Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access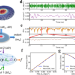 Forecasting the outcome of spintronic experiments with Neural Ordinary Differential Equations
Forecasting the outcome of spintronic experiments with Neural Ordinary Differential Equations
Deep learning has an increasing impact to assist research. Here, authors show that a dynamical neural network, trained on a minimal amount of data, can predict the behaviour of spintronic devices with high accuracy and an extremely efficient simulation time.
- Xing Chen
- , Flavio Abreu Araujo
- & Damien Querlioz
-
Article
| Open Access The emergence of macroscopic currents in photoconductive sampling of optical fields
The emergence of macroscopic currents in photoconductive sampling of optical fields
Photoconductive sampling of optical fields is a powerful measurement technique, but existing models fail to connect single-electron dynamics to measured signals. Here, the authors report a model that identifies the roles of electron-neutral scattering and mean-field charge interaction in photoconductive sampling.
- Johannes Schötz
- , Ancyline Maliakkal
- & Matthias F. Kling
-
Article
| Open Access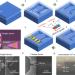 Waveguide coupled III-V photodiodes monolithically integrated on Si
Waveguide coupled III-V photodiodes monolithically integrated on Si
To realize on-chip optical communication schemes based on silicon, the integration of waveguides onto III-V devices must be achieved. Here, the authors report waveguide-coupled III-V heterostructure photodiodes monolithically integrated on silicon waveguides via aligned nanowire.
- Pengyan Wen
- , Preksha Tiwari
- & Kirsten E. Moselund
-
Article
| Open Access Versatile metal-wire waveguides for broadband terahertz signal processing and multiplexing
Versatile metal-wire waveguides for broadband terahertz signal processing and multiplexing
Waveguides that can provide complex signal-processing functionalities while guiding terahertz signals are desired. Here, the authors report the independent processing of multiplexed signals by engineering the metal surface of a four-wire waveguide.
- Junliang Dong
- , Alessandro Tomasino
- & Roberto Morandotti
-
Article
| Open Access Defect-driven antiferromagnetic domain walls in CuMnAs films
Defect-driven antiferromagnetic domain walls in CuMnAs films
Antiferromagnets offer the potential for higher speed and density than ferromagnetic materials for spintronic devices. Here, Reimers et al study the domain structure of CuMnAs, demonstrating the role of defects in stabilizing the location and orientation of antiferromagnetic domain walls.
- Sonka Reimers
- , Dominik Kriegner
- & Kevin W. Edmonds
-
Article
| Open Access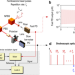 Femtometer-amplitude imaging of coherent super high frequency vibrations in micromechanical resonators
Femtometer-amplitude imaging of coherent super high frequency vibrations in micromechanical resonators
Methods for imaging vibrations in mechanical resonators have been limited to picometer amplitudes and frequencies above 2 GHz. Here, the authors use a stroboscopic optical sampling approach, with simultaneous high bandwidth and low noise-floor, and measure 70 fm displacements out to 12 GHz.
- Lei Shao
- , Vikrant J. Gokhale
- & Jason J. Gorman
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing defective interfaces in perovskite solar cells from highly sensitive sub-bandgap photocurrent spectroscopy using optical cavities
Revealing defective interfaces in perovskite solar cells from highly sensitive sub-bandgap photocurrent spectroscopy using optical cavities
Sensitive photocurrent spectroscopy and interference of light in perovskite solar cells with optical spacers reveal that electronic defects in these devices are localized at the interface between the semiconductor and the electron collecting contact.
- Bas T. van Gorkom
- , Tom P. A. van der Pol
- & René A. J. Janssen
-
Comment
| Open Access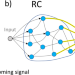 Connecting reservoir computing with statistical forecasting and deep neural networks
Connecting reservoir computing with statistical forecasting and deep neural networks
Among the existing machine learning frameworks, reservoir computing demonstrates fast and low-cost training, and its suitability for implementation in various physical systems. This Comment reports on how aspects of reservoir computing can be applied to classical forecasting methods to accelerate the learning process, and highlights a new approach that makes the hardware implementation of traditional machine learning algorithms practicable in electronic and photonic systems.
- Lina Jaurigue
- & Kathy Lüdge
-
Article
| Open Access Ultralow dark current in near-infrared perovskite photodiodes by reducing charge injection and interfacial charge generation
Ultralow dark current in near-infrared perovskite photodiodes by reducing charge injection and interfacial charge generation
In lead‐tin halide perovskite photodiodes, the interfacial energy offset at the charge transport layer controls the dark current. In this work, by increasing this offset, the authors demonstrates a photodiode with ultralow dark and noise currents and high near‐infrared sensitivity.
- Riccardo Ollearo
- , Junke Wang
- & Gerwin H. Gelinck
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of hybrid higher-order skin-topological effect in non-Hermitian topolectrical circuits
Observation of hybrid higher-order skin-topological effect in non-Hermitian topolectrical circuits
Even though exploiting skin-topological effects in topological insulators is attractive for topological switch design, current research has focused on theoretical demonstrations. Here, the authors experimentally demonstrate higher-order topological skin effects in nonreciprocal topoelectrical circuits.
- Deyuan Zou
- , Tian Chen
- & Xiangdong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Deep-ultraviolet electroluminescence and photocurrent generation in graphene/hBN/graphene heterostructures
Deep-ultraviolet electroluminescence and photocurrent generation in graphene/hBN/graphene heterostructures
Here, the authors report the observation of deep-ultraviolet (DUV) electroluminescence and photocurrent generation in van der Waals heterostructures based on hBN crystals, showing potential for DUV light emitting and detection devices.
- Su-Beom Song
- , Sangho Yoon
- & Jonghwan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Electron shelving of a superconducting artificial atom
Electron shelving of a superconducting artificial atom
Existing schemes for coherent control and measurements in superconducting circuits rely on the coupling between superconducting qubits and cavity photons. Here the authors implement conditional fluorescence readout of a fluxonium qubit placed inside an open waveguide, with no coupling to cavity modes.
- Nathanaël Cottet
- , Haonan Xiong
- & Vladimir E. Manucharyan
-
Article
| Open Access Ferroelectric 2D ice under graphene confinement
Ferroelectric 2D ice under graphene confinement
Ferroelectric ordering of water has been at the heart of intense debates due to its importance in enhancing our understanding of the condensed matter. Here, the authors observe ferroelectric properties of water ice in a two dimensional phase under confinement between two graphene layers.
- Hao-Ting Chin
- , Jiri Klimes
- & Ya-Ping Hsieh
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically switchable van der Waals magnon valves
Electrically switchable van der Waals magnon valves
A major challenge in magnon based approaches to information processing lies in developing valves to allow or supress the magnon signal. Here, Chen et al demonstrate a van der Waals magnet based magnon valve which can be tuned electrically over an exceptionally wide range.
- Guangyi Chen
- , Shaomian Qi
- & Jian-Hao Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic memory driven by topological insulators
Magnetic memory driven by topological insulators
It remains challenging to integrate topological insulators (TI) with magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJ) for spintronics applications. Here, the authors achieve a large tunneling magnetoresistance ratio and a low switching current density in a TI-MTJ device at room temperature, very promising for TI-driven magnetic memory.
- Hao Wu
- , Aitian Chen
- & Kang L. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Transverse barrier formation by electrical triggering of a metal-to-insulator transition
Transverse barrier formation by electrical triggering of a metal-to-insulator transition
Resistive switching usually occurs by the formation of conducting filaments in the direction of current flow. Here the authors study an intriguing type of volatile metal-to-insulator resistive switching in (La,Sr)MnO3, which occurs by the formation of an insulating barrier perpendicular to the current.
- Pavel Salev
- , Lorenzo Fratino
- & Ivan K. Schuller
-
Article
| Open Access Reprogrammable plasmonic topological insulators with ultrafast control
Reprogrammable plasmonic topological insulators with ultrafast control
The development of fast and dynamic topological photonic platforms is an ongoing challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a reprogrammable plasmonic topological insulator in which ultrafast electric switches allow for nanosecond-level switching time between different configurations.
- Jian Wei You
- , Qian Ma
- & Tie Jun Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Preliminary demonstration of a persistent Josephson phase-slip memory cell with topological protection
Preliminary demonstration of a persistent Josephson phase-slip memory cell with topological protection
Superconducting computing promises enhanced computational power, but scalable and fast superconducting memories are still not implemented. Here, the authors demonstrate a superconducting memory cell based on hysteretic phase-slip transition, without degradation up to ~1 K over several days.
- Nadia Ligato
- , Elia Strambini
- & Francesco Giazotto
-
Article
| Open Access Precision measurement of electron-electron scattering in GaAs/AlGaAs using transverse magnetic focusing
Precision measurement of electron-electron scattering in GaAs/AlGaAs using transverse magnetic focusing
Electron-electron scattering plays a crucial role in many solid state phenomena; however, the direct measurement of electron-electron scattering length is challenging. Here, the authors use transverse magnetic focusing to measure this quantity in high-mobility GaAs/AlGaAs heterostructures.
- Adbhut Gupta
- , J. J. Heremans
- & M. J. Manfra
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance photonic transformers for DC voltage conversion
High-performance photonic transformers for DC voltage conversion
Conventional DC-DC converters rely on switching operations and energy storing components which face both noise and scaling difficulties. Here, the authors present an alternative design for a DC-to-DC converter based on closely coupled LEDs and photovoltaic cells, which exhibits high efficiency, low noise, and miniaturizability.
- Bo Zhao
- , Sid Assawaworrarit
- & Shanhui Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Wavelength conversion through plasmon-coupled surface states
Wavelength conversion through plasmon-coupled surface states
Semiconductor surface states often stand in the way of device performance, but here, the authors take advantage of them for wavelength conversion. They present a compact, passive conversion device insensitive to optical alignment by using plasmon-coupled surface states that enable the efficient conversion without nonlinear phenomena.
- Deniz Turan
- , Ping Keng Lu
- & Mona Jarrahi
-
Article
| Open Access Field-free spin-orbit torque-induced switching of perpendicular magnetization in a ferrimagnetic layer with a vertical composition gradient
Field-free spin-orbit torque-induced switching of perpendicular magnetization in a ferrimagnetic layer with a vertical composition gradient
Switching of ferrimagnets by current-induced spin-orbit torque is promising for spintronics, due to their high-speed dynamics and small macroscopic magnetization. Switching of perpendicularly magnetized materials, however, requires a bias field for symmetry breaking. Here, Zheng et al demonstrate field-free current-induced switching of perpendicular ferrimagnets, using a compositional gradient-driven Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction.
- Zhenyi Zheng
- , Yue Zhang
- & Pedram Khalili Amiri
-
Article
| Open Access Bidirectional interconversion of microwave and light with thin-film lithium niobate
Bidirectional interconversion of microwave and light with thin-film lithium niobate
Coherent conversion between optical and microwave photonics is needed for future quantum applications. Here, the authors combine thin-film lithium niobate and superconductor platforms as a hybrid electro-optic system to achieve high-efficiency frequency conversion between microwave and optical modes.
- Yuntao Xu
- , Ayed Al Sayem
- & Hong X. Tang
-
Article
| Open Access A low-noise photonic heterodyne synthesizer and its application to millimeter-wave radar
A low-noise photonic heterodyne synthesizer and its application to millimeter-wave radar
Photonics-based radars offer intriguing potential but face tradeoffs in tunability, complexity, and noise. Here the authors present microwave generation in a photonics platform by heterodyning of two low-noise, self-injection-locked lasers, and demonstrate its advantages in an FMCW radar system.
- Eric A. Kittlaus
- , Danny Eliyahu
- & Siamak Forouhar
-
Article
| Open Access Generation of even and odd high harmonics in resonant metasurfaces using single and multiple ultra-intense laser pulses
Generation of even and odd high harmonics in resonant metasurfaces using single and multiple ultra-intense laser pulses
Strong nonlinearities, like high harmonic generation in optical systems, can lead to interesting applications in photonics. Here the authors fabricate a thin resonant gallium phosphide metasurface capable of avoiding the laser-induced damage and demonstrate efficient even and odd high harmonic generation from it when driven by mid-infrared laser pulses.
- Maxim R. Shcherbakov
- , Haizhong Zhang
- & Gennady Shvets
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of current-induced switching in non-collinear antiferromagnetic IrMn3 by differential voltage measurements
Observation of current-induced switching in non-collinear antiferromagnetic IrMn3 by differential voltage measurements
Anti-ferromagnetic based memories have a wide range of advantages over their ferromagnetic counterparts, however, their electrical signatures of switching are complicated by spurious signals. Here, Arpaci et al demonstrate an experimental method to distinguish between anti-ferromagnetic switching, and such spurious signatures.
- Sevdenur Arpaci
- , Victor Lopez-Dominguez
- & Pedram Khalili Amiri
-
Article
| Open Access Theoretical demonstration of a capacitive rotor for generation of alternating current from mechanical motion
Theoretical demonstration of a capacitive rotor for generation of alternating current from mechanical motion
Energy harvesting devices based on micro-electromechanisms (MEMS) is attractive for sustainable energy applications. Here, the authors report the theoretical working principle of a lightweight, low-voltage AC-current generating MEMS-based capacitive rotor device for Watts-level power generation from everyday walking.
- Ehud Haimov
- , Aidan Chapman
- & Alexei A. Kornyshev
-
Article
| Open Access A single atom change turns insulating saturated wires into molecular conductors
A single atom change turns insulating saturated wires into molecular conductors
In molecular junctions, where a molecule is placed between two electrodes, the current passed decays exponentially as a function of length. Here, Chen et al. show that this exponentially attenuation can be controlled by changing a single atom at the end of the molecular wire.
- Xiaoping Chen
- , Bernhard Kretz
- & Christian A. Nijhuis
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced responsivity and detectivity of fast WSe2 phototransistor using electrostatically tunable in-plane lateral p-n homojunction
Enhanced responsivity and detectivity of fast WSe2 phototransistor using electrostatically tunable in-plane lateral p-n homojunction
In photodetectors based on 2D materials, a trade-off often exists between responsivity and speed. Here, the authors attenuate this issue via integration of a lateral, in-plane, electrostatically tunable p-n homojunction with a conventional WSe2 phototransistor.
- Sayantan Ghosh
- , Abin Varghese
- & Saurabh Lodha
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-compact dual-band smart NEMS magnetoelectric antennas for simultaneous wireless energy harvesting and magnetic field sensing
Ultra-compact dual-band smart NEMS magnetoelectric antennas for simultaneous wireless energy harvesting and magnetic field sensing
Wireless implantable medical devices (IMDs) are hamstrung by both size and efficiency required for wireless power transfer. Here, Zaeimbashi et al. present a magnetoelectric nano-electromechanical systems that can harvest energy and sense weak magnetic fields like those arising from neural activity.
- Mohsen Zaeimbashi
- , Mehdi Nasrollahpour
- & Nian X. Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Reducing the impact of radioactivity on quantum circuits in a deep-underground facility
Reducing the impact of radioactivity on quantum circuits in a deep-underground facility
Background radiation has been identified as a key factor limiting the coherence times of superconducting circuits. Here, the authors measure the impact of environmental and cosmic radiation on a superconducting resonator with varying degrees of shielding, including an underground facility.
- L. Cardani
- , F. Valenti
- & I. M. Pop
-
Article
| Open Access Controllable field-free switching of perpendicular magnetization through bulk spin-orbit torque in symmetry-broken ferromagnetic films
Controllable field-free switching of perpendicular magnetization through bulk spin-orbit torque in symmetry-broken ferromagnetic films
A major challenge of spintronics is achieving magnetic field free electrical control of magnetisation. Here, Xie et al. achieve perpendicular magnetisation switching in a CoPt alloy, breaking inversion symmetry by varying the composition of the alloy in the growth direction.
- Xuejie Xie
- , Xiaonan Zhao
- & Shishen Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Improving organic photovoltaic cells by forcing electrode work function well beyond onset of Ohmic transition
Improving organic photovoltaic cells by forcing electrode work function well beyond onset of Ohmic transition
Both open-circuit voltage and fill factor of organic solar cells are affected by the metal-organic semiconductor interface. Here, the authors demonstrate that the voltage can continue to rise when the Fermi level is forced up to the semiconductor density-of-states tail.
- Chao Zhao
- , Cindy G. Tang
- & Peter K. H. Ho
-
Article
| Open Access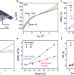 Giant gauge factor of Van der Waals material based strain sensors
Giant gauge factor of Van der Waals material based strain sensors
The Gauge factor (GF) enhancement in strain sensors remains a key challenge. Here the authors leverage the piezoelectric and photoelectric effects in a class of van der Waals materials to tune the GF, and obtain a record GF up to 3933 for a SnS2-based strain sensor.
- Wenjie Yan
- , Huei-Ru Fuh
- & Han-Chun Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Polariton-assisted excitation energy channeling in organic heterojunctions
Polariton-assisted excitation energy channeling in organic heterojunctions
Exploiting delocalized organic polaritons for enhanced exciton harvesting has been advantageous for organic optoelectronic with planar heterojunctions. Here, the authors report polariton-assisted excitation energy channeling in organic heterojunctions coupled to the same cavity mode.
- Mao Wang
- , Manuel Hertzog
- & Karl Börjesson
-
Article
| Open Access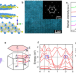 High-frequency rectifiers based on type-II Dirac fermions
High-frequency rectifiers based on type-II Dirac fermions
High-frequency rectifiers at terahertz regime are pivotal components in modern communication, whereas the drawbacks in semiconductor junctions-based devices inhibit their usages. Here, the authors report electromagnetic rectification with high signal-to-noise ratio driven by chiral Bloch-electrons in type-II Dirac semimetal NiTe2-based device allowing for efficient THz detection.
- Libo Zhang
- , Zhiqingzi Chen
- & Wei Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Crystallization of CsPbBr3 single crystals in water for X-ray detection
Crystallization of CsPbBr3 single crystals in water for X-ray detection
Perovskite single crystals are commonly grown in organic solvents, which require relatively high temperature condition. Here, the authors develop a low-temperature crystallisation strategy to grow CsPbBr3 single crystals in water with improved charge transport properties and stability.
- Jiali Peng
- , Chelsea Q. Xia
- & Qianqian Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient and bright warm-white electroluminescence from lead-free metal halides
Efficient and bright warm-white electroluminescence from lead-free metal halides
Designing efficient light-emitting diodes with white-light-emission from broadband-emission metal halides remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate bright and efficient lead-free LEDs based on cesium copper halides enabled by introducing Tween organic additive in the precursor.
- Hong Chen
- , Lin Zhu
- & Jianpu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A superconducting switch actuated by injection of high-energy electrons
A superconducting switch actuated by injection of high-energy electrons
A recent finding of tuning critical current in metallic nanowires by application of small gate voltages seems at odds with general understanding. Here, Ritter et al. study similar nanowires and link the origin of the critical current suppression to tunneling of few high-energy electrons between gate and nanowire, ruling out direct tuning by electric fields.
- M. F. Ritter
- , A. Fuhrer
- & F. Nichele
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired multisensory neural network with crossmodal integration and recognition
Bioinspired multisensory neural network with crossmodal integration and recognition
Human-like robotic sensing aims at extracting and processing complicated environmental information via multisensory integration and interaction. Tan et al. report an artificial spiking multisensory neural network that integrates five primary senses and mimics the crossmodal perception of biological brains.
- Hongwei Tan
- , Yifan Zhou
- & Sebastiaan van Dijken
-
Article
| Open Access Highly efficient photoelectric effect in halide perovskites for regenerative electron sources
Highly efficient photoelectric effect in halide perovskites for regenerative electron sources
Electron sources play as important component in a wide range of applications. Here, the authors demonstrate efficient, regenerative, and low-cost electron sources based on solution-processed halide perovskite thin films with quantum efficiency up to 2.2% and a lifetime of more than 25 h.
- Fangze Liu
- , Siraj Sidhik
- & Aditya D. Mohite
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time Hall-effect detection of current-induced magnetization dynamics in ferrimagnets
Real-time Hall-effect detection of current-induced magnetization dynamics in ferrimagnets
Measuring real time magnetization dynamics resulting from Hall effects is hard due to the small signal size. Here Sala et al demonstrate a method of performing Hall resistance measurements with sub-ns resolution, and use it to investigate the switching of GdFeCo dots induced by spin-orbit torques.
- G. Sala
- , V. Krizakova
- & P. Gambardella
-
Article
| Open Access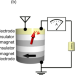 Uncooled sub-GHz spin bolometer driven by auto-oscillation
Uncooled sub-GHz spin bolometer driven by auto-oscillation
Goto et al present a bolometer based around the heat generation in magnetic tunnel junctions under auto-oscillation conditions. Unlike superconducting bolometers, the presented device operates at room temperature and sub-GHz frequencies, opening possibilities for use in microwave devices.
- Minori Goto
- , Yuma Yamada
- & Yoshishige Suzuki
-
Article
| Open Access Reverse dark current in organic photodetectors and the major role of traps as source of noise
Reverse dark current in organic photodetectors and the major role of traps as source of noise
The suppression of dark current in organic photodetectors (OPDs) is important for maximizing the performance of the devices. Here, the authors report the relationship between the high dark saturation current and the presence of mid-gap trap states in OPDs with a donor–acceptor structure.
- Jonas Kublitski
- , Andreas Hofacker
- & Karl Leo
-
Article
| Open Access An optical neural chip for implementing complex-valued neural network
An optical neural chip for implementing complex-valued neural network
Most demonstrations of optical neural networks for computing have been so far limited to real-valued frameworks. Here, the authors implement complex-valued operations in an optical neural chip that integrates input preparation, weight multiplication and output generation within a single device.
- H. Zhang
- , M. Gu
- & A. Q. Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneous sparse learning for PCM-based memristor neural networks
Spontaneous sparse learning for PCM-based memristor neural networks
Designing energy efficient and scalable artificial networks for neuromorphic computing remains a challenge. Here, the authors present 1 Gb phase change memory memristor array with a spontaneous sparse learning scheme able to leverage the resistance drift issue improving the classification accuracy on MNIST handwritten digit dataset.
- Dong-Hyeok Lim
- , Shuang Wu
- & Luping Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Conditional quantum operation of two exchange-coupled single-donor spin qubits in a MOS-compatible silicon device
Conditional quantum operation of two exchange-coupled single-donor spin qubits in a MOS-compatible silicon device
Operating donor-based quantum computers in silicon is hindered by the dependence of inter-qubit coupling on the precise donor position. Here, the authors show controlled rotation operation on exchange-coupled electron spins in the weak-exchange regime, loosening the requirements on positioning precision.
- Mateusz T. Ma̧dzik
- , Arne Laucht
- & Andrea Morello
-
Article
| Open Access Thermoelectric current in a graphene Cooper pair splitter
Thermoelectric current in a graphene Cooper pair splitter
Thermoelectricity due to the interplay of the nonlocal Cooper pair splitting and the elastic co-tunneling in normal metal-superconductor-normal metal structure is predicted. Here, the authors observe the non-local Seebeck effect in a graphene-based Cooper pair splitting device.
- Z. B. Tan
- , A. Laitinen
- & P. J. Hakonen
-
Article
| Open Access Long-distance spin-transport across the Morin phase transition up to room temperature in ultra-low damping single crystals of the antiferromagnet α-Fe2O3
Long-distance spin-transport across the Morin phase transition up to room temperature in ultra-low damping single crystals of the antiferromagnet α-Fe2O3
Hitherto, only circularly polarized antiferromagnetic (AFM) spin-waves (SWs) were expected to convey spin-information. Here, the authors present persistent spin-transport over long distances in the easy-plane AFM phase of hematite, α-Fe2O3, via linearly polarized SW pairs with ultra-low damping.
- R. Lebrun
- , A. Ross
- & M. Kläui

 Ultralarge anti-Stokes lasing through tandem upconversion
Ultralarge anti-Stokes lasing through tandem upconversion