Featured
-
-
Review
| Open Access Leveraging mechanochemistry for sustainable polymer degradation
Leveraging mechanochemistry for sustainable polymer degradation
Mechanochemistry is a promising technology to tackle current and future polymer waste streams for a sustainable future. With this review, we take into account synthetic, computational, technical, and engineering perspectives to converge trituration and polymer mechanochemistry with a particular focus on the fate of commodity polymers and potential technologies to monitor mechanochemical reactions while they occur. We highlight the need for future transdisciplinary research to tackle the high-leverage parameters governing an eventually successful mechanochemical polymer degradation approach for a circular economy.
- Simay Aydonat
- , Adrian H. Hergesell
- & Robert Göstl
-
Rapid Communication
| Open Access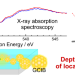 Depth analysis of local conformation in poly(methyl methacrylate) adsorbed onto SiOx studied by soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy combined with an Ar gas cluster ion beam
Depth analysis of local conformation in poly(methyl methacrylate) adsorbed onto SiOx studied by soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy combined with an Ar gas cluster ion beam
The aggregation states from the interface to the bulk of the adhesive/adherend is a key to unraveling adhesion at the molecular level. We applied X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) in combination with an Ar gas cluster ion beam (Ar GCIB) to poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) films adsorbed onto a SiOx/Si(111) surface. GCIB-XAS analysis revealed that the orientation of the C=O group in the side chain of PMMA differs between the region from the SiOx interface to a distance on the order of 1 nanometer and the bulk PMMA region.
- Hiroyuki Yamane
- , Masaki Oura
- & Takaki Hatsui
-
Original Article
| Open Access Evaluation of pigment distribution in contact lenses with iris patterns by multiprobe analysis methods
Evaluation of pigment distribution in contact lenses with iris patterns by multiprobe analysis methods
We propose a simple method to detect depth information of ink components and pigment distribution observed by transmission electron microscopy on commercially available cosmetic contact lenses using multiple probes such as STEM EDS, XPS, HAXPES, and XAFS. These provide important information on the safety of cosmetic contact lenses, which are medical devices.
- Eri Ito
- , Hiroshi Takase
- & Katsuhiro Yamamoto
-
Focus Review
| Open Access Visualization of Nanomechanical Properties of Polymer Composites Using Atomic Force Microscopy
Visualization of Nanomechanical Properties of Polymer Composites Using Atomic Force Microscopy
Atomic force microscopy (AFM)-based nanomechanical characterization techniques have been extensively used to investigate the mechanical properties and mechanisms of polymeric materials. This technique enables direct visualization of the micromechanical properties of material surfaces and is referred to as the AFM nanomechanics technique. This review article discusses the application of this technique to studying polymer composites with a specific focus on the significant advances made in tracking the microscopic deformation behavior and visualizing the microscopic stress distribution of materials.
- Xiaobin Liang
-
Original Article |
 Kinetics and morphologies of syndiotactic polystyrene crystallized isothermally over a wide temperature range
Kinetics and morphologies of syndiotactic polystyrene crystallized isothermally over a wide temperature range
Time-resolved FTIR was used to study the crystallization kinetics of syndiotactic polystyrene. Isothermal crystallization from the melt by cooling and from the glass by heating was used to determine the temperature (Tc) dependence of the crystallization rate (k). Based on the derived k and the crystal growth rates (G) obtained from OM and depolarized light scattering, the density of primary nucleation was readily calculated. The magnitudes of the nucleation densities in the cold-crystallized samples were ~5−6 orders higher than those of the melt-crystallized samples despite the similar k values.
- Chun-Yu Lo
- & Chi Wang
-
Original Article |
 Dispersion of submicron-sized SiO2/Al2O3-coated TiO2 particles and efficient encapsulation via the emulsion copolymerization of methacrylates using a thermoresponsive polymerizable nonionic surfactant
Dispersion of submicron-sized SiO2/Al2O3-coated TiO2 particles and efficient encapsulation via the emulsion copolymerization of methacrylates using a thermoresponsive polymerizable nonionic surfactant
Submicron-sized SiO2/Al2O3(Si/Al)-coated titanium dioxide (Si/Al-TiO2) particles were encapsulated through the emulsion copolymerization of methacrylates using a thermoresponsive polymerizable nonionic surfactant, NE-10. An optimized water-dispersion method was developed to disperse Si/Al-TiO2 dried powders using an ultrasonic homogenizer, a paint shaker, and a pot mill rotator in the presence of partially neutralized poly(isobutylene-alt-maleic acid). The encapsulation efficiency (Fen) was affected by the monomer and initiator types, NE-10, and sodium dodecyl sulfonate concentrations. Fen > 90% was achieved by a two-step semibatch emulsion copolymerization under optimized conditions.
- Md. Kamrul Hasan
- , Kazushi Enomoto
- & Seigou Kawaguchi
-
Original Article |
 Highly reliable determination of the interdetector delay volume in SEC-MALS for precise characterization of macromolecules having narrow and broad molar mass distributions
Highly reliable determination of the interdetector delay volume in SEC-MALS for precise characterization of macromolecules having narrow and broad molar mass distributions
The interdetector delay volumes (IDV) for multiangle light scattering (MALS) and differential refractometer detectors are essential instrumental parameters affecting reliability and accuracy. However, a reliable and accurate determination method has not yet been established. The paper proposes a method for determining the IDV value. An SEC-MALS setup with the correct IDV value provides more accurate estimates of not only the weight average molar mass and z-average mean-square radius of gyration but also the number average molar mass and differential weight distribution function for polymer samples having narrow and broad molar mass distributions.
- Yoshinori Matsumoto
- , Moriya Kikuchi
- & Seigou Kawaguchi
-
Original Article |
 Investigation of the chemical changes and mechanism of the epoxy-amine system by in situ infrared spectroscopy and two-dimensional correlation analysis
Investigation of the chemical changes and mechanism of the epoxy-amine system by in situ infrared spectroscopy and two-dimensional correlation analysis
In situ infrared spectroscopy and two-dimensional (2D) correlation analysis was applied to research the chemical changes and curing reaction mechanism of epoxy resin and amine curing agents. The curing reaction mechanism can be deeply understood from the results. Due to the nucleophilic addition reaction of amino and epoxy groups, the nitrogen atoms easily combine with the carbon atoms, which forms new C-N groups. Then, the C-O bonds break; finally, as the N-H bonds in primary amines break, the hydrogen atoms combine with the oxygen atoms to form new hydroxyl groups.
- Zhipeng He
- , Wei Lv
- & Qinwei Yin
-
Focus Review |
 Data-driven approaches for structure-property relationships in polymer science for prediction and understanding
Data-driven approaches for structure-property relationships in polymer science for prediction and understanding
In this review, recent developments in data-driven approaches for structure-property relationships in polymer science based on statistical/informatics methods are introduced. A concept and some methods in data-driven science to obtain the desired properties and understand the mechanisms in polymeric materials are first explained. Additionally, various examples, such as the description of a single chain, phase separations, network polymers, crystalline polymers, and machine learning potential are introduced.
- Yoshifumi Amamoto
-
Original Article |
 Morphological characterization of the novel fine structure of the PMMA/PVDF blend
Morphological characterization of the novel fine structure of the PMMA/PVDF blend
Using LV-STEM, we found that there were previously unseen nanoscale structures inside the blends of PMMA/PVDF. These structures were formed on the same scale that did not deviate from the size of a single molecular chain, regardless of the solution casting, melt mixing, mixing ratios, and even amorphous or crystalline state of PVDF. The characteristics of these structures were discussed in accordance with thermophysical properties and intermolecular interaction properties, which provides some new findings for the first time.
- Akihiro Naruke
- , Xiaobin Liang
- & Toshio Nishi
-
Original Article |
 Spatial inhomogeneity of chain orientation associated with strain-induced density fluctuations in polyethylene
Spatial inhomogeneity of chain orientation associated with strain-induced density fluctuations in polyethylene
We visualized the spatial inhomogeneity of chain orientation on the submicron scale in high-density polyethylene associated with strain-induced density fluctuations using STXM and USAXS/SAXS/WAXD. Real-space images of the density fluctuations were obtained with STXM at the strain where a butterfly pattern was observed with USAXS. STXM observation also revealed that the chains in the low-density region were more often oriented parallel to the stretching direction than those in the high-density region.
- Masato Arakawa
- , Mizuki Kishimoto
- & Mikihito Takenaka
-
Focus Review |
 Dry-jet wet spinning of β-1,3-glucan and α-1,3-glucan
Dry-jet wet spinning of β-1,3-glucan and α-1,3-glucan
Regenerated fibers of β-1,3-glucan (curdlan) and α-1,3-glucan were fabricated by dry-jet wet spinning, and the fiber properties and structures are summarized in this review. The flexible and water-absorbent curdlan and the stiff and strong α-1,3-glucan would be utilized in different applications from conventional cellulose. As a new type of post-treatment, a two-step stretching method in water was developed for α-1,3-glucan by utilizing its crystal transition. This can be applied to various polysaccharides for future production of high-performance fibers.
- Shiori Suzuki
- , Azusa Togo
- & Tadahisa Iwata
-
Original Article |
 Boosting sericin extraction through alternative silk sources
Boosting sericin extraction through alternative silk sources
Three different silk sources were explore for sericin (SS) extraction and film formation. Features of each raw material, especially the degree of processing, have remarkable effects on the primary structure and the presence of nonprotein compounds in the sericin extract. As a result, sericin films exhibited distinctive properties that seemed to be correlated with the amount of natural impurities and the molecular properties of the SS extract obtained from each raw material.
- Natalia Jaramillo-Quiceno
- , Emanuela Callone
- & Antonella Motta
-
Original Article |
 Enhanced in-plane thermal conductivity of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene films via a new design of a two-step biaxial stretching mode
Enhanced in-plane thermal conductivity of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene films via a new design of a two-step biaxial stretching mode
A mesh-like crystal structure of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) films is achieved through a two-step biaxial stretching mode to construct a planar-oriented crystal network. This mesh-like crystal network structure was investigated through scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and 1-dimensional wide-angle X-ray diffraction (1D-WXRD). The corresponding in-plane thermal conductivity increases to 7.3 W.m/K at a total draw ratio of 25, much higher than samples with single temperature biaxial stretching modes.
- Qi Zhang
- , Tianci Zhang
- & Shaoyun Guo
-
Original Article |
 Chemically modified bamboo fiber/ABS composites for high-quality additive manufacturing
Chemically modified bamboo fiber/ABS composites for high-quality additive manufacturing
To improve the 3-dimensional (3D) printed quality of bio-based composites, bamboo fibers were chemically modified via a two-step reaction. In the first step, NCO groups (of a diisocyanate) were grafted onto the surface of fibers, which were subsequently reacted with a polyol. Afterward, 3D-printed objects were produced using these fibers. The advantage of using treated fibers was reflected in the improved mechanical performance of the obtained 3D specimens.
- Nuno Gama
- , Sandra Magina
- & Ana Barros-Timmons
-
Original Article |
 Enhanced self-humidification and proton conductivity in magnetically aligned NiO-Co3O4/chitosan nanocomposite membranes for high-temperature PEMFCs
Enhanced self-humidification and proton conductivity in magnetically aligned NiO-Co3O4/chitosan nanocomposite membranes for high-temperature PEMFCs
Free-standing, tartaric acid cross-linked chitosan thin films doped with magnetically aligned NiO-Co3O4 filler were successfully synthesized using facile solution-casting method under externally applied magnetic field. The aligned membranes displayed higher proton conductivity than Nafion-212 when measured by both two-probe and four-probe techniques in zero humid conditions. The membranes also showed excellent thermal, oxidation, and mechanical stability.
- A. I. Anu Karthi Swaghatha
- & Louis Cindrella
-
Original Article |
 Nanoribbons fabricated by melt electrospinning
Nanoribbons fabricated by melt electrospinning
This study focuses on employing multilayer melt electrospinning of polymers coupled with a delamination step to obtain nonwoven webs of ribbon-shaped fibers. A coextrusion technique with layer multipliers was used to melt electrospin cylindrical microfibers that have up to 257 alternating layers within each fiber prior to delamination. The bicomponent layered cylindrical microfibers are delaminated using sonication or solvent rinsing to obtain flat nanoribbon fibers, that are 150 nanometers to 200 nanometers thick.
- Eugene G. Joseph
- , Naresh Budhavaram
- & Arit Das
-
Original Article |
 Solution-processable ambipolar organic field-effect transistors with bilayer transport channels
Solution-processable ambipolar organic field-effect transistors with bilayer transport channels
An efficient ambipolar organic transistor (A-OFET) based on the bilayer architecture of p-type poly(benzodithiophene(2-thienyl)-pyrrolopyrrole-dione) (PBDTTPPD) and n-type [6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM) was demonstrated. The A-OFET exhibits clear bipolar transport and operates as an n-type and a p-type transistor in a single device.
- Dal Yong Lee
- , Vellaiappillai Tamilavan
- & Sung Heum Park
-
Technical Review |
 Development of a spray-type adhesion barrier
Development of a spray-type adhesion barrier
A novel spray-type dextrin hydrogel-based adhesion barrier is composed of N-hydroxysuccinimide-modified carboxymethyl dextrin that is biodegradable polymer material. The performance evaluation of a spray-type adhesion barrier in porcine laparoscopic model was showed significantly lowered adhesion rate than in the control group (p < 0.001), and no hydrogel residue was observed macroscopically at the spraying site 28 ± 1 days after surgery.
- Naotaka Chino
- , Hiroyuki Ishihara
- & Tetsuro Kawanishi
-
Original Article |
 Fine-tuning of the surface porosity of micropatterned polyethersulfone membranes prepared by phase separation micromolding
Fine-tuning of the surface porosity of micropatterned polyethersulfone membranes prepared by phase separation micromolding
This work presents a method on tailoring open pores on the patterned surface of polyethersulfone membrane prepared by the phase separation micromolding. By modifying both the thermodynamics of the casting solution and the dynamics of solvent/nonsolvent demixing, micropatterned membrane with average surface open pores in the diameter of 1095 nm and porosity as high as 31.4% was achieved. The size and number of pores were different depending on their locations on the patterned surface, which was caused by different solvent/nonsolvent demixing dynamics resulting from the physical discontinuity of micro-patterned membranes.
- Yida Liu
- , Takashi Kodama
- & Yu Hoshino
-
Original Article |
 Flame retardancy and toughening modification of glass fiber-reinforced polycarbonate composites
Flame retardancy and toughening modification of glass fiber-reinforced polycarbonate composites
The toughness and flame retardancy of glass fiber (GF)-reinforced polycarbonate (PC) composites were tested by adding four impact modifiers and three kinds of flame reardants. Silicon acrylate rubber (SiR) could significantly toughen the composites by 2.52 times. Then only by addition of 0.2 wt% oligomeric siloxane-containing potassium dodecyl diphenylsulfone sulfonate (SiKSS), PC/GF/SiR composites can achieve good flame retardancy with a V0 rating in UL-94 burning vertical test. This formulation also maintained the system a relative high heat deflection temperature around 120 °C.
- Jun Lin
- , Jiao Li
- & Liang Chen
-
Original Article |
 Mechanical properties of microcellular and nanocellular silicone rubber foams obtained by supercritical carbon dioxide
Mechanical properties of microcellular and nanocellular silicone rubber foams obtained by supercritical carbon dioxide
Microcellular and nanocellular silicone rubber foam are prepared by supercritical carbon dioxide in this work. The tpre and Ps are important factors which affect the open-cell content (OCC). When the tpre and Ps increases, the OCC sharply improves and could reach to more than 96%. The OCC has a significant effect on the mechanical properties of the nano/micro silicone rubber foam.
- Bin Xiang
- , Yalan Jia
- & Shikai Luo
-
Original Article |
 Role of strain rate in the strain-induced crystallization (SIC) of natural and synthetic isoprene rubber
Role of strain rate in the strain-induced crystallization (SIC) of natural and synthetic isoprene rubber
The role of strain rate (\(\dot \varepsilon\)) in strain induced crystallization (SIC) of vulcanized natural rubber (NR) and synthetic isoprene rubber (IR) was studied by in-situ wide angle X-ray scattering (WAXS). The nucleation rate (I) was determined by measuring the slope on the plot of the scattering intensity (IX) as a function of time (t). Various I values were determined for various \(\dot \varepsilon\). On the plot of I vs. \(\dot \varepsilon\), we found that I is proportional to \(\dot \varepsilon\); I ∝ \(\dot \varepsilon\)
.
- Yuji Kitamura
- , Kiyoka Okada
- & Masamichi Hikosaka
-
Original Article |
 Microscopic structural response of nanoparticles in styrene–butadiene rubber under cyclic uniaxial elongation
Microscopic structural response of nanoparticles in styrene–butadiene rubber under cyclic uniaxial elongation
Changes in the aggregated structure of silica in styrene–butadiene rubber are measured with small-angle X-ray scattering under cyclic uniaxial elongation. We employ a spherical harmonics expansion approach to quantitatively analyze the anisotropic scattering data and to separate the anisotropic response of the silica’s configuration upon the elongation from the isotropic component. This study demonstrates that the combination of time-resolved small-angle scattering measurement and an analysis using spherical harmonics expansion is quite useful for exploring the structural response of filled rubber systems to an external deformation.
- Yuya Shinohara
- , Hiroyuki Kishimoto
- & Yoshiyuki Amemiya
-
Original Article |
 Relationship between twisting phenomenon and structural discontinuity of stacked lamellae in the spherulite of poly(ethylene adipate) as studied by the synchrotron X-ray microbeam technique
Relationship between twisting phenomenon and structural discontinuity of stacked lamellae in the spherulite of poly(ethylene adipate) as studied by the synchrotron X-ray microbeam technique
Designer supramolecular polymers are a growing field of polymer materials. The designability and flexibility in their structures and functionality have attracted a great deal of attention in polymer science, as well as in supramolecular chemistry. These polymeric structures are formed from one or more molecular components via reversible bonds; therefore, monomeric and polymeric states are in equilibrium on the relevant experimental timescale. The dynamic nature of supramolecular polymers in terms of chain lifetime and conformational flexibility are determined by external conditions. This adaptivity can result in stimuli-responsive structures and properties. This article describes the use of our host–guest structures based on a calix[5]arene, a bisporphyrin, and a self-assembled capsule in the synthesis of supramolecular polymers.
- Kohji Tashiro
- , Taiyo Yoshioka
- & Hiroki Murase
-
Original Article |
 Adhesion force measurement of live cypris tentacles by scanning probe microscopy in seawater
Adhesion force measurement of live cypris tentacles by scanning probe microscopy in seawater
The adhesion force between the tentacle of a live cypris and polymer brushes on the sidewall of cover glass was directly measured by scanning probe microscopy in seawater. The cypris was immobilized on the cantilever with glue, and then forced to make contact with the modified surface. When the tentacle was detached by moving the cantilever away from the surface, the torsion of the cantilever caused the laser deflection on the photodiode corresponding to the adhesion force. Polymer brush surfaces exhibited extremely low adhesion to the cypris larva.
- Shohei Shiomoto
- , Yuka Yamaguchi
- & Motoyasu Kobayashi
-
Focus Review |
 Interfacial morphologies and associated processes of multicomponent polymers
Interfacial morphologies and associated processes of multicomponent polymers
Interfacial morphologies and associated processes in multicomponent polymer systems, e.g., block copolymers (BCPs) and polymer blends, are examined using three-dimensional (3D) microscopies. Because of the rich structural information in 3D images, various new types of structural parameters, including chain conformation inside BCPs nanodomains, chain packing frustration in BCPs, Genus etc., can be obtained. The stability and interfacial dynamics are also discussed.
- Hiroshi Jinnai
-
Original Article |
 Multivariate analysis of 13C NMR spectra to extract information about monomer sequences in poly(methyl methacrylate-co-benzyl methacrylate)s prepared by various polymer reactions
Multivariate analysis of 13C NMR spectra to extract information about monomer sequences in poly(methyl methacrylate-co-benzyl methacrylate)s prepared by various polymer reactions
MMA-BnMA copolymers with various monomer sequences (blocky, random, alternating tendency) were prepared by partial modifications of atactic poly(BnMA) or by direct copolymerization of MMA and BnMA. 13C NMR spectra of the copolymers were subjected to principal component analysis, one of the standard procedures of multivariate analysis. The analysis showed clearly the formation of highly blocky copolymers by hydrogenolysis as well as the formation of copolymers with somewhat alternating tendency by the acidic debenzylation, saponification, and transesterification at late processes of the reactions.
- Yuchin Hsu
- , Mingyeh Chuang
- & Koichi Ute
-
Original Article |
 Investigation of isothiocyanate release from electrospun modified poly(L-lactic acid)/mustard powder composite fibers
Investigation of isothiocyanate release from electrospun modified poly(L-lactic acid)/mustard powder composite fibers
UV can be used to investigate ITC release from electrospun modified PLLA/MP fibers by hexane extracting under the proper temperature and moisture.
- Junyan Yao
- , Shijie Zhang
- & Xiao Chen
-
Focus Review |
 Revealing mechanical and structural properties of molecules on surface by high-resolution atomic force microscopy
Revealing mechanical and structural properties of molecules on surface by high-resolution atomic force microscopy
The state-of-the-art atomic force microscopy allows us to observe inner structures of single molecules. Such observation is quite beneficial to study single and self-assembled molecules on surface as well as on-surface chemical reaction. This focus review describes recent technical improvement and achievements in the field of on-surface molecule studied with high-resolution atomic force microscopy.
- Shigeki Kawai
-
Original Article |
 Nanoporous polystyrene prepared via the selective removal of the low Mw component in polystyrene blends
Nanoporous polystyrene prepared via the selective removal of the low Mw component in polystyrene blends
We have prepared nanoporous polystyrene (PS) samples using a solvent extraction method starting from a solid sample with a mixture of high and low molecular weights. The resulting nanoporous samples are characterized using ellipsometry, atomic force microscopy and electron microscopy. This method can potentially be applied to many different polymer materials.
- Fan-Yen Lin
- , Chad Daley
- & James A Forrest
-
Note |
 Crystalline structure control of poly(vinylidene fluoride) films with the antisolvent addition method
Crystalline structure control of poly(vinylidene fluoride) films with the antisolvent addition method
This paper demonstrates a simple method for the preparation of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) films using the antisolvent addition method. The antisolvent addition method was performed by immersing PVDF solution-casted substrates into the antisolvent for PVDF at room temperature for a few minutes. After immersing and drying for a few hours, a PVDF film was easily obtained. Then, the crystalline structure of the resulting PVDF film was changed in the order of α, γ and β phases with increasing dipole moment of the solvent.
- Takashi Nishiyama
- , Takayuki Sumihara
- & Hideo Horibe
-
Original Article |
 Anomalous small-angle X-ray scattering study on the spatial distribution of hydrophobic molecules in polymer micelles
Anomalous small-angle X-ray scattering study on the spatial distribution of hydrophobic molecules in polymer micelles
The spatial distribution of bromine-labeled hydrophobic molecules—bromobenzene (BrBz) and 4-bromobenzylalcohol (BrBzOH)—incorporated in polymer micelles of poly(N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate)-block-poly(methyl methacrylate) (PDMAEMA-b-PMMA) was investigated using anomalous small-angle X-ray scattering (ASAXS) near the Br K-edge. ASAXS analyses revealed that BrBzOH was homogeneously dispersed in the hydrophobic PMMA core of the PDMAEMA-b-PMMA micelle, whereas BrBz was excluded from the vicinity of the core–shell interface of the PMMA core. The results indicate that the spatial distribution of hydrophobic molecules in polymer micelles strongly depend on the polarity of the encapsulated species.
- Ryosuke Nakanishi
- , Ginpei Machida
- & Isamu Akiba
-
Original Article |
 Study of the adhesion and interface of the low-temperature bonding of vacuum ultraviolet-irradiated cyclo-olefin polymer using electron microscopy
Study of the adhesion and interface of the low-temperature bonding of vacuum ultraviolet-irradiated cyclo-olefin polymer using electron microscopy
Surfaces of cyclo-olefin polymers (COP) are photoactivated by vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) light and can be bonded with a practical bonding strength at low temperatures below Tg. We investigated the mechanism of the low-temperature bonding of COP by nanofractography using high-resolution scanning electron microscopy. It was indicated that the interfaces were fractured via pull out of the polymer chains connected at the interface by hydrogen bonding.
- Shin Horiuchi
- , Hideki Hakukawa
- & Hiroyuki Sugimura
-
Original Article |
 Analysis of the end-segment distribution of a polymer at the interface of filler-filled material
Analysis of the end-segment distribution of a polymer at the interface of filler-filled material
Distribution of end of polymer in the filler-filled material is simulated using self-consistent field method. In our simulation results, the segregation of ends of polymer can be found at the interface of filler, though the depletion region of ends is also existed around the region in the distance of Rg from filler. Sizes and shape of filler are affected to the segregation of ends of polymer, and in the cases of smaller or spherical fillers, the density of ends of polymer near the interface of filler increases. These results can be explained by the entropic effect of polymer chain ends. The segregation of ends contributes to the stabilization of interface of filler adding the entropic part of free energy.
- Hiroshi Morita
- , Masatoshi Toda
- & Takashi Honda
-
Original Article |
 Quantitative analysis of the nucleation and growth of ferroelectric domains during the polarization reversal in thin films of vinylidene fluoride and trifluoroethylene copolymer
Quantitative analysis of the nucleation and growth of ferroelectric domains during the polarization reversal in thin films of vinylidene fluoride and trifluoroethylene copolymer
The distribution of polarization during the polarization reversal in a VDF/TrFE copolymer was studied by the piezoresponse force microscopy, PFM. After an application of a positive voltage pulse to a negatively polarized sample, PFM image was obtained. The regions of blue color corresponding to positively polarized domains were shown to nucleate and grow in negatively polarized regions (red color) as the duration of pulse increased. The change of each domain with the pulse duration was analyzed quantitatively and the nucleation rate and the growth speed of domains were obtained separately.
- Yoshiyuki Takahashi
- , Naoko Tomoda
- & Takeo Furukawa
-
Original Article |
 Structure and formation processes of syndiotactic-polystyrene or styrene-based copolymer-organic solvent gels studied using scanning microscopic light scattering
Structure and formation processes of syndiotactic-polystyrene or styrene-based copolymer-organic solvent gels studied using scanning microscopic light scattering
Network structure of syndiotactic-polystyrene (sPS) or syndiotactic-poly(styrene-co-4-R-styrene) (St/RSt) -organic solvents gels has been quantitatively studied by means of a scanning microscopic light scattering (SMILS). The SMILS analysis cleared that most of the gels showed relaxation peaks derived from small mesh size ~0.6–1.8 nm and large cluster structure ~1000–6000 nm, and a gel formation model was proposed based on the analysis. Interaction between R groups (R=OH, antracenecarbonyl) affected the network structure of the gels.
- Naofumi Naga
- , Takaaki Sakurai
- & Hidemitsu Furukawa
-
Focus Review |
 Importance of water in the control of calcite crystal growth by organic molecules
Importance of water in the control of calcite crystal growth by organic molecules
The binding conformation of aspartic acid (Asp) at the calcite surface is strongly affected by the structure of the surrounding water. On the {104} plane, Asp binds directly to the acute step edge, but not to the obtuse step edge, reflecting a difference in the structure of water near the step edge. This selective binding to the acute step edge causes a change in the step morphology on the {104} plane when Asp is added to real systems.
- Hiroki Nada
-
Focus Review |
 Photocrosslinkable polymers with degradable properties
Photocrosslinkable polymers with degradable properties
Photocrosslinkable polymers and UV-curable resins are significant materials in relation to the industrial applications for coatings, adhesives, photoresists and printing plates. Recently, much attention has been paid to recovery or recycling of crosslinked polymers due to the environmental regulations. This article reviews our recent research work on the synthesis, properties and applications of photocrosslinkable polymers and UV-curable resins with degradable property.
- Masamitsu Shirai
-
Original Article |
 Imidazolium-based polymer hydrogels with microdomains as carriers of hydrophobic molecules
Imidazolium-based polymer hydrogels with microdomains as carriers of hydrophobic molecules
Alkyl imidazolium-based polymer hydrogels produced by copolymerizing N-allylimidazolium chloride (AlImCl) bearing a long alkyl chain exerted a sol-gel phase transition in response to the addition of specific anions. Microscopic observation indicates that spherical microdomains of the polymer assembly were formed in the hydrogels. A hydrophobized fluorescent dye spontaneously accumulated and freely moved in the microdomains due to their high hydrophobicity and fluidity. The hydrogels with the unique domains are promising supports that can be used for multiple functional molecules in biosensing, bioproduction and a new type of drug delivery system.
- Satoshi Yamaguchi
- , Ryoichiro Kawabata
- & Teruyuki Nagamune
-
Invited Review |
 Development of die-bonding film by nano-structure control and mathematical optimization
Development of die-bonding film by nano-structure control and mathematical optimization
Die-bonding film is widely applied for semiconductor package of electronic equipments. The die-bonding film based on epoxy resin/acrylic polymer system shows the higher flexibility to thermal stress during the heat cycle test compared with epoxy–matrix systems. In addition, properties of the film vary widely depending on the ratio of epoxy resin and acrylic polymer contents. To satisfy the target properties, novel material design method named weak conditioned combinatorial linear programming was developed.
- Teiichi Inada
-
Rapid Communication |
 Precise characterization of outermost surface of crystalline–crystalline diblock copolymer thin films using synchrotron radiation soft X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
Precise characterization of outermost surface of crystalline–crystalline diblock copolymer thin films using synchrotron radiation soft X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
The effectiveness of energy-resolved (ER) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) with synchrotron radiation (SR) soft X-ray source for analysis of the outermost chemical composition of polymer materials is demonstrated. The surface molecular aggregation state of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)/poly(perfluorooctylethyl acrylate) (PFA-C8) was confirmed using ER-XPS. The XPS with SR soft X-ray source detect only the single bilayer structure of the PFA-C8 component, whereas the XPS with Mg Kα X-ray source detect both the PFA-C8 component at the outermost surface and PEG component at the interior.
- Shiki Nojima
- , Takamichi Shinohara
- & Atsushi Takahara
-
Focus Review |
 Interaction between synthetic particles and biomacromolecules: fundamental study of nonspecific interaction and design of nanoparticles that recognize target molecules
Interaction between synthetic particles and biomacromolecules: fundamental study of nonspecific interaction and design of nanoparticles that recognize target molecules
The interaction between synthetic particles and proteins has been studied to identify factors that govern the interaction in vitro. The composition and properties of the protein corona that forms on the surface of NPs have been studied in vivo. Recently, synthetic NPs that recognize target molecules are designed and prepared by optimizing the combination of functional groups on the particles, molecular imprinting, in combination with the affinity purification. Some particles are capable of recognizing target molecules and neutralizing their function, in the bloodstream of living animals, as ‘plastic antibodies.’
- Yu Hoshino
- , Haejoo Lee
- & Yoshiko Miura
-
Focus Review |
 Phenolic film engineering for template-mediated microcapsule preparation
Phenolic film engineering for template-mediated microcapsule preparation
This focus review summarizes advances in the recently emerging field of phenolic film engineering for template-mediated microcapsule preparation. By depositing polyphenol films on sacrificial particulate templates and subsequently removing the templates, hollow microcapsules can be readily prepared. Due to the pH-responsive properties, negligible cytotoxicity and the bioactivities of the phenolic building blocks (dopamine and tannic acid), phenolic microcapsules are promising for biomedical applications.
- Hirotaka Ejima
- , Joseph J Richardson
- & Frank Caruso
-
Original Article
| Open Access Quantitative evaluation of an epoxy resin dispersion by infrared spectroscopy
Quantitative evaluation of an epoxy resin dispersion by infrared spectroscopy
A new method for the quantitative analysis of an epoxy resin dispersion by infrared spectroscopy was described. The absorbance ratio of various peaks in different areas of the IR spectra of a resin mixture is applied to evaluate the conditions for epoxy resin dispersion. The standard deviations of the absorbance ratios in various regions of the spectra enabled quantitative evaluation of the epoxy resin dispersion.
- Shuichiro Yoshida
-
Original Article |
 Effects of melt annealing on the miscibility and crystallization of poly(butylene succinate)/poly(ethylene succinate) blends
Effects of melt annealing on the miscibility and crystallization of poly(butylene succinate)/poly(ethylene succinate) blends
Enhancement in miscibility of the crystalline/crystalline blends of poly(butylene succinate)/poly(ethylene succinate) (PBS/PES) by simple melt annealing and their crystallization process are discussed. Immiscible PBS/PES blends changed into miscible blends when annealed at 150 °C. The enhancement in miscibility should be caused by transesterification between PBS and PES, which results in the formation of PBS–PES copolyesters. In the miscible annealed blends, both PBS and PES crystallized and showed the formation of interpenetrating spherulites, that is, the spherulites of one component growing inside of those of the other component.
- Toshiyuki Kataoka
- , Kohji Hiramoto
- & Takayuki Ikehara
-
Original Article |
 Surface texturing of natural ‘urushi’ thermosetting polymer thin films
Surface texturing of natural ‘urushi’ thermosetting polymer thin films
Surface texturing of catechol derivative urushiol was achieved using a thermal imprinting technique. An indented surface was obtained by thermal curing at 100 °C for 10 min while pressing an urushi film with a patterned mold. The indented surface enhanced the static water contact angle in comparison with the flat urushi film.
- Hirohmi Watanabe
- , Aya Fujimoto
- & Atsushi Takahara
-
Original Article |
 Extension of polyethylene chains by formation of polypseudorotaxane structures with perpentylated pillar[5]arenes
Extension of polyethylene chains by formation of polypseudorotaxane structures with perpentylated pillar[5]arenes
Melt mixing of high-density polyethylenes and wheels of perpentylated pillar[5]arenes resulted in formation of polypseudorotaxane structures. Formation of the polypseudorotaxane structures led to extension of the high-density polyethylene chains, and dramatically increased the melting point of high-density polyethylene from 126 to 152 °C. We demonstrated molten state-to-solid and solid-to-molten state transitions of high-density polyethylene based on the host–guest system.
- Tomoki Ogoshi
- , Hitoshi Kayama
- & Motohiro Mizuno
-
Rapid Communication |
 Polymeric nanofibers: isodiametric design space and methodology for depositing aligned nanofiber arrays in single and multiple layers
Polymeric nanofibers: isodiametric design space and methodology for depositing aligned nanofiber arrays in single and multiple layers
STEP Isodiametric design space based deposition of polymeric micro/nanofibers in hierarchical multi-layer assemblies with control on fiber diameter, spacing and orientation.
- Amrinder S Nain
- & Ji Wang

 Structure and mechanical properties of biobased polyamide 11 specimens subjected to different heat treatments
Structure and mechanical properties of biobased polyamide 11 specimens subjected to different heat treatments