Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Spacer-free BODIPY fluorogens in antimicrobial peptides for direct imaging of fungal infection in human tissue
Spacer-free BODIPY fluorogens in antimicrobial peptides for direct imaging of fungal infection in human tissue
Functionalizing antimicrobial peptides with fluorescent groups is a useful strategy for imaging infection, but the tag can alter the performance of the probe. Here, the authors report a spacer-free method to directly functionalise an amino acid with a fluorogenic group and prepare peptide-based imaging agents for fungal infection.
- Lorena Mendive-Tapia
- , Can Zhao
- & Marc Vendrell
-
Article
| Open Access Lysosome triggered near-infrared fluorescence imaging of cellular trafficking processes in real time
Lysosome triggered near-infrared fluorescence imaging of cellular trafficking processes in real time
Real time cellular fluorescence imaging requires a probe that displays high degrees of localisation, low toxicity and good photostability. Here, the authors report a near infrared fluorophore that displays pH-sensitive fluorescence based on phenol/phenolate interconversion, showing real time imaging of cellular processes.
- Marco Grossi
- , Marina Morgunova
- & Donal F. O’Shea
-
Article
| Open Access A competitive and reversible deactivation approach to catalysis-based quantitative assays
A competitive and reversible deactivation approach to catalysis-based quantitative assays
Assays for catalytic systems—particularly ones with simple colorimetric readouts—are useful for the rapid evaluation of performance. Here, the authors report an assay based on a concurrent colour-forming reaction working across a wide range that can be stopped to allow measurements and subsequently restarted.
- Kazunori Koide
- , Matthew P. Tracey
- & Christopher J. Welch
-
Article
| Open Access Protein-targeted corona phase molecular recognition
Protein-targeted corona phase molecular recognition
Corona phase molecular recognition (CoPhMoRe) involves the deposition of a heteropolymer onto a nanoparticle surface, providing a recognition site for a given analyte. Here, the authors show that CoPhMoRe can be used to selectively detect proteins (fibrinogen) with high selectivity, including in a complex serum environment.
- Gili Bisker
- , Juyao Dong
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Article
| Open Access Nanopore sensing at ultra-low concentrations using single-molecule dielectrophoretic trapping
Nanopore sensing at ultra-low concentrations using single-molecule dielectrophoretic trapping
Nanopore sensors have shown tremendous potential for biomolecule sensing, though the diffusion-controlled capture can limit the speed of analysis. Here, the authors report a dielectrophoretic method to concentrate DNA near the tip of a nanopore, reducing the limit of detection by three orders of magnitude.
- Kevin J. Freedman
- , Lauren M. Otto
- & Joshua B. Edel
-
Article
| Open Access The microscopic structure of charge density waves in underdoped YBa2Cu3O6.54 revealed by X-ray diffraction
The microscopic structure of charge density waves in underdoped YBa2Cu3O6.54 revealed by X-ray diffraction
Near to the superconducting state, cuprates display spatially-periodic charge density variations. Here, the authors use x-ray diffraction to determine the microscopic structure, showing how charge density waves in underdoped YBa2Cu3O6.54break the symmetry of the superconducting layers.
- E. M. Forgan
- , E. Blackburn
- & S. M. Hayden
-
Article
| Open Access In situ X-ray diffraction and the evolution of polarization during the growth of ferroelectric superlattices
In situ X-ray diffraction and the evolution of polarization during the growth of ferroelectric superlattices
X-ray diffraction provides valuable information on the crystalline order of materials, such as the spacing of atomic layers. Here, the authors demonstrate rapid in situX-ray diffraction measurements of strained ferroelectric oxide thin film superlattices during their layer-by-layer deposition.
- Benjamin Bein
- , Hsiang-Chun Hsing
- & Matthew Dawber
-
Article
| Open Access Brightness-equalized quantum dots
Brightness-equalized quantum dots
Quantum dots with different size emit light at different wavelengths but also different brightness, which complicates analysis of fluorescence images. Here, the authors synthesize multicolour brightness-equalized quantum dots by controlling the composition and structure of core-shell HgCdSeS-CdZnS nanocrystals.
- Sung Jun Lim
- , Mohammad U. Zahid
- & Andrew M. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible and self-powered temperature–pressure dual-parameter sensors using microstructure-frame-supported organic thermoelectric materials
Flexible and self-powered temperature–pressure dual-parameter sensors using microstructure-frame-supported organic thermoelectric materials
The construction of electronic skin requires simultaneous temperature and pressure detection. Here Zhang et al. utilize independent thermoelectric and piezoresistive effect in a single self-powered device, which shows a temperature resolution of <0.1 K and a pressure sensitivity of 28.9 kPa−1.
- Fengjiao Zhang
- , Yaping Zang
- & Daoben Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast multidimensional Laplace NMR for a rapid and sensitive chemical analysis
Ultrafast multidimensional Laplace NMR for a rapid and sensitive chemical analysis
Laplace NMR provides complementary information to traditional NMR, such as details of molecular motion. Here, the authors report a correlation experiment capable of providing information on the physical environment of molecules while enhancing the chemical resolution and greatly reducing the experiment times.
- Susanna Ahola
- , Vladimir V Zhivonitko
- & Ville-Veikko Telkki
-
Article
| Open Access Covalency of hydrogen bonds in liquid water can be probed by proton nuclear magnetic resonance experiments
Covalency of hydrogen bonds in liquid water can be probed by proton nuclear magnetic resonance experiments
Covalency is a fundamental concept in chemical bonding, but experimentally it is not possible to measure the degree of covalency of a particular bond. Here, the authors report a model to link the covalency of hydrogen bonds in water with the anisotropy of the magnetic shielding tensor in the proton NMR.
- Hossam Elgabarty
- , Rustam Z. Khaliullin
- & Thomas D. Kühne
-
Article
| Open Access Unambiguous detection of nitrated explosive vapours by fluorescence quenching of dendrimer films
Unambiguous detection of nitrated explosive vapours by fluorescence quenching of dendrimer films
Selective standoff detection of explosives is challenging due to the presence of volatile interferents. Here, the authors report dendrimer thin films that display distinct fluorescence responses when exposed to explosives as opposed to common interferents, allowing selective detection of nitrated explosives.
- Yan Geng
- , Mohammad A. Ali
- & Paul E. Shaw
-
Article
| Open Access Polarization-resolved spectroscopy imaging of grain boundaries and optical excitations in crystalline organic thin films
Polarization-resolved spectroscopy imaging of grain boundaries and optical excitations in crystalline organic thin films
In-depth understanding of organic crystalline semiconductor thin films is critical for the development of many electronic and photonic devices. Here, the authors use combined linear dichroism and polarization-resolved photoluminescence scanning microscopy to unveil the nature of excited states in such systems.
- Z. Pan
- , N. Rawat
- & M. Furis
-
Article
| Open Access Combined operando X-ray diffraction–electrochemical impedance spectroscopy detecting solid solution reactions of LiFePO4 in batteries
Combined operando X-ray diffraction–electrochemical impedance spectroscopy detecting solid solution reactions of LiFePO4 in batteries
A clear understanding of the phase behaviour of lithium-ion electrode materials is essential for the development of the field. Here, the authors report a combined X-ray diffraction–electrochemical impedance spectroscopy method to detect solid solution reactions of LiFePO4.
- Michael Hess
- , Tsuyoshi Sasaki
- & Petr Novák
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast visualization of crystallization and grain growth in shock-compressed SiO2
Ultrafast visualization of crystallization and grain growth in shock-compressed SiO2
Pressure- and temperature-induced phase transitions have long been studied, but little is known about the processes by which the atoms rearrange. Here, the authors presentin situmeasurements on shock compressed fused silica, revealing an amorphous to crystalline high pressure stishovite phase transition.
- A. E. Gleason
- , C. A. Bolme
- & W. L. Mao
-
Review Article
| Open Access Wet-chemical synthesis and applications of non-layer structured two-dimensional nanomaterials
Wet-chemical synthesis and applications of non-layer structured two-dimensional nanomaterials
There is currently intensive research underway into the development of non-layer structured two dimensional nanomaterials. Here, Zhang et al.review the research progress on the most promising wet-chemical synthesis methods as well as a wide range of applications of this unique class of materials.
- Chaoliang Tan
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Hydride bridge in [NiFe]-hydrogenase observed by nuclear resonance vibrational spectroscopy
Hydride bridge in [NiFe]-hydrogenase observed by nuclear resonance vibrational spectroscopy
Understanding the catalytic mechanism of redox-active hydrogenases is a key to efficient hydrogen production and consumption. Here, the authors use nuclear resonance vibrational spectroscopy to study [NiFe]-hydrogenase, and observe a bridging hydride structure in an EPR silent intermediate.
- Hideaki Ogata
- , Tobias Krämer
- & Stephen P. Cramer
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular propeller effect for chiral separation and analysis
A molecular propeller effect for chiral separation and analysis
Separation and analysis of enantiomers is a difficult task due to the normally identical physical properties they display. Here, the authors show how chiral molecules with non-zero dipoles can be propelled in opposite directions under the influence of a rotating electric field.
- Jonathon B. Clemens
- , Osman Kibar
- & Mirianas Chachisvilis
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of phases, symmetries and defects through local crystallography
Identification of phases, symmetries and defects through local crystallography
High-resolution microscopy methods provide a rich source of information, and allow highly precise measurements of atomic coordinates. Here, the authors report a method for quantitative analysis of material structures using multivariate statistical analysis to identify and distinguish various phases, defects and symmetries.
- Alex Belianinov
- , Qian He
- & Sergei V. Kalinin
-
Article
| Open Access Noble metal-comparable SERS enhancement from semiconducting metal oxides by making oxygen vacancies
Noble metal-comparable SERS enhancement from semiconducting metal oxides by making oxygen vacancies
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy is widely used for rapid and sensitive molecular detection in chemistry and biology, but typically relies on noble metals. Here the authors report a non-stoichiometric semiconducting material with defect-rich surface that displays excellent detection limits and enhancement factors.
- Shan Cong
- , Yinyin Yuan
- & Zhigang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Hot electron-induced reduction of small molecules on photorecycling metal surfaces
Hot electron-induced reduction of small molecules on photorecycling metal surfaces
Hot electrons are generated when energy is transferred from an incoming photon, enabling an electron from a metal surface to become mobile. Here, the authors irradiate plasmonically active silver core-satellite superstructures and use the hot electrons to effect chemical reactions via photorecycling.
- Wei Xie
- & Sebastian Schlücker
-
Article
| Open Access Enantiomer-specific analysis of multi-component mixtures by correlated electron imaging–ion mass spectrometry
Enantiomer-specific analysis of multi-component mixtures by correlated electron imaging–ion mass spectrometry
Detecting enantiomers in dilute mixtures of volatile organic compounds is a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a method to identify enantiomers and enantiomeric excess in a multi-component mixture containing two chiral species using laser mass spectrometry and photoelectron circular dichroism.
- Mohammad M Rafiee Fanood
- , N. Bhargava Ram
- & Maurice H. M. Janssen
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic sensing of organic solvents through geometric study of dynamic reflection spectrum
Photonic sensing of organic solvents through geometric study of dynamic reflection spectrum
Photonic sensing is a method for detecting individual chemical species, but can fail when they are sufficiently similar in physical properties. Here, the authors report a method that can distinguish even very closely related species, such as homologues and chemical isomers.
- Yuqi Zhang
- , Qianqian Fu
- & Jianping Ge
-
Article
| Open Access STED nanoscopy with fluorescent quantum dots
STED nanoscopy with fluorescent quantum dots
STED nanoscopy enables sub-diffraction imaging with a wide range of fluorescent probes. Here, the authors show that a bright and very photostable class of fluorescent quantum dots can be super-resolved with STED as biolabels in cellular contexts.
- Janina Hanne
- , Henning J. Falk
- & Stefan W. Hell
-
Article
| Open Access Radiolysis as a solution for accelerated ageing studies of electrolytes in Lithium-ion batteries
Radiolysis as a solution for accelerated ageing studies of electrolytes in Lithium-ion batteries
The degradation of organic solvents used in lithium-ion batteries reduces battery performance. Here, the authors present a radiolysis technique which is not only more efficient than conventional thermally activated ageing methods, but also allows mechanistic analysis of the degradation process.
- Daniel Ortiz
- , Vincent Steinmetz
- & Sophie Le Caër
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive visual read-out of nucleic acids using electrocatalytic fluid displacement
Ultrasensitive visual read-out of nucleic acids using electrocatalytic fluid displacement
Point-of-care analytical devices are of interest for diagnostic applications where larger scale laboratory instruments are not feasible or available. Here, the authors present a direct read-out colorimetric sensor which uses catalytic gas production to visualize picomolar concentrations of DNA.
- Justin D. Besant
- , Jagotamoy Das
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
Article |
 Locating and classifying fluorescent tags behind turbid layers using time-resolved inversion
Locating and classifying fluorescent tags behind turbid layers using time-resolved inversion
Fluorescent patches can be localized in 3D and identified behind a diffusive layer by use of streak images taken from one horizontal line on the diffusive barrier. Satat et al. show that the time-resolved inversion along with sparse prior can be used to perform this with deeper recovery range.
- Guy Satat
- , Barmak Heshmat
- & Ramesh Raskar
-
Article |
 Rational design of a chalcogenopyrylium-based surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering nanoprobe with attomolar sensitivity
Rational design of a chalcogenopyrylium-based surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering nanoprobe with attomolar sensitivity
Raman imaging offers great potential in biomedical imaging due to the combination of specificity and sensitivity. Here, the authors show nanoparticles functionalized with a chalcogenopyrylium reporter molecule, giving bright probes with low limits of detection for in vivoimaging.
- Stefan Harmsen
- , Matthew A. Bedics
- & Moritz F. Kircher
-
Article |
 A graphene field-effect transistor as a molecule-specific probe of DNA nucleobases
A graphene field-effect transistor as a molecule-specific probe of DNA nucleobases
The development of improved DNA sequencing technologies relies on the ability to distinguish each of the four DNA nucleobases separately. Here, the authors fabricate a graphene field-effect transistor able to experimentally observe individual DNA nucleobases.
- Nikolai Dontschuk
- , Alastair Stacey
- & Jiri Cervenka
-
Article |
 In situ X-ray diffraction monitoring of a mechanochemical reaction reveals a unique topology metal-organic framework
In situ X-ray diffraction monitoring of a mechanochemical reaction reveals a unique topology metal-organic framework
Ball milling chemical reactions are of interest due to their environmental credentials and potential to achieve new reactions and materials. Here, the authors isolate a metastable material with a previously unknown net topology by in situmonitoring of the mechanosynthesis of a metal organic framework.
- Athanassios D. Katsenis
- , Andreas Puškarić
- & Tomislav Friščić
-
Article
| Open Access Neutral particle mass spectrometry with nanomechanical systems
Neutral particle mass spectrometry with nanomechanical systems
Mass spectrometry (MS) involves ionization of analytes with spectra dependent upon the mass-to-charge ratio. Here, the authors demonstrate that MS based on nanoelectromechanical systems gives results that are independent of the charge state and allow the mass spectrum of neutral species to be obtained.
- Eric Sage
- , Ariel Brenac
- & Sébastien Hentz
-
Article |
 Direct mechanochemical cleavage of functional groups from graphene
Direct mechanochemical cleavage of functional groups from graphene
Breaking chemical bonds with mechanical force can be a useful route to modify chemical species, but studying the process in detail can be challenging. Here, the authors use atomic force microscopy to apply pressure and monitor bond cleavage on chemically modified graphene.
- Jonathan R. Felts
- , Andrew J. Oyer
- & Paul E. Sheehan
-
Article
| Open Access Electron paramagnetic resonance imaging for real-time monitoring of Li-ion batteries
Electron paramagnetic resonance imaging for real-time monitoring of Li-ion batteries
It is important as well as challenging to in situ probe redox mechanisms occurring at battery electrodes. Here, the authors develop an in situelectron paramagnetic resonance imaging technique and provide measurements on the nucleation growth of the anionic and cationic redox species at a battery electrode.
- M. Sathiya
- , J.-B. Leriche
- & H. Vezin
-
Article |
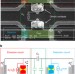 Detecting noise with shot noise using on-chip photon detector
Detecting noise with shot noise using on-chip photon detector
The detection of high-frequency radiation emitted by a quantum conductor is promising but current approaches exhibit limited sensitivity. Here, Jompol et al. propose on-chip radiation detection based on photo-assisted shot noise and show the response to be independent of the nature and geometry of the quantum conductor.
- Y. Jompol
- , P. Roulleau
- & D. C. Glattli
-
Article
| Open Access Capacitance-modulated transistor detects odorant binding protein chiral interactions
Capacitance-modulated transistor detects odorant binding protein chiral interactions
Organic bioelectronic devices can be used to convert biological recognition events to a signal output. Here, the authors show how a water gated field-effect transistor modified with odorant binding proteins can be used to analyse the enantioselectivity of carvone binding and also estimate free-energy changes.
- Mohammad Yusuf Mulla
- , Elena Tuccori
- & Luisa Torsi
-
Article |
 Nanoscale visualization of redox activity at lithium-ion battery cathodes
Nanoscale visualization of redox activity at lithium-ion battery cathodes
It is important as well as challenging to map out redox activity at battery electrodes. Here, the authors present a scanning electrochemical cell microscope approach, which allows redox activity and ion flux processes at battery electrodes to be visualized with high space and time resolution.
- Yasufumi Takahashi
- , Akichika Kumatani
- & Tomokazu Matsue
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid detection of single bacteria in unprocessed blood using Integrated Comprehensive Droplet Digital Detection
Rapid detection of single bacteria in unprocessed blood using Integrated Comprehensive Droplet Digital Detection
Early detection of blood stream infections is essential for providing effective treatments. Here the authors present a system integrating DNAzyme sensors, droplet microfluidics and a high-throughput 3D particle counter that can detect specific, single bacterial cells in blood within a few hours.
- Dong-Ku Kang
- , M. Monsur Ali
- & Weian Zhao
-
Article |
 Quantification of plasma HIV RNA using chemically engineered peptide nucleic acids
Quantification of plasma HIV RNA using chemically engineered peptide nucleic acids
There is a great need for inexpensive and sensitive tests to measure HIV viral load in patients’ samples. Here, Zhao et al. describe a cost-effective colorimetric method based on synthetic peptide nucleic acids that quantifies HIV RNA molecules from infected patients’ plasma.
- Chao Zhao
- , Travis Hoppe
- & Daniel H. Appella
-
Article |
 Ultra-sensitive optical oxygen sensors for characterization of nearly anoxic systems
Ultra-sensitive optical oxygen sensors for characterization of nearly anoxic systems
Accurately detecting low concentrations of oxygen is important in many fields, but current detection systems have limited sensitivity. Here, the authors report sensor materials based on phosphorescent boron or aluminium complexes in perfluorinated polymers, capable of detecting oxygen down to picomolar levels.
- Philipp Lehner
- , Christoph Staudinger
- & Ingo Klimant
-
Article |
 Coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering with single-molecule sensitivity using a plasmonic Fano resonance
Coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering with single-molecule sensitivity using a plasmonic Fano resonance
The field enhancements arising in plasmonic nanostructures make them ideal as substrates for molecular sensors. In this study, Zhang et al.achieve single molecule sensitivity with Fano resonances in a quadrumer nanostructure and coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy.
- Yu Zhang
- , Yu-Rong Zhen
- & Naomi J. Halas
-
Article |
 Taking snapshots of photosynthetic water oxidation using femtosecond X-ray diffraction and spectroscopy
Taking snapshots of photosynthetic water oxidation using femtosecond X-ray diffraction and spectroscopy
Photosystem II is the biosynthetic machinery that allows the conversion of water to oxygen using light. Here, the authors combine X-ray emission and diffraction data to probe the structural changes that take place during photosystem II catalysis.
- Jan Kern
- , Rosalie Tran
- & Vittal K. Yachandra
-
Article |
 Supersensitive fingerprinting of explosives by chemically modified nanosensors arrays
Supersensitive fingerprinting of explosives by chemically modified nanosensors arrays
Reliable detection and identification of explosives is difficult due to the large numbers of compounds and the trace amount of material with which to work. Here, the authors show a nanosensor array capable of fingerprinting individual explosives and detecting them down to the parts-per-quadrillion concentration range.
- Amir Lichtenstein
- , Ehud Havivi
- & Fernando Patolsky
-
Article
| Open Access A liquid crystalline chirality balance for vapours
A liquid crystalline chirality balance for vapours
Chiral determination of vapours is possible in biological systems as an important part of the olfactory system. Here, the authors describe a system that is capable of visually detecting and distinguishing the chirality of vapour-phase molecules by structural changes in a liquid crystal confined in open microchannels.
- Takuya Ohzono
- , Takahiro Yamamoto
- & Jun-ichi Fukuda
-
Article |
 Robust and versatile ionic liquid microarrays achieved by microcontact printing
Robust and versatile ionic liquid microarrays achieved by microcontact printing
Ionic liquids are widely used in diverse applications as solvents with high thermal and chemical stability. Gunawan et al.develop a protocol for fabrication of an ionic liquid microdroplet array using a soft lithography technique, and demonstrate its utility as a membrane-free high-performance gas sensor.
- Christian A. Gunawan
- , Mengchen Ge
- & Chuan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrochromic conjugated polymers for human sweat pore mapping
Hydrochromic conjugated polymers for human sweat pore mapping
Materials capable of colour changes in response to stimuli are useful in sensors and other applications. Here the authors show a conjugated polymer that rapidly responds to the presence of water, and use it as a sensor to map active sweat pores as a means of fingerprint analysis.
- Joosub Lee
- , Minkyeong Pyo
- & Jong-Man Kim
-
Article |
 Multimodal label-free detection and discrimination for small molecules using a nanoporous resonator
Multimodal label-free detection and discrimination for small molecules using a nanoporous resonator
When molecules bind to a cantilever, their resonant frequency shifts, providing a sensitive molecular detection scheme. Park et al.coat the surfaces of such resonators with nanoporous gold, enabling them to discriminate between molecules via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy.
- Jinsung Park
- , Doyeon Bang
- & Sungsoo Na
-
Article
| Open Access Hydride ions in oxide hosts hidden by hydroxide ions
Hydride ions in oxide hosts hidden by hydroxide ions
The oxidation state of hydride ions in oxide hosts is a matter of debate. Here, the authors address this question with a range of techniques and suggest that the electron density near an incorporated hydride ion is less than that at the hydrogen in a hydroxide ion, contrary to formal valence arguments.
- Katsuro Hayashi
- , Peter V. Sushko
- & Hideo Hosono
-
Article |
 Integrated circuit-based electrochemical sensor for spatially resolved detection of redox-active metabolites in biofilms
Integrated circuit-based electrochemical sensor for spatially resolved detection of redox-active metabolites in biofilms
The direct detection of metabolites secreted by cells can indicate how cellular dynamics affects population development. Here, the authors present an integrated circuit-based method for electrochemical imaging of redox-active signalling molecules with spatial resolution within bacterial colonies.
- Daniel L. Bellin
- , Hassan Sakhtah
- & Kenneth L. Shepard
-
Article |
 Highly stable organic polymer field-effect transistor sensor for selective detection in the marine environment
Highly stable organic polymer field-effect transistor sensor for selective detection in the marine environment
Field-effect transistors are widely used for environmental sensing and monitoring applications. Here, the authors present an organic field-effect transistor with the inherent advantages of low-cost and scalable fabrication, and which is sufficiently stable to be deployed in marine environments.
- Oren Knopfmacher
- , Mallory L. Hammock
- & Zhenan Bao

 Understanding silicate hydration from quantitative analyses of hydrating tricalcium silicates
Understanding silicate hydration from quantitative analyses of hydrating tricalcium silicates