Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access 3D skyrmion strings and their melting dynamics revealed via scalar-field electron tomography
3D skyrmion strings and their melting dynamics revealed via scalar-field electron tomography
3D skyrmion strings are topological spin textures promising for spintronics applications, but their manipulation and dynamics are challenging to understand. Here, high-resolution 3D phase imaging reveals the melting dynamics of metastable skyrmions, accompanied by the emergence of (anti)hedgehogs, in (Fe,Ni,Pd)3P and FeGe helimagnets.
- Xiuzhen Yu
- , Nobuto Nakanishi
- & Yoshinori Tokura
-
Article
| Open Access The collective photothermal effect of silver nanoparticles probed by a microbolometer
The collective photothermal effect of silver nanoparticles probed by a microbolometer
Due to their plasmonic properties, silver nanoparticles are promising across a vast range of applications, from physics instrumentation to biomedicine and environmental science. Here, the photon-to-heat conversion efficiency of individual nanoparticles is elucidated by designing and fabricating an ultra-sensitive bolometer with 26 pW power resolution.
- Hanliang Zhu
- , Evelína Gablech
- & Pavel Neuzil
-
Article
| Open Access Fabrication of stable monolayer liquid marbles with reduced particle coverage and locomotion on hydrophilic surface
Fabrication of stable monolayer liquid marbles with reduced particle coverage and locomotion on hydrophilic surface
Liquid marbles make use of surface particles to contain a water droplet, via a core-shell structure. Here, the fabrication of liquid marbles with a small quantity of surface polystyrene particles is demonstrated, and their rolling behavior on surfaces is studied.
- Jing Jin
- , Zheng Huang
- & Huaying Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Analyzing microstructure relationships in porous copper using a multi-method machine learning-based approach
Analyzing microstructure relationships in porous copper using a multi-method machine learning-based approach
Material properties prediction from a given microstructure is important for accelerated design but a comprehensive methodology is lacking. Here, a multi-method machine learning approach is utilized to understand the processing-structure-property relationship for differently processed porous materials.
- Andi Wijaya
- , Julian Wagner
- & Roland Brunner
-
Article
| Open Access Martensite decomposition during rapid heating of Ti-6Al-4V studied via in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction
Martensite decomposition during rapid heating of Ti-6Al-4V studied via in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction
Martensite in Ti-6Al-4V is known to decompose under heating. This study employs rapid laser heating in situ in a synchrotron to study changes in the diffraction profiles during the martensite decomposition process.
- Seunghee A. Oh
- , Joseph W. Aroh
- & Anthony D. Rollett
-
Article
| Open Access Activation of telecom emitters in silicon upon ion implantation and ns pulsed laser annealing
Activation of telecom emitters in silicon upon ion implantation and ns pulsed laser annealing
Defected silicon has uses in optically active telecom emitters. Here, nanosecond pulsed laser annealing is demonstrated as a non-invasive, localized method to activate the defects in high-purity silicon substrates.
- Greta Andrini
- , Gabriele Zanelli
- & Jacopo Forneris
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing thickness-dependent magnetic textures in few-layer Cr2Ge2Te6
Visualizing thickness-dependent magnetic textures in few-layer Cr2Ge2Te6
Magnetic ordering in 2D materials represents a promising platform for data storage, computing, and sensing. Here, nanometer scale imaging of few-layer Cr2Ge2Te6 reveals its thickness-dependent magnetic textures such as labyrinth domains and skyrmionic bubbles.
- Andriani Vervelaki
- , Kousik Bagani
- & Martino Poggio
-
Article
| Open Access Locally controlled MOF growth on functionalized carbon nanotubes
Locally controlled MOF growth on functionalized carbon nanotubes
Metal-organic frameworks are versatile materials but typically suffer from poor electrical conductivity. Here, a patterning technique allows controlled metal-organic framework growth on predefined areas of functionalized carbon nanotube for increased conductivity.
- Marvin J. Dzinnik
- , Necmettin E. Akmaz
- & Rolf J. Haug
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing per-grain and neighbourhood stress interactions of a deforming ferritic steel via three-dimensional X-ray diffraction
Revealing per-grain and neighbourhood stress interactions of a deforming ferritic steel via three-dimensional X-ray diffraction
The response of a polycrystalline material during loading is strongly dependent on grain-level effects, such as residual stress from plasticity and grain orientation. Here, in-situ three-dimensional X-ray diffraction reveals the role of local and interacting grain stresses in a ferritic steel.
- James A. D. Ball
- , Anna Kareer
- & David M. Collins
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional distribution of individual atoms in the channels of beryl
Three-dimensional distribution of individual atoms in the channels of beryl
Single atom detection in nanoporous materials is challenging due to their sensitivity to electron irradiation. Here, the three-dimensional atomic occupancy of natural beryl is quantitatively analysed using high-angle annular dark-field imaging in a scanning transmission electron microscope and statistical analysis.
- Daniel Knez
- , Christian Gspan
- & Ferdinand Hofer
-
Article
| Open Access Segregation-induced strength anomalies in complex single-crystalline superalloys
Segregation-induced strength anomalies in complex single-crystalline superalloys
The segregation of elements in superalloys is known to influence their mechanical properties. Here, atomic-scale imaging and theoretical calculations reveal a mechanism by which segregation causes a yield strength anomaly, strengthening the superalloy.
- Andreas Bezold
- , Jan Vollhüter
- & Steffen Neumeier
-
Article
| Open Access Unidirectional alignment and orientation pinning mechanism of h-BN nucleation on Ir(111) via reactive probe atomic force microscopy
Unidirectional alignment and orientation pinning mechanism of h-BN nucleation on Ir(111) via reactive probe atomic force microscopy
The epitaxial growth of large-scale single-crystalline 2D materials requires precise control over crystallographic orientation and morphology during the initial stages of nucleation. Here, noncontact atomic force microscopy and density functional theory provide atomic-scale mechanistic insights into the nucleation of hexagonal boron nitride on Ir(111).
- Jinliang Pan
- , Tongwei Wu
- & Xiaohui Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Ring-originated anisotropy of local structural ordering in amorphous and crystalline silicon dioxide
Ring-originated anisotropy of local structural ordering in amorphous and crystalline silicon dioxide
Quantification of large topological motifs is important for understanding chemical linkages between structural ordering and macroscopic behaviors. Here, two quantitative analysis methods based on rings are proposed to reveal information on orders and linkages in crystalline and amorphous materials.
- Motoki Shiga
- , Akihiko Hirata
- & Hirokazu Masai
-
Review Article
| Open Access Advantages and developments of Raman spectroscopy for electroceramics
Advantages and developments of Raman spectroscopy for electroceramics
Raman spectroscopy is a popular non-destructive characterisation technique, but its application to electroceramics is under-represented compared to other fields. In this review, the latest instrumentational and computational advances are discussed, suggesting key advantages in the study of electroceramics.
- Marco Deluca
- , Hailong Hu
- & Thomas Dieing
-
Article
| Open Access Algorithm for fast evaluation of in-plane fiber orientation in reinforced plastics using light microscopy images
Algorithm for fast evaluation of in-plane fiber orientation in reinforced plastics using light microscopy images
The orientation of reinforcing fibers in composite materials is key to their performance, yet is hard to determine as fibers are buried within a sample. Here, an algorithm allows for the rapid determination of in-plane fiber orientation, based on microscopy images of adjacent regions.
- Klara Wiegel
- , André Schlink
- & Hans-Peter Heim
-
Article
| Open Access Time gated Fourier transform spectroscopy as a technique for disentangling short- and long-lived luminescence
Time gated Fourier transform spectroscopy as a technique for disentangling short- and long-lived luminescence
Tools for characterizing materials both spectrally and temporally are important to investigate fundamental properties of materials. Here, 2D temporal-spectral maps are shown to be useful for characterizing and discriminating luminescence signals that occur on widely different timescales.
- Mikkel Baldtzer Liisberg
- & Tom Vosch
-
Review Article
| Open Access Advanced spectroscopic techniques for characterizing defects in perovskite solar cells
Advanced spectroscopic techniques for characterizing defects in perovskite solar cells
There is great interest in commercializing perovskite solar cells, however, the presence of defects and trap states hinder their performance. Here, recent developments in characterization techniques to investigate defects and ion migration in halide perovskites are reviewed.
- Saurabh Srivastava
- , Sudhir Ranjan
- & Kanwar S. Nalwa
-
Article
| Open Access Partial liquid metal dealloying to synthesize nickel-containing porous and composite ferrous and high-entropy alloys
Partial liquid metal dealloying to synthesize nickel-containing porous and composite ferrous and high-entropy alloys
Liquid metal dealloying is performed by immersing soluble and insoluble elements into a liquid metal bath but this prevents precise composition control. Here, the authors control the amount of soluble element remaining in the microstructure by partial dealloying and applied them to high-entropy alloys.
- Takeshi Wada
- , Pierre-Antoine Geslin
- & Hidemi Kato
-
Article
| Open Access Additive manufacturing of a high-performance aluminum alloy from cold mechanically derived non-spherical powder
Additive manufacturing of a high-performance aluminum alloy from cold mechanically derived non-spherical powder
Additive manufacturing typically uses spherical powder feedstock prepared by gas or plasma atomization. Here, a high-performance aluminum alloy is prepared from cold mechanically derived powder, showing the viability of non-spherical powders for good mechanical properties.
- J. Hunter Martin
- , John E. Barnes
- & David F. Bahr
-
Article
| Open Access Defect engineering of silicon with ion pulses from laser acceleration
Defect engineering of silicon with ion pulses from laser acceleration
Defect engineering and doping of semiconductors by ion irradiation are essential in large-scale integration of electronic devices. Here, intense ion pulses from a laser-accelerator, with flux levels up to 1022 ions cm-2 s-1, are used to induce and optimize silicon color centers and photon emitters in the telecom band.
- Walid Redjem
- , Ariel J. Amsellem
- & Thomas Schenkel
-
Article
| Open Access Probing the composition dependence of residual stress distribution in tungsten-titanium nanocrystalline thin films
Probing the composition dependence of residual stress distribution in tungsten-titanium nanocrystalline thin films
Nanocrystalline thin films fabricated by deposition often have high residual stresses, making them susceptible to defects. Here, stress distribution in tungsten-titanium nanocrystalline films are probed by experimental and simulation techniques, revealing the impact of solute concentration on residual stress.
- Rahulkumar Jagdishbhai Sinojiya
- , Priya Paulachan
- & Roland Brunner
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic molecular ordering in multiphasic nanoconfined ionic liquids detected with time-resolved diffusion NMR
Dynamic molecular ordering in multiphasic nanoconfined ionic liquids detected with time-resolved diffusion NMR
Molecular motion in nanosized pores can be extremely complex. Here, NMR diffusion experiments in different relaxation windows and molecular dynamics simulations suggest an unusual dynamic molecular ordering when an ionic liquid is confined in nanoporous silica.
- Marina Karagianni
- , Lydia Gkoura
- & Georgios Papavassiliou
-
Article
| Open Access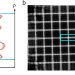 Sub-10 second fly-scan nano-tomography using machine learning
Sub-10 second fly-scan nano-tomography using machine learning
Image reconstruction algorithms used in x-ray computed tomography require that the sample not change throughout the scan, necessitating fast data collection times. Here, a machine learning approach for image processing enables sub-10 second data acquisition times and sub-50 nm pixel resolution.
- Jiayong Zhang
- , Wah-Keat Lee
- & Mingyuan Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Machine-learning for designing nanoarchitectured materials by dealloying
Machine-learning for designing nanoarchitectured materials by dealloying
Nanoporous metals produced by metal agent dealloying are attractive for multiple applications. Here, a machine learning-augmented framework is reported for predicting, synthesizing and characterizing ternary systems for dealloying.
- Chonghang Zhao
- , Cheng-Chu Chung
- & Yu-chen Karen Chen-Wiegart
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling the effect of collagen damage on bone fracture using in situ synchrotron microtomography with deep learning
Unraveling the effect of collagen damage on bone fracture using in situ synchrotron microtomography with deep learning
Collagen is known to play a key role in the fracture resistance of bone. Here, in situ synchrotron tomography during the mechanical testing of bone is combined with deep learning to mitigate radiation damage, revealing that a compromised collagen network lowers the efficacy of crack deflection.
- Michael Sieverts
- , Yoshihiro Obata
- & Claire Acevedo
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid molecular beam epitaxy of germanium-based oxides
Hybrid molecular beam epitaxy of germanium-based oxides
Germanium-based oxides are wide bandgap semiconductors with the prospects of ambipolar doping. Here, a hybrid molecular beam epitaxy is demonstrated for the growth of both rutile Sn1-xGexO2 and perovskite SrSn1-xGexO3 films.
- Fengdeng Liu
- , Tristan K. Truttmann
- & Bharat Jalan
-
Article
| Open Access Nanomechanical signatures of degradation-free influence of water on halide perovskite mechanics
Nanomechanical signatures of degradation-free influence of water on halide perovskite mechanics
Humidity can change the properties of halide perovskites used in functional devices. Here, indentation experiments reveal that humidity causes an increase in elastic modulus and a decrease in hardness, which is correlated to bond length, hydrogen bonding and polarizability of the ions.
- Isaac Buchine
- , Irit Rosenhek-Goldian
- & Sidney R. Cohen
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically tuneable terahertz metasurface enabled by a graphene/gold bilayer structure
Electrically tuneable terahertz metasurface enabled by a graphene/gold bilayer structure
Reconfigurable and tunable terahertz electronic devices are promising for various technological applications, for which metamaterials are receiving interest. Here, a graphene/gold bilayer metasurface enables the creation of a frequency-selective absorber with electrical tuning in the 0.1–1 THz range.
- Andrew D. Squires
- , Xiang Gao
- & Tim van der Laan
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding irradiation damage in high-temperature superconductors for fusion reactors using high resolution X-ray absorption spectroscopy
Understanding irradiation damage in high-temperature superconductors for fusion reactors using high resolution X-ray absorption spectroscopy
Understanding the effects of fast neutrons on high-temperature superconductors is important for their application in fusion reactors. Here, a combined experimental and theoretical study reveals that ion irradiation disrupts superconductivity by introducing defects within the copper-oxygen planes.
- Rebecca J. Nicholls
- , Sofia Diaz-Moreno
- & Susannah C. Speller
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional in situ imaging of single-grain growth in polycrystalline In2O3:Zr films
Three-dimensional in situ imaging of single-grain growth in polycrystalline In2O3:Zr films
Understanding grain morphology and kinetics of solid-phase crystallization is important for controlling the functional properties of polycrystalline materials. Here, in situ coherent X-ray diffraction imaging and transmission electron microscopy elucidate quantitatively the kinetics of a single-grain growth in Zr-doped In2O3 films.
- Dmitry Dzhigaev
- , Yury Smirnov
- & Michael Elias Stuckelberger
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional imaging of grain boundaries via quantitative fluorescence X-ray tomography analysis
Three-dimensional imaging of grain boundaries via quantitative fluorescence X-ray tomography analysis
Visualizing the composition of grain networks is key for understanding the structure evolution and functional properties of composite materials. Here, X-ray fluorescence tomography, coupled with an absorption correction algorithm, reveals mechanistic insights in the phase transformations and transport properties of a mixed ionic-electronic conductor.
- Mingyuan Ge
- , Xiaojing Huang
- & Yong S. Chu
-
Article
| Open Access Shear band formation during nanoindentation of EuB6 rare-earth hexaboride
Shear band formation during nanoindentation of EuB6 rare-earth hexaboride
Rare-earth hexaborides are of interest for their pressure-induced phase transformations, but further understanding is needed regarding their failure mechanisms. Here, nanoindentation of EuB6 causes dislocation-mediated shear band formation, driven by the breaking of boron-boron bonds.
- Rajamallu Karre
- , Yidi Shen
- & Kolan Madhav Reddy
-
Article
| Open Access Corrosion resistant and high-strength dual-phase Mg-Li-Al-Zn alloy by friction stir processing
Corrosion resistant and high-strength dual-phase Mg-Li-Al-Zn alloy by friction stir processing
Mg-Li alloys are attractive for their low density, yet typically suffer from limited strength and rapid corrosion. Here, both these issues are addressed in a Mg-Li-Al alloy by friction stir processing followed by liquid CO2 quenching, resulting in a durable microstructure.
- Zhuoran Zeng
- , Mengran Zhou
- & Nick Birbilis
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput exploration of halide perovskite compositionally-graded films and degradation mechanisms
High-throughput exploration of halide perovskite compositionally-graded films and degradation mechanisms
High-throughput materials discovery can reduce the time taken to identify high-performing materials. Here, compositionally-graded films are fabricated in a binary halide perovskite system, of interest for solar cells, and their stability investigated during artificial aging.
- Shahram Moradi
- , Soumya Kundu
- & Makhsud I. Saidaminov
-
Article
| Open Access A consistent picture of excitations in cubic BaSnO3 revealed by combining theory and experiment
A consistent picture of excitations in cubic BaSnO3 revealed by combining theory and experiment
The BaSnO3 perovskite is promising for electronic applications due to its transparency and high room-temperature mobility, but its effective masses, band gaps, and absorption edge are still controversial. Here, a combined theoretical and experimental study provides a consistent picture of its electronic structure and optical excitations.
- Wahib Aggoune
- , Alberto Eljarrat
- & Claudia Draxl
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable metal contacts at layered black-arsenic/metal interface forming during metal deposition for device fabrication
Tunable metal contacts at layered black-arsenic/metal interface forming during metal deposition for device fabrication
In 2D materials devices, understanding interfacial reactions in the formation of metal contacts is important for tuning their properties. Here, electron microscopy reveals the formation of an intermetallic contact layer, characterized by an efficient edge-type charge transfer, when nickel, chromium, or titanium is deposited onto black-arsenic films.
- Subhajit Kundu
- , Prafful Golani
- & K. Andre Mkhoyan
-
Article
| Open Access Disentangling surface atomic motions from surface field effects in ultrafast low-energy electron diffraction
Disentangling surface atomic motions from surface field effects in ultrafast low-energy electron diffraction
Ultrafast low-energy electron diffraction allows the direct observation of atomic motions in structural transitions, but is accompanied by a strong photoinduced emission resulting in surface field effects. Here, these effects are quantified, enabling the isolation of the structural dynamics of interest.
- Chiwon Lee
- , Alexander Marx
- & R. J. Dwayne Miller
-
Article
| Open Access Ptychography at the carbon K-edge
Ptychography at the carbon K-edge
Ptychography is an imaging technique based on algorithmic reconstruction of diffraction patterns that improves the spatial resolution of scanning transmission X-ray microscopy. Here, the possibility of ptychography at the carbon K-edge is demonstrated on carbon nanotube bundles, using a defocused beam to reduce radiation damage.
- Nicolas Mille
- , Hao Yuan
- & Adam P. Hitchcock
-
Article
| Open Access Charged domain boundaries stabilized by translational symmetry breaking in the hybrid improper ferroelectric Ca3–xSrxTi2O7
Charged domain boundaries stabilized by translational symmetry breaking in the hybrid improper ferroelectric Ca3–xSrxTi2O7
Charged domain walls in ferroelectrics are interesting as they may enhance electrical conductivity. Here, atomic-resolution imaging of Ca3–xSrxTi2O7 reveals that charged domain boundaries are stabilized by an out-of-phase translational shift of crystallographic domains and that Sr ions accumulate at the boundaries.
- Hiroshi Nakajima
- , Kosuke Kurushima
- & Shigeo Mori
-
Article
| Open Access Utilizing local phase transformation strengthening for nickel-base superalloys
Utilizing local phase transformation strengthening for nickel-base superalloys
There is an ongoing need to increase the operating temperature of jet engines, requiring new high-temperature materials. Here, local phase transformations at superlattice stacking faults contribute to a three times improvement in creep strength in a Ni-based superalloy.
- Timothy M. Smith
- , Nikolai A. Zarkevich
- & Michael J. Mills
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible and high precision thermal metasurface
Flexible and high precision thermal metasurface
Thermal cloak metamaterials are important in heat camouflage and protection of electronic devices, but are often purely metallic and limited in flexibility. Here, a durable, non-cracking, and anti-corrosive thermal metasurface is fabricated by laser engraving a graphene coating onto a copper substrate.
- Jiyao Wang
- , Ling Qin
- & Wei Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Electron dynamics of tip-tunable oxygen species on TiO2 surface
Electron dynamics of tip-tunable oxygen species on TiO2 surface
Oxygen species on a TiO2 surface exist in different redox states, which can be switched between by electron tunneling with an atomic force tip. Here, a fast experimental setup enables statistically significant tunneling rates to be determined, revealing changes in electronic structure.
- Yuuki Adachi
- , Ján Brndiar
- & Lev Kantorovich
-
Article
| Open Access X-ray free electron laser heating of water and gold at high static pressure
X-ray free electron laser heating of water and gold at high static pressure
The study of water at high pressure and temperature is essential for understanding planetary interiors but is hampered by the high reactivity of water at extreme conditions. Here, indirect X-ray laser heating of water in a diamond anvil cell is realized via a gold absorber, showing no evidence of reactivity.
- Rachel J. Husband
- , R. Stewart McWilliams
- & Hanns-Peter Liermann
-
Article
| Open Access In situ plant materials hyperspectral imaging by multimodal scattering near-field optical microscopy
In situ plant materials hyperspectral imaging by multimodal scattering near-field optical microscopy
Plant cells are elaborate three-dimensional polymer nano-constructs with complex chemistry. Here, multimodal scattering nearfield optical microscopy of poplar trees is used to establish in situ high-resolution mappings of the local dielectric functions and compositional distribution of lignin and cellulose in plant cell walls.
- Anne M. Charrier
- , Aubin C. Normand
- & Aude L. Lereu
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution stereolithography using a static liquid constrained interface
High-resolution stereolithography using a static liquid constrained interface
Stiction between polymerized layers and the constraining solid interface during stereolithography limits resolution. Here, a static inert liquid is used as a constraining interface to mitigate stiction, enabling high resolution parts to be fabricated with feature sizes spanning tens to thousands of microns.
- Aftab A. Bhanvadia
- , Richard T. Farley
- & Toshikazu Nishida
-
Article
| Open Access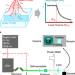 Direct correlation of local fluence to single-pulse ultrashort laser ablated morphology
Direct correlation of local fluence to single-pulse ultrashort laser ablated morphology
Describing the laser ablation process with reduction-free data is important for furthering its use in modern manufacturing. Here, fluence maps, correlating laser beam intensity and ablated depth at each point in a full two-dimensional space, provide a method to probe ablation morphology in cases of arbitrary beam and crater profiles.
- Haruyuki Sakurai
- , Kuniaki Konishi
- & Makoto Kuwata-Gonokami
-
Article
| Open Access Fish-inspired flexible protective material systems with anisotropic bending stiffness
Fish-inspired flexible protective material systems with anisotropic bending stiffness
Armored fish exoskeletons combine flexibility and protection from predators and territorial attacks. Here, using modeling, 3D printing, and experimental testing, the mechanical origin of anisotropic bending stiffness in fish scale architectures is revealed, providing design guidelines for biomimetics.
- Katia Zolotovsky
- , Swati Varshney
- & Christine Ortiz
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum magnetoconductivity characterization of interface disorder in indium-tin-oxide films on fused silica
Quantum magnetoconductivity characterization of interface disorder in indium-tin-oxide films on fused silica
Disorder in semiconductors may lead to quantum interference and positive magnetoconductivity, whose maximum value in 3D is independent of material properties. Here, an apparent violation of this upper bound, in Sn-doped In2O3 films on fused silica, is explained by a model that accounts for additional disorder close to the interface.
- David C. Look
- , Kevin D. Leedy
- & Stefan C. Badescu
-
Article
| Open Access Transient morphology of lithium anodes in batteries monitored by in operando pulse electron paramagnetic resonance
Transient morphology of lithium anodes in batteries monitored by in operando pulse electron paramagnetic resonance
Knowing the morphology of lithium anodes is important for designing batteries with long service life. Here, pulse electron paramagnetic resonance is used to monitor pulsed plating of lithium on a timescale of 100 ms, revealing transient morphology changes after the charging pulse ended.
- Conrad Szczuka
- , Jörg Ackermann
- & Josef Granwehr

 In situ observation and reduction of hot-cracks in laser additive manufacturing
In situ observation and reduction of hot-cracks in laser additive manufacturing