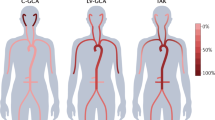
Abstract
The introduction of targeted biologic agents directed against tumor necrosis factor (TNF) has represented a novel and exciting avenue for investigation into therapies for the vasculitic diseases. In vasculitic diseases that are associated with granuloma formation, anti-TNF agents are a particularly attractive approach to treatment in that their mechanism of action targets immunologic pathways that are thought to have a role in disease pathogenesis. To date, a number of important trials have investigated the use of anti-TNF agents in patients with a vasculitic disease: most notably, Wegener's granulomatosis, giant-cell arteritis, Takayasu's arteritis, and Behçet's disease. Randomized, placebo-controlled trials of anti-TNF therapies for vasculitic diseases have advanced our knowledge not only in terms of their clinical results but also by demonstrating that networks of researchers can conduct multicenter trials in these uncommon diseases. Experience with the use of anti-TNF agents in patients with Wegener's granulomatosis or giant-cell arteritis has emphasized the crucial role of randomized trials in determining whether a treatment is effective, even in the face of promising preliminary data. Caution is necessary in clinical practice until such data become available.Box 1
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Laar JA et al. (2007) Adalimumab: a new modality for Behçet's disease? Ann Rheum Dis 66: 565–566
Ahmed MM et al. (2007) Treatment of refractory temporal arteritis with adalimumab. Clin Rheumatol 26: 1353–1355
Mushtaq B et al. (2007) Adalimumab for sight-threatening uveitis in Behçet's disease. Eye 21: 824–825
Tato F et al. (2005) Refractory Takayasu's arteritis successfully treated with the human, monoclonal anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody adalimumab. Int Angiol 24: 304–307
Weyand CM and Goronzy JJ (2003) Medium- and large-vessel vasculitis. N Engl J Med 349: 160–169
Weyand CM et al. (2005) Vascular dendritic cells in giant cell arteritis. Ann NY Acad Sci 1062: 195–208
Jennette JC et al. (2006) Pathogenesis of vascular inflammation by anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 1235–1242
Csernok E et al. (2006) Wegener autoantigen induces maturation of dendritic cells and licenses them for TH1 priming via the protease-activated receptor-2 pathway. Blood 107: 4440–4448
Ludviksson BR et al. (1998) Active Wegener's granulomatosis is associated with HLA-DR+ CD4+ T cells exhibiting an unbalanced TH1-type T cell cytokine pattern: reversal with IL-10. J Immunol 160: 3602–3609
Pay S et al. (2007) Immunopathogenesis of Behçet's disease with special emphasis on the possible role of antigen presenting cells. Rheumatol Int 27: 417–424
Tripathy NK et al. (2006) High TNF-α and low IL-2 producing T cells characterize active disease in Takayasu's arteritis. Clin Immunol 118: 154–158
Stone JH et al. (2001) Etanercept combined with conventional treatment in Wegener's granulomatosis: a six-month open-label trial to evaluate safety. Arthritis Rheum 44: 1149–1154
Wegener's Granulomatosis Etanercept Trial (WGET) Research Group (2005) Etanercept plus standard therapy for Wegener's granulomatosis. N Engl J Med 352: 351–361
Stone JH et al. (2006) Solid malignancies among patients in the Wegener's Granulomatosis Etanercept Trial. Arthritis Rheum 54: 1608–1618
Aries PM et al. (2007) Biological therapies: new treatment options for ANCA-associated vasculitis? Expert Opin Biol Ther 7: 521–533
Mukhtyar C and Luqmani R (2005) Current state of tumour necrosis factor α blockade in Wegener's granulomatosis. Ann Rheum Dis 64 (Suppl 4): S31–S36
Lamprecht P et al. (2002) Effectiveness of TNF-α blockade with infliximab in refractory Wegener's granulomatosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41: 1303–1307
Booth AD et al. (2002) Safety and efficacy of TNFα blockade in relapsing vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 61: 559
Bartolucci P et al. (2002) Efficacy of the anti-TNF-α antibody infliximab against refractory systemic vasculitides: an open pilot study on 10 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41: 1126–1132
Booth A et al. (2004) Prospective study of TNFα blockade with infliximab in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated systemic vasculitis. J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 717–721
Cantini F et al. (2001) Treatment of longstanding active giant cell arteritis with infliximab: report of four cases. Arthritis Rheum 44: 2933–2935
Andonopoulos AP et al. (2003) Experience with infliximab (anti-TNF alpha monoclonal antibody) as monotherapy for giant cell arteritis. Ann Rheum Dis 62: 1116
Airo P et al. (2002) Anti-tumour necrosis factor treatment with infliximab in a case of giant cell arteritis resistant to steroid and immunosuppressive drugs. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41: 347–349
Tan AL et al. (2003) Successful treatment of resistant giant cell arteritis with etanercept. Ann Rheum Dis 62: 373–374
Hoffman GS et al. (2007) Infliximab for maintenance of glucocorticosteroid-induced remission of giant cell arteritis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 146: 621–630
Salvarani C et al. (2007) Infliximab plus prednisone or placebo plus prednisone for the initial treatment of polymyalgia rheumatica: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 146: 631–639
Hoffman GS et al. (2004) Anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in patients with difficult to treat Takayasu arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 50: 2296–2304
Della Rossa A et al. (2005) Two Takayasu arteritis patients successfully treated with infliximab: a potential disease-modifying agent? Rheumatology (Oxford) 44: 1074–1075
Karageorgaki ZT et al. (2007) Infliximab in Takayasu arteritis: a safe alternative? Clin Rheumatol 26: 984–987
Jolly M and Curran JJ (2005) Infliximab-responsive uveitis and vasculitis in a patient with Takayasu arteritis. J Clin Rheumatol 11: 213–215
Tanaka F et al. (2006) Infliximab is effective for Takayasu arteritis refractory to glucocorticoid and methotrexate. Intern Med 45: 313–316
Sfikakis PP et al. (2004) Infliximab for recurrent, sight-threatening ocular inflammation in Adamantiades–Behçet disease. Ann Intern Med 140: 404–406
Niccoli L et al. (2007) Long-term efficacy of infliximab in refractory posterior uveitis of Behçet's disease: a 24-month follow-up study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46: 1161–1164
Tugal-Tutkun I et al. (2005) Efficacy of infliximab in the treatment of uveitis that is resistant to treatment with the combination of azathioprine, cyclosporine, and corticosteroids in Behçet's disease: an open-label trial. Arthritis Rheum 52: 2478–2484
Ohno S et al. (2004) Efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of multiple administration of infliximab in Behçet's disease with refractory uveoretinitis. J Rheumatol 31: 1362–1368
Abu El-Asrar AM et al. (2005) Long-term safety and efficacy of infliximab therapy in refractory uveitis due to Behçet's disease. Int Ophthalmol 26: 83–92
Tognon S et al. (2007) Anti-TNF-alpha therapy in seven patients with Behçet's uveitis: advantages and controversial aspects. Ann NY Acad Sci 1110: 474–484
Benitez-del-Castillo JM et al. (2005) Long-term treatment of refractory posterior uveitis with anti-TNFalpha (infliximab). Eye 19: 841–845
Melikoglu M et al. (2005) Short-term trial of etanercept in Behçet's disease: a double blind, placebo controlled study. J Rheumatol 32: 98–105
Ju JH et al. (2007) Successful treatment of life-threatening intestinal ulcer in Behçet's disease with infliximab: rapid healing of Behçet's ulcer with infliximab. Clin Rheumatol 26: 1383–1385
Byeon JS et al. (2007) Antitumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy for early postoperative recurrence of gastrointestinal Behçet's disease: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum 50: 672–676
Endo LM et al. (2007) Pulmonary aneurysms and intracardiac thrombi due to Behçet's disease in an African-American adolescent with oculocutaneous albinism. Clin Rheumatol 26: 1537–1539
Baki K et al. (2006) Behçet's disease with life-threatening haemoptoe and pulmonary aneurysms: complete remission after infliximab treatment. Ann Rheum Dis 65: 1531–1532
Fujikawa K et al. (2007) Successful treatment of refractory neuro-Behçet's disease with infliximab: a case report to show its efficacy by magnetic resonance imaging, transcranial magnetic stimulation and cytokine profile. Ann Rheum Dis 66: 136–137
Alty JE et al. (2007) A patient with neuro-Behçet's disease is successfully treated with etanercept: further evidence for the value of TNFα blockade. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 109: 279–281
Sfikakis PP et al. (2007) Anti-TNF therapy in the management of Behçet's disease—review and basis for recommendations. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46: 736–741
Rosenbaum JT (2004) Blind insight: eyeing anti-tumor necrosis factor treatment in uveitis associated with Behçet's disease. J Rheumatol 31: 1241–1243
Burns JC et al. (2005) Infliximab treatment for refractory Kawasaki syndrome. J Pediatr 146: 662–667
Stenbog EV et al. (2006) The effect of TNFα blockade in complicated, refractory Kawasaki disease. Scand J Rheumatol 35: 318–321
Weiss JE et al. (2004) Infliximab as a novel therapy for refractory Kawasaki disease. J Rheumatol 31: 808–810
Arbach O et al. (2002) Treatment of refractory Churg–Strauss Syndrome (CSS) by TNF-alpha blockade. Immunobiology 206: 496–501
Tiliakos A et al. (2004) The use of infliximab in a patient with steroid-dependent Churg–Strauss syndrome. J Clin Rheumatol 10: 96–97
Al-Bishri J et al. (2005) Refractory polyarteritis nodosa successfully treated with infliximab. J Rheumatol 32: 1371–1373
Wu K and Throssell D (2006) A new treatment for polyarteritis nodosa. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21: 1710–1712
Vega Gutierrez J et al. (2007) Successful treatment of childhood cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa with infliximab. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 21: 570–571
Mang R et al. (2004) Therapy for severe necrotizing vasculitis with infliximab. J Am Acad Dermatol 51: 321–322
Uthman IW et al. (2005) Response of deep cutaneous vasculitis to infliximab. J Am Acad Dermatol 53: 353–354
Chandesris MO et al. (2004) Infliximab in the treatment of refractory vasculitis secondary to hepatitis C-associated mixed cryoglobulinaemia. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43: 532–533
ClinicalTrials.gov [http://www.clinicaltrials.gov]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author has received grant and/or research support (including for clinical trials) from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Genentech.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Langford, C. Drug Insight: anti-tumor necrosis factor therapies for the vasculitic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 4, 364–370 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncprheum0825
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncprheum0825
This article is cited by
-
Regulation of tumour necrosis factor signalling: live or let die
Nature Reviews Immunology (2015)
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors in patients with Takayasu's arteritis refractory to standard immunosuppressive treatment: cases series and review of the literature
Clinical Rheumatology (2013)