Featured
-
-
News & Views |
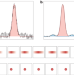 Spot the defects
Spot the defects
The ability to extract information from diffuse background signals in ultrafast electron diffraction experiments now enables a direct view of the formation of topological defects during a light-induced phase transition.
- Isabella Gierz
-
Article |
 Ultrafast formation of topological defects in a two-dimensional charge density wave
Ultrafast formation of topological defects in a two-dimensional charge density wave
Topological defects play a crucial role in the behaviour of strongly correlated materials out of equilibrium. Now, ultrafast electron diffraction measurements on 1T-TiSe2 shed light on the defect formation process at sub-picosecond timescales.
- Yun Cheng
- , Alfred Zong
- & Dao Xiang
-
News & Views |
 Rearranged under stress
Rearranged under stress
Permanent deformation in solids results from atoms not aligning with the external stress causing the deformation. Detecting such non-affine atomic rearrangements and connecting them to measurable mechanical effects is now shown to be feasible by means of high-energy X-ray diffraction.
- Saswati Ganguly
-
Article |
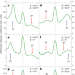 Observation of the boson peak in a two-dimensional material
Observation of the boson peak in a two-dimensional material
The boson peak refers to an excess in the phonon density of states seen in three-dimensional amorphous materials. Helium-atom scattering experiments have now revealed a boson peak in a two-dimensional material, too, at a frequency similar to that of the bulk material.
- Martin Tømterud
- , Sabrina D. Eder
- & Bodil Holst
-
Article
| Open Access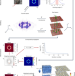 Three-dimensional neutron far-field tomography of a bulk skyrmion lattice
Three-dimensional neutron far-field tomography of a bulk skyrmion lattice
The three-dimensional spin textures of a skyrmion lattice have now been measured in a bulk material using a tomographic small-angle neutron scattering technique.
- M. E. Henderson
- , B. Heacock
- & D. A. Pushin
-
News & Views |
 Of electrons and photons
Of electrons and photons
Multi-colour light fields allow a nonlinear coupling between free electrons and propagating light by stimulated Compton scattering, without the need for near fields to mediate the interaction.
- Niklas Müller
- & Sascha Schäfer
-
Article
| Open Access Coulomb-correlated electron number states in a transmission electron microscope beam
Coulomb-correlated electron number states in a transmission electron microscope beam
Coulomb interactions in free-electron beams are usually seen as an adverse effect. The creation of distinctive number states with one, two, three and four electrons now reveals unexpected opportunities for electron microscopy and lithography from Coulomb correlations.
- Rudolf Haindl
- , Armin Feist
- & Claus Ropers
-
Article |
 Exploiting disorder to probe spin and energy hydrodynamics
Exploiting disorder to probe spin and energy hydrodynamics
Probing strongly interacting quantum systems with high spatial resolution can be challenging. An experiment now uses disorder in nuclear spin chains as a local probe to investigate spin and energy hydrodynamics.
- Pai Peng
- , Bingtian Ye
- & Paola Cappellaro
-
News & Views |
 Laser cooling unlocks metal tracer
Laser cooling unlocks metal tracer
Atom trap trace analysis has emerged as a powerful technique for detecting trace radioisotopes of noble gases. The successful application of the method to a calcium isotope now opens the possibility of extension to other metal isotopes.
- Rohan D. Glover
-
Article |
 Thermalization and dynamics of high-energy quasiparticles in a superconducting nanowire
Thermalization and dynamics of high-energy quasiparticles in a superconducting nanowire
The performance of superconducting devices is affected by the generation and relaxation of excitations called quasiparticles. A scanning tunnelling microscope can controllably inject quasiparticles so their dynamics can be better understood.
- T. Jalabert
- , E. F. C. Driessen
- & C. Chapelier
-
Article |
 Atom-trap trace analysis of 41Ca/Ca down to the 10–17 level
Atom-trap trace analysis of 41Ca/Ca down to the 10–17 level
The calcium isotope 41Ca is a promising candidate to complement dating methods relying on radiocarbon. Small levels of 41Ca can be measured with atom-trap trace analysis, which brings the use of 41Ca a step closer to applications.
- T.-Y. Xia
- , W.-W. Sun
- & Z.-T. Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-locked photon–electron interaction without a laser
Phase-locked photon–electron interaction without a laser
Ultrafast photon–electron spectroscopy commonly requires a driving laser. Now, an inverse approach based on cathodoluminescence spectroscopy has allowed a compact solution to spectral interferometry inside an electron microscope, without a laser.
- Masoud Taleb
- , Mario Hentschel
- & Nahid Talebi
-
Research Briefing |
 Identifying the quantum fingerprint of plasmon polaritons
Identifying the quantum fingerprint of plasmon polaritons
Coherent multidimensional spectroscopy with nanoscale spatial resolution was used to directly probe a plasmon polariton quantum wave packet. To reproduce these results an improved quantum model of photoemission was required, in which the coherent coupling between plasmons and electrons is accounted for with the plasmon excitations extending beyond a two-level model.
-
Letter
| Open Access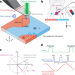 Imaging ferroelectric domains with a single-spin scanning quantum sensor
Imaging ferroelectric domains with a single-spin scanning quantum sensor
A scanning nitrogen-vacancy microscope is used to image ferroelectric domains in piezoelectric and improper ferroelectric samples with high sensitivity. The technique relies on the nitrogen-vacancy’s Stark shift produced by the samples’ electric field.
- William S. Huxter
- , Martin F. Sarott
- & Christian L. Degen
-
News & Views |
 A route to greener Big Science
A route to greener Big Science
By recovering energy from a relativistically accelerated electron beam in a multiturn configuration, a reduction of radiofrequency power has been demonstrated. This is a milestone toward more efficient and better performing accelerators.
- Peter Williams
-
Article |
 Realization of a multi-turn energy recovery accelerator
Realization of a multi-turn energy recovery accelerator
By combining energy recovery technology and a multi-turn accelerating scheme in a linear accelerator, high-power beams can be achieved with considerably reduced energy consumption.
- Felix Schliessmann
- , Michaela Arnold
- & Simon Weih
-
-
Article |
 Critical prethermal discrete time crystal created by two-frequency driving
Critical prethermal discrete time crystal created by two-frequency driving
Time-crystalline order appears in periodically driven systems with broken time-translation symmetry. Now, a protocol based on pulse drives of different frequencies is used to create and continuously observe time crystals with long lifetimes.
- William Beatrez
- , Christoph Fleckenstein
- & Ashok Ajoy
-
Letter |
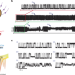 Enhanced statistical sampling reveals microscopic complexity in the talin mechanosensor folding energy landscape
Enhanced statistical sampling reveals microscopic complexity in the talin mechanosensor folding energy landscape
Single-molecule magnetic tweezers enable probing the folding dynamics of a single talin protein for long periods of time. This allows the observation of previously inaccessible rare and kinetically trapped conformations.
- Rafael Tapia-Rojo
- , Marc Mora
- & Sergi Garcia-Manyes
-
Article |
 Quantum microscopy with van der Waals heterostructures
Quantum microscopy with van der Waals heterostructures
Hexagonal boron nitride is a common component of 2D heterostructures. Defects implanted in boron nitride crystals can be used to perform spatially resolved sensing of properties, including temperature, magnetism and current.
- A. J. Healey
- , S. C. Scholten
- & J.-P. Tetienne
-
-
Perspective |
 Citation inequity and gendered citation practices in contemporary physics
Citation inequity and gendered citation practices in contemporary physics
The under-citation of woman authors in physics is quantified and measures that could overcome this inequity are presented.
- Erin G. Teich
- , Jason Z. Kim
- & Dani S. Bassett
-
Article |
 Coupled polarization and nanodomain evolution underpins large electromechanical responses in relaxors
Coupled polarization and nanodomain evolution underpins large electromechanical responses in relaxors
Properties of relaxor ferroelectrics are governed by polar nanodomains. Polarization rotation facilitated by these domains investigated by means of epitaxial strain reveals a competition between chemistry-driven disorder and strain-driven order.
- Jieun Kim
- , Abinash Kumar
- & Lane W. Martin
-
Perspective |
 From atomically resolved imaging to generative and causal models
From atomically resolved imaging to generative and causal models
High-resolution imaging methods have been instrumental in advancing our understanding of the structure of materials. To move microscopy and tomography methods forwards, approaches to reassess macroscopic concepts such as symmetry are needed.
- Sergei V. Kalinin
- , Ayana Ghosh
- & Maxim Ziatdinov
-
Letter |
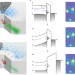 Coherence enhancement of solid-state qubits by local manipulation of the electron spin bath
Coherence enhancement of solid-state qubits by local manipulation of the electron spin bath
Nitrogen vacancy centres close to the surface of diamonds are a key component of quantum sensing technologies. Using an atomic force microscope to manipulate the surface electrostatic environment can significantly improve the sensing performance.
- Wentian Zheng
- , Ke Bian
- & Ying Jiang
-
Letter |
 Excitonic insulator in a heterojunction moiré superlattice
Excitonic insulator in a heterojunction moiré superlattice
Stacking monolayer WS2 on top of bilayer WSe2 creates conditions where electrons and holes can coexist in the structure. Their Coulomb interaction allows them to form bound pairs and hence an excitonic insulator state.
- Dongxue Chen
- , Zhen Lian
- & Su-Fei Shi
-
Comment |
 The expanding role of National Metrology Institutes in the quantum era
The expanding role of National Metrology Institutes in the quantum era
Emerging quantum technologies pose new measurement challenges, but also offer previously unknown measurement solutions. National metrology institutes are playing a leading role in this fast evolving world.
- Alexander Tzalenchuk
- , Nicolas Spethmann
- & Barbara L. Goldstein
-
News & Views |
 Good vibrations
Good vibrations
Originally suggested for the detection of gravitational waves, resonantly vibrating metal beams have been used in a recent laboratory experiment to measure Newton’s constant of gravitation and to verify Newton’s gravitational law.
- Christian Rothleitner
-
Article |
 Dynamic measurement of gravitational coupling between resonating beams in the hertz regime
Dynamic measurement of gravitational coupling between resonating beams in the hertz regime
Measurements of the gravitational interaction between two parallel beams vibrating in bending motion enable the quantitative investigation of dynamic gravitation in the hertz regime and allow the determination of the gravitational constant.
- Tobias Brack
- , Bernhard Zybach
- & Jürg Dual
-
-
Measure for Measure |
 The new kilogram for new technology
The new kilogram for new technology
The shift of the definition of the kilogram in 2019 away from an artefact to one relying on the Planck constant inspires technological innovation, as Naoki Kuramoto elucidates.
- Naoki Kuramoto
-
Measure for Measure |
 The unit that shall not be named
The unit that shall not be named
Juris Meija takes a look at the tumultuous past of the atomic unit of mass from its beginnings as an idea to its most recent revisions in a hotel bar.
- Juris Meija
-
Article |
 Real-space imaging of phase transitions in bridged artificial kagome spin ice
Real-space imaging of phase transitions in bridged artificial kagome spin ice
Artificial spin ice formed of nanomagnets arranged on a lattice mimics frustrated magnetism seen in condensed matter. By controlling magnetic interactions, theoretically predicted phase transitions are now observed in artificial kagome-lattice spin ice.
- Kevin Hofhuis
- , Sandra Helen Skjærvø
- & Laura Jane Heyderman
-
Editorial |
 Accelerate to the next level
Accelerate to the next level
The merits of conventional particle accelerators range from fundamental science to applications like radiotherapy. Plasma-based accelerators are getting up to speed and may overtake conventional ones in the near future.
-
Article
| Open Access X-ray multiphoton-induced Coulomb explosion images complex single molecules
X-ray multiphoton-induced Coulomb explosion images complex single molecules
Visualizing the structural dynamics of isolated molecules would help to understand chemical reactions, but this is difficult for complex structures. Intense femtosecond X-ray pulses allow the full imaging of exploding photoionized molecules, in this case, with eleven atoms.
- Rebecca Boll
- , Julia M. Schäfer
- & Till Jahnke
-
-
Article |
 Precision mass measurement of lightweight self-conjugate nucleus 80Zr
Precision mass measurement of lightweight self-conjugate nucleus 80Zr
High-precision mass measurements of exotic zirconium nuclei are reported, and reveal a double-shell closure for the deformed nucleus 80Zr, which is more strongly bound than previously thought.
- A. Hamaker
- , E. Leistenschneider
- & I. T. Yandow
-
Letter |
 Imaging local discharge cascades for correlated electrons in WS2/WSe2 moiré superlattices
Imaging local discharge cascades for correlated electrons in WS2/WSe2 moiré superlattices
The Hubbard model describes many fascinating phenomena, but relating it to complicated quantum materials is difficult. Now, atomic-resolution measurements can estimate the interaction parameters that appear in the model for real materials.
- Hongyuan Li
- , Shaowei Li
- & Feng Wang
-
News & Views |
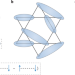 Singlets singled out
Singlets singled out
The state that forms at low temperatures in a quantum antiferromagnet on a kagome lattice has been debated for decades. Nuclear magnetic resonance has now shown the gradual emergence of entangled spin singlets in a disordered kagome antiferromagnet.
- Martin Klanjšek
-
Measure for Measure |
 One unit to rule them all
One unit to rule them all
Initially used to measure the brightness of radio sources, the jansky has spread to other areas of astronomy, as Natasha Hurley-Walker recounts.
- Natasha Hurley-Walker
-
-
Letter |
 Absolute 13C/12C isotope amount ratio for Vienna PeeDee Belemnite from infrared absorption spectroscopy
Absolute 13C/12C isotope amount ratio for Vienna PeeDee Belemnite from infrared absorption spectroscopy
Isotope ratio measurements are complicated by the instabilities of composition in reference samples. Now a calibration-free method relying on infrared spectroscopy provides measurements that are traceable to International System of Units standards.
- Adam J. Fleisher
- , Hongming Yi
- & Joseph T. Hodges
-
Comment |
 Instruments of change for academic tool
development
Instruments of change for academic tool
development
Scientific progress has always been driven by the ability to build an instrument to answer a specific question. But spreading the news of how to replicate that tool is an evolving art, ripe for an open-source revolution.
- Georg E. Fantner
- & Andrew C. Oates
-
News & Views |
 Polarization out of the vortex
Polarization out of the vortex
The virtual photons that are exchanged when a free-electron vortex beam interacts with a nanoscopic target unlock an explicit connection between polarized optical spectroscopy and the inelastic scattering of scalar electron waves.
- David J. Masiello
-
Article |
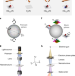 Optical polarization analogue in free electron beams
Optical polarization analogue in free electron beams
The functionality of electron energy loss spectroscopy can be extended to include a polarization analogue constructed via the dipole transition vector between two electronic states, bringing it closer to its optical counterpart.
- Hugo Lourenço-Martins
- , Davy Gérard
- & Mathieu Kociak
-
-
Measure for Measure |
 Political union through science
Political union through science
The metric system is one of the enduring achievements of the French Revolution. Martin Milton recounts how it was also intended to unite nations.
- Martin J. T. Milton
-
Article
| Open Access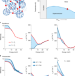 Evidence for metastable photo-induced superconductivity in K3C60
Evidence for metastable photo-induced superconductivity in K3C60
Evidence for light-induced superconductivity in K3C60 was limited to optical methods due to the short lifetime of the phase. Extending the lifetime from picoseconds to nanoseconds now allows measurement of its negligible electrical resistance.
- M. Budden
- , T. Gebert
- & A. Cavalleri
-
Letter
| Open Access Charge radii of exotic potassium isotopes challenge nuclear theory and the magic character of N = 32
Charge radii of exotic potassium isotopes challenge nuclear theory and the magic character of N = 32
The charge radii of potassium isotopes up to 52K are measured, and show no sign of magicity at 32 neutrons as previously suggested in calcium. The observations are interpreted with coupled cluster and density functional theory calculations.
- Á. Koszorús
- , X. F. Yang
- & S. G. Wilkins

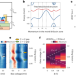 Manipulation of chiral interface states in a moiré quantum anomalous Hall insulator
Manipulation of chiral interface states in a moiré quantum anomalous Hall insulator Ultracold atoms visit curved universes
Ultracold atoms visit curved universes Inspired by disorder
Inspired by disorder A supermassive doughnut
A supermassive doughnut Speed at heart
Speed at heart Prosperous gold
Prosperous gold Light captured in flight
Light captured in flight