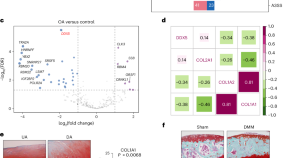
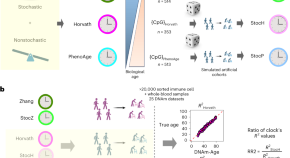
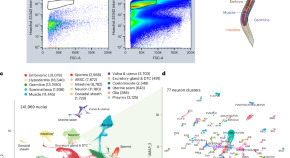
Featured

Announcements
-
-
-
-

Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals
Open for submissions
Advertisement
-
-

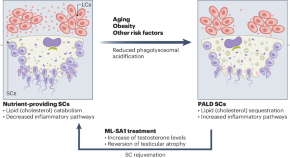
Small extracellular vesicles are rejuvenating factors in young blood
Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) derived from the blood of young mice are shown to have the potential to extend lifespan and rejuvenate physiological functions in aged mice. Mechanistically, microRNA (miRNA) cargoes within these sEVs alleviated age-related dysfunction by promoting the expression of PGC1α and enhancing mitochondrial energy metabolism.
-
-
Cancer and aging
This cross-journal Collection invites original research that explicitly explores the role of aging in cancer and vice versa, from the bench to the bedside.
Trending - Altmetric
-
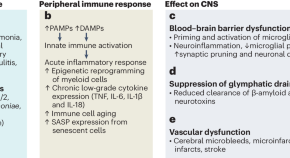
SGLT2 inhibition eliminates senescent cells and alleviates pathological aging
-
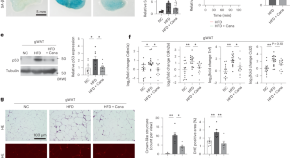
Small extracellular vesicles from young plasma reverse age-related functional declines by improving mitochondrial energy metabolism
-
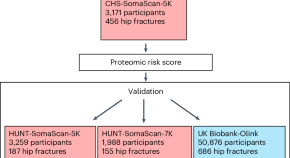
A plasma protein-based risk score to predict hip fractures
-
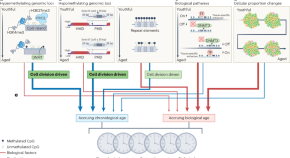
Aging atlas reveals cell-type-specific effects of pro-longevity strategies