Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Tuneable on-demand single-photon source in the microwave range
Tuneable on-demand single-photon source in the microwave range
Microwave single photon sources are important for quantum applications, but their design often incorporates a resonator that fixes the frequency of the emitted photon. Here, the authors demonstrate a tuneable on-demand photon source based on an artificial atom asymmetrically coupled to two transmission lines.
- Z. H. Peng
- , S. E. de Graaf
- & O. V. Astafiev
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated plasmonic circuitry on a vertical-cavity surface-emitting semiconductor laser platform
Integrated plasmonic circuitry on a vertical-cavity surface-emitting semiconductor laser platform
Integrated plasmonic sources are crucial in the development of plasmonic circuitry. Here, McPolin et al. show that vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers can be employed as an on-chip, electrically pumped source or detector of plasmonic signals and also demonstrate waveguiding and frequency conversion on this platform.
- Cillian P. T. McPolin
- , Jean-Sebastien Bouillard
- & Anatoly V. Zayats
-
Article
| Open Access Far-field nanoscale infrared spectroscopy of vibrational fingerprints of molecules with graphene plasmons
Far-field nanoscale infrared spectroscopy of vibrational fingerprints of molecules with graphene plasmons
Despite being a powerful tool for molecular vibrational mode detection, infrared spectrosocpy is limited by weak sensitivity. Here, the authors demonstrate a platform for enhanced molecular fingerprint sensing based on a graphene/CaF2nanofilm plasmonic structure.
- Hai Hu
- , Xiaoxia Yang
- & Qing Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Cavity optomechanical spring sensing of single molecules
Cavity optomechanical spring sensing of single molecules
Detection of a single nanoparticle or molecule is essential for many applications. Here, Yu et al.demonstrate the use of an optical cavity with optomechanical oscillation to detect single bovine serum albumin proteins, with potential for studying mechanical properties and interactions of individual molecules.
- Wenyan Yu
- , Wei C Jiang
- & Tao Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Single microwave-photon detector using an artificial Λ-type three-level system
Single microwave-photon detector using an artificial Λ-type three-level system
Single-photon detection is challenging in the microwave regime due to the small photon energy. Here, the authors demonstrate the deterministic detection of single microwave photons through an impedenance-matched artificial Λ system composed by a driven superconducting qubit and a microwave resonator.
- Kunihiro Inomata
- , Zhirong Lin
- & Yasunobu Nakamura
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-thermionic effect in vertical graphene heterostructures
Photo-thermionic effect in vertical graphene heterostructures
The detection of low-energy photons may be enabled by devices that make use of the excess thermal energy from photoexcited carriers as a result of light absorption. Here the authors demonstrate a vertical graphene-WSe2-graphene heterostructure that takes advantage of the photo-thermionic effect.
- M. Massicotte
- , P. Schmidt
- & F. H. L. Koppens
-
Article
| Open Access Probing the electrical switching of a memristive optical antenna by STEM EELS
Probing the electrical switching of a memristive optical antenna by STEM EELS
Scaling of photonic devices requires materials with sufficiently strong elecro-optic effects. Here, Schoen et al.demonstrate and analyze single electrically induced switching events that can operate in the visible with a small active volume using electron energy loss in a scanning transmission electron microscope.
- David T. Schoen
- , Aaron L. Holsteen
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-micrometre accurate free-form optics by three-dimensional printing on single-mode fibres
Sub-micrometre accurate free-form optics by three-dimensional printing on single-mode fibres
Combining freeform optics with micro- and nano-optics can permit wavefront shaping, phase engineering, k-space and polarization control. Here, Gissibl et al. use femtosecond 3D printing to manufacture free-form optical elements, giving sub-micrometre accuracy so that direct manufacturing on single-mode fibres is possible.
- Timo Gissibl
- , Simon Thiele
- & Harald Giessen
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically driven optical metamaterials
Electrically driven optical metamaterials
Active metamaterials are largely controlled by light, preventing integration in electronic systems. Here, the authors introduce electroluminescent metamaterials based on metal nano-inclusions hybridized with colloidal quantum dots and use this approach to weave intricate light-emitting surfaces.
- Quynh Le-Van
- , Xavier Le Roux
- & Aloyse Degiron
-
Article
| Open Access High-efficiency and air-stable P3HT-based polymer solar cells with a new non-fullerene acceptor
High-efficiency and air-stable P3HT-based polymer solar cells with a new non-fullerene acceptor
In organic photovoltaics, the best performing devices usually involve low-bandgap polymers whose limited solubility and stability constrain the scalability of organic solar cells. Here, Holliday et al. develop a new acceptor and pair it with canonical P3HT to obtain 6.4% efficient and stable devices.
- Sarah Holliday
- , Raja Shahid Ashraf
- & Iain McCulloch
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling thermal emission with refractory epsilon-near-zero metamaterials via topological transitions
Controlling thermal emission with refractory epsilon-near-zero metamaterials via topological transitions
The ability to control thermal radiation at high temperatures is of interest for thermal photovoltaics. Here, Dyachenko et al. engineer the epsilon-near-zero frequency of a metamaterial and connected optical topological transition to selectively enhance and suppress the thermal emission in the near-infrared spectrum.
- P. N. Dyachenko
- , S. Molesky
- & M. Eich
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-induced halide redistribution in organic–inorganic perovskite films
Photo-induced halide redistribution in organic–inorganic perovskite films
Visual evidence for photo-induced ionic migration in perovskite films without contacts is lacking. Here, the authors use a unique combination of confocal photoluminescence microscopy and chemical imaging to correlate the local changes in photophysics with composition in CH3NH3PbI3films under illumination.
- Dane W. deQuilettes
- , Wei Zhang
- & Samuel D. Stranks
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling the volatility of the written optical state in electrochromic DNA liquid crystals
Controlling the volatility of the written optical state in electrochromic DNA liquid crystals
Electrochromism, the dependence of light absorption upon electronic control, finds a wide range of applications in smart materials. Here, Liu et al. show an electrochromic DNA–surfactant liquid crystal system that exhibits electrically tunable optical absorption and thermally tunable memory.
- Kai Liu
- , Justin Varghese
- & Andreas Herrmann
-
Article
| Open Access Giant photoluminescence enhancement in tungsten-diselenide–gold plasmonic hybrid structures
Giant photoluminescence enhancement in tungsten-diselenide–gold plasmonic hybrid structures
Two-dimensional materials have excellent electrical properties, but poor luminescence limits their application in optoelectronics. Here, the authors demonstrate a plasmon-induced 20,000-fold enhancement in photoluminescence from tungsten diselenide suspended across a nanometre-scale gap.
- Zhuo Wang
- , Zhaogang Dong
- & Andrew T. S. Wee
-
Article
| Open Access Frequency and bandwidth conversion of single photons in a room-temperature diamond quantum memory
Frequency and bandwidth conversion of single photons in a room-temperature diamond quantum memory
Controlling the spectral properties of single photons is important for emerging optical quantum technologies, but doing so in a frequency-multiplexed framework is challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate quantum frequency conversion with a Raman quantum memory in room-temperature diamond.
- Kent A. G. Fisher
- , Duncan G. England
- & Benjamin J. Sussman
-
Article
| Open Access Giant photostriction in organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites
Giant photostriction in organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites
The photophysics of lead halide perovskites is under intense investigation. Here, the authors use force microscopy on single crystals to show that light induces drastic lattice changes, and propose that the weakening of the hydrogen coupling under illumination is responsible for the lattice dilatation.
- Yang Zhou
- , Lu You
- & Junling Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Exciton localization in solution-processed organolead trihalide perovskites
Exciton localization in solution-processed organolead trihalide perovskites
The recombination dynamics of photogenerated carriers in organolead trihalide perovskites are not well understood. Here, He et al.report that the recombination of photogenerated carriers in solution-processed methylammonium-lead-halide films is dominated by excitons weakly localized in band tail states.
- Haiping He
- , Qianqian Yu
- & Zhizhen Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Intensifying the response of distributed optical fibre sensors using 2D and 3D image restoration
Intensifying the response of distributed optical fibre sensors using 2D and 3D image restoration
Optical fibres offer a way of sensing across a wide area, providing a spatial and temporal map of the measured parameter. Here, the authors use image and video processing to remove noise and increase the contrast in such a distributed optical fibre sensor, improving the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of 100.
- Marcelo A. Soto
- , Jaime A. Ramírez
- & Luc Thévenaz
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of a near-IR line-referenced electro-optical laser frequency comb for precision radial velocity measurements in astronomy
Demonstration of a near-IR line-referenced electro-optical laser frequency comb for precision radial velocity measurements in astronomy
Laser frequency combs emit a spectrum of equally spaced peaks that can provide precise frequency references useful for astronomy. Here, the authors demonstrate a frequency comb using electro-optical modulation, which has a line spacing that is resolvable using grating spectrographs unlike the mode-locking approach.
- X. Yi
- , K. Vahala
- & C. Beichman
-
Article
| Open Access Substantial bulk photovoltaic effect enhancement via nanolayering
Substantial bulk photovoltaic effect enhancement via nanolayering
Spontaneous polarization in ferroelectric materials leads to their use as photovoltaic devices. Here, the authors show by first-principles calculations how nanolayering of PbTiO3with nickel ions and oxygen vacancies can result in enhanced photocurrents due to smaller bandgaps and photocurrent alignment.
- Fenggong Wang
- , Steve M. Young
- & Andrew M. Rappe
-
Article
| Open Access A series connection architecture for large-area organic photovoltaic modules with a 7.5% module efficiency
A series connection architecture for large-area organic photovoltaic modules with a 7.5% module efficiency
The fabrication of organic photovoltaic modules usually relies on patterning techniques which limit their efficiencies. Here, the authors propose a module structure that avoids the patterning steps, and use doctor-blade printing and slot-die coating to fabricate large-area modules reaching 7.5% efficiencies.
- Soonil Hong
- , Hongkyu Kang
- & Kwanghee Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible thin-film black gold membranes with ultrabroadband plasmonic nanofocusing for efficient solar vapour generation
Flexible thin-film black gold membranes with ultrabroadband plasmonic nanofocusing for efficient solar vapour generation
Efficient steam generation under solar irradiation is of interest for energy harvesting applications. Here, Bae et al. develop a plasmonic nanofocusing film consisting of metal coated alumina nanowires to efficiently generate solar vapour with an efficiency up to 57% at 20 kWm−2.
- Kyuyoung Bae
- , Gumin Kang
- & Willie J. Padilla
-
Article
| Open Access Broadband chirality-coded meta-aperture for photon-spin resolving
Broadband chirality-coded meta-aperture for photon-spin resolving
Nano-apertures cannot distinguish between distinct spin-states of photons because of information loss upon light-aperture interaction. Here, Du et al.report a subwavelength aperture integrated with metasurfaces which breaks spin degeneracy and produces opposite transmission spectra over a broad spectral range.
- Luping Du
- , Shan Shan Kou
- & Jiao Lin
-
Article
| Open Access High mobility emissive organic semiconductor
High mobility emissive organic semiconductor
Organic semiconductors with high mobility and strong fluorescence are necessary for optoelectronic devices. Here, Liu et al. show an organic semiconductor, 2,6-diphenylanthracene, satisfying both requirements with mobility of 34 cm2 V−1 s−1 and emission of 6,627 cd m−2at a turn-on voltage of 2.8 V.
- Jie Liu
- , Hantang Zhang
- & Alan J. Heeger
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced optoelectronic quality of perovskite thin films with hypophosphorous acid for planar heterojunction solar cells
Enhanced optoelectronic quality of perovskite thin films with hypophosphorous acid for planar heterojunction solar cells
An imbalance in I/Pb stoichiometry is thought to lead to defects in metal halide films. Here, Zhang et al. show that the addition of hypophosphorous acid in the precursor solution can significantly improve the film quality and enhance the photoluminescence intensity, leading to improved photovoltaic devices.
- Wei Zhang
- , Sandeep Pathak
- & Henry J. Snaith
-
Article
| Open Access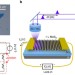 Ultrafast response of monolayer molybdenum disulfide photodetectors
Ultrafast response of monolayer molybdenum disulfide photodetectors
Two-dimensional transition-metal dichalcogenides are useful for optoelectronic applications, but the ultimate limit on the speed of photodetector operation is unknown. Here, the authors show that the optical response time of monolayer molybdenum disulfide can be as short as three picoseconds.
- Haining Wang
- , Changjian Zhang
- & Farhan Rana
-
Article
| Open Access Planar-integrated single-crystalline perovskite photodetectors
Planar-integrated single-crystalline perovskite photodetectors
Single crystals of organolead halide perovskites exhibit large carrier mobilities and long diffusion lengths. Here, the authors succeed in growing the single crystals on planar substrates and integrate them as the active layer of visible photodetectors with a large gain-bandwidth product.
- Makhsud I. Saidaminov
- , Valerio Adinolfi
- & Osman M. Bakr
-
Article
| Open Access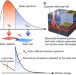 A hot-electron thermophotonic solar cell demonstrated by thermal up-conversion of sub-bandgap photons
A hot-electron thermophotonic solar cell demonstrated by thermal up-conversion of sub-bandgap photons
The efficiency of single junction solar cells is limited by their inability to absorb photons with an energy smaller than the bandgap. Here, the authors surpass the Shockley-Queisser limit by using an integrated hot-electron thermophotonic emitter to thermally up-convert sub-bandgap photons.
- Daniel J. Farrell
- , Hassanet Sodabanlu
- & Yoshitaka Okada
-
Article
| Open Access Stable ultrathin partially oxidized copper film electrode for highly efficient flexible solar cells
Stable ultrathin partially oxidized copper film electrode for highly efficient flexible solar cells
Light enters and exits optoelectronic devices through transparent conductive electrodes, which are one of their most expensive components. Here, the authors develop stable transparent conductive electrodes based on copper and oxide layers that lead to efficient flexible organic solar cells.
- Guoqing Zhao
- , Wei Wang
- & Jungheum Yun
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral splitting photovoltaics using perovskite and wideband dye-sensitized solar cells
Spectral splitting photovoltaics using perovskite and wideband dye-sensitized solar cells
Lead halide perovskite solar cells have a limited spectral response in the near infrared. Here, the authors present ruthenium dyes with extended near infrared absorbance and combine perovskite and dye-based solar cells by spectral splitting to obtain broadband, 21.5% efficient solar cells.
- Takumi Kinoshita
- , Kazuteru Nonomura
- & Hiroshi Segawa
-
Article
| Open Access Implementation of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with composable and one-sided-device-independent security against coherent attacks
Implementation of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with composable and one-sided-device-independent security against coherent attacks
When quantum key distribution is composed with other secure protocols the overall security has to be guaranteed, which adds further security requirements. Here, the authors demonstrate continuous-variable quantum key distribution with composable security and one-sided-device independence.
- Tobias Gehring
- , Vitus Händchen
- & Roman Schnabel
-
Article
| Open Access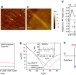 Planar carbon nanotube–graphene hybrid films for high-performance broadband photodetectors
Planar carbon nanotube–graphene hybrid films for high-performance broadband photodetectors
Graphene has excellent electronic properties but its photoresponsivity is limited by low absorption and the ultrafast recombination of photoexcited carriers. Here, the authors demonstrate fast, high responsivity and broadband photodetectors by combining graphene with single-wall carbon nanotubes.
- Yuanda Liu
- , Fengqiu Wang
- & Rong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access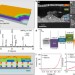 Light-induced pyroelectric effect as an effective approach for ultrafast ultraviolet nanosensing
Light-induced pyroelectric effect as an effective approach for ultrafast ultraviolet nanosensing
Zinc oxide is potentially a useful material for ultraviolet detectors, but a relatively long response time hinders practical implementation. Here, the authors demonstrate a zinc oxide nanowire/perovskite heterostructure detector with a five orders of magnitude improvement in both rising and falling edge time.
- Zhaona Wang
- , Ruomeng Yu
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Hot-carrier cooling and photoinduced refractive index changes in organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites
Hot-carrier cooling and photoinduced refractive index changes in organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites
The use of organic–inorganic metal-halide perovskites in hot-carrier devices depends on deepening the understanding of photoexcitations in these materials. Here, Price et al. use transient absorption spectroscopy to study hot-carrier distributions in CH3NH3PbI3and quantify key semiconductors parameters.
- Michael B. Price
- , Justinas Butkus
- & Felix Deschler
-
Article
| Open Access Proposal for a room-temperature diamond maser
Proposal for a room-temperature diamond maser
Maser applications are hindered by their demanding working conditions. Here, Jinet al. theoretically propose a room-temperature maser based on nitrogen vacancy centres in diamond. This numerical study demonstrates that the operation of the maser under readily accessible conditions is feasible.
- Liang Jin
- , Matthias Pfender
- & Ren-Bao Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient direct solar-to-hydrogen conversion by in situ interface transformation of a tandem structure
Efficient direct solar-to-hydrogen conversion by in situ interface transformation of a tandem structure
A future carbon-free energy economy requires an efficient photocatalytic route to hydrogen generation. Here, the authors employ surface modification techniques to raise the performance of an unassisted solar water splitting device to achieve exceptional performances.
- Matthias M. May
- , Hans-Joachim Lewerenz
- & Thomas Hannappel
-
Article
| Open Access Micromotors with asymmetric shape that efficiently convert light into work by thermocapillary effects
Micromotors with asymmetric shape that efficiently convert light into work by thermocapillary effects
The direct conversion of light into work allows the control of micromotors, but typically with low efficiencies and high power density requirements. Here, Maggiet al. demonstrate efficient thermocapillary propulsion of microgears on a liquid–air interface with wide-field, incoherent illumination.
- Claudio Maggi
- , Filippo Saglimbeni
- & Roberto Di Leonardo
-
Article
| Open Access Creating semiconductor metafilms with designer absorption spectra
Creating semiconductor metafilms with designer absorption spectra
Ultrathin semiconductor metafilms can be designed to achieve near-unity absorption in specific spectral regions. Here, Kim et al. engineer nanoscale optical resonances in sub-50-nm-thick germanium nanobeams metafilms to demonstrate near-unity absorption in one or more desired wavelength regions.
- Soo Jin Kim
- , Pengyu Fan
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
Article
| Open Access A generic concept to overcome bandgap limitations for designing highly efficient multi-junction photovoltaic cells
A generic concept to overcome bandgap limitations for designing highly efficient multi-junction photovoltaic cells
The efficiency of a single-junction photovoltaic cell is constrained by the Shockley-Queisser limit. Here, the authors adopt a triple-junction configuration which relaxes material and current-matching constraints, providing a generic strategy for advancing the efficiency roadmap of photovoltaic technologies.
- Fei Guo
- , Ning Li
- & Christoph J. Brabec
-
Article
| Open Access Distinguishing between plasmon-induced and photoexcited carriers in a device geometry
Distinguishing between plasmon-induced and photoexcited carriers in a device geometry
Plasmonic excitations of electrons in metallic nanostructures are promising for the enhanced conversion of light in semiconductor solar cells. Here, the authors are able to experimentally distinguish the absorption phenomena of plasmonic carrier generation and excitation of carriers by light absorption.
- Bob Y. Zheng
- , Hangqi Zhao
- & Naomi J. Halas
-
Article
| Open Access Vibronic origin of long-lived coherence in an artificial molecular light harvester
Vibronic origin of long-lived coherence in an artificial molecular light harvester
Two-dimensional spectroscopy revealed oscillatory signals in photosynthesis’ exciton dynamics, but crowded spectra impede the identification of what sustains the oscillations. Here the authors probe an J-aggregate, whose uncongested response shows that vibronic coupling is responsible for the sustained coherence.
- James Lim
- , David Paleček
- & Jürgen Hauer
-
Article
| Open Access Electric-field-induced strong enhancement of electroluminescence in multilayer molybdenum disulfide
Electric-field-induced strong enhancement of electroluminescence in multilayer molybdenum disulfide
The layer-number-dependent optical and electronic properties of transition metal dichalcogenides are promising in optoelectronics. Here, Li et al. demonstrate greatly enhanced electroluminescence emission in multi-layer MoS2attributed to the electric-field-induced carrier redistribution.
- Dehui Li
- , Rui Cheng
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Adiabatic elimination-based coupling control in densely packed subwavelength waveguides
Adiabatic elimination-based coupling control in densely packed subwavelength waveguides
Optical communications and quantum operations require active coupling control in closely packed integrated photonic circuits. Here, Mrejen et al.exploit adiabatic elimination to demonstrate active coupling control between two closely packed waveguides by tuning the mode index of an in-between decoupled waveguide.
- Michael Mrejen
- , Haim Suchowski
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Lead iodide perovskite light-emitting field-effect transistor
Lead iodide perovskite light-emitting field-effect transistor
Hybrid organic–inorganic perovskites have shown great potential for use in optoelectronic applications. Here, the authors create solution-processed lead iodide perovskite light-emitting field-effect transistors and demonstrate both ambipolar behaviour and gate-assisted electroluminescence.
- Xin Yu Chin
- , Daniele Cortecchia
- & Cesare Soci
-
Article |
 Aging mechanisms in amorphous phase-change materials
Aging mechanisms in amorphous phase-change materials
Phase-change materials are a route to high-density data storage, but changes in their properties in time are a limiting factor. Here, the authors combine numerical simulations, photothermal deflection spectroscopy and impedance spectroscopy experiments to investigate the aging process in germanium telluride.
- Jean Yves Raty
- , Wei Zhang
- & Matthias Wuttig
-
Article
| Open Access Ionic transport in hybrid lead iodide perovskite solar cells
Ionic transport in hybrid lead iodide perovskite solar cells
Understanding the mechanism of ionic transport in organic–inorganic halide perovskites is crucial for the design of future solar cells. Here, Eames et al.undertake a combined experimental and computational study to elucidate the ion conducting species and help rationalize the unusual behaviour observed in these perovskite-based devices.
- Christopher Eames
- , Jarvist M. Frost
- & M. Saiful Islam
-
Article |
 Temporal tweezing of light through the trapping and manipulation of temporal cavity solitons
Temporal tweezing of light through the trapping and manipulation of temporal cavity solitons
Optical tweezing typically refers to the trapping and manipulation of particles using lasers. Here, Jang et al. demonstrate analogous manipulation of ultrashort cavity soliton-pulses in the time domain, trapped by the phase modulation of a continuous wave laser beam, and moved by modifying the phase profile.
- Jae K. Jang
- , Miro Erkintalo
- & Stuart G. Murdoch
-
Article
| Open Access High-quality sandwiched black phosphorus heterostructure and its quantum oscillations
High-quality sandwiched black phosphorus heterostructure and its quantum oscillations
Black phosphorus is an atomically thin material that exhibits excellent properties for electronics applications, but these degrade in atmospheric conditions. Here, the authors demonstrate the fabrication of stable, ultra-clean and high-mobility black phosphorus sandwiched between the layers of boron nitride.
- Xiaolong Chen
- , Yingying Wu
- & Ning Wang
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance flexible perovskite solar cells exploiting Zn2SnO4 prepared in solution below 100 °C
High-performance flexible perovskite solar cells exploiting Zn2SnO4 prepared in solution below 100 °C
There has been impressive progress in the development of perovskite solar cells in recent years, but the best performing systems tend to be fabricated on glass surfaces. Here, the authors present a cell built on a polymer substrate, allowing flexibility whilst maintaining high efficiency.
- Seong Sik Shin
- , Woon Seok Yang
- & Sang Il Seok
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Adaptive optics
- Astronomical optics
- Atmospheric optics
- Displays
- Fibre optics and optical communications
- Integrated optics
- Laser material processing
- Microwave photonics
- Mid-infrared photonics
- Optical data storage
- Optical sensors
- Optoelectronic devices and components
- Solar energy and photovoltaic technology

 Broadband giant-refractive-index material based on mesoscopic space-filling curves
Broadband giant-refractive-index material based on mesoscopic space-filling curves