Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Multimodal interference-based imaging of nanoscale structure and macromolecular motion uncovers UV induced cellular paroxysm
Multimodal interference-based imaging of nanoscale structure and macromolecular motion uncovers UV induced cellular paroxysm
Methods to track molecular motion in eukaryotic cells mostly rely on fluorescent labels, transfection or photobleaching. Here the authors use multimodal partial wave spectroscopy to perform label-free live cell measurements of nanoscale structure and macromolecular motion with millisecond temporal resolution.
- Scott Gladstein
- , Luay M. Almassalha
- & Vadim Backman
-
Article
| Open Access Multicolor multiscale brain imaging with chromatic multiphoton serial microscopy
Multicolor multiscale brain imaging with chromatic multiphoton serial microscopy
Multicolour images are difficult to acquire with large-scale microscopy approaches. Here the authors present a microtome-assisted microscope capable of trichromatic two-photon excitation and label-free nonlinear modalities based on wavelength mixing, and use it to analyze astrocyte morphology and neuronal projections in thick brain samples.
- Lamiae Abdeladim
- , Katherine S. Matho
- & Emmanuel Beaurepaire
-
Article
| Open Access iFISH is a publically available resource enabling versatile DNA FISH to study genome architecture
iFISH is a publically available resource enabling versatile DNA FISH to study genome architecture
DNA FISH allows for the visual analysis of chromosomal organisation in individual cells. Here the authors present iFISH, an open-source repository of ready-to-use DNA FISH probes along with tools for probe design.
- Eleni Gelali
- , Gabriele Girelli
- & Magda Bienko
-
Article
| Open Access Global identification of functional microRNA-mRNA interactions in Drosophila
Global identification of functional microRNA-mRNA interactions in Drosophila
MicroRNAs are mediators of post-transcriptional gene expression silencing. Here authors provide a transcriptome-wide map of miRNA target sites in Drosophila.
- Hans-Hermann Wessels
- , Svetlana Lebedeva
- & Uwe Ohler
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient allelic-drive in Drosophila
Efficient allelic-drive in Drosophila
Gene-drives use CRISPR-Cas9 to be transmitted in a super-Mendelian fashion. Here the authors develop an allelic-drive for selective inheritance of a desired allele.
- Annabel Guichard
- , Tisha Haque
- & Ethan Bier
-
Article
| Open Access Gene correction for SCID-X1 in long-term hematopoietic stem cells
Gene correction for SCID-X1 in long-term hematopoietic stem cells
Gene correction in hematopoietic stem cells could be a powerful way to treat monogenic diseases of the blood and immune system. Here the authors develop a strategy using CRISPR-Cas9 and an aAdeno-Associated vVirus(AAV)-delivered IL2RG cDNA to correct X-linked sSevere Ccombined iImmunodeficiency (SCID-X1) with a high success rate.
- Mara Pavel-Dinu
- , Volker Wiebking
- & Matthew H. Porteus
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed Cas9 targeting reveals genomic location effects and gRNA-based staggered breaks influencing mutation efficiency
Multiplexed Cas9 targeting reveals genomic location effects and gRNA-based staggered breaks influencing mutation efficiency
Designing effective genome engineering strategies requires an understanding of the impact that genomic locus has on CRISPR-Cas9 activity. Here the authors use TRIP integrations to profile editing outcomes genome-wide and observe that gRNA sequence influences the structure of the double strand break.
- Santiago Gisler
- , Joana P. Gonçalves
- & Maarten van Lohuizen
-
Article
| Open Access Miniaturised interaction proteomics on a microfluidic platform with ultra-low input requirements
Miniaturised interaction proteomics on a microfluidic platform with ultra-low input requirements
Affinity purification-mass spectrometry (AP-MS) can identify endogenous protein interactions but the need for high amounts of input material still limits its applicability. Here, the authors present a microfluidic-based AP-MS workflow that can capture protein interactions from 50─100-fold less input material than conventional approaches.
- Cristina Furlan
- , René A. M. Dirks
- & Michiel Vermeulen
-
Article
| Open Access Reversible induction of mitophagy by an optogenetic bimodular system
Reversible induction of mitophagy by an optogenetic bimodular system
Autophagic degradation of mitochondria (mitophagy) is a key quality control mechanism in cellular homeostasis, and its misregulation is involved in neurodegenerative diseases. Here the authors develop an optogenetic system for reversible induction of mitophagy and validate its use in cell culture and zebrafish embryos.
- Pasquale D’Acunzo
- , Flavie Strappazzon
- & Francesco Cecconi
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics of genome reorganization during human cardiogenesis reveal an RBM20-dependent splicing factory
Dynamics of genome reorganization during human cardiogenesis reveal an RBM20-dependent splicing factory
The spatial organization of the genome plays an important but unclearly defined role in gene regulation. Here, the authors integrate Hi-C, RNA-seq and ATAC-seq data to map cardiogenesis from pluripotent stem cells and describe an RBM20-dependent splicing factory assembling the TTN locus with other RBM20 targets.
- Alessandro Bertero
- , Paul A. Fields
- & Charles E. Murry
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolic reaction network-based recursive metabolite annotation for untargeted metabolomics
Metabolic reaction network-based recursive metabolite annotation for untargeted metabolomics
Untargeted metabolomics detects large numbers of metabolites but their annotation remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a metabolic reaction network-based recursive algorithm that expands metabolite annotation by taking advantage of the mass spectral similarity of reaction-paired neighbor metabolites.
- Xiaotao Shen
- , Ruohong Wang
- & Zheng-Jiang Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Recollection in the human hippocampal-entorhinal cell circuitry
Recollection in the human hippocampal-entorhinal cell circuitry
The hippocampus is involved both in episodic memory recall and scene processing. Here, the authors show that hippocampal neurons first process scene cues before coordinating memory-guided pattern completion in adjacent entorhinal cortex.
- Bernhard P. Staresina
- , Thomas P. Reber
- & Florian Mormann
-
Article
| Open Access Ca2+-dependent regulation of sodium channels NaV1.4 and NaV1.5 is controlled by the post-IQ motif
Ca2+-dependent regulation of sodium channels NaV1.4 and NaV1.5 is controlled by the post-IQ motif
Skeletal muscle voltage-gated Na+ channel (NaV1.4) activity is subject to calmodulin (CaM) mediated Ca2 +-dependent inactivation while cardiac NaV1.5 is not. Here authors use structural biology, binding and electrophysiology to parse the Ca2 +-dependent changes of CaM when bound to the NaV1.4.
- Jesse B. Yoder
- , Manu Ben-Johny
- & L. Mario Amzel
-
Article
| Open Access Cortex-wide neural interfacing via transparent polymer skulls
Cortex-wide neural interfacing via transparent polymer skulls
Imaging the mouse brain using glass cranial windows has limitations in terms of flexibility and long-term imaging. Here the authors engineer transparent polymer skulls that can fit various skull morphologies and can be implanted for over 300 days, enabling simultaneous high resolution brain imaging and electrophysiology across large cortical areas.
- Leila Ghanbari
- , Russell E. Carter
- & Suhasa B. Kodandaramaiah
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of human D lactate dehydrogenase deficiency
Identification of human D lactate dehydrogenase deficiency
D-lactic acidosis typically occurs in the context of short bowel syndrome; excess D-lactate is produced by intestinal bacteria. Here, the authors identify two point mutations in the human lactate dehydrogenase D (LDHD) gene that cause enzymatic loss of function and are associated with elevated plasma D-lactate.
- Glen R. Monroe
- , Albertien M. van Eerde
- & Judith J. Jans
-
Article
| Open Access Intrinsic functional architecture of the non-human primate spinal cord derived from fMRI and electrophysiology
Intrinsic functional architecture of the non-human primate spinal cord derived from fMRI and electrophysiology
Resting-state fMRI shows networks of correlated activity in the spinal cord, similar to those in the brain, but whether fMRI is a valid measure of functional connectivity in spinal cord is unclear. Here, the authors show that fMRI corresponds well to electrophysiological measures of spinal cord activity.
- Tung-Lin Wu
- , Pai-Feng Yang
- & John C. Gore
-
Article
| Open Access The architecture of functional lateralisation and its relationship to callosal connectivity in the human brain
The architecture of functional lateralisation and its relationship to callosal connectivity in the human brain
Many functions of the human brain are lateralised i.e. associated more strongly with either the left or the right hemisphere of the brain. Here, the authors report the first complete map of functional asymmetries in the human brain, and its relationship with structural inter-hemispheric connectivity.
- Vyacheslav R. Karolis
- , Maurizio Corbetta
- & Michel Thiebaut de Schotten
-
Article
| Open Access Functional ultrasound imaging of the brain reveals propagation of task-related brain activity in behaving primates
Functional ultrasound imaging of the brain reveals propagation of task-related brain activity in behaving primates
Neuroimaging modalities such as MRI and EEG are able to record brain activity, but spatiotemporal resolution and sensitivity are limited. Here, the authors show how a recently developed method, functional ultrasound imaging (fUS), can measure brain activation during cognitive tasks in primates.
- Alexandre Dizeux
- , Marc Gesnik
- & Mickael Tanter
-
Article
| Open Access Directing curli polymerization with DNA origami nucleators
Directing curli polymerization with DNA origami nucleators
Curli are bacterial functional amyloids that have gained interest as self-assembling biomaterial for biotechnology applications. Here, the authors show that DNA origami decorated with CsgB nucleator proteins induced the site-specific nucleation and subsequent fibrillization of CsgA proteins.
- Xiuhai Mao
- , Ke Li
- & Chao Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Diagnosis of fusion genes using targeted RNA sequencing
Diagnosis of fusion genes using targeted RNA sequencing
Rapid and accurate detection of fusion genes is important in cancer diagnostics. Here, the authors demonstrate that targeted RNA sequencing provides fast, sensitive and quantitative gene fusion detection and overcomes the limitations of approaches currently in clinical use.
- Erin E. Heyer
- , Ira W. Deveson
- & James Blackburn
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming the thermodynamic equilibrium of an isomerization reaction through oxidoreductive reactions for biotransformation
Overcoming the thermodynamic equilibrium of an isomerization reaction through oxidoreductive reactions for biotransformation
A desired product cannot be obtained at higher concentration than its equilibrium concentration when isomerases are used for biotransformation. Here, the authors engineer in vivo oxidoreductive reactions in yeast to overcome the equilibrium limitation of in vitro isomerases-based tagatose production.
- Jing-Jing Liu
- , Guo-Chang Zhang
- & Yong-Su Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Capturing site-specific heterogeneity with large-scale N-glycoproteome analysis
Capturing site-specific heterogeneity with large-scale N-glycoproteome analysis
Mass spectrometry facilitates large-scale glycosylation profiling but in-depth analysis of intact glycopeptides is still challenging. Here, the authors show that activated ion electron transfer dissociation is suitable for glycopeptide fragmentation and improves glycoproteome coverage.
- Nicholas M. Riley
- , Alexander S. Hebert
- & Joshua J. Coon
-
Article
| Open Access A post-translational modification of human Norovirus capsid protein attenuates glycan binding
A post-translational modification of human Norovirus capsid protein attenuates glycan binding
Attachment of human noroviruses to histo blood group antigens (HBGAs) is essential for infection. Here the authors report that an asparagine residue located near the HBGA-attachment site can convert into an iso-aspartate residue through spontaneous deamidation and influence HBGA recognition.
- Alvaro Mallagaray
- , Robert Creutznacher
- & Thomas Peters
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate autocorrelation modeling substantially improves fMRI reliability
Accurate autocorrelation modeling substantially improves fMRI reliability
There has been recent controversy over the validity of commonly-used software packages for functional MRI (fMRI) data analysis. Here, the authors compare the performance of three leading packages (AFNI, FSL, SPM) in terms of temporal autocorrelation modeling, a key statistical step in fMRI analysis.
- Wiktor Olszowy
- , John Aston
- & Guy B. Williams
-
Article
| Open Access Flat-top TIRF illumination boosts DNA-PAINT imaging and quantification
Flat-top TIRF illumination boosts DNA-PAINT imaging and quantification
The use of TIRF microscopy for DNA-PAINT experiments is limited by inhomogeneous illumination. Here the authors show that quantitative analysis of single-molecule TIRF experiments can be improved by using a segment-wise analysis approach and overcome by using a beam-shaping device to give a flat-top illumination profile.
- Florian Stehr
- , Johannes Stein
- & Ralf Jungmann
-
Article
| Open Access Waveguide-PAINT offers an open platform for large field-of-view super-resolution imaging
Waveguide-PAINT offers an open platform for large field-of-view super-resolution imaging
TIRF imaging is limited by the size and uniformity of the illumination. Here the authors present a waveguide solution to create a large area of uniform evanescent illumination suitable for single molecule imaging coupled with a customised sample holder containing a reservoir for DNA-PAINT solutions.
- Anna Archetti
- , Evgenii Glushkov
- & Suliana Manley
-
Article
| Open Access Automating multimodal microscopy with NanoJ-Fluidics
Automating multimodal microscopy with NanoJ-Fluidics
Sample processing for biological imaging experiments involves elaborate protocols with low reproducibility and throughput. Here the authors develop an open-source system called NanoJ-Fluidics, composed of off-the-shelf Lego components and an ImageJ-based controller to achieve automated fixation, labelling and imaging of cells.
- Pedro Almada
- , Pedro M. Pereira
- & Ricardo Henriques
-
Article
| Open Access Lineage tracing using a Cas9-deaminase barcoding system targeting endogenous L1 elements
Lineage tracing using a Cas9-deaminase barcoding system targeting endogenous L1 elements
Lineage tracing has provided new insights into cell fate but defining cellular diversity remains a challenge. Here the authors target endogenous repeat regions in mammalian cells with cytidine deaminase fused to nCas9 to create genetic barcodes for fine-resolution mapping.
- Byungjin Hwang
- , Wookjae Lee
- & Duhee Bang
-
Article
| Open Access Phototrophic purple bacteria as optoacoustic in vivo reporters of macrophage activity
Phototrophic purple bacteria as optoacoustic in vivo reporters of macrophage activity
Current optoacoustic probes for cancer imaging have limitations including background noise, long-term toxicity and scarce imaging depth in living tissue. Here the authors use Rhodobacter, purple bacteria rich in bacteriochlorophyll a, as an optoacoustic reporter to image tumor-associated macrophages in mice in vivo.
- Lena Peters
- , Ina Weidenfeld
- & Andre C. Stiel
-
Article
| Open Access Contractile forces in platelet aggregates under microfluidic shear gradients reflect platelet inhibition and bleeding risk
Contractile forces in platelet aggregates under microfluidic shear gradients reflect platelet inhibition and bleeding risk
Platelet aggregates generate contractile forces that contribute to their cohesion and adhesion. Here, Ting et al. develop a microfluidic device to measure contractile forces generated by platelet aggregates, and find it can detect the response of platelets to pharmacological agents and predict bleeding risk in trauma patients.
- Lucas H. Ting
- , Shirin Feghhi
- & Nathan J. Sniadecki
-
Article
| Open Access Parallel analysis of tri-molecular biosynthesis with cell identity and function in single cells
Parallel analysis of tri-molecular biosynthesis with cell identity and function in single cells
Simultaneous quantification of DNA, RNA and protein at the single cell level has not yet been possible. Here the authors introduce a molecular labelling and detection strategy to quantify synthesis of these biomolecules and couple it to transient cell states through parallel quantification of state-dependent biomolecules.
- Samuel C. Kimmey
- , Luciene Borges
- & Sean C. Bendall
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic molecular changes during the first week of human life follow a robust developmental trajectory
Dynamic molecular changes during the first week of human life follow a robust developmental trajectory
The first week of life impacts health for all of life, but the mechanisms are little-understood. Here the authors extract multi-omic data from small volumes of blood to study the dynamic molecular changes during the first week of life, revealing a robust developmental trajectory common to different populations.
- Amy H. Lee
- , Casey P. Shannon
- & Tobias R. Kollmann
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying protein dynamics and stability in a living organism
Quantifying protein dynamics and stability in a living organism
Studying protein kinetics and stability in living organisms is challenging and most studies are performed in cell culture. Here the authors combine meganuclease-mediated transformation and fluorescence-detected temperature-jump microscopy to quantify protein stability in different tissues of living zebrafish.
- Ruopei Feng
- , Martin Gruebele
- & Caitlin M. Davis
-
Article
| Open Access Noninvasive sub-organ ultrasound stimulation for targeted neuromodulation
Noninvasive sub-organ ultrasound stimulation for targeted neuromodulation
Stimulation of peripheral nerve activity may be used to treat metabolic and inflammatory disorders, but current approaches need implanted devices. Here, the authors present a non-invasive approach, and show that ultrasound-mediated stimulation can be targeted to specific sub-organ locations in preclinical models and alter the response of metabolic and inflammatory neural pathways.
- Victoria Cotero
- , Ying Fan
- & Christopher Puleo
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule trapping and spectroscopy reveals photophysical heterogeneity of phycobilisomes quenched by Orange Carotenoid Protein
Single-molecule trapping and spectroscopy reveals photophysical heterogeneity of phycobilisomes quenched by Orange Carotenoid Protein
Upon photoactivation the Orange Carotenoid Protein (OCP) binds to the phycobilisome and prevents damage by thermally dissipating excess energy. Here authors use an Anti-Brownian ELectrokinetic trap to determine the photophysics of single OCP-quenched phycobilisomes and observe two distinct OCP-quenched states with either one or two OCPs bound.
- Allison H. Squires
- , Peter D. Dahlberg
- & W. E. Moerner
-
Article
| Open Access Noninvasive ultrasound stimulation of the spleen to treat inflammatory arthritis
Noninvasive ultrasound stimulation of the spleen to treat inflammatory arthritis
Modulation of the cholinergic pathway and spleen function can reduce inflammation with invasive implants. Here, the authors show that non-invasive ultrasound stimulation of the spleen reduces disease severity in a mouse model of inflammatory arthritis, partly via altering B and T cell function.
- Daniel P. Zachs
- , Sarah J. Offutt
- & Hubert H. Lim
-
Article
| Open Access Proteome-wide solubility and thermal stability profiling reveals distinct regulatory roles for ATP
Proteome-wide solubility and thermal stability profiling reveals distinct regulatory roles for ATP
ATP can function as a biological hydrotrope, but its global effects on protein solubility have not yet been characterized. Here, the authors quantify the effect of ATP on the thermal stability and solubility of the cellular proteome, providing insights into protein solubility regulation by ATP.
- Sindhuja Sridharan
- , Nils Kurzawa
- & Mikhail M. Savitski
-
Article
| Open Access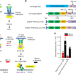 Neurotrophin receptor tyrosine kinases regulated with near-infrared light
Neurotrophin receptor tyrosine kinases regulated with near-infrared light
Optical control over receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) activity can find application in both basic biology and synthetic biology. Here the authors combine the photosensory module of DrBphP bacterial phytochrome with the Trk family of RTKs to obtain Trks that are reversibly switchable with near-infrared and far-red light.
- Anna V. Leopold
- , Konstantin G. Chernov
- & Vladislav V. Verkhusha
-
Article
| Open Access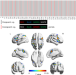 Characterization of the hemodynamic response function in white matter tracts for event-related fMRI
Characterization of the hemodynamic response function in white matter tracts for event-related fMRI
The hemodynamic response function (HRF) describes how changes in brain activity manifest as a transient signal (BOLD) that is detected by fMRI imaging. Here, the authors show that the HRF in white matter shows reduced magnitudes, delayed onsets, and prolonged initial dips compared to the grey matter HRF.
- Muwei Li
- , Allen T. Newton
- & John C. Gore
-
Article
| Open Access Topological scoring of protein interaction networks
Topological scoring of protein interaction networks
Inferring direct protein−protein interactions (PPIs) and modules in PPI networks remains a challenge. Here, the authors introduce an algorithm to infer potential direct PPIs from quantitative proteomic AP-MS data by identifying enriched interactions of each bait relative to the other baits.
- Mihaela E. Sardiu
- , Joshua M. Gilmore
- & Michael P. Washburn
-
Article
| Open Access Diversifying the structure of zinc finger nucleases for high-precision genome editing
Diversifying the structure of zinc finger nucleases for high-precision genome editing
Genome editing often requires cleavage within a narrow sequence window. Here the authors develop an expanded set of zinc finger nuclease architectures that increase the available configurations by a factor of 64 and can target almost every base at loci of therapeutic significance.
- David E. Paschon
- , Stephanie Lussier
- & Edward J. Rebar
-
Article
| Open Access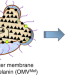 Bioengineered bacterial vesicles as biological nano-heaters for optoacoustic imaging
Bioengineered bacterial vesicles as biological nano-heaters for optoacoustic imaging
Bacterial outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) are increasingly used as carriers for drug delivery. Here the authors encapsulate biopolymer melanin into OMVs, extending their use to optoacoustic imaging both in vitro and in vivo, and demonstrate the potential of this tool for photothermal therapy applications.
- Vipul Gujrati
- , Jaya Prakash
- & Vasilis Ntziachristos
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging inflammation using an activated macrophage probe with Slc18b1 as the activation-selective gating target
Imaging inflammation using an activated macrophage probe with Slc18b1 as the activation-selective gating target
Attempts to image activated macrophages in vivo have been hampered by selectivity and delivery problems. Here the authors develop a small molecule fluorescent probe specific to activated M1 and M2 macrophages, identify the orphan receptor Slc18b1/SLC18B1 as the mechanism of uptake, and use it to image atherosclerosis in mice.
- Sung-Jin Park
- , Beomsue Kim
- & Young-Tae Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Mesoscopic and microscopic imaging of sensory responses in the same animal
Mesoscopic and microscopic imaging of sensory responses in the same animal
Neuronal activity leads to a local increase in blood flow and volume, a process termed hyperaemia. Here, the authors employ multiple imaging approaches of neuronal and vascular activity at varying resolution to delineate the spatiotemporal dynamics of neurovascular coupling evoked by odours in the olfactory bulb.
- Davide Boido
- , Ravi L. Rungta
- & Serge Charpak
-
Article
| Open Access Analysis of human acetylation stoichiometry defines mechanistic constraints on protein regulation
Analysis of human acetylation stoichiometry defines mechanistic constraints on protein regulation
Many human proteins are regulated by lysine acetylation, but the degree of acetylation at individual sites is poorly characterized. Here, the authors measure acetylation stoichiometry in the HeLa cell proteome, providing a resource to assess mechanistic constraints on acetylation-mediated protein regulation.
- Bogi Karbech Hansen
- , Rajat Gupta
- & Brian T. Weinert
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-quenching NIR-II molecular fluorophores for in vivo high-contrast imaging and pH sensing
Anti-quenching NIR-II molecular fluorophores for in vivo high-contrast imaging and pH sensing
Fluorophores operating in the second near-infrared window suffer from solvatochromism-caused fluorescence quenching in biological aqueous solution. Here, the authors synthesized a series of pH-responsive pentamethine cyanine fluorophores that afford stable absorption/emission beyond 1000 nm.
- Shangfeng Wang
- , Yong Fan
- & Fan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access The use of technical replication for detection of low-level somatic mutations in next-generation sequencing
The use of technical replication for detection of low-level somatic mutations in next-generation sequencing
Somatic mutations of low allele frequencies are often difficult to detect. Here, the authors develop RePlow, a computational method that leverages technical replication for detecting low-level somatic mutations using next-generation sequencing.
- Junho Kim
- , Dachan Kim
- & Sangwoo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of key whole-brain transitions and dynamics during human wakefulness and non-REM sleep
Discovery of key whole-brain transitions and dynamics during human wakefulness and non-REM sleep
Sleep is composed of a number of different stages, each associated with a different pattern of brain activity. Here, using a data-driven Hidden Markov Model (HMM) of fMRI data, the authors discover a more complex set of neural activity states underlying the conventional stages of non-REM sleep.
- A. B. A. Stevner
- , D. Vidaurre
- & M. L. Kringelbach
-
Article
| Open Access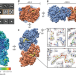 High-resolution structure determination of sub-100 kDa complexes using conventional cryo-EM
High-resolution structure determination of sub-100 kDa complexes using conventional cryo-EM
Despite many recent advances in cryo-EM, imaging smaller macromolecules (below 100 kDa) has remained a challenge. Here the authors show that biological specimens amassing <100 kDa can be resolved to better than 3 Å resolution using conventional defocus-based single-particle analysis methods.
- Mark A. Herzik Jr.
- , Mengyu Wu
- & Gabriel C. Lander
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical biochemistry
- Behavioural methods
- Bioinformatics
- Biological models
- Biophysical methods
- Cytological techniques
- Electrophysiology
- Epigenetics analysis
- Experimental organisms
- Gene delivery
- Gene expression analysis
- Genetic engineering
- Genetic techniques
- Genomic analysis
- High-throughput screening
- Imaging
- Immunological techniques
- Isolation, separation and purification
- Lab-on-a-chip
- Mass spectrometry
- Metabolomics
- Microbiology techniques
- Microscopy
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Optogenetics
- Proteomic analysis
- Sensors and probes
- Sequencing
- Software
- Optical spectroscopy
- Structure determination

 Platanus-allee is a de novo haplotype assembler enabling a comprehensive access to divergent heterozygous regions
Platanus-allee is a de novo haplotype assembler enabling a comprehensive access to divergent heterozygous regions