Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of trade on global aquatic food consumption patterns
Effect of trade on global aquatic food consumption patterns
Xu and colleagues find that the average trophic level of aquatic food items in the human diet is declining (from 3.42 to 3.18) because of the considerable increase in low-trophic level aquaculture species output relative to that of capture fisheries since 1976. Additionally they find that trade has contributed to increasing the availability and trophic level of aquatic foods in >60% of the world’s countries.
- Kangshun Zhao
- , Steven D. Gaines
- & Jun Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Modelling six sustainable development transformations in Australia and their accelerators, impediments, enablers, and interlinkages
Modelling six sustainable development transformations in Australia and their accelerators, impediments, enablers, and interlinkages
Global research has identified six critical transformations to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals by 2030. Here, Allen et al model all six transformations in a national context and discuss implications for accelerating progress on the goals.
- Cameron Allen
- , Annabel Biddulph
- & Shirin Malekpour
-
Article
| Open Access Projecting future carbon emissions from cement production in developing countries
Projecting future carbon emissions from cement production in developing countries
The rapid deployment of low-carbon measures is urgently needed to reduce cement emissions as cement CO2 emissions from developing countries will almost deplete the remaining cement emissions budget within climate targets.
- Danyang Cheng
- , David M. Reiner
- & Dabo Guan
-
Article
| Open Access Flood insurance is a driver of population growth in European floodplains
Flood insurance is a driver of population growth in European floodplains
This study finds that flood insurance policy design affects economic development in floodplains and, consequently, flood risk in Europe. Therefore, the authors advocate for flood insurance design to be integrated in climate change adaptation policy.
- Max Tesselaar
- , W. J. Wouter Botzen
- & Jeroen C. J. H. Aerts
-
Article
| Open Access A fish cartel for Africa
A fish cartel for Africa
Englander and Costello note that African coastal waters are among the world’s most biologically rich, but African countries earn much less than their peers from selling access to foreign fishers. They find forming a “fish cartel" would increase African fish biomass by 16% and profits by 23%.
- Gabriel Englander
- & Christopher Costello
-
Article
| Open Access A human-machine collaborative approach measures economic development using satellite imagery
A human-machine collaborative approach measures economic development using satellite imagery
A human-AI collaborative computer vision algorithm produces grid-level economic statistics using satellite images and lightweight human annotation, revealing granular development patterns in North Korea and five other least developed Asian countries.
- Donghyun Ahn
- , Jeasurk Yang
- & Sungwon Park
-
Article
| Open Access Achieving health-oriented air pollution control requires integrating unequal toxicities of industrial particles
Achieving health-oriented air pollution control requires integrating unequal toxicities of industrial particles
Health-oriented emissions reduction in China focusing on the iron and steel industry can reduce costs by 1.56 billion dollars while lowering the population-weighted toxic potency-adjusted exposure risk.
- Di Wu
- , Haotian Zheng
- & Jiming Hao
-
Article
| Open Access The global and regional air quality impacts of dietary change
The global and regional air quality impacts of dietary change
Food production, especially of animal products, is a major source of air pollutants. Here, the authors quantify the impacts dietary changes towards more plant-based diets could have for air quality, labour productivity, and human health.
- Marco Springmann
- , Rita Van Dingenen
- & Adrian Leip
-
Article
| Open Access Global fossil fuel reduction pathways under different climate mitigation strategies and ambitions
Global fossil fuel reduction pathways under different climate mitigation strategies and ambitions
An analysis of the IPCC AR6 scenarios database explores how quickly coal, oil, and gas production and use should be reduced in line with net-zero goals, and points to the need to adopt phase-out benchmarks alongside other climate mitigation targets.
- Ploy Achakulwisut
- , Peter Erickson
- & Steve Pye
-
Article
| Open Access Feeding climate and biodiversity goals with novel plant-based meat and milk alternatives
Feeding climate and biodiversity goals with novel plant-based meat and milk alternatives
Meat and dairy alternatives are promoted for diet sustainability. Here, the authors use a modelling approach to show that replacing 50% of pork, chicken, beef and milk globally with plant-based alternatives can reduce GHG emissions by 6.3 Gt CO2eq year-1 and more than half biodiversity loss by 2050.
- Marta Kozicka
- , Petr Havlík
- & Noel Gurwick
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring spatial feedbacks between adaptation policies and internal migration patterns due to sea-level rise
Exploring spatial feedbacks between adaptation policies and internal migration patterns due to sea-level rise
Adaptation policies can considerably influence the intensity and spatial patterns of sealevel rise-related migration, with managed retreat and setback zones leading to outmigration, while hard protection measures favor migration toward the coast.
- Lena Reimann
- , Bryan Jones
- & Athanasios T. Vafeidis
-
Article
| Open Access Incorporating human dimensions is associated with better wildlife translocation outcomes
Incorporating human dimensions is associated with better wildlife translocation outcomes
Conservation biologists have made calls for including human dimensions in wildlife conservation efforts. This quantitative synthesis of case studies from a global IUCN reintroduction program suggests that inclusion of local stakeholders in wildlife restoration programs boosts success rate.
- Mitchell W. Serota
- , Kristin J. Barker
- & Arthur D. Middleton
-
Article
| Open Access Predictability of fossil fuel CO2 from air quality emissions
Predictability of fossil fuel CO2 from air quality emissions
The historical changes in country emissions of greenhouse gases and air quality pollutants are classified together as a function of economic development, providing valuable guidance to emission scenario development.
- Kazuyuki Miyazaki
- & Kevin Bowman
-
Article
| Open Access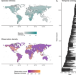 Socioeconomic factors predict population changes of large carnivores better than climate change or habitat loss
Socioeconomic factors predict population changes of large carnivores better than climate change or habitat loss
Habitat loss and climate change are widely acknowledged as drivers of wildlife population change, but socioeconomic impacts are relatively unexplored. This study explores drivers of population change in large carnivores and reveals that socioeconomic growth is more associated with population declines than habitat loss and climate change.
- Thomas F. Johnson
- , Nick J. B. Isaac
- & Manuela González-Suárez
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming global inequality is critical for land-based mitigation in line with the Paris Agreement
Overcoming global inequality is critical for land-based mitigation in line with the Paris Agreement
In a world of deepening inequalities, climate polices might be feasible in high-income countries only. Here the authors find that overcoming global inequality through sustainable socio-economic development is critical for land-based mitigation in line with the Paris Agreement.
- Florian Humpenöder
- , Alexander Popp
- & Quentin Lejeune
-
Article
| Open Access Inequality can double the energy required to secure universal decent living
Inequality can double the energy required to secure universal decent living
In exploring the energy required to provide decent living for all, the authors find the costs of inequality to be far greater than that of population growth. Nonetheless, population growth remains important for other reasons.
- Joel Millward-Hopkins
-
Article
| Open Access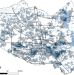 Social inequalities in climate change-attributed impacts of Hurricane Harvey
Social inequalities in climate change-attributed impacts of Hurricane Harvey
New study shows that up to 50% of properties flooded after hurricane Harvey flooded because of climate change, with low-income and Latina/x/o neighborhoods experiencing higher climate change-attributed impacts.
- Kevin T. Smiley
- , Ilan Noy
- & Oliver E. J. Wing
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient use of cement and concrete to reduce reliance on supply-side technologies for net-zero emissions
Efficient use of cement and concrete to reduce reliance on supply-side technologies for net-zero emissions
A new study finds supply-side efforts alone are unlikely to lead to net-zero emissions across the cement and concrete cycle by 2050, advocating for more efficient use of cement and concrete in the built environment and more strategic options for decarbonization.
- Takuma Watari
- , Zhi Cao
- & Keisuke Nansai
-
Article
| Open Access Accounting for interactions between Sustainable Development Goals is essential for water pollution control in China
Accounting for interactions between Sustainable Development Goals is essential for water pollution control in China
The UN’s 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are highly interrelated. This study finds 319 interactions between SDGs for the case of water pollution in China. Results show that effective pollution control requires accounting for these interactions.
- Mengru Wang
- , Annette B. G. Janssen
- & Carolien Kroeze
-
Article
| Open Access Past and future trends of Egypt’s water consumption and its sources
Past and future trends of Egypt’s water consumption and its sources
A historical reconstruction of water use in Egypt shows the change in relative use of Nile water versus virtual water import, especially in the highly consumptive agriculture sector. A range of future projections of water demand are offered based on several plausible socioeconomic scenarios.
- Catherine A. Nikiel
- & Elfatih A. B. Eltahir
-
Article
| Open Access 1.5 °C degrowth scenarios suggest the need for new mitigation pathways
1.5 °C degrowth scenarios suggest the need for new mitigation pathways
Established climate mitigation modelling relies on controversial negative emissions and unprecedented technological change, but neglects to consider degrowth scenarios. Here the authors show that degrowth scenarios minimize many key risks for feasibility and sustainability and thus need to be thoroughly assessed.
- Lorenz T. Keyßer
- & Manfred Lenzen
-
Article
| Open Access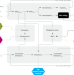 On the optimality of 2°C targets and a decomposition of uncertainty
On the optimality of 2°C targets and a decomposition of uncertainty
Determining attractive response strategies for international climate policy is a complex task. Here, the authors develop a meta-model that disentangles the main uncertainties using full literature ranges and use it to directly compare the insights of the cost-minimising and cost-benefit modelling communities.
- Kaj-Ivar van der Wijst
- , Andries F. Hof
- & Detlef P. van Vuuren
-
Article
| Open Access Impacts of long-term temperature change and variability on electricity investments
Impacts of long-term temperature change and variability on electricity investments
Temperature changes as a result of climate change are expected to impact electric capacity and investment. Here, the authors show that in the United States under socioeconomic pathway 2 and RCP 8.5 mean temperature rises will drive increased electricity demand (0.5-8%) by 2100, along increases in capital investments by 3-22%.
- Zarrar Khan
- , Gokul Iyer
- & Marshall Wise
-
Article
| Open Access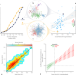 Inequality is rising where social network segregation interacts with urban topology
Inequality is rising where social network segregation interacts with urban topology
Not much is known about the joint relationships between social network structure, urban geography, and inequality. Here, the authors analyze an online social network and find that the fragmentation of social networks is significantly higher in towns in which residential neighborhoods are divided by physical barriers such as rivers and railroads.
- Gergő Tóth
- , Johannes Wachs
- & Balázs Lengyel
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming gender inequality for climate resilient development
Overcoming gender inequality for climate resilient development
Gender inequality increases vulnerability to climate change impacts and reduces societies’ adaptive capacity. Here the authors show how gender inequality may evolve in the future in five scenarios of socioeconomic development and highlight the importance of incorporating gender inequality in climate change research and policy.
- Marina Andrijevic
- , Jesus Crespo Cuaresma
- & Carl-Friedrich Schleussner
-
Article
| Open Access A social engineering model for poverty alleviation
A social engineering model for poverty alleviation
Current inequality and market consumption modelling appears to be subjective. Here the authors combined all three axes of poverty modelling - Engel-Krishnakumar’s microeconomics, Aoki-Chattopadhyay’s mathematical precept and found that multivariate construction is a key component of economic data analysis, implying all modes of income and expenditure need to be considered to arrive at a proper weighted prediction of poverty.
- Amit K. Chattopadhyay
- , T. Krishna Kumar
- & Iain Rice
-
Article
| Open Access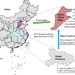 Impacts of irrigated agriculture on food–energy–water–CO2 nexus across metacoupled systems
Impacts of irrigated agriculture on food–energy–water–CO2 nexus across metacoupled systems
Local human activities can lead to cross-border environmental impacts through the food–energy–water–CO2 nexus. Here, the authors report wide variations in environmental impacts of irrigated agriculture across counties within the North China Plain under different environmental and socioeconomic scenarios.
- Zhenci Xu
- , Xiuzhi Chen
- & Yunkai Li
-
Article
| Open Access Fusing subnational with national climate action is central to decarbonization: the case of the United States
Fusing subnational with national climate action is central to decarbonization: the case of the United States
Climate action from local actors is vital in achieving nationally determined contributions under the Paris Agreement. Here the authors show that existing commitments from U.S. states, cities and business could reduce emissions 25% below 2005 levels by 2030, with expanded subnational action reducing emissions by 37% and federal action by up to 49%.
- Nathan E. Hultman
- , Leon Clarke
- & John O’Neill
-
Article
| Open Access Environmental-social-economic footprints of consumption and trade in the Asia-Pacific region
Environmental-social-economic footprints of consumption and trade in the Asia-Pacific region
The environmental and socio-economic implications of the growth in welfare and trade in Asia-Pacific (APAC) remain unclear. Here the authors show that over the past two decades (1995–2015), owing to intraregional trade, the APAC economies have grown increasingly interdependent in natural resource use, air emissions, and labor and economic productivity.
- Lan Yang
- , Yutao Wang
- & Yuanbo Qiao
-
Article
| Open Access Global correlates of terrestrial and marine coverage by protected areas on islands
Global correlates of terrestrial and marine coverage by protected areas on islands
Islands have disproportionate importance for biodiversity conservation, yet they may be underrepresented in protected areas. Here the authors assess how climate, geography, habitat diversity, and socio-economic conditions explain terrestrial and marine protected area coverage on inhabited islands and in the surrounding seas globally.
- David Mouillot
- , Laure Velez
- & Marc Troussellier
-
Perspective
| Open Access A transition to sustainable ocean governance
A transition to sustainable ocean governance
Oceans provide important natural resources, but the management and governance of the ocean is complex and the ecosystem is suffering as a result. The authors discuss current barriers to sustainable ocean governance and suggest pathways forward.
- Tanya Brodie Rudolph
- , Mary Ruckelshaus
- & Philile Mbatha
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping global urban land for the 21st century with data-driven simulations and Shared Socioeconomic Pathways
Mapping global urban land for the 21st century with data-driven simulations and Shared Socioeconomic Pathways
Here the authors develop a set of global, long-term, spatial projections of urban land expansion for understanding the planet’s potential urban futures. The global total amount of urban land increases by a factor of 1.8-5.9 over the 21st century, and the developed world experiences as much new urban development as the developing world.
- Jing Gao
- & Brian C. O’Neill
-
Article
| Open Access Global projections of future urban land expansion under shared socioeconomic pathways
Global projections of future urban land expansion under shared socioeconomic pathways
Shared socioeconomic pathways (SSPs) is a crucial scenario describing the potential of future socio-economic development. The authors here investigate long-term effects of various government policies suggested by different SSPs on urban land and reveal the impact of future urban expansion on other land and food production.
- Guangzhao Chen
- , Xia Li
- & Kangning Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Biodiversity can benefit from climate stabilization despite adverse side effects of land-based mitigation
Biodiversity can benefit from climate stabilization despite adverse side effects of land-based mitigation
Greenhouse gas mitigation can involve land-use changes that alter the habitat available for wildlife. Here, Ohashi et al. perform an integrated assessment showing that climate mitigation can be beneficial for global biodiversity but may entail local biodiversity losses where land-based mitigation is implemented.
- Haruka Ohashi
- , Tomoko Hasegawa
- & Tetsuya Matsui
-
Article
| Open Access Key determinants of global land-use projections
Key determinants of global land-use projections
There lacks model comparison of global land use change projections. Here the authors explored how different long-term drivers determine land use and food availability projections and they showed that the key determinants population growth and improvements in agricultural efficiency.
- Elke Stehfest
- , Willem-Jan van Zeist
- & Keith Wiebe
-
Article
| Open Access Feasible future global scenarios for human life evaluations
Feasible future global scenarios for human life evaluations
Traditional studies of subjective well-being explain national differences using social and economic proxy variables. Here the authors build on this approach to estimate how global human well-being might evolve over the next three decades, and find that changes in social factors could play a much larger role than changes in economic outcomes.
- Christopher Barrington-Leigh
- & Eric Galbraith
-
Article
| Open Access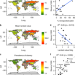 Modern slavery and the race to fish
Modern slavery and the race to fish
There have been growing concerns about the exploitation of workers in the fisheries sectors. Here, Tickler et al. use a country-level metric of slavery to determine the risk of fisheries-level slavery across 20 countries, and find it rises as unreported catch increases and mean value of catch decreases.
- David Tickler
- , Jessica J. Meeuwig
- & Dirk Zeller
-
Article
| Open Access Marine spatial planning makes room for offshore aquaculture in crowded coastal waters
Marine spatial planning makes room for offshore aquaculture in crowded coastal waters
Marine spatial planning is used to co-ordinate multiple ocean uses, and is frequently informed by tradeoffs and composite metrics. Here, Lester et al. introduce an approach that plans for multiple uses simultaneously whilst balancing individual objectives, using a case study of aquaculture development in California.
- S. E. Lester
- , J. M. Stevens
- & C. White
-
Article
| Open Access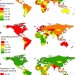 Multi-indicator sustainability assessment of global food systems
Multi-indicator sustainability assessment of global food systems
The development of sustainable food systems requires an understanding of potential trade-off between various objectives. Here, Chaudhary et al. examine how different nations score on food system performance across several domains, including environment, nutrition, and sociocultural wellbeing.
- Abhishek Chaudhary
- , David Gustafson
- & Alexander Mathys
-
Article
| Open Access Poverty eradication in a carbon constrained world
Poverty eradication in a carbon constrained world
The consequences of poverty eradication on limiting warming to 2 °C are not fully clear. Here, Hubacek et al. find that while ending extreme poverty does not jeopardize the climate target, moving everybody to a modest expenditure level increases required mitigation rate by 27%
- Klaus Hubacek
- , Giovanni Baiocchi
- & Anand Patwardhan
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding the origin of Paris Agreement emission uncertainties
Understanding the origin of Paris Agreement emission uncertainties
The pledges put forward by each country to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement are ambiguous. Rogeljet al. quantify the uncertainty arising from the interpretation of these pledges and find that by 2030 global emissions can vary by −10% to +20% around their median estimate of 52 GtCO2e yr−1.
- Joeri Rogelj
- , Oliver Fricko
- & Keywan Riahi
-
Article
| Open Access A coupled human-Earth model perspective on long-term trends in the global marine fishery
A coupled human-Earth model perspective on long-term trends in the global marine fishery
Global marine fish harvest increased over the 20th century, reaching a peak in the 1990s. Here, Galbraith and colleagues analyse a model combining both ecological and economic drivers to weigh the factors most likely to contribute to long-term changes in fish harvests.
- E. D. Galbraith
- , D. A. Carozza
- & D. Bianchi

 Substantially reducing global PM2.5-related deaths under SDG3.9 requires better air pollution control and healthcare
Substantially reducing global PM2.5-related deaths under SDG3.9 requires better air pollution control and healthcare