Featured
-
-
Article |
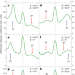 Observation of the boson peak in a two-dimensional material
Observation of the boson peak in a two-dimensional material
The boson peak refers to an excess in the phonon density of states seen in three-dimensional amorphous materials. Helium-atom scattering experiments have now revealed a boson peak in a two-dimensional material, too, at a frequency similar to that of the bulk material.
- Martin Tømterud
- , Sabrina D. Eder
- & Bodil Holst
-
News & Views |
 Laser cooling unlocks metal tracer
Laser cooling unlocks metal tracer
Atom trap trace analysis has emerged as a powerful technique for detecting trace radioisotopes of noble gases. The successful application of the method to a calcium isotope now opens the possibility of extension to other metal isotopes.
- Rohan D. Glover
-
Article |
 Atom-trap trace analysis of 41Ca/Ca down to the 10–17 level
Atom-trap trace analysis of 41Ca/Ca down to the 10–17 level
The calcium isotope 41Ca is a promising candidate to complement dating methods relying on radiocarbon. Small levels of 41Ca can be measured with atom-trap trace analysis, which brings the use of 41Ca a step closer to applications.
- T.-Y. Xia
- , W.-W. Sun
- & Z.-T. Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-locked photon–electron interaction without a laser
Phase-locked photon–electron interaction without a laser
Ultrafast photon–electron spectroscopy commonly requires a driving laser. Now, an inverse approach based on cathodoluminescence spectroscopy has allowed a compact solution to spectral interferometry inside an electron microscope, without a laser.
- Masoud Taleb
- , Mario Hentschel
- & Nahid Talebi
-
Letter |
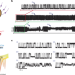 Enhanced statistical sampling reveals microscopic complexity in the talin mechanosensor folding energy landscape
Enhanced statistical sampling reveals microscopic complexity in the talin mechanosensor folding energy landscape
Single-molecule magnetic tweezers enable probing the folding dynamics of a single talin protein for long periods of time. This allows the observation of previously inaccessible rare and kinetically trapped conformations.
- Rafael Tapia-Rojo
- , Marc Mora
- & Sergi Garcia-Manyes
-
Perspective |
 Citation inequity and gendered citation practices in contemporary physics
Citation inequity and gendered citation practices in contemporary physics
The under-citation of woman authors in physics is quantified and measures that could overcome this inequity are presented.
- Erin G. Teich
- , Jason Z. Kim
- & Dani S. Bassett
-
Perspective |
 From atomically resolved imaging to generative and causal models
From atomically resolved imaging to generative and causal models
High-resolution imaging methods have been instrumental in advancing our understanding of the structure of materials. To move microscopy and tomography methods forwards, approaches to reassess macroscopic concepts such as symmetry are needed.
- Sergei V. Kalinin
- , Ayana Ghosh
- & Maxim Ziatdinov
-
Comment |
 The expanding role of National Metrology Institutes in the quantum era
The expanding role of National Metrology Institutes in the quantum era
Emerging quantum technologies pose new measurement challenges, but also offer previously unknown measurement solutions. National metrology institutes are playing a leading role in this fast evolving world.
- Alexander Tzalenchuk
- , Nicolas Spethmann
- & Barbara L. Goldstein
-
News & Views |
 Good vibrations
Good vibrations
Originally suggested for the detection of gravitational waves, resonantly vibrating metal beams have been used in a recent laboratory experiment to measure Newton’s constant of gravitation and to verify Newton’s gravitational law.
- Christian Rothleitner
-
Article |
 Dynamic measurement of gravitational coupling between resonating beams in the hertz regime
Dynamic measurement of gravitational coupling between resonating beams in the hertz regime
Measurements of the gravitational interaction between two parallel beams vibrating in bending motion enable the quantitative investigation of dynamic gravitation in the hertz regime and allow the determination of the gravitational constant.
- Tobias Brack
- , Bernhard Zybach
- & Jürg Dual
-
Measure for Measure |
 The new kilogram for new technology
The new kilogram for new technology
The shift of the definition of the kilogram in 2019 away from an artefact to one relying on the Planck constant inspires technological innovation, as Naoki Kuramoto elucidates.
- Naoki Kuramoto
-
Letter |
 Absolute 13C/12C isotope amount ratio for Vienna PeeDee Belemnite from infrared absorption spectroscopy
Absolute 13C/12C isotope amount ratio for Vienna PeeDee Belemnite from infrared absorption spectroscopy
Isotope ratio measurements are complicated by the instabilities of composition in reference samples. Now a calibration-free method relying on infrared spectroscopy provides measurements that are traceable to International System of Units standards.
- Adam J. Fleisher
- , Hongming Yi
- & Joseph T. Hodges
-
Letter |
 Experimental observation of vortex rings in a bulk magnet
Experimental observation of vortex rings in a bulk magnet
Three-dimensional structures of vortex loops in a bulk micromagnet GdCo2 have been observed using X-ray magnetic nanotomography. The cross-section of these loops consists of a vortex–antivortex pair stabilized by the dipolar interaction.
- Claire Donnelly
- , Konstantin L. Metlov
- & Sebastian Gliga
-
Measure for Measure |
 Metrology on a grand scale
Metrology on a grand scale
The assembly of the more than a million single parts of the ITER tokamak requires large-scale three-dimensional precision metrology. John Villanueva Jr gives us insights into the complexity of this project.
- John Villanueva Jr
-
-
News & Views |
The dark side of neutrons
The agent responsible for the accelerated expansion of the Universe is completely unknown. Delicate interference measurements of the quantum transitions of very slow neutrons bouncing on a flat table have constrained an interesting theoretical possibility.
- W. Michael Snow
-
-
Measure for Measure |
 Balancing energy and mass with neutrons
Balancing energy and mass with neutrons
Michael Jentschel and Klaus Blaum explain why the most famous equation of physics needs checking — and how to do it.
- Michael Jentschel
- & Klaus Blaum
-
Review Article |
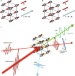 Antiferromagnetic opto-spintronics
Antiferromagnetic opto-spintronics
An overview of how electromagnetic radiation can be used for probing and modification of the magnetic order in antiferromagnets, and possible future research directions.
- P. Němec
- , M. Fiebig
- & A. V. Kimel
-
Letter |
 Neural-network quantum state tomography
Neural-network quantum state tomography
Unsupervised machine learning techniques can efficiently perform quantum state tomography of large, highly entangled states with high accuracy, and allow the reconstruction of many-body quantities from simple experimentally accessible measurements.
- Giacomo Torlai
- , Guglielmo Mazzola
- & Giuseppe Carleo
-
Article |
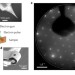 Phase ordering of charge density waves traced by ultrafast low-energy electron diffraction
Phase ordering of charge density waves traced by ultrafast low-energy electron diffraction
A tracing of the phase-ordering kinetics of a charge density wave system demonstrates the potential of ultrafast low-energy electron diffraction for studying phase transitions and ordering phenomena at surfaces and in low-dimensional systems.
- S. Vogelgesang
- , G. Storeck
- & C. Ropers
-
-
Letter |
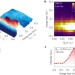 Dispersive charge density wave excitations in Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ
Dispersive charge density wave excitations in Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+δ
Ultrahigh-resolution resonant inelastic X-ray scattering shows how dispersive charge density wave excitations influence the charge and lattice degrees of freedom in a high-Tc cuprate, pointing to a connection to the mysterious pseudogap state.
- L. Chaix
- , G. Ghiringhelli
- & W.-S. Lee
-
Letter |
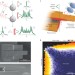 Ramsey-type phase control of free-electron beams
Ramsey-type phase control of free-electron beams
Using a technique inspired by Ramsey spectroscopy it is now possible to coherently control free electrons in an electron microscope.
- Katharina E. Echternkamp
- , Armin Feist
- & Claus Ropers
-
Measure for Measure |
 The slightness of gravimetry
The slightness of gravimetry
Michel Van Camp and Olivier de Viron are attracted to the fluctuations in the Earth's gravitational pull.
- Michel Van Camp
- & Olivier de Viron
-
Measure for Measure |
 Counting atoms
Counting atoms
Enrico Massa and Giovanni Mana expound on the substance of the Avogadro constant.
- Enrico Massa
- & Giovanni Mana
-
Measure for Measure |
 The electrical connection
The electrical connection
François Piquemal tells the story of the ampere, which bridges mechanical and electromagnetic units.
- François Piquemal
-
Measure for Measure |
 Gravity on the balance
Gravity on the balance
Despite intensified efforts, measurements of the gravitational constant continue to fail to converge, as Terry Quinn explains.
- Terry Quinn
-
Editorial |
 The art of measurement
The art of measurement
With a dedicated monthly column, Nature Physics draws attention to metrology. And a set of Commentaries in this issue focuses on various aspects of thermometry.
-
Commentary |
 The new system of units
The new system of units
The redefinition of several physical base units planned for 2018 requires precise knowledge of the values of certain fundamental physical constants. Scientists are working hard to meet the deadlines for realizing the ultimate International System of Units.
- Joachim Fischer
- & Joachim Ullrich
-
Commentary |
 Advances in thermometry
Advances in thermometry
The past 25 years have seen tremendous progress in thermometry across the moderate temperature range of 1 K to 1,235 K. Various primary thermometers, based on a wide range of different physics, have uncovered errors in the International Temperature Scale of 1990, and set the stage for the planned redefinition of the kelvin.
- Michael R. Moldover
- , Weston L. Tew
- & Howard W. Yoon
-
News & Views |
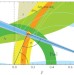 From generation to generation
From generation to generation
A new measurement from the LHCb experiment at CERN's Large Hadron Collider impinges on a puzzle that has been troubling physicists for decades — namely the breaking of the symmetry between matter and antimatter.
- Robert Kowalewski
-
Article
| Open Access Determination of the quark coupling strength |Vub| using baryonic decays
Determination of the quark coupling strength |Vub| using baryonic decays
The accurate determination of quark mixing parameters is essential for the understanding of the Standard Model. The LHCb collaboration now reports the coupling strength of the b quark to the u quark through the measurement of a baryonic decay mode.
- R. Aaij
- , B. Adeva
- & L. Zhong
-
News & Views |
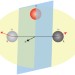 Giving directions
Giving directions
The Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction — the mechanism behind weak ferromagnetism — has been difficult to probe experimentally. Now, significant progress is reported that has important implications for a wide range of magnetic phenomena.
- Chong Der Hu
-
Letter |
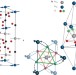 Measuring the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction in a weak ferromagnet
Measuring the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction in a weak ferromagnet
Oxygen-mediated superexchange (or Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya) interactions result in weak ferromagnetism in oxides. A method based on the interference of synchrotron X-ray radiation is now shown to enable the determination of the sign of the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction in the prototypical weak ferromagnet iron borate.
- V. E. Dmitrienko
- , E. N. Ovchinnikova
- & M. I. Katsnelson
-
News & Views |
 Picking up fine vibrations
Picking up fine vibrations
Femtosecond pulses from X-ray free-electron lasers offer a powerful method for studying charged collective excitations in materials, and provide a potential route to identifying bosonic quasiparticles in condensed-matter systems.
- Peter Abbamonte

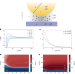 Magnetic-field tuning of the Casimir force
Magnetic-field tuning of the Casimir force