Featured
-
-
-
Original Article |
 Temperature dependence of the mean size of polyphenyleneoxide microvoids, as studied by Xe sorption and 129Xe NMR chemical shift analyses
Temperature dependence of the mean size of polyphenyleneoxide microvoids, as studied by Xe sorption and 129Xe NMR chemical shift analyses
129Xe NMR spectra of 129Xe in polyphenyleneoxide, PPO were measured at various temperatures below Tg. From the analysis of 129Xe NMR chemical shifts, the mean volume of individual microvoids in PPO, v could be determined. The temperature when value of v becomes same as a Xe atom, was very close to Tg of PPO. Temperature dependence of individual microvoid’s volume was very similar with that of CH′, which is obtained by dual-mode sorption model from Xe sorption isotherms and is corresponding to the unrelaxed volume of PPO in the glassy state.
- Hiroaki Yoshimizu
- , Satoshi Ohta
- & Yoshiharu Tsujita
-
Original Article |
 Characterization of the microvoids of a tetramethyl polycarbonate/polystyrene blend system using Xe sorption measurements and 129Xe NMR spectroscopy
Characterization of the microvoids of a tetramethyl polycarbonate/polystyrene blend system using Xe sorption measurements and 129Xe NMR spectroscopy
Xe sorption properties of tetramethyl bisphenol A polycarbonate (TMPC)/polystyrene (PS) blends indicated the reduction of microvoids by blending. From the analysis of 129Xe NMR chemical shifts of the 129Xe in these blends, the mean volume of individual microvoids (v) was calculated. The v values for these blends were smaller than those of predicted by a simple additive rule, as well as the cases of variation of density and Xe sorption properties. This fact indicates that the volume contraction induced by blending for TMPC/PS blends is mainly attributed to contraction volume of individual microvoids.
- Hiroaki Yoshimizu
- , Takafumi Murakami
- & Yoshiharu Tsujita
-
Original Article |
 Evaluation of hydrogen dissolved in rubber materials under high-pressure exposure using nuclear magnetic resonance
Evaluation of hydrogen dissolved in rubber materials under high-pressure exposure using nuclear magnetic resonance
The hydrogen dissolved in acrylonitrile butadiene rubber due to high-pressure hydrogen exposure was analyzed by solid-state 1H NMR. On the basis of pressure dependency of chemical shift of free hydrogen and relaxation time of dissolved hydrogen, the hydrogen with two different characters at 4.3 and 4.8 p.p.m. were ensured to be with different mobility. Conversion of the ratio of the two states of hydrogen suggested the transition of hydrogen from the state constrained to rubber chemical structure to free volume during hydrogen elimination process.
- Hirotada Fujiwara
- & Shin Nishimura
-
Original Article |
 Complete NMR assignment of a sulfonated aromatic block copolymer via heteronuclear single-quantum correlation, heteronuclear multiple-bond correlation and heteronuclear single-quantum correlation total correlation spectroscopy
Complete NMR assignment of a sulfonated aromatic block copolymer via heteronuclear single-quantum correlation, heteronuclear multiple-bond correlation and heteronuclear single-quantum correlation total correlation spectroscopy
A sulfonated aromatic block copolymer (SABC), consisting of hydrophobic and hydrophilic blocks, was analyzed by 2D NMR techniques of HSQC, HMBC and HSQC–TOCSY. Because of its complicated chemical structure with five different phenylene rings, 12 types of 1H signals and 24 types of 13C signals were observed in a narrow chemical shift range (7.0–8.0 p.p.m. for 1H and 118–162 p.p.m. for 13C). As a result of these studies, complete 1H and 13C NMR signal assignment of SABC was performed.
- Mari Takasaki
- , Kazuo Kimura
- & Masahiro Watanabe
-
Original Article |
 Statistical determination of chemical composition and monomer sequence distribution of poly(methyl methacrylate-co-tert-butyl methacrylate)s by multivariate analysis of 13C NMR spectra
Statistical determination of chemical composition and monomer sequence distribution of poly(methyl methacrylate-co-tert-butyl methacrylate)s by multivariate analysis of 13C NMR spectra
Multivariate analysis was applied to the 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of homopolymers, homopolymer blends and copolymers of methyl methacrylate (MMA) and tert-butyl methacrylate (TBMA). The first (PC1) and second (PC2) principal components reflected chemical composition of the copolymers and fraction of the MMA-TBMA dyad sequence (fMT), respectively. Dyad and triad sequence distributions of copolymers that were obtained at higher conversions were successfully determined by partial least squares regression with those of copolymers obtained at low conversions as a training set.
- Hikaru Momose
- , Tomoya Maeda
- & Koichi Ute
-
Original Article |
 Strain-induced 13C chemical shift change of natural rubber
Strain-induced 13C chemical shift change of natural rubber
The natural rubber (NR) without vulcanization is easily deformed and strained during magic-angle spinning (MAS). The elongated NR during MAS forms molecular orientation. The static 13C NMR spectra of elongated NR became anisotropic, although the static 13C NMR spectra of NR before MAS show isotropic. Angle-dependent 13C NMR spectra of strips cut from the restricted elongation NR were different from those from the maximum elongated NR. The disagreement indicated that 13C chemical shift depends on not only the molecular orientation but also the magnetic susceptibility resulting from the alignment of NR chains.
- Masashi Kitamura
- , Yoshiaki Hata
- & Atsushi Asano
-
Original Article |
 Characterization and structural determination of 3A-amino-3A-deoxy-(2AS, 3AS)-cyclodextrins by NMR spectroscopy
Characterization and structural determination of 3A-amino-3A-deoxy-(2AS, 3AS)-cyclodextrins by NMR spectroscopy
The proton and carbon NMR resonances have been assigned for 3A-amino-3A-deoxy(2AS,3AS)-α-, β- and γ-CyDs (3α, 3β and 3γ). In these CyDs, a glucose residue has been replaced by an altro-pyranose unit with an axial hydroxyl group. Assignments were made with one-dimensional NMR and COSY, TOCSY, ROESY and CHSHF (heteronuclear shift correlation) spectra. Titration by NMR shift changes gave amino-group pKa values of 7.73 and 8.84 for 3β (left) and 6A-amino-6A-deoxy-β-CyD (6β, right), respectively.
- Keiko Takahashi
- , Keita Andou
- & Shoji Fujiwara
-
Original Article |
 Structural studies of amphiphilic oligopeptides composed of alternating alanine and ionizable amino-acid residues using CD and 13C CP/MAS NMR spectroscopy
Structural studies of amphiphilic oligopeptides composed of alternating alanine and ionizable amino-acid residues using CD and 13C CP/MAS NMR spectroscopy
It was observed that the peptides resulted in β-sheet structure when the peptide solutions were mixed in combination of the side-chain charges being neutralized by each other. Additionally, formation speeds of the β-sheet structure were different between systems, AD12 and AK12 or AE12 and AK12. These phenomena were also observed under the higher concentration condition by 13C CP/MAS NMR. These results indicate that the mixing of the two kinds of peptide solutions will be a trigger for the peptide self-assembly and will be able to control the formation speed by the combination.
- Chikako T Nakazawa
- , Atsushi Asano
- & Takuzo Kurotsu
-
Original Article |
 Structural characterization of silk-polyurethane composite material for biomaterials using solid-state NMR
Structural characterization of silk-polyurethane composite material for biomaterials using solid-state NMR
In this study, we investigated the molecular structure of the composite material of silk fibroin and polyurethane as coating agent of vascular grafts by using solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques. To elucidate the structure and dynamics, 13C cross-polarization (CP)/magic angle spinning (MAS) NMR studies including NMR relaxation experiments were performed. These observations showed that there is a partial interacted portion between soft segment of PU and SF, in particular, the domain size of PU:SU=1:1 composite was smaller than that of the other composites. This study gave basic information on development of new silk-like materials for vascular grafts.
- Yasumoto Nakazawa
- , Atsushi Asano
- & Tetsuo Asakura
-
Original Article |
 Solid-state 1H-NMR relaxation behavior for ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene reactor powders with different morphologies
Solid-state 1H-NMR relaxation behavior for ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene reactor powders with different morphologies
The relaxation behaviors for several commercial ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene reactor powders were compared. On the basis of the morphological analyses, the reactor powder consisted of particles and fibrils between them, the relative amounts of which depended on the powder preparation conditions. The results of differential scanning calorimetry analysis could not distinguish these powder characteristics because of the remarkable reorganization of these reactor powders during heating scans. In contrast, molecular motions detected by solid-state proton nuclear magnetic resonance techniques characterize the structural differences between these powders.
- Hiroki Uehara
- , Hidekazu Tanaka
- & Takeshi Yamanobe
-
Original Article |
 Change in local dynamics of bacteriorhodopsin with retinal isomerization under pressure as studied by fast magic angle spinning NMR
Change in local dynamics of bacteriorhodopsin with retinal isomerization under pressure as studied by fast magic angle spinning NMR
Bacteriorhodopsin (bR) has a retinal with all-trans and 13-cis, 15-syn configurations whose isomeric ratio is close to 1 in the dark and the population of 13-cis, 15-syn configuration can be increased under the pressurized condition. Increase of pressure by fast magic angle spinning (MAS) induced dynamics change at around Ala81 and Ala84 in bR together with retinal isomerization from all-trans to 13-cis configurations. We demonstrated that fast MAS NMR provides a pressure sauce for investigating the structure and dynamics change of biomacromolecules.
- Izuru Kawamura
- , Satoru Yamaguchi
- & Akira Naito
-
Note |
 A two-dimensional spin-diffusion NMR study on the local structure of a water-soluble model peptide for Nephila clavipes dragline silk (MaSp1) before and after spinning
A two-dimensional spin-diffusion NMR study on the local structure of a water-soluble model peptide for Nephila clavipes dragline silk (MaSp1) before and after spinning
The local structure of the acidic-treated model peptides,(E)8GGLGGQGAG(A)6GGAGQGGYGG, derived from the consensus sequence of Nephila clavipes fibroin major ampullate spidroin 1 was determined using two-dimensional proton-driven spin-diffusion solid-state NMR under off-magic-angle spinning coupled with 13C isotope double labeling of specific residues. We observed a positional dependence on the torsion angles of Ala residues in the β sheet. Torsion angle of the Ala residue at the center of poly-Ala domain concentrates around at (ϕ, ψ) = (−150°, 150°), while that of its periphery is distorted and more distributed.
- Koji Yazawa
- , Erika Yamaguchi
- & Tetsuo Asakura
-
Original Article |
 Estimation of the hydrodynamic screening length in κ-carrageenan solutions using NMR diffusion measurements
Estimation of the hydrodynamic screening length in κ-carrageenan solutions using NMR diffusion measurements
The hydrodynamic screening length ξ in κ-carrageenan solution was estimated by observing the restriction on the diffusion of pullulan probes with different molecular weights. Signal intensity of κ-carrageenan chains without gradient Ikappa(0) decreased and ξ increased below the sol-to-gel transition temperature Tsg. It is considered that κ-carrageenan chains formed helical aggregates, and enlarged the networks of solute κ-carrageenan chains and the aggregates.
- Qiuhua Zhao
- & Shingo Matsukawa
-
Review |
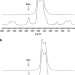 Some aspects of the NMR chemical shift/structure correlation in the structural characterization of polymers and biopolymers
Some aspects of the NMR chemical shift/structure correlation in the structural characterization of polymers and biopolymers
Studies on NMR methodology of characterizing the structure of polymers and biopolymers based on understanding of NMR chemical shift/structure correlation by solution-state and solid-state NMR experiments, development of NMR chemical shift theory and their combination have been reviewed.
- Isao Ando
-
Original Article |
 NMR analysis and chemical shift calculations of poly(lactic acid) dimer model compounds with different tacticities
NMR analysis and chemical shift calculations of poly(lactic acid) dimer model compounds with different tacticities
Isotactic and syndiotactic poly(lactic acid) dimer model compounds were synthesized, and studied by 1H and 13C NMR in three solvents, CDCl3/CCl4 (20/80 v/v), CDCl3 and DMSO-d6. All the peaks in the 1H and 13C NMR spectra were assigned with the help of two-dimensional NMR. The tacticity splitting of the dimers showed no significant difference among the solvents. The chemical shifts were calculated and compared with the experimental shifts to understand the origin of the tacticity splitting in PLA. The observed tacticity splitting of the chemical shifts between isotactic and syndiotactic 1H and 13C NMR peaks were reproduced particularly well using the combination of Becke’s three parameter hybrid method for conformational energy calculation and Hartree-Fock for chemical shift calculation.
- Koto Suganuma
- , Ken Horiuchi
- & Tetsuo Asakura
-
Original Article |
 Solid-state 19F MAS and 1H→19F CP/MAS NMR study of the phase-transition behavior of vinylidene fluoride–trifluoroethylene copolymers: 2. semi-crystalline films of VDF 75% copolymer
Solid-state 19F MAS and 1H→19F CP/MAS NMR study of the phase-transition behavior of vinylidene fluoride–trifluoroethylene copolymers: 2. semi-crystalline films of VDF 75% copolymer
Changes in the crystalline phase structures and molecular mobility of a semi-crystalline P(VDF75/TrFE25) have been analyzed using solid-state 19F MAS and 1H→19F CP/MAS NMR spectroscopy. The conformational exchange motion at the head-to-tail linkage has a key role for the ferroelectric→paraelectric phase transition. The anomalous decrease in the signal intensity of the amorphous peaks and its T1ρF value similar to the crystalline domain at 122 °C indicate the existence of cooperative motion occurring in both phases just above the transition temperature (Tc).
- Keitaro Aimi
- & Shinji Ando
-
Original Article |
 Proton NMR spin-diffusion studies of PS-PB block copolymers at low field: two- vs three-phase model and recalibration of spin-diffusion coefficients
Proton NMR spin-diffusion studies of PS-PB block copolymers at low field: two- vs three-phase model and recalibration of spin-diffusion coefficients
Proton spin diffusion (SD) experiments performed on low-field NMR spectrometers are a valuable means for the estimation of domain sizes in phase-separated polymers. We here investigate the interplay of the SD effect and fast T1 relaxation by means of fits of data taken for two different polystyrene-polybutadiene di- and multiblock copolymers to numerical simulations. We demonstrate the necessity to explicitly include an interphase of intermediate mobility, and further show that a previously published, popular calibration of the SD coefficient for mobile polymer phases based on the transverse relaxation time T2 should be revised.
- Henriette W Meyer
- , Horst Schneider
- & Kay Saalwächter
-
Original Article |
 A utilization of internal/external quasi-static magnetic field gradients: transport phenomenon and magnetic resonance imaging of solid polymers
A utilization of internal/external quasi-static magnetic field gradients: transport phenomenon and magnetic resonance imaging of solid polymers
Two topics concerning the utilization of internal and external magnetic field gradients are discussed. The first topic concerns the transport of conformons in the quasi-ordered phase of a regioregular, π-conjugated polymer, poly(4-methylthiazole-2,5-diyl), using a combination of longitudinal and transverse relaxation dispersion measurements. The effects of conformon diffusion on the relaxation exponent were successfully estimated via a numerical approach that used the Fourier spectrum solution of the one-dimensional Bloch-Torrey equation. The second topic demonstrates a low-cost magnetic resonance imaging method using a magnetic field gradient from a neodymium ferromagnet. Spin echo experiments are shown for three-layered thin films of PDMS/PTFE/PDMS under a large magnetic field.
- Naoki Asakawa
- & Toshiki Obata
-
Original Article |
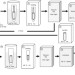 1H MRI study of small-diameter silk vascular grafts in water
1H MRI study of small-diameter silk vascular grafts in water
The images of 1H spin density, 1H T2 and diffusion coefficient (D) of water molecules in the layer of silk-based vascular grafts (VG) coated by different materials that are silk fibroin or polyurethane were non-destructively observed in water using 1H MR imaging. The inner and outer coating materials affect significantly the amount and mobility of water molecules in the VG.
- Shigeki Kuroki
- , Masahito Kanekiyo
- & Tetsuo Asakura
-
Original Article |
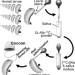 Quantifying the fraction of alanine residues in an α-helical conformation in hornet silk using solid-state NMR
Quantifying the fraction of alanine residues in an α-helical conformation in hornet silk using solid-state NMR
An isotope-labeled hornet (Vespa) cocoon in which the Ala carbons of silk proteins were substituted with 13C was successfully obtained by feeding a mixture of larval saliva with [13C3]Ala to mature larvae. The Ala fraction in the α-helix conformation of hornet silk was estimated by obtaining high-resolution 13C solid-state NMR spectra of the labeled cocoon, which also helped in understanding the molecular structure of hornet silk.
- Tsunenori Kameda
-
Original Article |
 Crystalline structure and molecular mobility of PVDF chains in PVDF/PMMA blend films analyzed by solid-state 19F MAS NMR spectroscopy
Crystalline structure and molecular mobility of PVDF chains in PVDF/PMMA blend films analyzed by solid-state 19F MAS NMR spectroscopy
The crystalline structure and molecular mobility of PVDF blended with PMMA at various fractions were investigated by solid-state 19F MAS NMR spectroscopy. The origin of the characteristic peaks observed for typical polymorphs of PVDF (α-, β- and γ-forms) are explained based on DFT calculations. The dominant crystalline form in the blends of [PVDF/PMMA]=[80/20], [70/20] and [50/50] is α-form containing a small portion of β-form, whereas that of [65/35], [60/40] and [55/45] consists of β-form and γ-form. In contrast, no crystalline structure is found in [45/55], [40/60] and [20/80], indicating that PVDF and PMMA chains are miscible at the molecular level.
- Yu Koseki
- , Keitaro Aimi
- & Shinji Ando
-
Original Article
| Open Access Statistical approach for solid-state NMR spectra of cellulose derived from a series of variable parameters
Statistical approach for solid-state NMR spectra of cellulose derived from a series of variable parameters
A multivariate analysis was used to extract components in solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra from bacterial cellulose (BC). Polymers such as cellulose have several domain structures, and their structure and dynamics are reflected in the variety of solid-state spectra derived from different parameters. Multivariate analysis, such as principle component analysis (PCA), is suggested as an option to improve analyses of complex NMR spectra from relaxation measurements. In this study we demonstrate the extraction of peak components using PCA from cross polarization experiment data with variable contact time spectra of BC.
- Keiko Okushita
- , Takanori Komatsu
- & Jun Kikuchi
-
Original Article |
 Application of multivariate analysis of NMR spectra of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) to assignment of stereostructures and prediction of tacticity distribution
Application of multivariate analysis of NMR spectra of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) to assignment of stereostructures and prediction of tacticity distribution
This paper reports multivariate analyses such as principal component analysis and partial least-squares regression of NMR spectra of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)s [poly(NIPAAm)s]. Principal component analysis successfully interpreted the assignments of 1H and 13C NMR spectra of methylene protons and methine carbons, respectively, of poly(NIPAAm)s in terms of stereostructures. Furthermore, triad tacticity was successfully predicted by partial least-squares regression of 1H NMR spectra of the methine and methylene groups. Consequently, it is assumed that chemometric analysis of NMR spectra is a promising method for the characterization of synthetic polymers.
- Tomohiro Hirano
- , Takuya Anmoto
- & Koichi Ute
-
Original Article |
 Field-dependent 19F NMR study of sperm whale myoglobin reconstituted with a ring-fluorinated heme
Field-dependent 19F NMR study of sperm whale myoglobin reconstituted with a ring-fluorinated heme
A fluorinated heme was incorporated into Mb, and the field dependence of the line width of 19F NMR signals of the protein with S values ranging from 0 to 5/2 was analyzed in order to gain a quantitative insight into the 19F transverse relaxation mechanism in the protein. In the cases of S=2 and S=5/2 forms, the significant contribution of Curie spin relaxation to the relaxation was demonstrated and analysis of the Curie spin relaxation was useful to estimate the overall correlation time of the protein.
- Yasuhiko Yamamoto
- , Satoshi Nagao
- & Akihiro Suzuki
-
Original Article |
 Influence of magic angle spinning on T1H of SBR studied by solid state 1H NMR
Influence of magic angle spinning on T1H of SBR studied by solid state 1H NMR
Temperature-dependent curves of T1H for the SBR with and without end-chain modification in the SBR/Si composites showed the increment of the T1H values as the MAS rate increases and the considerable change at the fast MAS rate of 25 kHz. The increase of T1H values is represented by the factor f that decides the observed T1H minimum value. The plot of centrifugal pressure caused by MAS as a function of 1/f exhibited the similar trend to that of the stress–strain curve. The differences in the T1H between the end-chain-modified and normal SBR under fast MAS was attributed to the Payne effect.
- Atsushi Asano
- , Shunsuke Hori
- & Takuzo Kurotsu
-
Original Article |
 A high-resolution solid-state NMR study on starch–clay nanocomposites and the effect of aging on clay dispersion
A high-resolution solid-state NMR study on starch–clay nanocomposites and the effect of aging on clay dispersion
The high-resolution solid-state NMR technique was applied as a bulk analysis method to provide an indication of nano-clay dispersion in starch–clay nanocomposites. The effects of having polyvinyl alcohol as additives and aging up to 105 days were also investigated.
- Xiaoqing Zhang
- , Katherine Dean
- & Iko M Burgar
-
Original Article |
 Novel polymerizable surfactants: synthesis and application in the emulsion polymerization of styrene
Novel polymerizable surfactants: synthesis and application in the emulsion polymerization of styrene
Novel anionic polymerizable surfactants were prepared by reacting maleic anhydride with different benzyl alcohols. These surfmers were evaluated in the emulsion polymerization of styrene in the presence of potassium persulfate as the initiator. Special attention was focused on the effect of the concentration of surfmers on the polymerization kinetic and the final particle size through polymerization conversion particle size and size distribution determination.
- Sofiane Mekki
- , Salima Saïdi-Besbes
- & Aïcha Derdour
-
Rapid Communication |
 Local conformation of serine residues in a silk model peptide, (Ala–Gly–Ser–Gly–Ala–Gly)5, studied with solid-state NMR:REDOR
Local conformation of serine residues in a silk model peptide, (Ala–Gly–Ser–Gly–Ala–Gly)5, studied with solid-state NMR:REDOR
- Yu Suzuki
- & Tetsuo Asakura
-
Invited Article |
 Molecular dynamics and orientation of stretched rubber by solid-state 13C NMR
Molecular dynamics and orientation of stretched rubber by solid-state 13C NMR
The molecular dynamics and orientation of vulcanized natural rubber stretched at low extension ratio were studied by solid-state 13C NMR and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Isoprene units of the oriented rubber chains in stretched NR rotate rapidly around an axis that almost aligned with C=C bond direction of polyisoprene.
- Hideaki Kimura
- , Hidehiko Dohi
- & Tetsuo Asakura

 Nanoscale heterogeneous structure of polyacrylonitrile-co-butadiene with different molecular mobilities analyzed by spin–spin relaxation time
Nanoscale heterogeneous structure of polyacrylonitrile-co-butadiene with different molecular mobilities analyzed by spin–spin relaxation time