Research Highlights |
Featured
-
-
Article |
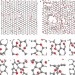 Structural evolution during the reduction of chemically derived graphene oxide
Structural evolution during the reduction of chemically derived graphene oxide
Thermal reduction of graphene oxide is an attractive route towards the preparation of graphene, but complete removal of residual oxygen is problematic. Now, molecular dynamics simulations elucidate the chemical changes involved in this process.
- Akbar Bagri
- , Cecilia Mattevi
- & Vivek B. Shenoy
-
News & Views |
 Springing into action
Springing into action
Controlling the movements of molecular systems through external stimuli is crucial for the construction of nanoscale mechanical machines. A spring-like compound has now been prepared — a double helicate that retains its handedness under ion-triggered extension and contraction.
- Ben L. Feringa
-
Article |
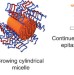 Monodisperse cylindrical micelles by crystallization-driven living self-assembly
Monodisperse cylindrical micelles by crystallization-driven living self-assembly
In analogy to classical living polymerizations, the controlled formation of highly monodisperse cylindrical micelles — ranging from approximately 200 nm to 2 µm in length — has been demonstrated using very small and uniform crystallite seeds as initiators for the crystallization-driven living self-assembly of block copolymers with a crystallizable, core-forming metalloblock.
- Joe B. Gilroy
- , Torben Gädt
- & Ian Manners
-
Research Highlights |
 Filled and functional
Filled and functional
Radioactive iodide can be aimed at specific organs in the body by trapping it inside sugar-functionalized carbon nanotubes.
- Stephen Davey
-
Article |
 Synthesis of a metal oxide with a room-temperature photoreversible phase transition
Synthesis of a metal oxide with a room-temperature photoreversible phase transition
Optically driven phase transitions are widely used in optical memory devices, and the materials showing this effect are normally chalcogenides or organic compounds. Now a room-temperature light-induced phase transition between metal and semiconducting phases has been observed in a titanium oxide material.
- Shin-ichi Ohkoshi
- , Yoshihide Tsunobuchi
- & Hiroko Tokoro
-
Article |
 Direct transformation of graphene to fullerene
Direct transformation of graphene to fullerene
Although fullerenes have been synthesized from graphite for a long time, the exact mechanism is relatively unknown. Now, in situ microscopy and quantum chemical modelling have directly followed the formation of fullerenes from a single graphitic sheet — graphene.
- Andrey Chuvilin
- , Ute Kaiser
- & Andrei N. Khlobystov
-
Article |
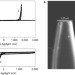 Electrochemistry through glass
Electrochemistry through glass
Glass is widely used as an electrical insulator in electrodes, but in spite of its high resistance, 100-nm-thick layers of glass have now been shown to be sufficiently conductive for electrochemical measurements. Obtaining redox couples through glass-covered nanoelectrodes suggests that the pH response of the glass is due to the formation of a hydrogel layer in acidic solution.
- Jeyavel Velmurugan
- , Dongping Zhan
- & Michael V. Mirkin
-
Research Highlights |
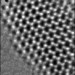 Inorganic graphene
Inorganic graphene
Molybdenum and tungsten sulfide nanosheets, analogous to graphene, have been made.
- Neil Withers
-
Article |
 Enhancement of anhydrous proton transport by supramolecular nanochannels in comb polymers
Enhancement of anhydrous proton transport by supramolecular nanochannels in comb polymers
Efficient conduction of protons on a micrometre scale is critical for the development of fuel cell membranes — a key component of clean energy sources. Now, self-assembling amphiphilic polymers have been shown to provide a nanoscale organization of proton-conducting functionalities that dramatically increases anhydrous proton conductivity.
- Yangbin Chen
- , Michael Thorn
- & S. Thayumanavan
-
Article |
 Lattice-strain control of the activity in dealloyed core–shell fuel cell catalysts
Lattice-strain control of the activity in dealloyed core–shell fuel cell catalysts
The rational design of catalytic materials requires synthetic control over their reactive properties. Now, the activity of dealloyed Pt–Cu bimetallic nanoparticles, which catalyse the oxygen reduction reaction, can be tuned through control of the geometric strain at their surface.
- Peter Strasser
- , Shirlaine Koh
- & Anders Nilsson
-
Article |
 Rapid preparation of flexible porous coordination polymer nanocrystals with accelerated guest adsorption kinetics
Rapid preparation of flexible porous coordination polymer nanocrystals with accelerated guest adsorption kinetics
Porous coordination polymers — PCPs, also known as metal–organic framework materials — have been widely investigated for their useful properties, but controlling their size and shape in a nanocrystalline form is difficult. Now, a rapid method of preparing porous crystalline nanosized PCPs that uses a microemulsion system under ultrasonic irradiation has been reported.
- Daisuke Tanaka
- , Artur Henke
- & Juergen Groll
-
News & Views |
 Protons on tap
Protons on tap
Electrochemistry has so far been mostly centred around measuring factors and coefficients. Through the reversible reduction and oxidation of an electrode coating formed from three-dimensional hybrid aniline–gold nanoparticles, it has now moved on to controlling the pH of a solution, thus triggering specific reactions.
- Reginald M. Penner
-
Article |
 Quantum size effects in ambient CO oxidation catalysed by ligand-protected gold clusters
Quantum size effects in ambient CO oxidation catalysed by ligand-protected gold clusters
Gold nanoparticles can catalyse oxidation reactions in remarkably mild conditions and have excited much interest in recent years. With experimental studies disagreeing over the size of the most active nanoparticles, density functional calculations have now shown that limiting the particle size to below two nanometres is crucial.
- Olga Lopez-Acevedo
- , Katarzyna A. Kacprzak
- & Hannu Häkkinen
-
Research Highlights |
Sunscreen size studies
A comparison of models for the sun-protection factor, transparency and production of reactive oxygen species leads to a prediction of the optimum size of titania nanoparticles for use in sunscreen.
- Stephen Davey
-
Article |
 Loading and selective release of cargo in DNA nanotubes with longitudinal variation
Loading and selective release of cargo in DNA nanotubes with longitudinal variation
Nanotubular structures made from different materials are being investigated for applications ranging from sensing to drug delivery, but controlling how they interact with ‘cargo’ molecules has proved challenging. Now, the selective uptake, precise positioning and triggered release of gold nanoparticles has been achieved with nanotubes assembled from triangular DNA building blocks.
- Pik Kwan Lo
- , Pierre Karam
- & Hanadi F. Sleiman
-
-
Article |
 Nanocrystalline intermetallics on mesoporous carbon for direct formic acid fuel cell anodes
Nanocrystalline intermetallics on mesoporous carbon for direct formic acid fuel cell anodes
Formic acid fuel cells require nanosized intermetallic nanoparticles as anode catalysts, but current techniques are poor at producing the small size required. Now, surface-modified ordered mesoporous carbons have been used to produce nanocrystallites as small as 1.5 nm that are extremely active catalysts.
- Xiulei Ji
- , Kyu Tae Lee
- & Linda F. Nazar
-
Research Highlights |
 An illuminating twist
An illuminating twist
The slow oxidation of tellurium in semiconductor cadmium telluride nanoparticles, accompanied by the replacement of tellurium by sulfur, has led to CdS/CdTe nanoparticles that self-assemble under visible light into twisted nanoribbons.
- Anne Pichon
-
Article |
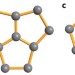 Chlorofullerenes featuring triple sequentially fused pentagons
Chlorofullerenes featuring triple sequentially fused pentagons
Fullerene cages that break the isolated pentagon rule are rare and often unstable. Now a range of fullerenes that feature three sequentially fused pentagons of carbon have been stabilized by chlorination.
- Yuan-Zhi Tan
- , Jia Li
- & Lan-Sun Zheng
-
News & Views |
 Visualizing fullerene chemistry
Visualizing fullerene chemistry
Chemical reactions of fullerenes and metallofullerenes lined up inside single-walled carbon nanotubes can be monitored at the atomic scale inside an aberration-corrected transmission electron microscope.
- Mauricio Terrones
-
News & Views |
 Tiny steps
Tiny steps
A molecular 'walker' can be made to move up and down a molecular 'track' by alternately locking and unlocking the two different types of covalent bonds that join the two components together. By changing the conditions under which one of the bond-forming/bond-breaking processes occurs, a directional bias for walking can be achieved.
- Sijbren Otto
-
Article |
 Analysis of the reactivity and selectivity of fullerene dimerization reactions at the atomic level
Analysis of the reactivity and selectivity of fullerene dimerization reactions at the atomic level
Well-resolved images of small molecules and their motions can be obtained with high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. It has now been shown that this technique can also be used to visualize individual chemical reactions involving the dimerization of fullerenes and metallo-fullerenes trapped inside carbon nanotubes by monitoring how the positions of their atoms change over time.
- Masanori Koshino
- , Yoshiko Niimi
- & Sumio Iijima
-
Research Highlights |
 Nanoparticles ring the changes
Nanoparticles ring the changes
More predictable chemical patterns have been created by using nanoparticles instead of ions.
- Neil Withers

 Surfactant sheets
Surfactant sheets Nanoparticles ring the changes
Nanoparticles ring the changes