Featured
-
-
Article |
 LPCAT1-mediated membrane phospholipid remodelling promotes ferroptosis evasion and tumour growth
LPCAT1-mediated membrane phospholipid remodelling promotes ferroptosis evasion and tumour growth
- Ziwen Li
- , Yameng Hu
- & Jun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Pooled multicolour tagging for visualizing subcellular protein dynamics
Pooled multicolour tagging for visualizing subcellular protein dynamics
Reicher, Reiniš et al. report a method for multicolour tagging using genome-scale intron-targeting sgRNA libraries that, in combination with computer vision, enables the systematic detection of protein localization changes.
- Andreas Reicher
- , Jiří Reiniš
- & Stefan Kubicek
-
Article |
 A chaperone-like function of FUS ensures TAZ condensate dynamics and transcriptional activation
A chaperone-like function of FUS ensures TAZ condensate dynamics and transcriptional activation
Shao et al. report that FUS interacts with the transcriptional coactivator TAZ, maintaining liquid-like properties of TAZ biomolecular condensates and enhancing TAZ transcriptional activity.
- Yangqing Shao
- , Xin Shu
- & Huasong Lu
-
News & Views |
 Mediterranean mechanisms of longevity
Mediterranean mechanisms of longevity
The Mediterranean diet correlates with increased human lifespan; it is rich in foods with high levels of cis-monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), such as olive oil. A study now shows that MUFAs stimulate a lipid droplet–peroxisome organelle network to decrease lipid oxidation and protect cell membranes during ageing.
- Alexander Richard Mendenhall
-
Technical Report |
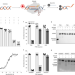 A general approach to identify cell-permeable and synthetic anti-CRISPR small molecules
A general approach to identify cell-permeable and synthetic anti-CRISPR small molecules
Lim et al. developed a fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based assay to identify anti-CRISPR molecules and discovered an SpCas9 inhibitor that is twofold more efficient in inhibiting Cas9 at diverse genomic loci than existing inhibitors and easy to synthesize.
- Donghyun Lim
- , Qingxuan Zhou
- & Amit Choudhary
-
Comment |
Quick tips for re-using metabolomics data
Publicly shared metabolomics data may contain key answers to central questions in cell biology, but re-use of the data is complicated by the lack of standardized experimental and computational methods in the field. This Comment provides some tips to help ensure that shared metabolomics data are re-used appropriately.
- Ethan Stancliffe
- & Gary J. Patti
-
Technical Report
| Open Access METALIC reveals interorganelle lipid flux in live cells by enzymatic mass tagging
METALIC reveals interorganelle lipid flux in live cells by enzymatic mass tagging
John Peter et al. develop METALIC (Mass tagging-Enabled TrAcking of Lipids In Cells), an approach to track interorganelle lipid flux in live cells using organelle-targeted enzymatic labelling of lipid subpopulations and mass spectrometry.
- Arun T. John Peter
- , Carmelina Petrungaro
- & Benoît Kornmann
-
Article |
 Cysteine oxidation of copper transporter CTR1 drives VEGFR2 signalling and angiogenesis
Cysteine oxidation of copper transporter CTR1 drives VEGFR2 signalling and angiogenesis
Das et al. show that the copper transporter CTR1 functions as a redox sensor in endothelial cells. CTR1 is modified after redox stress, which induces CTR1–VEGFR2 complex formation and promotes VEGFR2 signalling and angiogenesis.
- Archita Das
- , Dipankar Ash
- & Masuko Ushio-Fukai
-
Article |
 PKCβII phosphorylates ACSL4 to amplify lipid peroxidation to induce ferroptosis
PKCβII phosphorylates ACSL4 to amplify lipid peroxidation to induce ferroptosis
Through CRISPR–Cas9 and kinase inhibitor screening, Zhang et al. show that PKCβII phosphorylates and activates ACSL4 to enhance polyunsaturated fatty acid-containing lipid biosynthesis, thereby promoting accumulation of lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis.
- Hai-Liang Zhang
- , Bing-Xin Hu
- & Xiao-Feng Zhu
-
Letter |
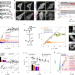 Nucleated transcriptional condensates amplify gene expression
Nucleated transcriptional condensates amplify gene expression
Wei et al. show that clusters of unphosphorylated RNA polymerase II seed the nucleation of phase-separated condensates of TAF15, which further recruit RNA polymerase II to amplify transcriptional activation.
- Ming-Tzo Wei
- , Yi-Che Chang
- & Clifford P. Brangwynne
-
Article |
 Heterochromatin establishment during early mammalian development is regulated by pericentromeric RNA and characterized by non-repressive H3K9me3
Heterochromatin establishment during early mammalian development is regulated by pericentromeric RNA and characterized by non-repressive H3K9me3
Burton et al. show that H3K9me3 deposition catalysed by SUV39H2 and regulated by pericentromeric RNAs in the mouse paternal pronucleus does not suppress gene expression, but bookmarks promoters for compaction.
- Adam Burton
- , Vincent Brochard
- & Maria-Elena Torres-Padilla
-
Article |
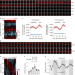 Diurnal oscillations of endogenous H2O2 sustained by p66Shc regulate circadian clocks
Diurnal oscillations of endogenous H2O2 sustained by p66Shc regulate circadian clocks
Pei et al. show that rhythmic redox signalling controls CLOCK through endogenous H2O2 oscillations via reversible oxidative modifications, and that p66Shc modulates the rhythm of H2O2 levels.
- Jian-Fei Pei
- , Xun-Kai Li
- & De-Pei Liu
-
Review Article |
 Nuclear actin filaments in DNA repair dynamics
Nuclear actin filaments in DNA repair dynamics
In this Review, Caridi et al. discuss actin filaments in the nucleus and the functions of nuclear F-actin in response to DNA double-strand break repair.
- Christopher Patrick Caridi
- , Matthias Plessner
- & Irene Chiolo
-
Article |
 ALOX12 is required for p53-mediated tumour suppression through a distinct ferroptosis pathway
ALOX12 is required for p53-mediated tumour suppression through a distinct ferroptosis pathway
Chu et al. identify the lipoxygenase ALOX12 as essential for p53-dependent ferroptosis in a pathway independent of GPX4. Monoallelic deletion of Alox12 abrogates p53-mediated suppression in a model of Eµ-Myc-driven lymphoma.
- Bo Chu
- , Ning Kon
- & Wei Gu
-
Article |
 Distinct functions of ATG16L1 isoforms in membrane binding and LC3B lipidation in autophagy-related processes
Distinct functions of ATG16L1 isoforms in membrane binding and LC3B lipidation in autophagy-related processes
Lystad et al. identify distinct membrane binding regions in ATG16L1 and show that the β-isoform-specific C-terminal region is required for VPS34/ULK1/2-independent non-canonical autophagy.
- Alf Håkon Lystad
- , Sven R. Carlsson
- & Anne Simonsen
-
News & Views |
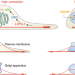 Golgi mechanics controls lipid metabolism
Golgi mechanics controls lipid metabolism
Cell metabolism ensures that cell dynamics and continued renewal are supported by a constant flow of matter that consumes energy. A new study shows that cell metabolism is sensitive to mechanical cues, revealing that the level of cell contraction modulates the production and storage of lipids, which could serve as fuel for energy production.
- Manuel Théry
- & Mario Pende
-
Article |
 Extracellular matrix mechanical cues regulate lipid metabolism through Lipin-1 and SREBP
Extracellular matrix mechanical cues regulate lipid metabolism through Lipin-1 and SREBP
Romani et al. identify a response to reduced actomyosin contractility involving inhibition of Lipin-1, accumulation of SREBP transcription factors at the Golgi apparatus and activation of SREBP transcription driving increased lipid synthesis.
- Patrizia Romani
- , Irene Brian
- & Sirio Dupont
-
News & Views |
 Atypical matrix adhesions guide cell division
Atypical matrix adhesions guide cell division
Classical actin-dependent, integrin-mediated cell–matrix adhesions disassemble before mitotic rounding. Yet, to transmit positional information and facilitate daughter-cell separation, dividing cells maintain connections to the matrix. A previously unidentified class of actin-independent integrin adhesions may fulfil this task.
- Ronen Zaidel-Bar
-
Article |
 Reticular adhesions are a distinct class of cell-matrix adhesions that mediate attachment during mitosis
Reticular adhesions are a distinct class of cell-matrix adhesions that mediate attachment during mitosis
Lock et al. identify reticular adhesion complexes that maintain cell–extracellular-matrix attachments during cell division. Reticular adhesions transmit spatial memory between cell generations, mediated by αvβ5 integrin and PtdIns(4,5)P2.
- John G. Lock
- , Matthew C. Jones
- & Staffan Strömblad
-
Letter |
 FBP17 and CIP4 recruit SHIP2 and lamellipodin to prime the plasma membrane for fast endophilin-mediated endocytosis
FBP17 and CIP4 recruit SHIP2 and lamellipodin to prime the plasma membrane for fast endophilin-mediated endocytosis
Chan Wah Hak et al. show how plasma membrane patches are primed for fast endophilin-mediated endocytosis and disassembly, in the absence of receptor stimulation, through FBP17 and CIP4 binding to SHIP2 and lamellipodin.
- Laura Chan Wah Hak
- , Shaheen Khan
- & Emmanuel Boucrot
-
Review Article |
 YAP/TAZ upstream signals and downstream responses
YAP/TAZ upstream signals and downstream responses
Stefano Piccolo and co-authors review recent insights into how YAP and TAZ transcription factors respond to the tissue environment, and how they mediate altered cell behaviour. Feedback mechanisms and crosstalk with other pathways are discussed, as are outstanding questions in the field.
- Antonio Totaro
- , Tito Panciera
- & Stefano Piccolo
-
Article |
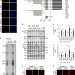 Senescence-associated ribosome biogenesis defects contributes to cell cycle arrest through the Rb pathway
Senescence-associated ribosome biogenesis defects contributes to cell cycle arrest through the Rb pathway
Lassard et al. demonstrate a relationship between cellular senescence and perturbed ribosome biogenesis and find that the ribosomal protein S14 is an inhibitor of CDK4, inducing an Rb-dependent cell cycle arrest.
- Frédéric Lessard
- , Sebastian Igelmann
- & Gerardo Ferbeyre
-
-
Letter |
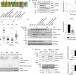 Distinct kinetics of serine and threonine dephosphorylation are essential for mitosis
Distinct kinetics of serine and threonine dephosphorylation are essential for mitosis
Cdk1-mediated phosphorylation of threonine and serine residues on cell cycle regulators needs to be removed after mitosis. Hein et al. show that the known preference of the PP2A–B55 phosphatase for threonine provides temporal regulation of mitotic exit.
- Jamin B. Hein
- , Emil P. T. Hertz
- & Jakob Nilsson
-
News & Views |
 Integrating insulin secretion and ER stress in pancreatic β-cells
Integrating insulin secretion and ER stress in pancreatic β-cells
After food consumption, insulin-secreting pancreatic β-cells detect increased glucose and incretin hormones, and respond by releasing insulin. Wolfram syndrome 1, a protein that mitigates endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, is now shown to regulate insulin synthesis and release — revealing a molecular point of convergence between the ER stress and insulin release pathways.
- Katleen Lemaire
- & Frans Schuit
-
Resource |
 Defining human ERAD networks through an integrative mapping strategy
Defining human ERAD networks through an integrative mapping strategy
Improperly folded proteins are targeted for destruction through the endoplasmic-reticulum-associated degradation pathway (ERAD). Kopito and colleagues present a high-resolution interaction analysis of the ERAD system in combination with functional genomics, and identify new ERAD components.
- John C. Christianson
- , James A. Olzmann
- & Ron R. Kopito
-
-
Article |
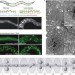 Apicobasal domain identities of expanding tubular membranes depend on glycosphingolipid biosynthesis
Apicobasal domain identities of expanding tubular membranes depend on glycosphingolipid biosynthesis
Cell polarity is critically important for organogenesis. Using a series of RNA-interference-based screens, Göbel and colleagues reveal the role of the glycosphingolipid glucosylceramide (GlcCer) in determining apicobasal polarity and maintaining the organization of the intestinal lumen in the developing worm.
- Hongjie Zhang
- , Nessy Abraham
- & Verena Göbel
-
News & Views |
 p53 guards the metabolic pathway less travelled
p53 guards the metabolic pathway less travelled
Glucose is an important source of energy and carbon, and is required for cell growth. As such, glucose utilization is increased in rapidly dividing cancer cells. The tumour suppressor p53 has now been reported to block a metabolic pathway (the pentose phosphate pathway) that diverts glucose away from bioenergetic into biosynthetic routes.
- Eyal Gottlieb
-
Letter |
 p53 regulates biosynthesis through direct inactivation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
p53 regulates biosynthesis through direct inactivation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
Cancer cells preferentially use aerobic glycolysis to generate ATP, consuming glucose in the process. The tumour suppressor p53 is now shown to suppress glucose consumption by inhibiting the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). Tumour-associated p53 mutations lack this inhibitory effect.
- Peng Jiang
- , Wenjing Du
- & Xiaolu Yang
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Biocatalysis
- Biophysical chemistry
- Biosynthesis
- Carbohydrates
- Chemical ecology
- Chemical genetics
- Chemical libraries
- Chemical modification
- Chemical tools
- Cheminformatics
- Combinatorial libraries
- Computational chemistry
- DNA
- Drug delivery
- Enzyme mechanisms
- Enzymes
- Glycobiology
- Glycomics
- Ion channels
- Kinases
- Lipidomics
- Lipids
- Mechanism of action
- Membranes
- Metabolic pathways
- Metabolomics
- Metals
- Natural products
- Networks and systems biology
- Nucleic acids
- Peptides
- Pharmacology
- Post-translational modifications
- Proteases
- Protein design
- Protein folding
- Proteins
- Proteomics
- RNA
- Screening
- Small molecules
- Synthetic biology
- Target identification
- Target validation
- Transporters

 Adding intrinsically disordered proteins to biological ageing clocks
Adding intrinsically disordered proteins to biological ageing clocks