Featured
-
-
-
Interview |
 Femtophotography
Femtophotography
A burst-mode camera developed in Japan called STAMP with a femtosecond frame rate could become a powerful tool for studying ultrafast dynamics. Nature Photonics asked Keiichi Nakagawa about the technique.
- Noriaki Horiuchi
-
Letter |
 Sequentially timed all-optical mapping photography (STAMP)
Sequentially timed all-optical mapping photography (STAMP)
A single-shot burst camera has been developed that can generate motion pictures without performing repetitive measurements. It has a frame rate of 4.4 trillion frames per second and a high pixel resolution of 450 × 450 pixels, making it a powerful tool for observing difficult-to-reproduce or non-repetitive events in real time.
- K. Nakagawa
- , A. Iwasaki
- & I. Sakuma
-
News & Views |
 Watching a molecule breathe
Watching a molecule breathe
Marrying the single-molecule detection ability of surface-enhanced Raman scattering with the extreme time resolution of ultrafast coherent spectroscopy enables the vibrations of a single molecule to be observed.
- Lukasz Piatkowski
- , James T. Hugall
- & Niek F. van Hulst
-
-
Article |
 Shape-induced force fields in optical trapping
Shape-induced force fields in optical trapping
Through shaping of colloidal particles, optical traps with prescribed force–displacement profiles are generated and are used to design a microscopic constant-force spring capable of delivering a constant piconewton-scale restoring force for displacements of several micrometres. Potential future applications include the imaging of sensitive biological membranes.
- D. B. Phillips
- , M. J. Padgett
- & S. H. Simpson
-
-
-
Letter |
 Simultaneous measurement of nanoscale electric and magnetic optical fields
Simultaneous measurement of nanoscale electric and magnetic optical fields
Simultaneous detection of electric and magnetic fields with a subwavelength resolution is achieved by a near-field scanning approach. Additionally, theoretical considerations provide guidelines for designing probes sensitive to specific desired combinations of electric- and magnetic-field components.
- B. le Feber
- , N. Rotenberg
- & L. Kuipers
-
Letter |
 Tunable lifetime multiplexing using luminescent nanocrystals
Tunable lifetime multiplexing using luminescent nanocrystals
Control over the luminescence lifetimes of upconversion nanocrystals allows a new form of temporal multiplexing for imaging and data-storage applications.
- Yiqing Lu
- , Jiangbo Zhao
- & Dayong Jin
-
-
-
Letter |
 Multiphoton absorption in amyloid protein fibres
Multiphoton absorption in amyloid protein fibres
Two-, three- and higher multiphoton absorption processes are shown to occur in amyloid protein fibres, which are thought to play a role in various diseases, including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. The nonlinear optical behaviour of such proteins may also be useful for fabricating photonics devices.
- Piotr Hanczyc
- , Marek Samoc
- & Bengt Norden
-
-
-
Article |
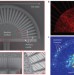 Compact spectrometer based on a disordered photonic chip
Compact spectrometer based on a disordered photonic chip
A miniature spectrometer has been developed that employs light scattering in a photonic chip with a random structure. It generates wavelength-dependent speckle patterns, which are detected and analysed to recover the spectrum of the input signal. It has a resolution of 0.75 nm in the 1,500 nm wavelength region.
- Brandon Redding
- , Seng Fatt Liew
- & Hui Cao
-
Article |
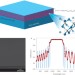 Tenfold reduction of Brownian noise in high-reflectivity optical coatings
Tenfold reduction of Brownian noise in high-reflectivity optical coatings
By employing monocrystalline semiconductor materials as high-quality optical coatings, the long-standing challenge of minimizing the optical phase noise produced by Brownian motion in a multilayer has been overcome. A thermally limited noise floor consistent with a tenfold reduction in mechanical damping relative to that in the best dielectric multilayers is achieved.
- Garrett D. Cole
- , Wei Zhang
- & Markus Aspelmeyer
-
Letter |
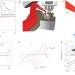 An ultrafast terahertz scanning tunnelling microscope
An ultrafast terahertz scanning tunnelling microscope
An ultrafast terahertz (THz) scanning tunnelling microscope (STM) with subpicosecond time resolution and nanometre spatial resolution has been developed. THz pulses are coupled to the metal tip of a commercial STM and THz-pulse-induced tunnelling is observed in the STM. The THz-STM can directly image ultrafast carrier capture by a single InAs nanodot.
- Tyler L. Cocker
- , Vedran Jelic
- & Frank A. Hegmann
-
-
-
Letter |
 Selection-rule breakdown in plasmon-induced electronic excitation of an isolated single-walled carbon nanotube
Selection-rule breakdown in plasmon-induced electronic excitation of an isolated single-walled carbon nanotube
Raman spectroscopy reveals selection-rule breakdown in the transitions of an isolated single-walled carbon nanotube. The breakdown may be caused by metal dimers and the high field gradient in the radial direction of the tubes.
- Mai Takase
- , Hiroshi Ajiki
- & Kei Murakoshi
-
-
Letter |
 Flat dielectric grating reflectors with focusing abilities
Flat dielectric grating reflectors with focusing abilities
Microscale planar optical elements based on high-reflectivity, non-periodic gratings provide a compact and convenient means for focusing and shaping light.
- David Fattal
- , Jingjing Li
- & Raymond G. Beausoleil
-
Letter |
 Highly power-efficient quantum cascade lasers
Highly power-efficient quantum cascade lasers
A quantum cascade laser with a wall-plug efficiency of up to 50% is experimentally realized when operated at low temperatures and in pulsed mode. The high-efficiency performance is achieved by implementing an ultrastrong coupling between the injector and active regions.
- Peter Q. Liu
- , Anthony J. Hoffman
- & Claire F. Gmachl
-
Letter |
 Quantum cascade lasers that emit more light than heat
Quantum cascade lasers that emit more light than heat
A mid-infrared quantum cascade laser that emits more light than heat and features a high wall-plug efficiency of up to 53% when operated a temperature of 40 K is reported. The device utilizes a single-well injector design.
- Yanbo Bai
- , Steven Slivken
- & Manijeh Razeghi

 Chemical composition mapping with nanometre resolution by soft X-ray microscopy
Chemical composition mapping with nanometre resolution by soft X-ray microscopy Colour imaging with single-pixel detectors
Colour imaging with single-pixel detectors Polymer yields 3D video
Polymer yields 3D video