Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Consequences of tropical land use for multitrophic biodiversity and ecosystem functioning
Consequences of tropical land use for multitrophic biodiversity and ecosystem functioning
Transformation of natural ecosystems into agricultural land is usually accompanied by extensive biodiversity loss. Calculating multitrophic energy fluxes, Barnes et al.report severe reductions of biodiversity and ecosystem functioning from tropical rainforest to oil-palm plantations.
- Andrew D. Barnes
- , Malte Jochum
- & Ulrich Brose
-
Review Article |
 On the unfounded enthusiasm for soft selective sweeps
On the unfounded enthusiasm for soft selective sweeps
Patterns of genomic variation can be used to identify targets of positive selection but understanding their mode of evolution is challenging. This review discusses theory and empirical evidence regarding soft sweep models and concludes that the recent enthusiasm for soft sweeps is unfounded.
- Jeffrey D Jensen
-
Article |
 Parallel evolution of Nicaraguan crater lake cichlid fishes via non-parallel routes
Parallel evolution of Nicaraguan crater lake cichlid fishes via non-parallel routes
Similar morphologies can evolve repeatedly in similar environments. Here, the authors show morphological, ecological and genetic differentiation between sympatric ecomorphs across two independent radiations of crater lake cichlids, but a different order of speciation events across radiations.
- Kathryn R. Elmer
- , Shaohua Fan
- & Axel Meyer
-
Article |
 Extant diversity of bryophytes emerged from successive post-Mesozoic diversification bursts
Extant diversity of bryophytes emerged from successive post-Mesozoic diversification bursts
The macroevolutionary history of bryophytes is poorly understood. Here, the authors show that, while overall diversification rates of bryophytes are substantially lower than those reported in ferns and angiosperms, they increase over time and become comparable to angiosperms in the most recent lineages.
- B. Laenen
- , B. Shaw
- & A. J. Shaw
-
Article |
 Pattern formation at multiple spatial scales drives the resilience of mussel bed ecosystems
Pattern formation at multiple spatial scales drives the resilience of mussel bed ecosystems
Self-organized patterns at multiple spatial scales are widespread in nature, although little is known about their effect on ecosystem functioning. Here, Liu et al.show how two self-organization processes at individual and ecosystem scale interact to increase the resilience of intertidal mussel beds.
- Quan-Xing Liu
- , Peter M. J. Herman
- & Johan van de Koppel
-
Article
| Open Access Satellite telemetry and social modeling offer new insights into the origin of primate multilevel societies
Satellite telemetry and social modeling offer new insights into the origin of primate multilevel societies
Multilevel societies (MLS) are a complex form of group organization found in mammals, yet the origin of MLS is poorly understood. Here the authors show that MLS of the golden snub-nosed monkey evolved from the aggregation of independent one-male, multifemale units found in ancestral Asian colobines.
- Xiao-Guang Qi
- , Paul A. Garber
- & Bao-Guo Li
-
Article |
 Consumer co-evolution as an important component of the eco-evolutionary feedback
Consumer co-evolution as an important component of the eco-evolutionary feedback
The role of predator evolution in eco-evolutionary dynamics has received less attention than that of prey. Here, Hiltunen and Becks show that prey anti-predator traits evolve faster and are more variable in the presence of co-evolved predators, resulting in altered community dynamics.
- Teppo Hiltunen
- & Lutz Becks
-
Article
| Open Access Meiofauna increases bacterial denitrification in marine sediments
Meiofauna increases bacterial denitrification in marine sediments
Excessive nutrient loading is a threat to aquatic ecosystems; however, denitrification may be key in removing large amounts of reactive nitrogen and, therefore, mitigating consequent eutrophication. Here, the authors explore how meiofauna may impact the rate of denitrification in sediments.
- S. Bonaglia
- , F. J. A Nascimento
- & V. Brüchert
-
Article |
 Evidence for a weakening relationship between interannual temperature variability and northern vegetation activity
Evidence for a weakening relationship between interannual temperature variability and northern vegetation activity
Northern Hemisphere photosynthesis is thought to respond positively to temperature variations, yet the strength of this relationship may change over time. Here, using a combination of satellite data and models, the authors assess the temporal change of this relationship over the past three decades.
- Shilong Piao
- , Huijuan Nan
- & Anping Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Broad impacts of fine-scale dynamics on seascape structure from zooplankton to seabirds
Broad impacts of fine-scale dynamics on seascape structure from zooplankton to seabirds
Ocean circulations can strongly influence ecological dynamics in marine ecosystem over multiple spatial scales. Here, Bertrand et al.find that the majority of these interactions occur within small-scale hotspots that concentrate interactions across many trophic levels from zooplankton to seabirds.
- Arnaud Bertrand
- , Daniel Grados
- & Ronan Fablet
-
Article |
 Host–parasite network structure is associated with community-level immunogenetic diversity
Host–parasite network structure is associated with community-level immunogenetic diversity
Genes of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) are crucial for immune response, yet it is unclear what shapes their diversity at a community level. Here, the authors show that indirect effects among rodent hosts and their helminth parasites can play a crucial role in shaping host MHC diversity.
- Shai Pilosof
- , Miguel A. Fortuna
- & Jordi Bascompte
-
Article |
 Carbonate-hosted methanotrophy represents an unrecognized methane sink in the deep sea
Carbonate-hosted methanotrophy represents an unrecognized methane sink in the deep sea
Methane is a significant contributor to greenhouse forcing, and determining its fluxes and reservoirs is important in understanding the methane cycle. Here, the authors investigate microbial methane oxidation in carbonates of the deep sea that represent a previously unrecognized biological sink for methane.
- Jeffrey J. Marlow
- , Joshua A. Steele
- & Victoria J. Orphan
-
Article |
 A necessarily complex model to explain the biogeography of the amphibians and reptiles of Madagascar
A necessarily complex model to explain the biogeography of the amphibians and reptiles of Madagascar
Inferring evolutionary processes from biogeographic patterns is challenging. Here, the authors present a new method to examine spatial patterns of biodiversity and show that biogeographic patterns of Malagasy amphibians and reptiles are influenced by a combination of diversification processes.
- Jason L. Brown
- , Alison Cameron
- & Miguel Vences
-
Article
| Open Access Middle-Eastern plant communities tolerate 9 years of drought in a multi-site climate manipulation experiment
Middle-Eastern plant communities tolerate 9 years of drought in a multi-site climate manipulation experiment
Semi-arid and Mediterranean ecosystems are predicted to be vulnerable to climate change. Here, Tielbörger et al. show that plants along a steep climatic gradient in a biodiversity hotspot are resistant to both irrigation and drought in multiple years of experimental rainfall manipulation.
- Katja Tielbörger
- , Mark C. Bilton
- & Marcelo Sternberg
-
Article |
 Species traits and phylogenetic conservatism of climate-induced range shifts in stream fishes
Species traits and phylogenetic conservatism of climate-induced range shifts in stream fishes
Climate change is causing many species to shift their distributional ranges. Here, Comte et al.show that, among stream fish, shifts at the leading edge and the trailing edge of the range are influenced by different mechanisms related to individual species traits and their phylogenetic history.
- Lise Comte
- , Jérôme Murienne
- & Gaël Grenouillet
-
Article
| Open Access Seasonal changes in predator community switch the direction of selection for prey defences
Seasonal changes in predator community switch the direction of selection for prey defences
The coexistence of alternative antipredatory strategies is poorly understood. Here, the authors show that warning colours lose their effectiveness when passerine birds, their main predators, fledge their young, which suggests that predators’ learning impacts selection for conspicuous warning signals.
- Johanna Mappes
- , Hanna Kokko
- & Leena Lindström
-
Article
| Open Access Species-specific defence responses facilitate conspecifics and inhibit heterospecifics in above–belowground herbivore interactions
Species-specific defence responses facilitate conspecifics and inhibit heterospecifics in above–belowground herbivore interactions
It is unclear how herbivores determine community structure. Here the authors show how interactions between aboveground adults and belowground larvae of a tree flea beetle and multiple heterospecific aboveground species interact via plant defence responses to determine herbivore performance.
- Wei Huang
- , Evan Siemann
- & Jianqing Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Mutually beneficial host exploitation and ultra-biased sex ratios in quasisocial parasitoids
Mutually beneficial host exploitation and ultra-biased sex ratios in quasisocial parasitoids
The evolution of social behaviour is usually explained by kin selection. Here, the authors show that mutual host exploitation by a parasitoid wasp maximizes the average reproductive success of individual females, which suggests that cooperative brood care does not rely on kin selection in these wasps.
- Xiuyun Tang
- , Ling Meng
- & Baoping Li
-
Article
| Open Access Forest stand growth dynamics in Central Europe have accelerated since 1870
Forest stand growth dynamics in Central Europe have accelerated since 1870
The growth dynamics of forest ecosystems undergoing climatic change are not well understood. Here Pretzsch et al. show that two of the dominant tree species of Central Europe have undergone significantly accelerated growth dynamics during the past century.
- Hans Pretzsch
- , Peter Biber
- & Thomas Rötzer
-
Article
| Open Access Ecological succession of a Jurassic shallow-water ichthyosaur fall
Ecological succession of a Jurassic shallow-water ichthyosaur fall
Little is known about Mesozoic marine reptile dead-falls. Here, the authors reconstruct the ecological succession of a Late Jurassic shallow-water ichthyosaur fall community and show that it fulfilled ecological roles similar to shallow whale falls and did not support specialized chemosynthetic communities.
- Silvia Danise
- , Richard J. Twitchett
- & Katie Matts
-
Article |
 Massive outbreaks of Noctiluca scintillans blooms in the Arabian Sea due to spread of hypoxia
Massive outbreaks of Noctiluca scintillans blooms in the Arabian Sea due to spread of hypoxia
Phytoplankton blooms in the northern Arabian Sea have shifted from diatoms to green dinoflagellates in the last decade. Here, the authors show that influx of oxygen deficient waters, together with the ability of dinoflagellates’ endosymbionts to fix carbon under such conditions, facilitated the bloom shift.
- Helga do Rosário Gomes
- , Joaquim I. Goes
- & Prasad Thoppil
-
Article |
 Aridity threshold in controlling ecosystem nitrogen cycling in arid and semi-arid grasslands
Aridity threshold in controlling ecosystem nitrogen cycling in arid and semi-arid grasslands
Understanding the relationship between aridity and ecosystem N-cycling is important in predicting the effects of global climate change. Here, the authors present N isotopes across an aridity gradient and identify a tipping point, which marks a divergence in N-cycling controlling factors and mechanisms.
- Chao Wang
- , Xiaobo Wang
- & Edith Bai
-
Article |
 Magnetic properties of uncultivated magnetotactic bacteria and their contribution to a stratified estuary iron cycle
Magnetic properties of uncultivated magnetotactic bacteria and their contribution to a stratified estuary iron cycle
Magnetotactic bacteria synthesize magnetite or greigite magnetosomes that, when fossilized, can serve as biomarkers of past ocean redox shifts. Here, Chen et al.show that these magnetosome types have very similar coercivity distributions, with implications for the analysis of sedimentary magnetic records.
- A.P. Chen
- , V.M. Berounsky
- & N.G.F. Vella
-
Article |
 Differentiated availability of geochemical mercury pools controls methylmercury levels in estuarine sediment and biota
Differentiated availability of geochemical mercury pools controls methylmercury levels in estuarine sediment and biota
Methylmercury in aquatic biota constitutes a severe environmental issue globally, but models struggle to provide accurate quantification. Here, the authors combine experimental approaches to assess contributions from different pools and use the data to interpret the mercury cycle in an estuarine setting.
- Sofi Jonsson
- , Ulf Skyllberg
- & Erik Björn
-
Article |
 Interpreting carbonate and organic carbon isotope covariance in the sedimentary record
Interpreting carbonate and organic carbon isotope covariance in the sedimentary record
To date, covariance of carbonate and organic carbon isotope records has been assumed to denote fidelity of the original signal. This study shows that post-depositional alteration can create strong correlations, raising doubts about the use of correlated records to imply important changes in past global carbon cycling.
- Amanda M. Oehlert
- & Peter K. Swart
-
Article |
 Fumigant methyl iodide can methylate inorganic mercury species in natural waters
Fumigant methyl iodide can methylate inorganic mercury species in natural waters
Methyl iodide is a fumigant registered for use in many countries and its usage is increasing. Here, the authors identify a new pathway of mercury methylation via methyl iodide in sunlit water, suggesting the necessity for a more comprehensive risk assessment for the use of methyl iodide as a fumigant.
- Yongguang Yin
- , Yanbin Li
- & Guibin Jiang
-
Article |
 Unveiling viral–host interactions within the ‘microbial dark matter’
Unveiling viral–host interactions within the ‘microbial dark matter’
Identification of virus–host pairs requires cultivation, otherwise it is based on tentative assignment using genomic signatures. Here, the authors describe a method that can unambiguously assign viruses to hosts and does not require their cultivation.
- Manuel Martínez-García
- , Fernando Santos
- & Josefa Antón
-
Article |
 Clustering in community structure across replicate ecosystems following a long-term bacterial evolution experiment
Clustering in community structure across replicate ecosystems following a long-term bacterial evolution experiment
It is unclear how predictable adaptive evolution is in multispecies ecosystems. Here, the authors show that relative abundance of bacterial species varies after long-term evolution, but that the final community composition clusters within a few types, which suggests that evolution follows only a few paths.
- Hasan Celiker
- & Jeff Gore
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperative secretions facilitate host range expansion in bacteria
Cooperative secretions facilitate host range expansion in bacteria
Understanding the factors determining pathogen host range is critical for human health. Here, the authors show that bacteria use cooperative secretions to modify their environment and to infect multiple host species, which suggests that cooperative secretions are key determinants of host range in bacteria.
- Luke McNally
- , Mafalda Viana
- & Sam P. Brown
-
Article
| Open Access Suppressing subordinate reproduction provides benefits to dominants in cooperative societies of meerkats
Suppressing subordinate reproduction provides benefits to dominants in cooperative societies of meerkats
In hierarchical animal societies, dominant females suppress breeding by subordinate females. Here, the authors experimentally suppress breeding by subordinate female meerkats and observe that dominants give birth to heavier pups which grow faster, suggesting this behaviour improves fitness of dominants.
- M. B. V. Bell
- , M. A. Cant
- & T. H. Clutton-Brock
-
Article |
 Phylogenetic measures of biodiversity and neo- and paleo-endemism in Australian Acacia
Phylogenetic measures of biodiversity and neo- and paleo-endemism in Australian Acacia
Assessing spatial patterns of biodiversity using phylogenetic methods is a promising approach for conservation planning. Here, Mishler et al. develop a method to distinguish between recent and old endemism and provide new insights about biodiversity across space and time for the Australian Acacia.
- Brent D. Mishler
- , Nunzio Knerr
- & Joseph T. Miller
-
Article |
 Evolution of increased phenotypic diversity enhances population performance by reducing sexual harassment in damselflies
Evolution of increased phenotypic diversity enhances population performance by reducing sexual harassment in damselflies
The mechanisms by which morphological variation affect evolutionary dynamics are poorly understood. Here, the authors show that increased phenotypic diversity in female damselflies decreases the risk of sexual harassment by males, and enhances population performance.
- Yuma Takahashi
- , Kotaro Kagawa
- & Masakado Kawata
-
Article |
 A 520 million-year-old chelicerate larva
A 520 million-year-old chelicerate larva
Modern arthropods present niche differentiation between larvae and adult stages. Here, Liu et al. describe a larval fossil of Leanchoilia illecebrosa, an early Cambrian arthropod from China, and show a feeding appendage, unknown in adults, that suggests that niche differentiation originated in the early Cambrian.
- Yu Liu
- , Joachim T. Haug
- & Xianguang Hou
-
Article
| Open Access An electromagnetic field disrupts negative geotaxis in Drosophila via a CRY-dependent pathway
An electromagnetic field disrupts negative geotaxis in Drosophila via a CRY-dependent pathway
The earth’s electromagnetic field has a modest effect on the behaviour of Drosophila melanogaster. Here, Fedele et al. use an assessment of climbing behaviour to describe how the blue-light circadian photoreceptor cryptochrome mediates a negative movement response to gravity in flies.
- Giorgio Fedele
- , Edward W. Green
- & Charalambos P. Kyriacou
-
Article |
 Pesticide risk assessment in free-ranging bees is weather and landscape dependent
Pesticide risk assessment in free-ranging bees is weather and landscape dependent
Determining how pesticides found in nectar and pollen impair pollinator behaviour in the field requires setting standards for measuring effects in free-ranging insects. Here, Henry et al.show that sublethal effects of a neonicotinoid pesticide in bees depends on the landscape and time of exposure.
- Mickaël Henry
- , Colette Bertrand
- & Axel Decourtye
-
Article |
 Winter and spring controls on the summer food web of the coastal West Antarctic Peninsula
Winter and spring controls on the summer food web of the coastal West Antarctic Peninsula
The Western Antarctic Peninsular is subject to climate change, including increased winter temperatures and melting sea ice. In this study, the authors demonstrate that climate change in this area effects bacteria and phytoplankton levels, which culminates in an altered diet for the apex predator, the Adélie penguin.
- Grace K. Saba
- , William R. Fraser
- & Oscar M. Schofield
-
Article |
 Methane production by phosphate-starved SAR11 chemoheterotrophic marine bacteria
Methane production by phosphate-starved SAR11 chemoheterotrophic marine bacteria
Methane levels in the oceans’ surface waters are higher than those in the atmosphere, which is puzzling. Here the authors show that marine bacteria of the ubiquitous SAR11 group can release significant amounts of methane when feeding on phosphorus-containing compounds such as methylphosphonic acid.
- Paul Carini
- , Angelicque E. White
- & Stephen J. Giovannoni
-
Article
| Open Access Global relationship between phytoplankton diversity and productivity in the ocean
Global relationship between phytoplankton diversity and productivity in the ocean
The mechanisms that determine the relationship between diversity and productivity in marine phytoplankton remain unclear. Here, Vallina et al.show that selective predation and transient competitive exclusion determine phytoplankton community composition.
- S. M. Vallina
- , M. J. Follows
- & M. Loreau
-
Article
| Open Access Extreme diving behaviour in devil rays links surface waters and the deep ocean
Extreme diving behaviour in devil rays links surface waters and the deep ocean
Many pelagic fishes and squids live at ocean depths below the euphotic zone but whether surface predators dive to these depths to feed on them is unclear. Here, the authors tag Chilean devil rays and demonstrate that they regularly make dives to at least 1,500 m, suggesting that the rays forage for food at these depths.
- Simon R. Thorrold
- , Pedro Afonso
- & Michael L. Berumen
-
Article |
 Differentiating moss from higher plants is critical in studying the carbon cycle of the boreal biome
Differentiating moss from higher plants is critical in studying the carbon cycle of the boreal biome
Satellite-derived indices used to estimate gross primary production and carbon cycling rarely differentiate between boreal mosses and vascular plants, despite differences in photosynthetic capacity. Here, the authors show that this may have led to an overestimation of the boreal carbon budget.
- Wenping Yuan
- , Shuguang Liu
- & Timo Vesala
-
Article
| Open Access A magnetic compass aids monarch butterfly migration
A magnetic compass aids monarch butterfly migration
Monarch butterflies (Danaus plexippus) migrate from North America to central Mexico during the fall. Here, Guerra et al. show that, in addition to a sun compass orientation, monarch butterflies use a magnetic compass to help direct their flight towards the equator.
- Patrick A Guerra
- , Robert J Gegear
- & Steven M Reppert
-
Article |
 Gains to species diversity in organically farmed fields are not propagated at the farm level
Gains to species diversity in organically farmed fields are not propagated at the farm level
Organic farming is proposed to increase the biodiversity of organisms within a field. In this study, Schneider et al.show that while biodiversity is increased in organically farmed fields compared to conventionally farmed land, these effects are not seen at a greater spatial level.
- Manuel K. Schneider
- , Gisela Lüscher
- & Felix Herzog
-
Article |
 Atlantic salmon show capability for cardiac acclimation to warm temperatures
Atlantic salmon show capability for cardiac acclimation to warm temperatures
Cardiac function can limit high-temperature tolerance in fish. Here, Antilla et al.show similar cardiac responses to warming for two wild Atlantic salmon populations with different environmental temperatures, which suggests that cardiac plasticity is independent of natural habitat.
- Katja Anttila
- , Christine S. Couturier
- & Anthony P. Farrell
-
Article |
 Pattern recognition algorithm reveals how birds evolve individual egg pattern signatures
Pattern recognition algorithm reveals how birds evolve individual egg pattern signatures
It is unclear how birds differentiate their own eggs from cuckoo’s eggs that parasitize their nests. Here, the authors develop a computer vision tool that simulates how brains process pattern information and show that cuckoos’ hosts have evolved unique egg patterns to distinguish their own eggs from a cuckoo’s.
- Mary Caswell Stoddard
- , Rebecca M. Kilner
- & Christopher Town
-
Article
| Open Access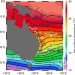 Intensification of the meridional temperature gradient in the Great Barrier Reef following the Last Glacial Maximum
Intensification of the meridional temperature gradient in the Great Barrier Reef following the Last Glacial Maximum
The Great Barrier Reef (GBR) is under threat from rising ocean temperatures, yet its response to past temperature change is poorly known. Felis et al. show that the GBR experienced a much steeper temperature gradient during the last deglaciation, suggesting it may be more resilient than previously thought.
- Thomas Felis
- , Helen V. McGregor
- & Jody M. Webster
-
Article |
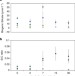 Silicate deposition during decomposition of cyanobacteria may promote export of picophytoplankton to the deep ocean
Silicate deposition during decomposition of cyanobacteria may promote export of picophytoplankton to the deep ocean
The contribution of picophytoplankton to particle transport in the marine environment is relatively unknown. Here, the authors perform incubation experiments and show that decomposing picophytoplankton provides an efficient transport pathway for silica-enriched marine particles.
- Tiantian Tang
- , Kim Kisslinger
- & Cindy Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Selective fishing induces density-dependent growth
Selective fishing induces density-dependent growth
The effects of fishing policies that adjust selectivity are unclear. Here, Svedäng and Hornborg show that fishing practices that increase selectivity of the Eastern Baltic cod have negatively affected its productivity, suggesting that fishing policies should prioritize catch rates over yield.
- Henrik Svedäng
- & Sara Hornborg
-
Article |
 A fast and unbiased procedure to randomize ecological binary matrices with fixed row and column totals
A fast and unbiased procedure to randomize ecological binary matrices with fixed row and column totals
Available methods to randomize binary matrices with fixed row and column sums are computationally intensive and tend to generate matrix configurations with unequal frequency. Here, the authors introduce a fast and unbiased procedure that requires reduced computational effort and produces uniformly distributed null matrices.
- Giovanni Strona
- , Domenico Nappo
- & Jesus San-Miguel-Ayanz
-
Article
| Open Access Forests fuel fish growth in freshwater deltas
Forests fuel fish growth in freshwater deltas
Vegetation close to streams and lakes provides organic matter to aquatic ecosystems. Here, the authors show that the dense forest cover around lakes feeds the near-shore lake food web through organic matter subsidies, leading to faster growth in planktivorous fish.
- Andrew J. Tanentzap
- , Erik J. Szkokan-Emilson
- & John M. Gunn
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Agroecology
- Animal migration
- Behavioural ecology
- Biodiversity
- Biogeochemistry
- Biogeography
- Biooceanography
- Boreal ecology
- Climate-change ecology
- Community ecology
- Conservation biology
- Ecological epidemiology
- Ecological genetics
- Ecological modelling
- Ecological networks
- Ecophysiology
- Ecosystem ecology
- Ecosystem services
- Environmental economics
- Evolutionary ecology
- Fire ecology
- Forest ecology
- Forestry
- Freshwater ecology
- Grassland ecology
- Invasive species
- Macroecology
- Microbial ecology
- Molecular ecology
- Palaeoecology
- Population dynamics
- Restoration ecology
- Riparian ecology
- Stable isotope analysis
- Theoretical ecology
- Tropical ecology
- Urban ecology
- Wetlands ecology

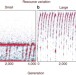 Diversifying evolution of competitiveness
Diversifying evolution of competitiveness