread of COVID-19 threatens supply. Roskill https://roskill.com/news/cobalt-the-spread-of-covid-19-threatens-supply/ (2020).
U.S. Geological Survey, (USGS), Science for a changing world. https://www.usgs.gov/.
European Commission. Battery 2030+ Roadmap: Investing the sustainable battery of the future. https://battery2030.eu/digitalAssets/861/c_861008-l_1-k_roadmap-27-march.pdf (2020).
Jack, F. & Mark, G. Apple in Talks to Buy Cobalt Directly From Miners. Bloomberg.com https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2018-02-21/apple-is-said-to-negotiate-buying-cobalt-direct-from-miners (2018).
Gersdorf, T., Hertzke, P., Schaufuss, P. & Schenk, S. McKinsey Electric Vehicle Index: Europe cushions a global plunge in EV sales. https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/industries/automotive%20and%20assembly/our%20insights/mckinsey%20electric%20vehicle%20index%20europe%20cushions%20a%20global%20plunge%20in%20ev%20sales/mckinsey-electric-vehicle-index-europe-cushions-a-global-plunge-in-ev-sales-vf.pdf?shouldIndex=false (2020).
Lee-Jones, S. Tesla Launches Entry Model 3 with Newer LFP Battery Tech in the U.S. TeslaNorth.com https://teslanorth.com/2021/08/26/tesla-launches-entry-model-3-with-newer-lfp-battery-tech-in-the-u-s/ (2021).
Liu, G. & Müller, D. B. Centennial Evolution of Aluminum In-Use Stocks on Our Aluminized Planet. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 4882–4888 (2013).
B. Müller, D. Stock dynamics for forecasting material flows—Case study for housing in The Netherlands. Ecol. Econ. 59, 142–156 (2006).
Liu, G., Bangs, C. E. & Müller, D. B. Stock dynamics and emission pathways of the global aluminium cycle. Nat. Clim. Change 3, 338–342 (2013).
Müller, E., Hilty, L. M., Widmer, R., Schluep, M. & Faulstich, M. Modeling Metal Stocks and Flows: A Review of Dynamic Material Flow Analysis Methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 2102–2113 (2014).
Pauliuk, S., Wang, T. & Müller, D. B. Moving Toward the Circular Economy: The Role of Stocks in the Chinese Steel Cycle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46, 148–154 (2012).
Liu, G., Bangs, C. E. & Müller, D. B. Unearthing Potentials for Decarbonizing the U.S. Aluminum Cycle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 9515–9522 (2011).
Pillot, C. The Rechargeable Battery Market and Main Trends 2011-2020. https://niobium.tech/-/media/NiobiumTech/Documentos/2019-Formula-E---Berlin/NT_The-rechargeable-battery-market-and-main-trends.pdf (2016).
Hao, H., Cheng, X., Liu, Z. & Zhao, F. China’s traction battery technology roadmap: Targets, impacts and concerns. Energy Policy. 108, 355–358 (2017).
Azevedo, M. et al. Lithium and cobalt—a tale of two commodities. https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/industries/metals%20and%20mining/our%20insights/lithium%20and%20cobalt%20a%20tale%20of%20two%20commodities/lithium-and-cobalt-a-tale-of-two-commodities.pdf (2018).
Lee, S.-H., Lee, S., Jin, B.-S. & Kim, H.-S. Optimized electrochemical performance of Ni rich LiNi0.91Co0.06Mn0.03O2 cathodes for high-energy lithium ion batteries. Sci. Rep. 9, 8901 (2019).
Chen, R., Zhao, T., Zhang, X., Li, L. & Wu, F. Advanced cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries using nanoarchitectonics. Nanoscale Horiz. 1, 423–444 (2016).
Wentker, M., Greenwood, M. & Leker, J. A Bottom-Up Approach to Lithium-Ion Battery Cost Modeling with a Focus on Cathode Active Materials. Energies 12, 504 (2019).
Jia, H. et al. Toward the Practical Use of Cobalt-Free Lithium-Ion Batteries by an Advanced Ether-Based Electrolyte. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 44339–44347 (2021).
Ely, T. O., Kamzabek, D., Chakraborty, D. & Doherty, M. F. Lithium–Sulfur Batteries: State of the Art and Future Directions. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 1, 1783–1814 (2018).
Kato, Y. et al. High-power all-solid-state batteries using sulfide superionic conductors. Nat. Energy 1, 16030 (2016).
O’Donovan, A., Frith, J. & McKerracher, C. Electric Buses in Cities: Driving Towards Cleaner Air and Lower CO2. https://assets.bbhub.io/professional/sites/24/2018/05/Electric-Buses-in-Cities-Report-BNEF-C40-Citi.pdf (2018).
Zablocki, A. Fact Sheet: Energy Storage. https://www.eesi.org/files/FactSheet_Energy_Storage_0219.pdf (2019).
Yu, Z. et al. Molecular design for electrolyte solvents enabling energy-dense and long-cycling lithium metal batteries. Nat. Energy 5, 526–533 (2020).
Richa, K., Babbitt, C. W., Gaustad, G. & Wang, X. A future perspective on lithium-ion battery waste flows from electric vehicles. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 83, 63–76 (2014).
Wang, X., Gaustad, G., Babbitt, C. W. & Richa, K. Economies of scale for future lithium-ion battery recycling infrastructure. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 83, 53–62 (2014).
Li, W., Erickson, E. M. & Manthiram, A. High-nickel layered oxide cathodes for lithium-based automotive batteries. Nat. Energy 5, 26–34 (2020).
Zhao, Q., Liu, X., Stalin, S., Khan, K. & Archer, L. A. Solid-state polymer electrolytes with in-built fast interfacial transport for secondary lithium batteries. Nat. Energy 4, 365–373 (2019).
International Energy Agency, (IEA). Global EV Outlook 2019: Scaling-up the transition to electric mobility. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/energy/global-ev-outlook-2019_35fb60bd-en (2019).
International Renewable Energy Agency, (IRENA). Electricity storage and renewables: Costs and markets to 2030. https://www.irena.org/publications/2017/Oct/Electricity-storage-and-renewables-costs-and-markets (2017).
Vandeputte, K. Increasing the gap in Rechargeable Battery Materials. https://www.umicore.com/storage/group/powering-ahead-kurt-vandeputte.pdf (2018).
International Energy Agency, (IEA). World Energy Outlook 2018. https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/77ecf96c-5f4b-4d0d-9d93-d81b938217cb/World_Energy_Outlook_2018.pdf (2018).
Graedel, T. E., Harper, E. M., Nassar, N. T., Nuss, P. & Reck, B. K. Criticality of metals and metalloids. PNAS 112, 4257–4262 (2015).
United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. World Population Prospects 2019. https://population.un.org/wpp/Download/Standard/Population/ (2019).
Gulley, A. L., McCullough, E. A. & Shedd, K. B. China’s domestic and foreign influence in the global cobalt supply chain. Resour. Policy 62, 317–323 (2019).
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (71991484 to L.T.L. and G.L., 71633006 to T.D., 72088101 and 71991480 to A.J.W., 71874210 to X.H.Z., 71874207 and 72104253 to A.Q.Z.), the Annual Innovation-driven Project of Central South University (2019CX016 to A.Q.Z.), Independent Research Fund Denmark (ReCAP to W.C. and G.L.), and the Villum Center for Science of Sustainable Fuels and Chemicals (Villum Fonden grant no. 9455 to K.D.R., W.C., and G.L.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.L. conceived the idea and designed the research. X.H.Z., T.D., A.J.W., and G.L. supervised and led the work. W.C., A.Q.Z., K.D.R., and G.L. developed the model. M.L., D.B.M., J.T., L.T.L., T.D., and A.J.W. contributed to system definition and data collection. A.Q.Z. and W.C. run the simulation and prepared the figures. J.K.K., T.D., and A.J.W. enhanced the scenarios and discussion on supply potential. A.Q.Z., W.C., and G.L. drafted the paper. A.Q.Z., W.C., K.D.R., X.H.Z., M.L., D.B.M., J.T., J.K.K., L.T.L., T.D., A.J.W., and G.L. analyzed the results and contributed to writing this paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, A., Chen, W., Rasmussen, K.D. et al. Battery technology and recycling alone will not save the electric mobility transition from future cobalt shortages. Nat Commun 13, 1341 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29022-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29022-z
This article is cited by
-
Regional rare-earth element supply and demand balanced with circular economy strategies
Nature Geoscience (2024)
-
Metal electrodes for next-generation rechargeable batteries
Nature Reviews Electrical Engineering (2024)
-
Operando Li metal plating diagnostics via MHz band electromagnetics
Nature Communications (2023)
-
A contact-electro-catalytic cathode recycling method for spent lithium-ion batteries
Nature Energy (2023)
-
Trade-off between critical metal requirement and transportation decarbonization in automotive electrification
Nature Communications (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.