Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Narrowband microwave-photonic notch filters using Brillouin-based signal transduction in silicon
Narrowband microwave-photonic notch filters using Brillouin-based signal transduction in silicon
It remains challenging to realize narrowband filters needed for high-performance communications systems using integrated photonics. Using a multi-port Brillouin-based optomechanical system, the authors demonstrate an ultra-narrowband notch filter with high rejection with CMOS compatible techniques.
- Shai Gertler
- , Nils T. Otterstrom
- & Peter T. Rakich
-
Article
| Open Access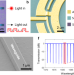 Integrated silicon carbide electro-optic modulator
Integrated silicon carbide electro-optic modulator
Electro-optic modulator is used to encode electrical signals onto light. Here the authors demonstrate an electro-optic modulator, based on Silicon Carbide, which can be useful for quantum and optical communications.
- Keith Powell
- , Liwei Li
- & Xiaoke Yi
-
Article
| Open Access Hollow-core optical fibre sensors for operando Raman spectroscopy investigation of Li-ion battery liquid electrolytes
Hollow-core optical fibre sensors for operando Raman spectroscopy investigation of Li-ion battery liquid electrolytes
New analytical tools are needed to identify chemical degradation and failure mechanisms in Li-ion batteries. Here, the authors report an operando Raman spectroscopy method, based on hollow-core optical fibres, that enables monitoring the chemistry of liquid electrolytes during battery cycling.
- Ermanno Miele
- , Wesley M. Dose
- & Tijmen G. Euser
-
Article
| Open Access The speed limit of optoelectronics
The speed limit of optoelectronics
Though strong-field induced carrier excitation allows for exploring ultrafast electronic properties of a material, characterizing post-excitation dynamics is a challenge. Here, the authors report linear petahertz photoconductive sampling in a solid and use it to real-time probe conduction band electron motion.
- M. Ossiander
- , K. Golyari
- & M. Schultze
-
Article
| Open Access Longitudinal piezoelectric resonant photoelastic modulator for efficient intensity modulation at megahertz frequencies
Longitudinal piezoelectric resonant photoelastic modulator for efficient intensity modulation at megahertz frequencies
Optical intensity modulators are an important component in optics. Here, the authors demonstrate a type of resonant intensity modulator operating in the megahertz frequency regime with record high efficiency and use it for time-of-flight imaging.
- Okan Atalar
- , Raphaël Van Laer
- & Amin Arbabian
-
Article
| Open Access Noncontact human-machine interaction based on hand-responsive infrared structural color
Noncontact human-machine interaction based on hand-responsive infrared structural color
The IR radiation from human hand can selectively interact with grating patterns in the generation of distinct IR structural colors, which can be used for human-machine interaction with flexible interaction distance in low or no light conditions.
- Shun An
- , Hanrui Zhu
- & Tao Deng
-
Article
| Open Access All-fiber high-speed image detection enabled by deep learning
All-fiber high-speed image detection enabled by deep learning
Here, the authors demonstrate high-speed imaging through multimode optical fibers by using the high intermodal dispersion to transform 2D spatial information into 1D temporal pulsed signal streams. Deep learning is used to reconstruct the images of micron-scale objects at high frame rates.
- Zhoutian Liu
- , Lele Wang
- & Qirong Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Large evanescently-induced Brillouin scattering at the surrounding of a nanofibre
Large evanescently-induced Brillouin scattering at the surrounding of a nanofibre
The authors observe efficient Brillouin scattering generated by an evanescent field nearby a single pass sub-wavelength waveguide. This work creates an important bridge between Brillouin scattering in waveguides, Brillouin spectroscopy and microscopy.
- Fan Yang
- , Flavien Gyger
- & Luc Thévenaz
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated dual-laser photonic chip for high-purity carrier generation enabling ultrafast terahertz wireless communications
Integrated dual-laser photonic chip for high-purity carrier generation enabling ultrafast terahertz wireless communications
A photonic Terahertz source based on injection-locking an integrated dual-laser chip generates and transmits a 131 Gbps THz signal over 10.7-m distance, showing great potential towards fully integrated and energy-efficient THz transmitters for 6G.
- Shi Jia
- , Mu-Chieh Lo
- & Leif K. Oxenløwe
-
Article
| Open Access λ/30 inorganic features achieved by multi-photon 3D lithography
λ/30 inorganic features achieved by multi-photon 3D lithography
Stereolithography has progressed over the years but resolution and feature size is still limited by the properties of materials and resins. Here, the authors demonstrate femtosecond laser direct writing of a hydrogen silsesquioxane photoresist using a 780 nm femtosecond laser demonstrating feature sizes of 26 nm.
- Feng Jin
- , Jie Liu
- & Xuan-Ming Duan
-
Article
| Open Access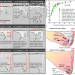 Keyhole fluctuation and pore formation mechanisms during laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing
Keyhole fluctuation and pore formation mechanisms during laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing
Understanding the keyhole porosity formation is important in laser powder bed fusion. Here the authors reveal the dynamics of keyhole fluctuation, and collapse that induces bubble formation with three main stages of evolution; growth, shrinkage, and being captured by the solidification front.
- Yuze Huang
- , Tristan G. Fleming
- & Peter D. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent optical communications using coherence-cloned Kerr soliton microcombs
Coherent optical communications using coherence-cloned Kerr soliton microcombs
Kerr frequency combs are a promising laser source for future optical networks. The authors demonstrate coherence-cloning between two remote Kerr combs and improve optical coherent communication in terms of performance, power consumption, and simplicity.
- Yong Geng
- , Heng Zhou
- & Kun Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access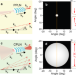 Wide-field mid-infrared single-photon upconversion imaging
Wide-field mid-infrared single-photon upconversion imaging
The authors present a simple yet effective solution to dramatically boost the performances of an upconversion imaging system, which leads to unprecedented mid-infrared imaging features with large field of view, single-photon sensitivity and a MHz-level frame rate.
- Kun Huang
- , Jianan Fang
- & Heping Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access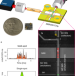 Fast custom wavelet analysis technique for single molecule detection and identification
Fast custom wavelet analysis technique for single molecule detection and identification
The authors introduce an accurate, fast and efficient technique to analyze sensory data. They use a continuous wavelet transform concept to look for certain patterns in noisy raw data. The superiority of this approach is demonstrated with fluorescence signals from a chip-based, optofluidic single particle sensor.
- Vahid Ganjalizadeh
- , Gopikrishnan G. Meena
- & Holger Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access Space-efficient optical computing with an integrated chip diffractive neural network
Space-efficient optical computing with an integrated chip diffractive neural network
Here, we propose the integrated diffractive optical network for implementing parallel Fourier transforms, convolution operations and application-specific optical computing with reduced footprint and energy consumption.
- H. H. Zhu
- , J. Zou
- & A. Q. Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Shaping lightwaves in time and frequency for optical fiber communication
Shaping lightwaves in time and frequency for optical fiber communication
The authors report nonlinear interference changes with shaping block length, modulation symbol rate, and chromatic dispersion when sphere-shaped lightwaves propagate through optical fibre, and suggest a method to predict that change.
- Junho Cho
- , Xi Chen
- & Robert Tkach
-
Article
| Open Access Perovskite multifunctional logic gates via bipolar photoresponse of single photodetector
Perovskite multifunctional logic gates via bipolar photoresponse of single photodetector
The authors present a novel all-in-one optoelectronic logic gates based on the bipolar spectral photo-response characteristics of self-powered perovskite photodetector. Five representative logic gates are demonstrated with only a single detector via photocurrent polarity control.
- Woochul Kim
- , Hyeonghun Kim
- & Yusin Pak
-
Article
| Open Access Operando monitoring of ion activities in aqueous batteries with plasmonic fiber-optic sensors
Operando monitoring of ion activities in aqueous batteries with plasmonic fiber-optic sensors
Operando tracking the ion dynamics/states of battery is critical to understanding of electrolyte-electrode interactions. Here the authors propose to use the surface plasmon waves to rapidly screen localized electrochemical events on a sub-μm-scale thickness adjacent to the electrode interface, without perturbing battery operation.
- Runlin Wang
- , Haozhe Zhang
- & Tuan Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrastable microwave and soliton-pulse generation from fibre-photonic-stabilized microcombs
Ultrastable microwave and soliton-pulse generation from fibre-photonic-stabilized microcombs
A compact yet high-performance stabilization method has been the missing ingredient for microcombs. Here, optical fibre is used for stabilizing microcombs, enabling the generation of ultrastable soliton pulses and microwaves from palm-sized platforms
- Dohyeon Kwon
- , Dongin Jeong
- & Jungwon Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Comparing ultrastable lasers at 7 × 10−17 fractional frequency instability through a 2220 km optical fibre network
Comparing ultrastable lasers at 7 × 10−17 fractional frequency instability through a 2220 km optical fibre network
Precision measurement plays an important role in frequency metrology and optical communications. Here the authors compare two geographically separate ultrastable lasers at 7 × 10−17 fractional frequency instability over a 2220 km optical fibre link and these measurements can be useful for dissemination of ultrastable light to distant optical clocks.
- M. Schioppo
- , J. Kronjäger
- & G. Grosche
-
Article
| Open Access Asymmetric topological pumping in nonparaxial photonics
Asymmetric topological pumping in nonparaxial photonics
The understanding of the topological properties of light is at the base of the future optical devices development. In this work the authors aim to suggesting a different paradigm for topological transport and manipulation of nonparaxial light, paving the way toward the new developments in the field of topological photonics
- Qingqing Cheng
- , Huaiqiang Wang
- & Yiming Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Revisiting silk: a lens-free optical physical unclonable function
Revisiting silk: a lens-free optical physical unclonable function
Although conventional optical physical unclonable functions (PUFs) are attractive for security applications, existing optical PUFs have inherent complexity. Here, the authors report a low-cost, lens-free and compact optical PUF that uses silk microfiber-based stochastic diffraction.
- Min Seok Kim
- , Gil Ju Lee
- & Young Min Song
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent phase transfer for real-world twin-field quantum key distribution
Coherent phase transfer for real-world twin-field quantum key distribution
Exploiting technologies derived from the optical clocks community, the authors demonstrate a setup for twin-field QKD which extends the coherence times by three orders of magnitude, overcoming the main challenge towards real-world implementation.
- Cecilia Clivati
- , Alice Meda
- & Davide Calonico
-
Article
| Open Access An optical neural network using less than 1 photon per multiplication
An optical neural network using less than 1 photon per multiplication
Though theory suggests that highly energy efficient optical neural networks (ONNs) based on optical matrix-vector multipliers are possible, an experimental validation is lacking. Here, the authors report an ONN with >90% accuracy image classification using <1 detected photon per scalar multiplication.
- Tianyu Wang
- , Shi-Yuan Ma
- & Peter L. McMahon
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated near-infrared spectral sensing
Integrated near-infrared spectral sensing
What are the minimal hardware requirements for a given class of sensing problems? Here, authors investigate this while proposing a miniaturized near-infrared spectral sensor, based on an array of resonant-cavity enhanced photodetectors, and capable of operating without the need for spectral reconstruction.
- Kaylee D. Hakkel
- , Maurangelo Petruzzella
- & Andrea Fiore
-
Article
| Open Access Single-photon detection and cryogenic reconfigurability in lithium niobate nanophotonic circuits
Single-photon detection and cryogenic reconfigurability in lithium niobate nanophotonic circuits
The combination of superconducting nanowire single photon detectors and electro-optically reconfigurable circuits in a cryogenic environment is notoriously difficult to reach. Here, the authors realise this on a Lithium-Niobate-On-Insulator platform, reaching high speed modulation at a frequency up to 1 GHz.
- Emma Lomonte
- , Martin A. Wolff
- & Francesco Lenzini
-
Article
| Open Access Fast non-line-of-sight imaging with high-resolution and wide field of view using synthetic wavelength holography
Fast non-line-of-sight imaging with high-resolution and wide field of view using synthetic wavelength holography
Here, the authors present Synthetic Wavelength Holography, an approach for Non-Line-of-Sight imaging. By exploiting spectral correlations in scattered light, the authors transform real world surfaces such as walls or scatterers into High-Resolution, Wide-Field-of-View imaging portals that provide holograms of objects obscured from view.
- Florian Willomitzer
- , Prasanna V. Rangarajan
- & Oliver Cossairt
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo volumetric imaging of calcium and glutamate activity at synapses with high spatiotemporal resolution
In vivo volumetric imaging of calcium and glutamate activity at synapses with high spatiotemporal resolution
Adaptive optics (AO) corrects sample aberrations and allows high spatial resolution at depth in vivo. Here the authors report an AO method for Bessel focus; they apply AO Bessel focus scanning fluorescence microscopy to volumetric imaging and measure synaptic calcium and glutamate activity in vivo.
- Wei Chen
- , Ryan G. Natan
- & Na Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Architecture for microcomb-based GHz-mid-infrared dual-comb spectroscopy
Architecture for microcomb-based GHz-mid-infrared dual-comb spectroscopy
Chip-based architectures for mid-infrared gas sensing could enable many applications. In this direction, the authors demonstrate a microcomb-based dual-comb spectroscopy sensor with GHz resolution in the mid-IR band, with stability completely determined by a single high-Q microresonator.
- Chengying Bao
- , Zhiquan Yuan
- & Kerry J. Vahala
-
Article
| Open Access Low-latency time-of-flight non-line-of-sight imaging at 5 frames per second
Low-latency time-of-flight non-line-of-sight imaging at 5 frames per second
Non-line-of-sight imaging can recover the 3D geometry of hidden objects, but is limited by weak multibounce signals. Here, the authors introduce a multipixel time-of-flight NLOS imaging approach, combining array detectors and a fast algorithm, for live reconstruction of natural nonretroreflective objects.
- Ji Hyun Nam
- , Eric Brandt
- & Andreas Velten
-
Article
| Open Access Tracking Brownian motion in three dimensions and characterization of individual nanoparticles using a fiber-based high-finesse microcavity
Tracking Brownian motion in three dimensions and characterization of individual nanoparticles using a fiber-based high-finesse microcavity
Tracking of nanoparticle dynamics in solution often require labelling. Here, the authors use a high-finesse microcavity and simultaneously measure dispersive frequency shifts of three transverse modes, demonstrating 3D tracking of unlabelled single nanospheres, and quantitatively determine their physical properties.
- Larissa Kohler
- , Matthias Mader
- & David Hunger
-
Article
| Open Access Laser nano-filament explosion for enabling open-grating sensing in optical fibre
Laser nano-filament explosion for enabling open-grating sensing in optical fibre
Engineered stop bands to sense an ambient environment can enable many applications. Here, the authors demonstrate well-controlled processes to open high-aspect ratio nanoholes through optical fibre for Bragg gratings in the telecomm spectrum and to enable high-resolution refractive index sensing
- Keivan Mahmoud Aghdami
- , Abdullah Rahnama
- & Peter R. Herman
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced on-chip phase measurement by inverse weak value amplification
Enhanced on-chip phase measurement by inverse weak value amplification
Weak value amplification in a compact format can lead to improved measurement capabilities in practical applications. Here the authors demonstrate weak value amplification in an integrated photonic chip with a multimode interferometer.
- Meiting Song
- , John Steinmetz
- & Jaime Cardenas
-
Article
| Open Access Structuring total angular momentum of light along the propagation direction with polarization-controlled meta-optics
Structuring total angular momentum of light along the propagation direction with polarization-controlled meta-optics
Creating complex forms of structured light typically requires bulky optics and multiple interactions with incident light. Here the authors demonstrate versatile control over light’s polarization and orbital angular momentum along the propagation direction with a single metasurface.
- Ahmed H. Dorrah
- , Noah A. Rubin
- & Federico Capasso
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental demonstration of peripherally-excited antenna arrays
Experimental demonstration of peripherally-excited antenna arrays
Two-dimensional antennas that can create and steer narrow beams are of interest for modern communication systems. Here, the authors demonstrate a scalable antenna array design that performs these functions with fewer elements than standard approaches and excited only with peripheral sources.
- Ayman H. Dorrah
- & George V. Eleftheriades
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast optical circuit switching for data centers using integrated soliton microcombs
Ultrafast optical circuit switching for data centers using integrated soliton microcombs
Optical technologies could enable fast and power-efficient networks for data centers. Here, the authors report Si3N4 microcomb based ultrafast photonic switching to provide enhanced performance for data center applications.
- Arslan Sajid Raja
- , Sophie Lange
- & Hitesh Ballani
-
Article
| Open Access Angle-based wavefront sensing enabled by the near fields of flat optics
Angle-based wavefront sensing enabled by the near fields of flat optics
Generally, wavefronts are measured using angle-based sensors like the Shack-Hartmann sensor. Here, the authors present an angle-sensitive device that uses flat optics integrated on a focal plane array for compact wavefront sensing with improved resolution.
- Soongyu Yi
- , Jin Xiang
- & Zongfu Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Electro-optic spatial light modulator from an engineered organic layer
Electro-optic spatial light modulator from an engineered organic layer
Spatial light modulators (SLM) provide tailored light fields for many applications. Here, the authors present an SLM device based on an organic electro-optic material that manipulates the properties of individual pixels by electronic signals at speeds up to 50 MHz.
- Ileana-Cristina Benea-Chelmus
- , Maryna L. Meretska
- & Federico Capasso
-
Article
| Open Access On-chip terahertz isolator with ultrahigh isolation ratios
On-chip terahertz isolator with ultrahigh isolation ratios
Nonreciprocal devices are crucial in scientific research and practical applications at all frequencies. Here the authors demonstrate an integrated terahertz optical isolator based on the magneto-optical effect in a nonreciprocal resonator.
- Shixing Yuan
- , Liao Chen
- & Xinliang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Determination of X-ray detection limit and applications in perovskite X-ray detectors
Determination of X-ray detection limit and applications in perovskite X-ray detectors
The limit of X-ray detection is an important figure of merit for X-ray detectors, yet the suitability of method adopted from Currie’s 1968 paper and the following international standard is in doubt. Here, the authors propose a statistical model that correlates dark current and photo-current, show how it can be used to determine detection limit.
- Lei Pan
- , Shreetu Shrestha
- & Lei R. Cao
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrahigh-speed graphene-based optical coherent receiver
Ultrahigh-speed graphene-based optical coherent receiver
Graphene-based photodetectors have many advantages for applications. Here, the authors demonstrate a high-speed optical coherent receiver for optical communications based on graphene-on-plasmonic slot waveguide photodetectors.
- Yilun Wang
- , Xiang Li
- & Xinliang Zhang
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Evaluating measurement uncertainty in Brillouin distributed optical fibre sensors using image denoising
Evaluating measurement uncertainty in Brillouin distributed optical fibre sensors using image denoising
- Marcelo A. Soto
- , Zhisheng Yang
- & Luc Thévenaz
-
Article
| Open Access A self-healing ferroelectric liquid crystal electro-optic shutter based on vertical surface-relief grating alignment
A self-healing ferroelectric liquid crystal electro-optic shutter based on vertical surface-relief grating alignment
Ferroelectric liquid crystals (FLCs) have faster optical response times than nematic crystals, but they are also less robust to external shock. Here the authors develop an FLC geometry that reduces the sensitivity to external disruption through self-healing, making them more stable for applications.
- Peter J. M. Wyatt
- , James Bailey
- & J. Cliff Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Visible light photonic integrated Brillouin laser
Visible light photonic integrated Brillouin laser
In this work the authors demonstrate on-chip integration of Brillouin lasing operating at visible wavelengths, with engineered design for stable output. This technical and scientific advance will help develop integrated light sources for quantum computing or atomic and molecular spectroscopy.
- Nitesh Chauhan
- , Andrei Isichenko
- & Daniel J. Blumenthal
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance photonic transformers for DC voltage conversion
High-performance photonic transformers for DC voltage conversion
Conventional DC-DC converters rely on switching operations and energy storing components which face both noise and scaling difficulties. Here, the authors present an alternative design for a DC-to-DC converter based on closely coupled LEDs and photovoltaic cells, which exhibits high efficiency, low noise, and miniaturizability.
- Bo Zhao
- , Sid Assawaworrarit
- & Shanhui Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Wavelength conversion through plasmon-coupled surface states
Wavelength conversion through plasmon-coupled surface states
Semiconductor surface states often stand in the way of device performance, but here, the authors take advantage of them for wavelength conversion. They present a compact, passive conversion device insensitive to optical alignment by using plasmon-coupled surface states that enable the efficient conversion without nonlinear phenomena.
- Deniz Turan
- , Ping Keng Lu
- & Mona Jarrahi
-
Article
| Open Access Bidirectional interconversion of microwave and light with thin-film lithium niobate
Bidirectional interconversion of microwave and light with thin-film lithium niobate
Coherent conversion between optical and microwave photonics is needed for future quantum applications. Here, the authors combine thin-film lithium niobate and superconductor platforms as a hybrid electro-optic system to achieve high-efficiency frequency conversion between microwave and optical modes.
- Yuntao Xu
- , Ayed Al Sayem
- & Hong X. Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Full-duplex reflective beamsteering metasurface featuring magnetless nonreciprocal amplification
Full-duplex reflective beamsteering metasurface featuring magnetless nonreciprocal amplification
Metasurfaces promise complex functionalities in electromagnetic wave control. Here the authors present an architecture for full-duplex reflective beamsteering based on series-connected radiative patches and nonreciprocal phase shifters.
- Sajjad Taravati
- & George V. Eleftheriades
-
Article
| Open Access A low-noise photonic heterodyne synthesizer and its application to millimeter-wave radar
A low-noise photonic heterodyne synthesizer and its application to millimeter-wave radar
Photonics-based radars offer intriguing potential but face tradeoffs in tunability, complexity, and noise. Here the authors present microwave generation in a photonics platform by heterodyning of two low-noise, self-injection-locked lasers, and demonstrate its advantages in an FMCW radar system.
- Eric A. Kittlaus
- , Danny Eliyahu
- & Siamak Forouhar
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Adaptive optics
- Astronomical optics
- Atmospheric optics
- Displays
- Fibre optics and optical communications
- Integrated optics
- Laser material processing
- Microwave photonics
- Mid-infrared photonics
- Optical data storage
- Optical sensors
- Optoelectronic devices and components
- Solar energy and photovoltaic technology

 Fast encirclement of an exceptional point for highly efficient and compact chiral mode converters
Fast encirclement of an exceptional point for highly efficient and compact chiral mode converters