Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of the electronic structure in open-shell donor-acceptor organic semiconductors
Evolution of the electronic structure in open-shell donor-acceptor organic semiconductors
The classical narrow bandgap donor-acceptor organic semiconductors show great application potential in organic electronics, bio-imaging and other fields. Here, the authors systematically and rigorously demonstrate their open-shell diradical character via experimental and theoretical investigation.
- Zhongxin Chen
- , Wenqiang Li
- & Fei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular design approach towards elastic and multifunctional polymer electronics
A molecular design approach towards elastic and multifunctional polymer electronics
Next-generation skin-inspired electronics require enhanced mechanical robustness and device complexity including elasticity, solvent resistance, and facile patternability. Here, the authors show a molecular design concept that simultaneously achieves all these requirements by covalently linking an in-situ formed rubber matrix with polymer electronic materials.
- Yu Zheng
- , Zhiao Yu
- & Zhenan Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Giant room temperature electrocaloric effect in a layered hybrid perovskite ferroelectric: [(CH3)2CHCH2NH3]2PbCl4
Giant room temperature electrocaloric effect in a layered hybrid perovskite ferroelectric: [(CH3)2CHCH2NH3]2PbCl4
Most known electrocaloric materials show relatively poor cooling performance near room temperature, hindering their applications. Here, the authors achieve large electrocaloric effect near room temperature in a hybrid perovskite ferroelectric, useful for high-performance solid-state refrigeration.
- Xitao Liu
- , Zhenyue Wu
- & Junhua Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Element selection for crystalline inorganic solid discovery guided by unsupervised machine learning of experimentally explored chemistry
Element selection for crystalline inorganic solid discovery guided by unsupervised machine learning of experimentally explored chemistry
Machine learning has the potential to significantly speed-up the discovery of new materials in synthetic materials chemistry. Here the authors combine unsupervised machine learning and crystal structure prediction to predict a novel quaternary lithium solid electrolyte that is then synthesized.
- Andrij Vasylenko
- , Jacinthe Gamon
- & Matthew J. Rosseinsky
-
Article
| Open Access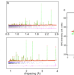 Directed synthesis of a hybrid improper magnetoelectric multiferroic material
Directed synthesis of a hybrid improper magnetoelectric multiferroic material
Fabricating materials with simultaneously spontaneous magnetic and electrical polarisations is challenging due to contradictory electronic features. Here, the authors report a synthesis path toward a perovskite MnSrTa2O7 by performing low-temperature cation-exchange reactions on Li2SrTa2O7.
- Tong Zhu
- , Fabio Orlandi
- & Michael A. Hayward
-
Article
| Open Access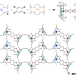 Manipulating electron redistribution to achieve electronic pyroelectricity in molecular [FeCo] crystals
Manipulating electron redistribution to achieve electronic pyroelectricity in molecular [FeCo] crystals
Pyroelectric materials exhibiting large and nearly constant pyroelectric coefficients over a wide temperature range are highly desirable. Here, the authors develop molecular [FeCo] crystals with continuous pyroelectricity, originating from a transition between three distinct electronic structures.
- Pritam Sadhukhan
- , Shu-Qi Wu
- & Osamu Sato
-
Article
| Open Access A chalcogenide-cluster-based semiconducting nanotube array with oriented photoconductive behavior
A chalcogenide-cluster-based semiconducting nanotube array with oriented photoconductive behavior
Interesting properties of carbon nanotubes prompt a search for diverse inorganic nanotubes. Here, the authors report a supertetrahedral chalcogenide cluster-based semiconducting nanotube array that exhibits high electric conductivity and oriented photoconductive behavior.
- Jiaqi Tang
- , Xiang Wang
- & Tao Wu
-
Article
| Open Access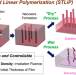 Ubiquitous organic molecule-based free-standing nanowires with ultra-high aspect ratios
Ubiquitous organic molecule-based free-standing nanowires with ultra-high aspect ratios
Extension of nanostructure fabrication in the single-nm regime is a promising but fabrication of nanostructures with high aspect ratios remains challenging. Here, the authors use high energy charged particles to produce free-standing 1D organic nanostructures with extremely high aspect ratios and controlled number density.
- Koshi Kamiya
- , Kazuto Kayama
- & Shu Seki
-
Article
| Open Access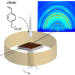 Multication perovskite 2D/3D interfaces form via progressive dimensional reduction
Multication perovskite 2D/3D interfaces form via progressive dimensional reduction
Many best-performing perovskite photovoltaics use 2D/3D interfaces to improve efficiency and stability, yet the mechanism of interface assembly is unclear. Here, Proppe et al. use in-situ GIWAXS to resolve this transformation, observing progressive dimensional reduction from 3D to 2D perovskites.
- Andrew H. Proppe
- , Andrew Johnston
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access Are Shockley-Read-Hall and ABC models valid for lead halide perovskites?
Are Shockley-Read-Hall and ABC models valid for lead halide perovskites?
Charge dynamics in perovskite is not well-understood, limited by the knowledge of defect physics and charge recombination mechanism, yet the ABC and SRH models are widely used. Here, the authors introduce advanced PLQY mapping as function of excitation pulse energy and repetition frequency to examine the validity of these models.
- Alexander Kiligaridis
- , Pavel A. Frantsuzov
- & Ivan G. Scheblykin
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming the water oxidative limit for ultra-high-workfunction hole-doped polymers
Overcoming the water oxidative limit for ultra-high-workfunction hole-doped polymers
Realizing ultra-high work functions (UHWFs) in hole-doped polymer semiconductors remains a challenge due to water-oxidation reactions. Here, the authors determine the role of water-anion complexes in limiting the work function and develop a design strategy for realizing UHWF polymers.
- Qi-Mian Koh
- , Cindy Guanyu Tang
- & Peter K. H. Ho
-
Review Article
| Open Access Toward a mechanistic understanding of electrocatalytic nanocarbon
Toward a mechanistic understanding of electrocatalytic nanocarbon
Electrocatalytic nanocarbon (EN) is a class of materials receiving intense interest as next generation electrocatalysts. Although impressive platforms, work is still required to develop our mechanistic understanding of them to that of molecular electrocatalysts.
- Erik J. Askins
- , Marija R. Zoric
- & Ksenija D. Glusac
-
Article
| Open Access Covalency does not suppress O2 formation in 4d and 5d Li-rich O-redox cathodes
Covalency does not suppress O2 formation in 4d and 5d Li-rich O-redox cathodes
In this work, authors show that O-redox in 4d and 5d transition metal oxides involves the formation of molecular oxygen trapped in the particles. These results are in accord with observations in 3d oxides and show that the greater covalency of the 4d and 5d oxides does not stabilise peroxo-like species.
- Robert A. House
- , John-Joseph Marie
- & Peter G. Bruce
-
Article
| Open Access A high-conductivity n-type polymeric ink for printed electronics
A high-conductivity n-type polymeric ink for printed electronics
The development of n-type conductive polymer inks is critical for the development of next-generation opto-electronic devices that rely on efficient hole and electron transport. Here, the authors report an alcohol-based, high performance and stable n-type conductive ink for printed electronics.
- Chi-Yuan Yang
- , Marc-Antoine Stoeckel
- & Simone Fabiano
-
Article
| Open Access Orthogonal photochemistry-assisted printing of 3D tough and stretchable conductive hydrogels
Orthogonal photochemistry-assisted printing of 3D tough and stretchable conductive hydrogels
3D-printing tough conductive hydrogels (TCHs) with complex structures is still a challenging task due to their inherent contrasting multinetworks, uncontrollable and slow polymerization. Here the authors show an orthogonal photochemistry-assisted printing strategy to make 3D TCHs in one pot.
- Hongqiu Wei
- , Ming Lei
- & You Yu
-
Article
| Open Access 90% yield production of polymer nano-memristor for in-memory computing
90% yield production of polymer nano-memristor for in-memory computing
Though polymer memristors are promising for low‐power flexible edge computing applications, realizing efficient nanometer‐scale arrays remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a record high 90% production yield in nm‐scale 2D conjugated polymer memristors with homogeneous resistive switching.
- Bin Zhang
- , Weilin Chen
- & Yu Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling pairing of π-conjugated electrons in 2D covalent organic radical frameworks via in-plane strain
Controlling pairing of π-conjugated electrons in 2D covalent organic radical frameworks via in-plane strain
Controlling the electronic states of molecules is a fundamental challenge for future sub-nanoscale device technologies but the external dynamical control of these states still awaits experimental realization. Here, via quantum chemical calculations, the authors demonstrate that in-plane uniaxial strain of 2D covalently linked arrays of radical units induces controlled pairing of π-conjugated electrons in a reversible way.
- Isaac Alcón
- , Raúl Santiago
- & Stefan T. Bromley
-
Article
| Open Access Pressure-induced ferroelectric-like transition creates a polar metal in defect antiperovskites Hg3Te2X2 (X = Cl, Br)
Pressure-induced ferroelectric-like transition creates a polar metal in defect antiperovskites Hg3Te2X2 (X = Cl, Br)
Generally, ferroelectricity in ABO3 perovskites is suppressed by hydrostatic compression, but the evidence for pressure-induced ferroelectricity remains elusive. Here, the authors find a direct ferroelectric-like structural transition induced by pressure in defect antiperovskites.
- Weizhao Cai
- , Jiangang He
- & Shanti Deemyad
-
Article
| Open Access Optical-field driven charge-transfer modulations near composite nanostructures
Optical-field driven charge-transfer modulations near composite nanostructures
Controlling and modulating charge transfer dynamics in composite nanostructures, though promising for optoelectronic applications, remains a challenge. Here, the authors report optical control of charge separation and recombination processes in organic semiconductor-based composite nanostructures.
- Kwang Jin Lee
- , Elke Beyreuther
- & Pascal André
-
Article
| Open Access Strain-induced creation and switching of anion vacancy layers in perovskite oxynitrides
Strain-induced creation and switching of anion vacancy layers in perovskite oxynitrides
Properties of perovskite oxides can be changed by manipulating anion-vacancy order patterns, but they are difficult to control. Here the authors show strain-induced creation and switching of anion vacancies in perovskite films in which the direction or periodicity of anion-vacancy planes is altered depending on the substrate employed.
- Takafumi Yamamoto
- , Akira Chikamatsu
- & Hiroshi Kageyama
-
Article
| Open Access Solid cyclooctatetraene-based triplet quencher demonstrating excellent suppression of singlet–triplet annihilation in optical and electrical excitation
Solid cyclooctatetraene-based triplet quencher demonstrating excellent suppression of singlet–triplet annihilation in optical and electrical excitation
Though reducing non-emissive triplet excited-states using quenchers effectively improves organic semiconductor laser diode (OSLD) performance, existing quenchers are not suitable for devices. Here, the authors designed a solid-state triplet quencher for OSLD under optical and electrical excitation.
- Van T. N. Mai
- , Viqar Ahmad
- & Shih-Chun Lo
-
Article
| Open Access Solution-processable integrated CMOS circuits based on colloidal CuInSe2 quantum dots
Solution-processable integrated CMOS circuits based on colloidal CuInSe2 quantum dots
Designing efficient toxic-element-free technologies in solution-processable CMOS electronics remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate integrated logic CMOS circuits based on heavy-metal-free colloidal CuInSe2 quantum dots with low switching voltages and with degradation-free performance on month-long time scales.
- Hyeong Jin Yun
- , Jaehoon Lim
- & Victor I. Klimov
-
Article
| Open Access Reversible multicolor chromism in layered formamidinium metal halide perovskites
Reversible multicolor chromism in layered formamidinium metal halide perovskites
Metal halide perovskites feature crystalline-like electronic band structures and liquid-like physical properties that allow chemical manipulation of the structure with low energy input. Here, the authors leverage the low formation energy of 2D metal halide perovskites to demonstrate films that reversibly switch between multiple colors using tunable quantum well thickness.
- Bryan A. Rosales
- , Laura E. Mundt
- & Lance M. Wheeler
-
Article
| Open Access Modulated structure determination and ion transport mechanism of oxide-ion conductor CeNbO4+δ
Modulated structure determination and ion transport mechanism of oxide-ion conductor CeNbO4+δ
Materials with oxygen hyperstoichiometry received great attention in solid oxide fuel cells field because of the low activation energy of interstitial ion migration. Here the authors revealed the relationship between the structure and oxide ion migration for the whole series of CeNbO4+δ compounds.
- Jian Li
- , Fengjuan Pan
- & Junliang Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Computational screen-out strategy for electrically pumped organic laser materials
Computational screen-out strategy for electrically pumped organic laser materials
Though the goal of current organic solid-state laser research remains the realization of electrically pumped lasing, identifying organic semiconductors with ideal properties remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a computational strategy for screening electrical pumping lasing molecules.
- Qi Ou
- , Qian Peng
- & Zhigang Shuai
-
Article
| Open Access Exciton-driven change of phonon modes causes strong temperature dependent bandgap shift in nanoclusters
Exciton-driven change of phonon modes causes strong temperature dependent bandgap shift in nanoclusters
The bandgap of nanostructures usually follows the bulk value upon temperature change. Here, the authors find that in small nanocrystals a weakening of the bonds due to optical excitation causes a pronounced phonon shift, leading to a drastic enhancement of the bandgap’s temperature dependence.
- Franziska Muckel
- , Severin Lorenz
- & Gerd Bacher
-
Article
| Open Access Highly reversible oxygen redox in layered compounds enabled by surface polyanions
Highly reversible oxygen redox in layered compounds enabled by surface polyanions
Oxygen-anion redox in lithium-rich layered oxides can boost the capacity of lithium-ion battery cathodes. Here, the authors investigate the mechanism of surface degradation caused by oxygen oxidation and the kinetics of surface reconstruction.
- Qing Chen
- , Yi Pei
- & Graeme Henkelman
-
Article
| Open Access A thermally activated and highly miscible dopant for n-type organic thermoelectrics
A thermally activated and highly miscible dopant for n-type organic thermoelectrics
Realizing efficient n-doping in organic thermoelectrics remains a challenge due to dopant-semiconductor immiscibility, poor dopant stability and low doping efficiency. Here, the authors use computer-assisted screening to develop n-dopants for thermoelectric polymers that show record power factors.
- Chi-Yuan Yang
- , Yi-Fan Ding
- & Jian Pei
-
Article
| Open Access Sn(IV)-free tin perovskite films realized by in situ Sn(0) nanoparticle treatment of the precursor solution
Sn(IV)-free tin perovskite films realized by in situ Sn(0) nanoparticle treatment of the precursor solution
Tin based perovskites are easily oxidized, which generates large density of defects and compromised the solar cell efficiency. Here Nakamura et al. add metallic tin nanoparticles in the precursor solution to suppress tin (IV) impurities and enable high efficiency tin based perovskite solar cells.
- Tomoya Nakamura
- , Shinya Yakumaru
- & Atsushi Wakamiya
-
Article
| Open Access A foundation for complex oxide electronics -low temperature perovskite epitaxy
A foundation for complex oxide electronics -low temperature perovskite epitaxy
Designing complex oxides with appreciable low-temperature synthesis remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate an atomic layer deposition process for LaNiO3 to enable epitaxial thin films on LaAlO3 and SrTiO3 substrates deposited at 225 °C, with no annealing required to achieve good electronic properties.
- Henrik H. Sønsteby
- , Erik Skaar
- & Ola Nilsen
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning molecular emission of organic emitters from fluorescence to phosphorescence through push-pull electronic effects
Tuning molecular emission of organic emitters from fluorescence to phosphorescence through push-pull electronic effects
Though organic emitters with room temperature phosphorescence (RTP) are attractive for various applications, realizing highly efficient and long lifetime emission remains a challenge. Here, the authors report the role of push-pull electronic effects on emission for organic RTP emitters.
- Hai-Tao Feng
- , Jiajie Zeng
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Establishing charge-transfer excitons in 2D perovskite heterostructures
Establishing charge-transfer excitons in 2D perovskite heterostructures
Forming charge transfer excitons (CTEs) exclusively within perovskite structures remains as an unexplored issue. Here, the authors report the establishment of CTEs for demonstrating broad light emission within quasi-2D perovskite heterostructures, presenting “intermolecular-type” excited states.
- Jia Zhang
- , Xixiang Zhu
- & Bin Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Macroscopic Polarization Change via Electron Transfer in a Valence Tautomeric Cobalt Complex
Macroscopic Polarization Change via Electron Transfer in a Valence Tautomeric Cobalt Complex
Polarization change from directional electron transfer attracts considerable attention owing to its fast switching rate and potential light control. Here, the authors provide a proof-of-concept of electronic pyroelectricity induced by intramolecular electron transfer in the single crystal of a valence tautomeric compound.
- Shu-Qi Wu
- , Meijiao Liu
- & Osamu Sato
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming the exciton binding energy in two-dimensional perovskite nanoplatelets by attachment of conjugated organic chromophores
Overcoming the exciton binding energy in two-dimensional perovskite nanoplatelets by attachment of conjugated organic chromophores
Functionalizing two-dimensional (2D) hybrid perovskites with organic chromophores is a novel approach to tune their optoelectronic properties. Here, the authors report efficient charge separation and conduction in 2D hybrid perovskite nanoplatelets by incorporating an electron acceptor chromophore.
- María C. Gélvez-Rueda
- , Magnus B. Fridriksson
- & Ferdinand C. Grozema
-
Article
| Open Access Highly efficient blue organic light-emitting diodes based on carbene-metal-amides
Highly efficient blue organic light-emitting diodes based on carbene-metal-amides
Realizing efficient blue-emitting organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) with long operational lifetime is key to the development of future display technologies. Here, the authors report efficient host-guest and host-free OLEDs featuring designed carbene-metal-amide-type deep-blue photoemitters.
- Patrick J. Conaghan
- , Campbell S. B. Matthews
- & Alexander S. Romanov
-
Article
| Open Access Site-selective doping of ordered charge states in magnetite
Site-selective doping of ordered charge states in magnetite
Charge ordering in magnetite is an important example of the complex behaviour that emerges in transition metal oxides. Here the authors show that doping causes selective oxidation of one site in the established trimeron pattern, introducing an additional charge-ordered structure.
- E. Pachoud
- , J. Cumby
- & J. P. Attfield
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance particulate matter including nanoscale particle removal by a self-powered air filter
High-performance particulate matter including nanoscale particle removal by a self-powered air filter
Particulate matter (PM) pollutants have been considered serious threats to public health but effective removal of nanoscale particles (NPs) by filter materials is challenging. Here, the authors fabricate an ionic liquid based self-powered air filter that can be used in high-efficiency removal of PM, including NPs.
- Guo-Hao Zhang
- , Qiu-Hong Zhu
- & Guo-Hong Tao
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous enhanced efficiency and thermal stability in organic solar cells from a polymer acceptor additive
Simultaneous enhanced efficiency and thermal stability in organic solar cells from a polymer acceptor additive
Thermal instability is a critical bottleneck for bulk heterojunction organic solar cells. Here Yang et al. use barely 1 wt% of a polymer acceptor as an additive to simultaneously improve the device efficiency and thermal stability of several state-of-the-art organic photovoltaic systems at high temperatures.
- Wenyan Yang
- , Zhenghui Luo
- & Jie Min
-
Article
| Open Access Directed self-assembly of viologen-based 2D semiconductors with intrinsic UV–SWIR photoresponse after photo/thermo activation
Directed self-assembly of viologen-based 2D semiconductors with intrinsic UV–SWIR photoresponse after photo/thermo activation
Developing new materials with broadband photoresponse is highly desirable for realizing commercial photodetectors with extended detection ranges. Here, the authors report a cyanide-bridged layer-directed intercalation approach to design viologen compounds with enhanced broadband photoresponse.
- Xiao-Qing Yu
- , Cai Sun
- & Guo-Cong Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced control of self-doping in halide perovskites for improved thermoelectric performance
Enhanced control of self-doping in halide perovskites for improved thermoelectric performance
Metal halide perovskites show excellent optoelectronic properties but the understanding on their thermoelectric properties has been limited. Here Liu et al. develop a strategy for controlled doping and achieve a high figure of merit ZT value of 0.14 via careful composition engineering.
- Tianjun Liu
- , Xiaoming Zhao
- & Oliver Fenwick
-
Article
| Open Access Triplet–triplet upconversion enhanced by spin–orbit coupling in organic light-emitting diodes
Triplet–triplet upconversion enhanced by spin–orbit coupling in organic light-emitting diodes
Though triplet-triplet upconversion is a promising strategy for designing new deep blue-emitting organic materials, maximizing the efficiency of this process remains difficult. Here, the authors report the upconversion efficiency in anthracene derivatives based on a spin-orbit coupling mechanism.
- Ryota Ieuji
- , Kenichi Goushi
- & Chihaya Adachi
-
Article
| Open Access A sodium-ion sulfide solid electrolyte with unprecedented conductivity at room temperature
A sodium-ion sulfide solid electrolyte with unprecedented conductivity at room temperature
Solid-state rechargeable batteries using solid electrolytes instead of liquid ones could address the safety and energy density issues. Here the authors report a Na-ion solid electrolyte Na2.88Sb0.88W0.12S4 which exhibits record high ionic conductivity of 32 mS/cm at room temperature.
- A. Hayashi
- , N. Masuzawa
- & M. Tatsumisago
-
Article
| Open Access Repurposing DNA-binding agents as H-bonded organic semiconductors
Repurposing DNA-binding agents as H-bonded organic semiconductors
To unlock the potential of biological semiconductors for printed flexible electronics, experimental evidence that reveals the material’s charge transport mechanism is required. Here, the authors report the charge transport mechanism in hydrogen-bonded DNA topoisomerase inhibitors.
- Fengjiao Zhang
- , Vincent Lemaur
- & Ying Diao
-
Article
| Open Access Multistep nucleation and growth mechanisms of organic crystals from amorphous solid states
Multistep nucleation and growth mechanisms of organic crystals from amorphous solid states
Little attention has been paid to the fundamental mechanism of molecular self-assembly into crystallised films or wires on surfaces. Here the authors use real time in-situ scanning probe microscopy to monitor the growth trajectories of organic semiconducting films as they crystallize from an amorphous solid state under ambient conditions.
- Hongliang Chen
- , Mingliang Li
- & Xuefeng Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Vapor-deposited zeolitic imidazolate frameworks as gap-filling ultra-low-k dielectrics
Vapor-deposited zeolitic imidazolate frameworks as gap-filling ultra-low-k dielectrics
Insulating materials combining a high mechanical stability, a low dielectric constant and the ability to completely fill narrow gaps are essential to fabricate interconnects for future high-performance chips. Here, the authors integrate zeolitic imidazolate frameworks as ultra-low-k dielectrics within a 90 nm pitch metallization layer via selective vapor-based conversion of metal oxide films.
- Mikhail Krishtab
- , Ivo Stassen
- & Rob Ameloot
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing photoelectrochemical water splitting by combining work function tuning and heterojunction engineering
Enhancing photoelectrochemical water splitting by combining work function tuning and heterojunction engineering
While photoelectrodes represent a promising solar-to-fuel conversion technology, material challenges limit performances. Here, authors improve the onset potential and charge separation of bismuth vanadate photoanode water splitting performances by work function tuning and heterojunction engineering.
- Kai-Hang Ye
- , Haibo Li
- & Shihe Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time optical and electronic sensing with a β-amino enone linked, triazine-containing 2D covalent organic framework
Real-time optical and electronic sensing with a β-amino enone linked, triazine-containing 2D covalent organic framework
Aromatic two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks (2D COFs) are hailed as candidates for electronic and optical devices, yet only few applications were demonstrated. Here, the authors show a triazine based COF with UV/VIS real-time response and increase in bulk conductivity to HCl vapour as a chemical trigger.
- Ranjit Kulkarni
- , Yu Noda
- & Michael J. Bojdys
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning charge transport dynamics via clustering of doping in organic semiconductor thin films
Tuning charge transport dynamics via clustering of doping in organic semiconductor thin films
Designing organic thermoelectric materials with high electrical conductivity and Seebeck coefficient is challenging due to the direct relationship between these two properties. Here, the authors explore the role of dopant spatial distribution on thermoelectric performance in conjugated polymers.
- Connor J. Boyle
- , Meenakshi Upadhyaya
- & D. Venkataraman
-
Article
| Open Access Anatomy of the energetic driving force for charge generation in organic solar cells
Anatomy of the energetic driving force for charge generation in organic solar cells
Understanding the energetic driving force is important for optimizing the performance of organic solar cells. Here Nakano et al. suggest that the dominant driving force is the energy difference between the singlet excited state and the charge transfer state after assessing 16 material combinations.
- Kyohei Nakano
- , Yujiao Chen
- & Keisuke Tajima

 Striping of orbital-order with charge-disorder in optimally doped manganites
Striping of orbital-order with charge-disorder in optimally doped manganites