Featured
-
-
Review Article |
 Global epidemiology of epithelial ovarian cancer
Global epidemiology of epithelial ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer, accounting for 4.7% of cancer deaths in women in 2020, remains highly prevalent globally. Nonetheless, owing to changes in environmental exposures, the approach to preventive measures and disease classification, both incidence and mortality have been declining in economically developed countries since the early 2000s. Conversely, parts of Asia and eastern Europe have seen increases in the incidence of ovarian cancer over this period of time. In this Review, the authors summarize the epidemiology of ovarian cancer, including the roles of the various risk factors and the potential for prevention.
- Penelope M. Webb
- & Susan J. Jordan
-
Review Article |
 Global burden of gastric cancer: epidemiological trends, risk factors, screening and prevention
Global burden of gastric cancer: epidemiological trends, risk factors, screening and prevention
Globally, gastric cancer is a common and highly fatal cancer with two anatomical subtypes, non-cardia and cardia gastric cancer. Helicobacter pylori causes almost 90% of distal gastric cancers worldwide. The authors of this Review summarize the current epidemiology of gastric cancer and the evidence and implications of primary and secondary prevention efforts.
- Aaron P. Thrift
- , Theresa Nguyen Wenker
- & Hashem B. El-Serag
-
Review Article |
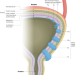 Global trends in the epidemiology of bladder cancer: challenges for public health and clinical practice
Global trends in the epidemiology of bladder cancer: challenges for public health and clinical practice
Bladder cancer is among the ten most common cancers worldwide and therefore constitutes a substantial health-care burden. This Review summarizes the global trends in bladder cancer incidence and mortality, and describes the main risk factors associated with bladder cancer occurrence and outcomes. The implications, challenges and opportunities of these epidemiological trends for public health and clinical practice are also discussed.
- Lisa M. C. van Hoogstraten
- , Alina Vrieling
- & Lambertus A. Kiemeney
-
Review Article |
 Is early-onset cancer an emerging global epidemic? Current evidence and future implications
Is early-onset cancer an emerging global epidemic? Current evidence and future implications
The incidence of early-onset forms of many cancers (defined as cancers diagnosed in individuals <50 years of age) has increased in a number of countries over the past several decades. The underlying reasons for this apparent increase probably include greater use of screening programmes, but also changing patterns in early-life exposures. In this Review, the authors describe the emerging global increase in the incidence of early-onset cancers and suggest changes that might address this situation.
- Tomotaka Ugai
- , Naoko Sasamoto
- & Shuji Ogino
-
Perspective |
 Planning for tomorrow: global cancer incidence and the role of prevention 2020–2070
Planning for tomorrow: global cancer incidence and the role of prevention 2020–2070
Assuming that the latest incidence trends continue for the major cancer types, the incidence of all cancers combined will double by 2070 relative to 2020, with the greatest increases predicted in lower-resource settings. The authors of this Perspective discuss how population-level approaches with amenable goals should be considered an integral part of cancer control.
- Isabelle Soerjomataram
- & Freddie Bray
-
Review Article |
 Targeting cancer-promoting inflammation — have anti-inflammatory therapies come of age?
Targeting cancer-promoting inflammation — have anti-inflammatory therapies come of age?
Chronic inflammation can promote the development of various cancers. In this Review, the current clinical advances in ameliorating inflammation for the prevention or treatment of cancer are highlighted, and the experimental insights into the biological mechanisms supporting current and potential novel anti-inflammatory approaches to the management of cancer are discussed.
- Jiajie Hou
- , Michael Karin
- & Beicheng Sun
-
Perspective |
 Rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer — a call to action
Rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer — a call to action
The incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer (CRC) is increasing worldwide for reasons that are currently unclear. Herein, the authors review the current epidemiological, clinical, pathological and molecular understanding of early-onset CRC that occurs in patients ≥50 years of age, drawing contrasts with later-onset CRC. They also discuss future research strategies for improved understanding, prevention, early detection and clinical management of early-onset CRC.
- Naohiko Akimoto
- , Tomotaka Ugai
- & Shuji Ogino
-
Review Article |
 The role of genomics in global cancer prevention
The role of genomics in global cancer prevention
Technological advances have enabled the analysis of whole genomes, leading to the identification of causal factors that present new opportunities to prevent cancer. The authors of this Review discuss relevant findings in cancer genetics and genomics from the perspective of global cancer prevention and present a conceptual framework for the translation of such findings into clinical practice and evidence-based policies.
- Ophira Ginsburg
- , Patricia Ashton-Prolla
- & Paul Brennan
-
Perspective |
 The changing landscape of cancer in the USA — opportunities for advancing prevention and treatment
The changing landscape of cancer in the USA — opportunities for advancing prevention and treatment
Monitoring both cancer incidence and death rates is important for guiding health policy and the direction of future research. In this Perspective, the authors describe changes in cancer incidence and death rates in the USA, highlighting the effects of specific policies and research developments, and providing insight into unmet needs that should be addressed by future health policies.
- Farhad Islami
- , Rebecca L. Siegel
- & Ahmedin Jemal
-
News & Views |
 Health burden in cancer survivors: below the tip of the iceberg
Health burden in cancer survivors: below the tip of the iceberg
In recent decades, cancer survival has improved dramatically, resulting in a growing population of cancer survivors with chronic health needs and disease risks. While large epidemiological studies are useful in tracking broad trends in health outcomes of cancer survivors, they lack the level of detail needed to inform the delivery of appropriate clinical care and optimal allocation of resources.
- Eden R. Brauer
- & Patricia A. Ganz
-
Perspective |
 Integrated molecular and clinical staging defines the spectrum of metastatic cancer
Integrated molecular and clinical staging defines the spectrum of metastatic cancer
The oligometastatic paradigm challenges the prevailing view of metastasis as a disseminated process and proposes the existence of a spectrum of biological virulence within metastatic lesions. The authors present evidence for this heterogeneity and discuss how it affects the staging and treatment of patients with metastatic cancer.
- Sean P. Pitroda
- & Ralph R. Weichselbaum
-
Review Article |
 Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes in the era of immune-checkpoint inhibitors
Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes in the era of immune-checkpoint inhibitors
Immunotherapy with immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) is a new pillar in the treatment of cancer but can a have range of immune-related adverse effects, including some rare neurological toxicities that constitute paraneoplastic neurological syndromes (PNSs). In this Review, the authors provide an overview of PNSs, the associations of these conditions with ICI therapy and recommendations for the prevention and management of ICI-associated PNSs.
- Francesc Graus
- & Josep Dalmau
-
Correspondence |
Time for a change and to adopt a novel molecular genomic approach in NETs
- Lisa Bodei
- , Eric Liu
- & Ronald R. Salem
-
Correspondence |
Reply to ‘Time for a change and to adopt a novel molecular genomic approach in NETs’
- Guido Rindi
- & Bertram Wiedenmann
-
Review Article |
 Liquid biopsy and minimal residual disease — latest advances and implications for cure
Liquid biopsy and minimal residual disease — latest advances and implications for cure
In this Review, Pantel and Alix-Panabières provide an overview of approaches for the detection and characterization of minimal residual disease (MRD) using circulating tumour cells and circulating tumour DNA. They also discuss the clinical implications of such liquid biopsy approaches to MRD monitoring for the management of patients with cancer.
- Klaus Pantel
- & Catherine Alix-Panabières
-
-
News & Views |
Neuroendocrine neoplasia goes molecular — time for a change
In a cohort of 100 patients with neuroendocrine cancer, the use of NETest enabled earlier prediction of tumour progression and resulted in a reduction in the frequency of follow-up procedures. These outcomes are exciting and promising, but limited in value by the heterogeneity of the study cohort and by suboptimal assay sensitivity and specificity.
- Guido Rindi
- & Bertram Wiedenmann
-
-
News & Views |
How to eliminate gastric cancer-related death worldwide?
Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy is effective in preventing gastric cancer, even in patients with advanced pre-neoplastic lesions (gastric atrophy and/or intestinal metaplasia). We must now focus on how to accomplish the goal of eliminating gastric cancer-related death worldwide; strategies for screening and treatment of gastric neoplasia (primary prevention) and post-treatment surveillance (secondary prevention) are discussed herein.
- Yoshio Yamaoka
-
Review Article |
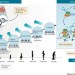 Epigenome-based cancer risk prediction: rationale, opportunities and challenges
Epigenome-based cancer risk prediction: rationale, opportunities and challenges
The development of cancer involves several epigenomic alterations, and the presence of certain alterations before the development of cancer is associated with cancer risk. In this Review, the authors describe the potential of epigenomics-based assays to predict an individual's risk of cancer, including discussions of technical, practical and societal issues regarding the implementation of such assays.
- Martin Widschwendter
- , Allison Jones
- & Nora Pashayan
-
Review Article |
 Exogenous reproductive hormone use in breast cancer survivors and previvors
Exogenous reproductive hormone use in breast cancer survivors and previvors
The safety of elective exogenous hormonal exposure among breast cancer survivors or women at high risk of having the disease has been debated for decades. Herein, the authors discuss the available data and present clinical recommendations regarding four areas of potential exogenous exposure to hormones: hormonal contraception; systemic hormone-replacement therapy; localized hormone-replacement therapy; and hormonal manipulation for fertility preservation or enhancement. Further research is needed to improve patient management in the future.
- Ines Vaz-Luis
- & Ann H. Partridge
-
-
-
Review Article |
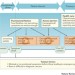 Diagnosis of cancer as an emergency: a critical review of current evidence
Diagnosis of cancer as an emergency: a critical review of current evidence
Patients diagnosed with cancer through an emergency presentation have worse outcomes compared with those in whom cancer is diagnosed through other routes; therefore, reducing the number of patients presenting as an emergency with cancer will improve patients' outcomes. In this Review, the authors describe the available evidence in this area, and provide recommendations for future research, clinical practice and public health policy.
- Yin Zhou
- , Gary A. Abel
- & Georgios Lyratzopoulos
-
Research Highlight |
 Genetic signature might spare 100,000 women annually from chemotherapy
Genetic signature might spare 100,000 women annually from chemotherapy
- David Killock
-
-
Review Article |
 Cancer, obesity, diabetes, and antidiabetic drugs: is the fog clearing?
Cancer, obesity, diabetes, and antidiabetic drugs: is the fog clearing?
The prevalence rates of obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and cancer are increasing globally. Herein, the relationships between these diseases and their treatments are reviewed, and the practical principles relevant to the increasingly common challenge of managing patients who have been diagnosed with both diabetes and cancer are outlined.
- Adi J. Klil-Drori
- , Laurent Azoulay
- & Michael N. Pollak
-
-
News & Views |
A risk-based framework to decide who benefits from screening
We believe that current controversies surrounding screening might be better approached by shifting the question from 'does screening work?' to 'for whom does screening work?' We propose a 'rule-out/rule-in' principle as an intellectual basis and starting point for screening. Finally, we advocate the 'equal management of equal risks' principle as an unifying framework for developing simplified and consistent screening guidelines and practice.
- Philip E. Castle
- & Hormuzd A. Katki
-
-
Review Article |
 Diet, nutrition, and cancer: past, present and future
Diet, nutrition, and cancer: past, present and future
Diet has long been linked with the development and progression of cancer, and indeed obesity is a clear risk factor for many cancers; however, teasing out the relationships between nutritional factors and cancer aetiology has proved difficult, complicating the development of dietary recommendations for cancer prevention. In this Review, the issues and challenges in diet–cancer research are discussed, including those relating to the design of epidemiological studies, dietary data collection methods, and factors that affect the outcome of intervention trials.
- Susan T. Mayne
- , Mary C. Playdon
- & Cheryl L. Rock
-
News & Views |
 Personalized risk — stratified screening or abandoning it altogether?
Personalized risk — stratified screening or abandoning it altogether?
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA)-based screening approaches are associated with reduced prostate-cancer mortality, but can lead to overdiagnosis, unnecessary biopsies and overtreatment. Two solutions for this problem exist: to abandon PSA-based screening completely, or to improve the accuracy of PSA-based screening methods to solve the benefit-to-harm equation. Herein we explore these solutions by examining three recent publications.
- Sigrid V. Carlsson
- & Michael W. Kattan
-
-
Review Article |
 Revisiting tumour aneuploidy — the place of ploidy assessment in the molecular era
Revisiting tumour aneuploidy — the place of ploidy assessment in the molecular era
Chromosome instability (CIN) is gaining increasing interest as a central process in cancer, and is indicated whenever tumour cells harbour an abnormal quantity of DNA, termed 'aneuploidy'. In this Review, the authors review the literature published since 2000 that support the hypothesis that aneuploidy is a predictor of a poor prognosis in patients with cancer, focusing on the evidence from studies of seven common epithelial cancer types that performed multivariate analyses. The implications of ploidy analysis with regard to our theoretical understanding of the role of CIN in carcinogenesis, as well as its prognostic use in the clinic, are discussed.
- Håvard E. Danielsen
- , Manohar Pradhan
- & Marco Novelli
-
-
News & Views |
 What do breast and CRC cancers and MS have in common?
What do breast and CRC cancers and MS have in common?
Dairy cattle meat and milk factors are proposed as risks for colon and breast cancers. Several novel small circular DNAs that are genetically active in human cells have been isolated from bovine sera and milk. Such agents have also been detected in two lesions of multiple sclerosis. A unifying concept is presented putatively explaining the risks for these diseases that are associated with these factors.
- Harald zur Hausen
-
-
-
-
Research Highlight |
Management of patients with prostate cancer: evolution towards a risk-stratified approach
- Peter Sidaway
-
News & Views |
 Oophorectomy for BRCA1 ER-negative disease—an open debate
Oophorectomy for BRCA1 ER-negative disease—an open debate
Risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy (RRSO) is a standard intervention in BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation carriers owing to its associated reduction in mortality related to ovarian and breast cancer. A study has now reported a beneficial impact of adjuvant RRSO in patients with BRCA1 mutations and breast cancer. However, various biases confound these results.
- Noah Kauff
- & Mark Robson
-
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
New standard of care—HPV testing for cervical cancer screening
High-risk human papillomavirus (hrHPV) types cause cervical cancer. Hence, a negative hrHPV test provides excellent reassurance against cervical precancer and cancer, superior to a negative cervical smear (Papanicolaou or Pap) test. Screening first for hrHPV might improve the accuracy and positive predictive value of secondary Pap testing in hrHPV-positive women, and thus guide decisions on what care is needed.
- Philip E. Castle
-
-
Review Article |
 Cancer-related fatigue—mechanisms, risk factors, and treatments
Cancer-related fatigue—mechanisms, risk factors, and treatments
Fatigue is one of the most common adverse effects of cancer that might persist for years after treatment completion. Among the biological mechanisms underlying cancer-related fatigue, inflammation processes have a key role in the development and persistence of this symptom. In addition, genetic, biological, psychosocial, and behavioural risk factors are also associated with the occurrence of cancer-related fatigue. This Review describes the mechanisms, risk factors, and possible interventions for cancer-related fatigue.
- Julienne E. Bower
-
Review Article |
 Management of low risk prostate cancer—active surveillance and focal therapy
Management of low risk prostate cancer—active surveillance and focal therapy
Low-risk prostate cancer is diagnosed in nearly half of men undergoing screening. About a third of these men harbour high-grade cancer that is not detected by conventional systematic biopsy. Should we treat men with low-risk prostate on the basis that it might be of higher grade than it seems? Should we treat it to prevent future progression to a more aggressive form of cancer? What are the nonivasive treatment options for these men? In this Review, Mark Emberton and Laurence Klotz discuss the two current choices to manage low-risk prostate cancer: active surveillance and focal therapy.
- Laurence Klotz
- & Mark Emberton

 Epidemiology of HPV-associated cancers past, present and future: towards prevention and elimination
Epidemiology of HPV-associated cancers past, present and future: towards prevention and elimination CTCs ‘piggyback’ off neutrophils
CTCs ‘piggyback’ off neutrophils AS—contemplation, not intervention
AS—contemplation, not intervention