Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access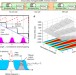 All-optical regenerator of multi-channel signals
All-optical regenerator of multi-channel signals
Nonlinear optical processing devices are not yet fully practical as they are single channel. Here the authors demonstrate all-optical regeneration of up to 16 channels by one device, employing a group-delay-managed nonlinear medium where strong self-phase modulation is achieved without nonlinear inter-channel crosstalk.
- Lu Li
- , Pallavi G. Patki
- & Michael Vasilyev
-
Article
| Open Access Color-selective photodetection from intermediate colloidal quantum dots buried in amorphous-oxide semiconductors
Color-selective photodetection from intermediate colloidal quantum dots buried in amorphous-oxide semiconductors
The development of highly sensitive photodetectors is important for image sensing and optical communication applications. Cho et al., report ultra-sensitive photodetectors based on monolayered quantum dots buried in between amorphous-oxide semiconductors and demonstrate color-detecting logic gates.
- Kyung-Sang Cho
- , Keun Heo
- & Sang Yeol Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Synchronized conductivity modulation to realize broadband lossless magnetic-free non-reciprocity
Synchronized conductivity modulation to realize broadband lossless magnetic-free non-reciprocity
Optical non-reciprocity achieved through refractive index modulation can have its challenges and limitations. Here, Dinc et al. introduce the concept of non-reciprocity based on synchronized spatio-temporal modulation of conductivity to achieve different types of non-reciprocal functionality.
- Tolga Dinc
- , Mykhailo Tymchenko
- & Harish Krishnaswamy
-
Article
| Open Access Crossing the threshold of ultrafast laser writing in bulk silicon
Crossing the threshold of ultrafast laser writing in bulk silicon
Ultrafast laser processing is a versatile three-dimensional photonic structuring method but it has been limited to wide band gap materials like glasses. Here, Chanal et al. demonstrate direct refractive-index modification in the bulk of silicon by extreme localization of the energy deposition.
- Margaux Chanal
- , Vladimir Yu. Fedorov
- & David Grojo
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay of hot electrons from localized and propagating plasmons
Interplay of hot electrons from localized and propagating plasmons
Plasmon-induced hot electrons have potential applications spanning photodetection and photocatalysis. Here, Hoang et al. study the interplay between hot electrons generated by localized and propagating plasmons, and demonstrate wavelength-controlled polarity-switchable photoconductivity
- Chung V. Hoang
- , Koki Hayashi
- & Hiroaki Misawa
-
Article
| Open Access Multipurpose silicon photonics signal processor core
Multipurpose silicon photonics signal processor core
Integrated optical circuits today are typically designed for a few special functionalities and require complex design and development procedures. Here, the authors demonstrate a reconfigurable but simple silicon waveguide mesh with different functionalities.
- Daniel Pérez
- , Ivana Gasulla
- & José Capmany
-
Article
| Open Access Silicon single-photon avalanche diodes with nano-structured light trapping
Silicon single-photon avalanche diodes with nano-structured light trapping
The performance of silicon single-photon avalanche detectors is currently limited by the trade-off between photon detection efficiency and timing jitter. Here, the authors demonstrate how a CMOS-compatible, nanostructured, thin junction structure can make use of tailored light trapping to break this trade-off.
- Kai Zang
- , Xiao Jiang
- & James S. Harris
-
Article
| Open Access A chip-integrated coherent photonic-phononic memory
A chip-integrated coherent photonic-phononic memory
Optical storage implementations based on optomechanical resonator are limited to one wavelength. Here, exploiting stimulated Brillouin scattering, the authors demonstrate a coherent optical memory based on a planar integrated waveguide, which can operate at different wavelengths without cross-talk.
- Moritz Merklein
- , Birgit Stiller
- & Benjamin J. Eggleton
-
Article
| Open Access On-chip single photon filtering and multiplexing in hybrid quantum photonic circuits
On-chip single photon filtering and multiplexing in hybrid quantum photonic circuits
Combining different integration platforms on the same chip is currently one of the main challenges for quantum technologies. Here, Elshaari et al. show III-V Quantum Dots embedded in nanowires operating in a CMOS compatible circuit, with controlled on-chip filtering and tunable routing.
- Ali W. Elshaari
- , Iman Esmaeil Zadeh
- & Klaus D. Jöns
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast carrier thermalization in lead iodide perovskite probed with two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy
Ultrafast carrier thermalization in lead iodide perovskite probed with two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy
Carrier-carrier scattering rates determine the fundamental limits of carrier transport and electronic coherence. Using two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy with sub-10 fs resolution, Richter and Branchi et al. extract carrier thermalization times of 10 to 85 fs in hybrid perovskites.
- Johannes M. Richter
- , Federico Branchi
- & Felix Deschler
-
Article
| Open Access Conformal metasurface-coated dielectric waveguides for highly confined broadband optical activity with simultaneous low-visibility and reduced crosstalk
Conformal metasurface-coated dielectric waveguides for highly confined broadband optical activity with simultaneous low-visibility and reduced crosstalk
Controlling all the optical properties of dielectric waveguides is a challenging task and often requires complicated core- and cladding designs. Here, Jiang et al. demonstrate that a thin metasurface coating can control several optical properties simultaneously over a broad frequency range.
- Zhi Hao Jiang
- , Lei Kang
- & Douglas H. Werner
-
Article
| Open Access Electromagnetic reprogrammable coding-metasurface holograms
Electromagnetic reprogrammable coding-metasurface holograms
Realizing metasurfaces with reconfigurability, high efficiency, and control over phase and amplitude is a challenge. Here, Li et al. introduce a reprogrammable hologram based on a 1-bit coding metasurface, where the state of each unit cell of the coding metasurface can be switched electrically.
- Lianlin Li
- , Tie Jun Cui
- & Shuang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Distribution of high-dimensional entanglement via an intra-city free-space link
Distribution of high-dimensional entanglement via an intra-city free-space link
Increasing the dimensionality of entangled states improves robustness and capacity of secure quantum communications, but it requires suitably modified setups. Here the authors report the distribution of high-dimensional polarization and energy-time entangled photons via a 1.2 km-long free-space link.
- Fabian Steinlechner
- , Sebastian Ecker
- & Rupert Ursin
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of topological surface-state arcs in photonic metamaterials
Direct observation of topological surface-state arcs in photonic metamaterials
Topological effects known from condensed matter physics have recently also been explored in photonic systems. Here, the authors directly observe topological surface-state arcs in momentum space by near-field scanning the surface of a chiral hyperbolic metamaterial.
- Biao Yang
- , Qinghua Guo
- & Shuang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access On-chip inter-modal Brillouin scattering
On-chip inter-modal Brillouin scattering
Here, Kittlauset al. demonstrate stimulated inter-modal Brillouin scattering on-chip. Through this process, a Brillouin interaction couples light fields that propagate in distinct spatial modes of a Brillouin-active silicon waveguide, which may allow a variety of new processes in silicon photonics.
- Eric A. Kittlaus
- , Nils T. Otterstrom
- & Peter T. Rakich
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of reflectionless absorption due to spatial Kramers–Kronig profile
Observation of reflectionless absorption due to spatial Kramers–Kronig profile
Reflectionless absorption independent of the angle of incidence usually requires the introduction of gain media into the system. Here, Ye et al. implement a recent theoretical proposal to achieve this with a spatially varying permittivity, showing that this approach is experimentally feasible.
- Dexin Ye
- , Cheng Cao
- & Lixin Ran
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible integration of free-standing nanowires into silicon photonics
Flexible integration of free-standing nanowires into silicon photonics
Precisely assembling free-standing nanowires for on-demand photonic functionality remains a challenge. Here, Chen et al. integrate free-standing nanowires into silicon waveguides and show all-optical modulation and light generation on silicon photonic chips.
- Bigeng Chen
- , Hao Wu
- & Limin Tong
-
Article
| Open Access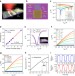 Carbon nanotube-based three-dimensional monolithic optoelectronic integrated system
Carbon nanotube-based three-dimensional monolithic optoelectronic integrated system
Single-material monolithic optoelectronic integrated circuits via CMOS compatible low-temperature approaches are crucial to the continued development of post-Moore electronics. Liuet al., report carbon nanotube based electrically driven 3D monolithic optoelectronic integrated circuits.
- Yang Liu
- , Sheng Wang
- & Lian-Mao Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Organic narrowband near-infrared photodetectors based on intermolecular charge-transfer absorption
Organic narrowband near-infrared photodetectors based on intermolecular charge-transfer absorption
Interfaces of organic donor-acceptor blends provide intermolecular charge-transfer states with red-shifted but weak absorption. By introducing an optical micro-cavity; Siegmundet al., enhance their photoresponse to achieve narrowband NIR photodetection with broad spectral tunability.
- Bernhard Siegmund
- , Andreas Mischok
- & Koen Vandewal
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing speckle for a sub-femtometre resolved broadband wavemeter and laser stabilization
Harnessing speckle for a sub-femtometre resolved broadband wavemeter and laser stabilization
The complex speckle pattern produced by coherent multiple scattering contains information about the incident light field, which has recently been used for imaging. Metzgeret al. use speckle to construct a wavemeter with sub-femtometre resolution which is subsequently used for laser stabilization.
- Nikolaus Klaus Metzger
- , Roman Spesyvtsev
- & Kishan Dholakia
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic computing of spatial differentiation
Plasmonic computing of spatial differentiation
For specific problems, analog optical computing can be faster and more computationally efficient than digital methods. Here, Zhuet al. simplify the often metamaterial-based approach to a single thin metal film, with which they demonstrate spatial differentiation.
- Tengfeng Zhu
- , Yihan Zhou
- & Shanhui Fan
-
Article
| Open Access An integrated parity-time symmetric wavelength-tunable single-mode microring laser
An integrated parity-time symmetric wavelength-tunable single-mode microring laser
The breaking of parity-time symmetric gain and loss profiles can be used to achieve single-mode lasing in coupled microring resonators. Here, Liuet al. show that this effect can be electrically controlled with a tunable lasing wavelength and strong sidemode suppression.
- Weilin Liu
- , Ming Li
- & Jianping Yao
-
Article
| Open Access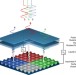 Actively addressed single pixel full-colour plasmonic display
Actively addressed single pixel full-colour plasmonic display
Tuning of plasmonic nanostructures has yet to cover a full colour basis set with a single nanostructure. Franklinet al. demonstrate a liquid crystal-plasmonic system that covers the full red-green-blue colour basis set as a function of voltage and which can be actively addressed with thin-film-transistor technology.
- Daniel Franklin
- , Russell Frank
- & Debashis Chanda
-
Article
| Open Access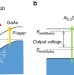 Two-step photon up-conversion solar cells
Two-step photon up-conversion solar cells
Harvesting incident photons with energy below the bandgap may lead to highly efficient solar cells. By introducing InAs quantum dots at the hetero-interface, Asahiet al. achieve efficient two step photon up-conversion resulting in additional photocurrent and very high external quantum efficiency.
- Shigeo Asahi
- , Haruyuki Teranishi
- & Takashi Kita
-
Article
| Open Access Field-emission from quantum-dot-in-perovskite solids
Field-emission from quantum-dot-in-perovskite solids
Efficient implementation of quantum dot and well architectures are restricted to costly vacuum-epitaxially-grown semiconductors. The authors use quantum dots in perovskite to build field-emission photodiodes that are sensitive across the visible and into the short-wavelength infrared.
- F. Pelayo García de Arquer
- , Xiwen Gong
- & Edward Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access Disorder-induced single-mode transmission
Disorder-induced single-mode transmission
Here Leonettiet al. report the observation of single-mode states in the regime of transverse Anderson localization in a disordered optical fibre, with negligible crosstalk accompanied by an inherent resilience to fibre bending and invariance with respect to the launch conditions.
- Giancarlo Ruocco
- , Behnam Abaie
- & Marco Leonetti
-
Article
| Open Access Control of randomly scattered surface plasmon polaritons for multiple-input and multiple-output plasmonic switching devices
Control of randomly scattered surface plasmon polaritons for multiple-input and multiple-output plasmonic switching devices
Losses of bandwidth are inevitable when interfacing between optical and electronic components. Here the authors present a switching device consisting of a two-dimensional disordered array of nanoholes that can potentially transfer information about 40 times faster than conventional switching devices.
- Wonjun Choi
- , Yonghyeon Jo
- & Wonshik Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic plasmonic colour display
Dynamic plasmonic colour display
Here Duanet al. demonstrate dynamic plasmonic colour displays using catalytic magnesium metasurfaces. Controlled hydrogenation and dehydrogenation of the constituent nanoparticles, which serve as dynamic pixels, allow plasmonic colour printing, tuning, erasing, restoration of colour and encoding of information.
- Xiaoyang Duan
- , Simon Kamin
- & Na Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Chip-based quantum key distribution
Chip-based quantum key distribution
Quantum key distribution has not been widely adopted in part due to technical hurdles preventing it being fully integrated in classical communication networks. Here the authors report quantum key distribution between two photonic chips manufactured with state-of-the-art telecoms industry processes.
- P. Sibson
- , C. Erven
- & M. G. Thompson
-
Article
| Open Access Slow-light-enhanced energy efficiency for graphene microheaters on silicon photonic crystal waveguides
Slow-light-enhanced energy efficiency for graphene microheaters on silicon photonic crystal waveguides
Slow light can be used to sustain strong light–matter interaction in silicon photonics. Here, the authors combine graphene with a silicon slow-light photonic crystal waveguide, demonstrating a fast and energy-efficient graphene microheater.
- Siqi Yan
- , Xiaolong Zhu
- & Yunhong Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene-based mid-infrared room-temperature pyroelectric bolometers with ultrahigh temperature coefficient of resistance
Graphene-based mid-infrared room-temperature pyroelectric bolometers with ultrahigh temperature coefficient of resistance
There is emerging interest in photodetectors in the mid-infrared driven by increasing need to monitor the environment for security and healthcare purposes. Sassiet al. show a thermal photodetector, based on the coupling between graphene and a pyroelectric crystal, which shows high temperature sensitivity.
- U. Sassi
- , R. Parret
- & A. Colli
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed single-mode wavelength-to-time mapping of multimode light
Multiplexed single-mode wavelength-to-time mapping of multimode light
Photonic lanterns are made by merging several single-mode cores into one multimode core. Here, the authors show this type of structure can both perform wavelength-to-time mapping of multimode states of light and couple such light to an array of single-photon avalanche detectors.
- Harikumar K Chandrasekharan
- , Frauke Izdebski
- & Robert R. Thomson
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum interference between transverse spatial waveguide modes
Quantum interference between transverse spatial waveguide modes
Practical implementations of quantum photonic circuits consist primarily of large waveguide networks to path-encode information. Here, Mohantyet al. demonstrate quantum interference between transverse spatial modes in a single silicon nitride waveguide, enabling robust quantum information processing.
- Aseema Mohanty
- , Mian Zhang
- & Michal Lipson
-
Article
| Open Access Extremely broadband, on-chip optical nonreciprocity enabled by mimicking nonlinear anti-adiabatic quantum jumps near exceptional points
Extremely broadband, on-chip optical nonreciprocity enabled by mimicking nonlinear anti-adiabatic quantum jumps near exceptional points
Nonreciprocal optical devices can be designed based on symmetry breaking at singular points associated with non-Hermitian physics. Here, Choiet al. theoretically show that encircling of exceptional points enables the broadband operation and chip integration of such devices.
- Youngsun Choi
- , Choloong Hahn
- & Pierre Berini
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically tunable organic–inorganic hybrid polaritons with monolayer WS2
Electrically tunable organic–inorganic hybrid polaritons with monolayer WS2
Hybrid polariton states originating from the strong coupling of photonic and excitonic states hold promise for control of nonlinear light behaviour. Here, the authors fabricate a microcavity containing organic dye and WS2, featuring hybrid polaritons arising from both Frenkel and Wannier-Mott excitons.
- Lucas C. Flatten
- , David M. Coles
- & Jason M. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Electromagnetic polarization-controlled perfect switching effect with high-refractive-index dimers and the beam-splitter configuration
Electromagnetic polarization-controlled perfect switching effect with high-refractive-index dimers and the beam-splitter configuration
Traditional metallic communication elements suffer from substantial losses in the visible and near-infrared. Here, Barredaet al. show in a proof of principle in the microwave regime that a pair of high-index dielectric spheres can operate as a perfect switch in a beam-splitter configuration.
- Ángela I. Barreda
- , Hassan Saleh
- & Fernando Moreno
-
Article
| Open Access An antireflection transparent conductor with ultralow optical loss (<2 %) and electrical resistance (<6 Ω sq−1)
An antireflection transparent conductor with ultralow optical loss (<2 %) and electrical resistance (<6 Ω sq−1)
Transparent conductors are fundamental for optoelectronics. Using the transfer matrix method to optimise a multistructure of anti-reflection coatings containing an ultrathin metal film, Maniyaraet al. achieve the highest transmittance of an antireflection transparent conductor combined with low resistance.
- Rinu Abraham Maniyara
- , Vahagn K. Mkhitaryan
- & Valerio Pruneri
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging electric field dynamics with graphene optoelectronics
Imaging electric field dynamics with graphene optoelectronics
Detection of electric fields, central to chemical and biological processes, has been limited to measurements of current (e.g., electrodes) and secondary reporters (e.g., fluorescent dyes). Here, the authors demonstrate an optical platform capable of imaging electric field dynamics with high spatio-temporal resolution.
- Jason Horng
- , Halleh B. Balch
- & Feng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Miniature optical planar camera based on a wide-angle metasurface doublet corrected for monochromatic aberrations
Miniature optical planar camera based on a wide-angle metasurface doublet corrected for monochromatic aberrations
Metasurfaces have the potential to be used in imaging systems since they can modify optical wavefronts at subwavelength spatial resolution. Here, Arbabi et al. demonstrate a metasurface lens doublet corrected for monochromatic aberrations, and integrate it with an image sensor to realize a miniature planar camera.
- Amir Arbabi
- , Ehsan Arbabi
- & Andrei Faraon
-
Article
| Open Access Mid-infrared ultra-high-Q resonators based on fluoride crystalline materials
Mid-infrared ultra-high-Q resonators based on fluoride crystalline materials
Highly sensitive trace-gas detection is possible in the mid-infrared range with transparent microresonators. Here, the authors directly measure the necessary ultra-high quality factors of microresonators made from fluoride crystal materials using a tapered chalcogenide fibre.
- C. Lecaplain
- , C. Javerzac-Galy
- & T. J. Kippenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive plasmonic sensing in air using optical fibre spectral combs
Ultrasensitive plasmonic sensing in air using optical fibre spectral combs
Fibre sensors are key to many minimally-invasive detection techniques but, owing to an index mismatch, they are often limited to aqueous environments. Here, Caucheteur et al. develop a high-resolution fibre gas sensor with a tilted in-fibre grating that allows coupling to higher-order plasmon modes.
- Christophe Caucheteur
- , Tuan Guo
- & Jacques Albert
-
Article
| Open Access Increasing the density of passive photonic-integrated circuits via nanophotonic cloaking
Increasing the density of passive photonic-integrated circuits via nanophotonic cloaking
Photonic-integrated devices need to be spaced apart to prevent signal crosstalk, which limits their packing density. Here, Shen et al. report the use of nanophotonic cloaking to render neighbouring devices invisible to one another, which allows them to be placed closer together than is otherwise achievable.
- Bing Shen
- , Randy Polson
- & Rajesh Menon
-
Article
| Open Access Monitoring peripheral nerve degeneration in ALS by label-free stimulated Raman scattering imaging
Monitoring peripheral nerve degeneration in ALS by label-free stimulated Raman scattering imaging
Sensitive and label-free imaging methods to visualize nerve degeneration are currently lacking. Here authors show that stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) microscopy can be used to monitor peripheral nerve degeneration in mouse models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and in postmortem tissue from ALS patients.
- Feng Tian
- , Wenlong Yang
- & Kevin Eggan
-
Article
| Open Access Laser recrystallization and inscription of compositional microstructures in crystalline SiGe-core fibres
Laser recrystallization and inscription of compositional microstructures in crystalline SiGe-core fibres
Using SiGe in the core of optical fibres extends the wavelength range and potential optical functionality, but fabrication challenges exist. Here, Coucheronet al. report the fabrication and tailoring of SiGe-core optical fibres using CO2laser irradiation to heat the glass cladding and recrystallize the core.
- David A. Coucheron
- , Michael Fokine
- & Ursula J. Gibson
-
Article
| Open Access Thermally enhanced photoluminescence for heat harvesting in photovoltaics
Thermally enhanced photoluminescence for heat harvesting in photovoltaics
In photovoltaics, sub-band gap energy photons can be harvested using up-conversion strategies. Here, the authors show that the thermally enhanced up-converted photoluminescence results in enhanced energy conversion, for an accessible temperature range and with a broad range of incident photon energy.
- Assaf Manor
- , Nimrod Kruger
- & Carmel Rotschild
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembled fibre optoelectronics with discrete translational symmetry
Self-assembled fibre optoelectronics with discrete translational symmetry
The thermal-draw technique offers fibre devices with a multiplicity of geometries, but these are constrainted to being translationally symmetric. Here, the authors disrupt this symmetry by applying selective capillary instability, resulting in electrically connected spherical photodetecting elements.
- Michael Rein
- , Etgar Levy
- & Yoel Fink
-
Article
| Open Access Projection-type see-through holographic three-dimensional display
Projection-type see-through holographic three-dimensional display
The design of holographic displays usually involves a trade-off between size and viewing angle. Here, the authors combine holographic projection with a digitally designed holographic optical element so that display size and the visual angle can be designed independently.
- Koki Wakunami
- , Po-Yuan Hsieh
- & Kenji Yamamoto
-
Article
| Open Access Wideband dynamic microwave frequency identification system using a low-power ultracompact silicon photonic chip
Wideband dynamic microwave frequency identification system using a low-power ultracompact silicon photonic chip
Photonic-based instantaneous frequency measurement systems are usually bulky or require high optical power. Here, Burla et al. demonstrate an integrated measurement system that can identify frequency-varying signals in a dynamic fashion, without the need for fast measurement instrumentation.
- Maurizio Burla
- , Xu Wang
- & José Azaña
-
Article
| Open Access Optimization of hierarchical structure and nanoscale-enabled plasmonic refraction for window electrodes in photovoltaics
Optimization of hierarchical structure and nanoscale-enabled plasmonic refraction for window electrodes in photovoltaics
In photovoltaics window electrodes must display uniform current transport, as well as high light transmission from the substrate. Here, Han et al.show that quasi-fractal metallic networks provide a practical realization of an electrode structure with an optimal surface coverage and a uniform current density.
- Bing Han
- , Qiang Peng
- & Jinwei Gao
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Adaptive optics
- Astronomical optics
- Atmospheric optics
- Displays
- Fibre optics and optical communications
- Integrated optics
- Laser material processing
- Microwave photonics
- Mid-infrared photonics
- Optical data storage
- Optical sensors
- Optoelectronic devices and components
- Solar energy and photovoltaic technology

 Mechanical on-chip microwave circulator
Mechanical on-chip microwave circulator