Editorial |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Any surprises from selective oestrogen-receptor modulators?
Any surprises from selective oestrogen-receptor modulators?
The marriage of medicinal chemistry, molecular biology and medicine is perhaps best exemplified by the evolution of selective oestrogen-receptor modulators (SERMs). Translational studies might be useful for predicting the myriad clinical responses to SERMs, contributing to improvements in women's health.
- V. Craig Jordan
-
-
Review Article |
 Adaptive designs for dual-agent phase I dose-escalation studies
Adaptive designs for dual-agent phase I dose-escalation studies
With increasing numbers of anticancer drugs requiring testing, new adaptive model-based phase I trial designs can improve on current practice by exploring a wider range of dose combinations than standard phase I methods. In this Review, the authors describe the methods available as well as the opportunities and challenges faced in dual-agent phase I trials.
- Jennifer A. Harrington
- , Graham M. Wheeler
- & Duncan I. Jodrell
-
Review Article |
 Development of PI3K inhibitors: lessons learned from early clinical trials
Development of PI3K inhibitors: lessons learned from early clinical trials
Agents targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway have been shown to be safe and effective in treating a number of tumour types. This Review outlines the background to these inhibitors and discusses the second-generation inhibitors of this pathway. The authors propose that the way forward for the development of inhibitors of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway might be a systems biology approach and biomarker-driven studies.
- Jordi Rodon
- , Rodrigo Dienstmann
- & Josep Tabernero
-
Review Article |
Safety and feasibility of targeted agent combinations in solid tumours
Combination strategies of molecular-targeted agents (MTAs) are being used in the hope of optimizing antitumour efficacy and to minimize the development of resistance, but very little effort is focused on molecular vulnerabilities of normal tissues. This Review discusses the main toxicities and the lack of tolerability of some common MTA combinations, and highlights what steps can be introduced for new preclinical testing paradigms for the assessment of chronic toxicities.
- Sook Ryun Park
- , Myrtle Davis
- & Shivaani Kummar
-
Year in Review |
 New drugs, new knowledge, new targets
New drugs, new knowledge, new targets
In 2012, we increased our knowledge of the molecular portrait of breast cancer. The BOLERO-2 and CLEOPATRA trials led to the approval of everolimus and pertuzumab; and the EMILIA trial will likely result in the approval of T-DM1. Some of these findings represent a paradigm shift in the way we think about the biology and management of breast cancer.
- Mariana Chavez-MacGregor
- & Ana Maria Gonzalez-Angulo
-
-
-
Correspondence |
The microenvironment and resistance to personalized cancer therapy
- Shigeo Masuda
- & Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Targeted therapy for melanoma: is double hitting a home run?
Targeted therapy for melanoma: is double hitting a home run?
A phase II trial comparing dual MAPK pathway inhibition by combining BRAF and MEK inhibitors with BRAF inhibition alone showed increased progression-free survival and reduced incidence of secondary malignancies in patients with mutant BRAF V600 melanoma. This trial provides strong support for developing combinations hitting the same pathway in melanoma.
- Keiran S. M. Smalley
- & Vernon K. Sondak
-
-
Review Article |
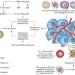 Clinical opportunities and challenges in targeting tumour dormancy
Clinical opportunities and challenges in targeting tumour dormancy
Tumour dormancy is when cancer sleeps undetected for periods that can last up to decades. The therapeutic potential of inducing or maintaining this dormant period is clear. This Review describes the mechanisms of dormancy and uses genitourinary cancers as models to demonstrate how dormancy principles could be exploited clinically.
- Jonathan A. Hensel
- , Thomas W. Flaig
- & Dan Theodorescu
-
News & Views |
The benefits of intermittent androgen-deprivation therapy
The large randomized study by Crook et al. demonstrated that intermittent administration of androgen deprivation therapy should be considered the standard of care when patients with moderate and well-differentiated localized prostate cancer are treated for rising PSA levels after definitive radiotherapy.
- Timur Mitin
- , Jason A. Efstathiou
- & William U. Shipley
-
-
News & Views |
 Ziv-aflibercept: binding to more than VEGF-A—does more matter?
Ziv-aflibercept: binding to more than VEGF-A—does more matter?
The VELOUR and VITAL studies recently demonstrated ziv-aflibercept improved overall survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC), including those previously treated with bevacizumab, but did not improve overall survival in non-small-cell lung cancer. Thus, VEGF-directed agents might be useful throughout the continuum of care in mCRC, but biomarkers are needed to identify patients likely to benefit.
- Jeffrey M. Clarke
- & Herbert I. Hurwitz
-
News & Views |
Abiraterone and its place in the treatment of metastatic CRPC
An update of the COU-AA-301 study confirms a survival advantage with abiraterone–prednisone compared to prednisone in post-docetaxel patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. We place these data in the context of earlier disease states and other novel agents and explore practical issues concerning the future use of abiraterone.
- Oliver Sartor
- & Sumanta K. Pal
-
Perspectives |
 Is there still a role for SPECT–CT in oncology in the PET–CT era?
Is there still a role for SPECT–CT in oncology in the PET–CT era?
PET or SPECT, is that the question? Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) are both tomographic techniques that enable 3D-localization of the tumour and can be combined with CT for hybrid imaging; but is one better that the other? In oncology imaging nothing is black or white, and Rod Hicks and Michael Hofman provide us with an in-depth analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of each technique.
- Rodney J. Hicks
- & Michael S. Hofman
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
Aprepitant and control of emesis induced by 5-day chemotherapy
Addition of aprepitant, an NK-1 receptor antagonist, to dexamethasone and a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist contributes substantially to emetic control in patients receiving 5-day cisplatin-containing chemotherapy, a new trial shows. Some needs in antiemetic therapy remain unmet, including control of emesis with multiple-day chemotherapy and control of nausea.
- Richard J. Gralla
-
-
News & Views |
 Enzalutamide in metastatic CRPC—old dog, new tricks
Enzalutamide in metastatic CRPC—old dog, new tricks
Two novel agents targeting the androgen receptor signalling axis, even after chemotherapy treatment, have been demonstrated to be effective in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Enzalutamide is the newest approved treatment that improves survival in this lethal and morbid disease.
- Che-Kai Tsao
- & William K. Oh
-
Correspondence |
Cancer-treatment toxicity: can nutrition help?
- Alessandro Laviano
- , Alessio Molfino
- & Filippo Rossi Fanelli
-
Review Article |
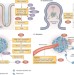 Aspirin as adjuvant therapy for colorectal cancer—reinterpreting paradigms
Aspirin as adjuvant therapy for colorectal cancer—reinterpreting paradigms
Aspirin has been widely reported to be associated with cancer prevention, and now its use as a cancer therapy option is being explored. In this Review, the authors discuss evidence from trials that suggest that aspirin initiation after the diagnosis of colorectal cancer improves survival. The issues of dosage, duration, toxicity and patient selection are also described.
- Whay Kuang Chia
- , Raghib Ali
- & Han Chong Toh
-
News & Views |
 Cetuximab dosing by rash—is the scaling of EVEREST meaningful?
Cetuximab dosing by rash—is the scaling of EVEREST meaningful?
The small EVEREST trial has shown that the concept of guiding cetuximab dose escalation using the clinical parameter of acneiform skin rash is safe. However, as no significant increase of cetuximab efficacy could be observed, data from the ongoing EVEREST II trial must be awaited before dose escalation can be considered for clinical use.
- Sebastian Stintzing
- & Heinz-Josef Lenz
-
-
News & Views |
First-line bevacizumab for ovarian cancer—new standard of care?
Demonstration of the clinically significant activity of bevacizumab in advanced-stage ovarian cancer has attracted a great deal of interest. Here, we summarize the two positive phase III trials that led to EMA approval of bevacizumab as first-line therapy and discuss the optimum use of the drug in this disease.
boxed-text - Susana Banerjee
- & Stan B. Kaye
-
Review Article |
 Drug development and clinical trials—the path to an approved cancer drug
Drug development and clinical trials—the path to an approved cancer drug
The current system for the development of anticancer drugs is not fit for purpose. In this Review article, this system is examined from the perspective of the drug company, offering a fresh look at development from target identification up to registration.
- Eric H. Rubin
- & D. Gary Gilliland
-
-
Review Article |
 Latest advances and current challenges in the treatment of multiple myeloma
Latest advances and current challenges in the treatment of multiple myeloma
Despite advances in treating multiple myeloma with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib and the immunomodulatory drugs thalidomide and lenalidomide, most patients eventually relapse. In this Review, the authors discuss how next-generation inhibitors and immunotherapy agents have been developed based on an improved understanding of the biology of the disease, and highlight the challenges associated with these therapeutic approaches.
- Anuj Mahindra
- , Jacob Laubach
- & Kenneth Anderson
-
Review Article |
 Tumor control versus adverse events with targeted anticancer therapies
Tumor control versus adverse events with targeted anticancer therapies
This Review article approaches the area of targeted therapies from two angles: efficacy and side effects. The authors outline the successes that have been achieved in treating cancer with targeted therapies and also discuss the pitfalls and quality of life issues that still need to be addressed.
- Dorothy M. K. Keefe
- & Emma H. Bateman
-
Review Article |
 Treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer: current status and future perspectives
Treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer: current status and future perspectives
Despite the advent of HER2-directed therapies, many patients with HER2-positive early stage breast cancer relapse and die of this disease. Trials to define, refine and optimize the use of the approved HER2-targeted agents are ongoing. New approaches are being developed and a series of large trials in the adjuvant and neoadjuvant settings are planned or in progress. In this Review, Arteaga et al. describe the current treatment for HER2-positive breast cancer and provide an update on ongoing clinical trials and translational research.
- Carlos L. Arteaga
- , Mark X. Sliwkowski
- & Luca Gianni
-
Opinion |
 Personalized cancer medicine—advances and socio-economic challenges
Personalized cancer medicine—advances and socio-economic challenges
The use of therapy that is truly targeted to the needs and biological requirements of an individual patient is an aim for many in the oncology field. Jackson and Sood discuss the implications of targeted therapies on patients and the health-care system and discuss methods that might be used to maximize efficiency, cost effectiveness and patient survival.
- David B. Jackson
- & Anil K. Sood
-
-
Case Study |
 Treatment with olaparib in a patient with PTEN-deficient endometrioid endometrial cancer
Treatment with olaparib in a patient with PTEN-deficient endometrioid endometrial cancer
Oral poly(ADP)-ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors have been shown to have great promise in the treatment of cancer inBRCA mutation carriers. This case provides evidence that these agents are efficacious in patients with PTEN deficiency but no BRCAmutations, opening up a new patient cohort for this treatment.
- Martin D. Forster
- , Konstantin J. Dedes
- & L. Rhoda Molife
-
-
News & Views |
 Setting the standard for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
Setting the standard for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
The treatment of multiple myeloma has evolved rapidly with the use of the immunomodulatory agents thalidomide and lenalidomide as well as the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib. Cavo and colleagues recently reported results of a landmark phase III study comparing thalidomide–dexamethasone with bortezomib–thalidomide–dexamethasone in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma.
- Jacob Laubach
- , Paul G. Richardson
- & Kenneth Anderson
-
-
News & Views |
 Bevacizumab—has it reached its final resting place?
Bevacizumab—has it reached its final resting place?
The recent failure of bevacizumab in the adjuvant setting has forced us to consider what has gone wrong. It is possible that with careful analysis and novel biomarkers, we may not yet have to lay bevacizumab to rest.
- David J. Kerr
- & Annie M. Young
-
-
Review Article |
 Targeted therapy in GIST: in silico modeling for prediction of resistance
Targeted therapy in GIST: in silico modeling for prediction of resistance
New techniques, such as crystallography and three-dimensional modeling, can be used to assist the development of selective targeted agents for cancer treatment. In this Review, Pierotti and colleagues discuss the molecular features of KIT and PDGFRA receptor tyrosine kinases, which are druggable targets in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. The authors focus on the major challenge in kinase drug discovery—the emergence of resistance—and discuss techniques for predicting and preventing this adverse event.
- Marco A. Pierotti
- , Elena Tamborini
- & Silvana Pilotti
-
Review Article |
 Methodological and practical challenges for personalized cancer therapies
Methodological and practical challenges for personalized cancer therapies
Many clinical trials of targeted therapies have produced disappointing results, indicating that many challenges must be addressed to advance this field. The authors discuss the importance of novel statistical designs, the need for biopsy sampling in clinical trials and appropriate biomarker identification for improving treatment outcomes.
- Ignacio I. Wistuba
- , Juri G. Gelovani
- & Roy S. Herbst
-
Review Article |
 The biological and therapeutic relevance of mRNA translation in cancer
The biological and therapeutic relevance of mRNA translation in cancer
The translation of mRNA is a tightly regulated process that is necessary for protein synthesis, and dysregulation of this process is associated with the development and progression of cancers. This Review highlights the components of translation machinery and how alterations in these proteins and their principle upstream signaling pathways can impact on cancer. Drugs that are currently being developed to target the translational machinery are also discussed.
- Sarah P. Blagden
- & Anne E. Willis
-
Review Article |
 Antiangiogenic therapy: impact on invasion, disease progression, and metastasis
Antiangiogenic therapy: impact on invasion, disease progression, and metastasis
The progression-free survival benefits from approved antiangiogenic drugs are modest and are frequently not accompanied by overall survival improvements. Recent disappointing clinical trial results (for example AVANT) have highlighted questions about the basis of drug resistance, the limitations of predictive preclinical models, and whether antiangiogenic therapy may lead to more invasive or metastatic tumor behavior.
- John M. L. Ebos
- & Robert S. Kerbel
-
Review Article |
 Can some patients avoid adjuvant chemotherapy for early-stage breast cancer?
Can some patients avoid adjuvant chemotherapy for early-stage breast cancer?
For the treatment of early-stage breast cancer, a provocative question is whether some patients can safely be spared chemotherapy? This Review addresses this question by discussing a range of clinicopathological, biomarker and genomic techniques that may help to guide current clinical practice.
- Philippe L. Bedard
- & Fatima Cardoso

 Intensified therapy for Ewing sarcoma
Intensified therapy for Ewing sarcoma Introducing new steps with a FOxTROT
Introducing new steps with a FOxTROT