Research Briefing |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 The devil is in the defects
The devil is in the defects
Calculations support experiments in predicting the existence and properties of point defects in solids but often do not correctly capture their details. A different method can significantly improve the prediction of defect structures and properties.
- Arun Mannodi-Kanakkithodi
-
Article |
 Visualizing slow internal relaxations in a two-dimensional glassy system
Visualizing slow internal relaxations in a two-dimensional glassy system
Glasses relax internally even when their structure is frozen. Observations of a two-dimensional glass former now show that although structure relaxation freezes with the glass transition, non-constrained bonds survive; this accounts for persisting internal relaxation.
- Yanshuang Chen
- , Zefang Ye
- & Peng Tan
-
Article |
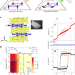 Spontaneous topological Hall effect induced by non-coplanar antiferromagnetic order in intercalated van der Waals materials
Spontaneous topological Hall effect induced by non-coplanar antiferromagnetic order in intercalated van der Waals materials
The spontaneous topological Hall effect, combining non-coplanar antiferromagnetic order with finite scalar spin chirality in the absence of a magnetic field, is now experimentally demonstrated for the triangular lattice compounds CoTa3S6 and CoNb3S6.
- H. Takagi
- , R. Takagi
- & S. Seki
-
News & Views |
 Surface-state limbo
Surface-state limbo
The combination of magnetic and non-magnetic layers in (MnBi2Te4)(Bi2Te3) is predicted to produce topologically protected states on the surface. Experiments now show that the nature of the topmost layer controls the location of these states.
- Matthew Brahlek
- & Robert G. Moore
-
Article |
 Layer-by-layer disentanglement of Bloch states
Layer-by-layer disentanglement of Bloch states
Layering quantum materials can produce interesting phenomena by combining the different behaviour of electronic states in each layer. A layer-sensitive measurement technique provides insights into the physics of a magnetic topological insulator.
- Woojoo Lee
- , Sebastian Fernandez-Mulligan
- & Shuolong Yang
-
Article |
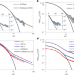 Signature of collective elastic glass physics in surface-induced long-range tails in dynamical gradients
Signature of collective elastic glass physics in surface-induced long-range tails in dynamical gradients
Large-system molecular dynamics simulations of films of glass-forming polymers reveal spatially long-range tails of interface-driven gradients of the glass transition temperature, suggestive of a combined local caging and long-range collective elasticity origin of relaxation and vitrification in glass-forming liquids.
- Asieh Ghanekarade
- , Anh D. Phan
- & David S. Simmons
-
Article
| Open Access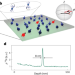 Probing many-body dynamics in a two-dimensional dipolar spin ensemble
Probing many-body dynamics in a two-dimensional dipolar spin ensemble
Solid-state systems are established candidates to study models of many-body physics but have limited control and readout capabilities. Ensembles of defects in diamond may provide a solution for studying dipolar systems.
- E. J. Davis
- , B. Ye
- & N. Y. Yao
-
News & Views |
 Berry does both
Berry does both
Local magnetometry measurements on a magnetic Chern insulator suggest that the Berry curvature of the topological band — responsible for the intrinsic magnetism — also enables ultra-low current switching of the magnetization.
- Yonglong Xie
-
Article |
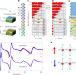 Coexistence and coupling of ferroelectricity and magnetism in an oxide two-dimensional electron gas
Coexistence and coupling of ferroelectricity and magnetism in an oxide two-dimensional electron gas
Materials that simultaneously display ferroelectricity and magnetism, and are metallic, are very rare. Now, the two-dimensional electron gas in an oxide heterostructure brings all of this behaviour together.
- Julien Bréhin
- , Yu Chen
- & Manuel Bibes
-
News & Views |
 Contaminated bubble bursting
Contaminated bubble bursting
Oil-coated bubbles bursting across interfaces enhance aerosol formation and transmission by producing jets that are smaller and faster than those formed by pristine bubbles.
- Samantha A. McBride
-
Article |
 Enhanced singular jet formation in oil-coated bubble bursting
Enhanced singular jet formation in oil-coated bubble bursting
A bursting bubble produces a jet drop previously estimated to be too large to contribute to aerosolization. Oil-coated bubbles produce fast and thin jets, which break up into much smaller drops with potential implications for airborne transmission.
- Zhengyu Yang
- , Bingqiang Ji
- & Jie Feng
-
World View |
 Why competition is bad for science
Why competition is bad for science
Bibliometric evaluation causes competition and stalls scientific progress. We need to abandon it and encourage collaboration.
- Jakub Železný
-
Article
| Open Access Unidirectional scattering with spatial homogeneity using correlated photonic time disorder
Unidirectional scattering with spatial homogeneity using correlated photonic time disorder
Photonic systems can exploit time as a degree of freedom analogous to space, eliminating the need for spatial patterning to achieve functionality. A Green’s function approach allows the design of disordered time scatterers with desired properties.
- Jungmin Kim
- , Dayeong Lee
- & Namkyoo Park
-
News & Views |
 Freeze in or breeze out
Freeze in or breeze out
Phase-change processes, such as condensation or freezing, are known to compromise a surface’s water-repelling capability. It now turns out that tuning the freezing conditions can enable the spontaneous expulsion of water droplets.
- Jonathan B. Boreyko
-
Article |
 Polymorphic crystalline wetting layers on crystal surfaces
Polymorphic crystalline wetting layers on crystal surfaces
Premelting refers to the formation of a thin liquid film on a crystal’s surface before it properly melts. Now, a similar mechanism is shown to occur before solid–solid transitions in colloidal crystals: the formation of a polymorphic crystalline layer.
- Xipeng Wang
- , Bo Li
- & Yilong Han
-
Letter |
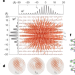 Polarons in two-dimensional atomic crystals
Polarons in two-dimensional atomic crystals
When electrons in a crystal interact with the surrounding lattice, they can form quasiparticles known as polarons. A computational approach to studying polarons in two-dimensional materials explains why they are rarely observed in these systems.
- Weng Hong Sio
- & Feliciano Giustino
-
Letter
| Open Access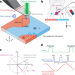 Imaging ferroelectric domains with a single-spin scanning quantum sensor
Imaging ferroelectric domains with a single-spin scanning quantum sensor
A scanning nitrogen-vacancy microscope is used to image ferroelectric domains in piezoelectric and improper ferroelectric samples with high sensitivity. The technique relies on the nitrogen-vacancy’s Stark shift produced by the samples’ electric field.
- William S. Huxter
- , Martin F. Sarott
- & Christian L. Degen
-
Letter |
 Unidirectional coherent quasiparticles in the high-temperature rotational symmetry broken phase of AV3Sb5 kagome superconductors
Unidirectional coherent quasiparticles in the high-temperature rotational symmetry broken phase of AV3Sb5 kagome superconductors
The charge density wave state in kagome superconductors is not fully understood. Now, evidence suggests that the rotational symmetry of the lattice is broken before coherence of unidirectional quasiparticles is established at a lower temperature.
- Hong Li
- , He Zhao
- & Ilija Zeljkovic
-
Article
| Open Access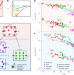 Thermal expansion and the glass transition
Thermal expansion and the glass transition
The Lindemann criterion states that crystals melt when thermal vibrations overcome binding forces. It is now found that this picture does not hold for glasses, and that there is a universal relationship between glass temperature and thermal expansion.
- Peter Lunkenheimer
- , Alois Loidl
- & Konrad Samwer
-
Article
| Open Access Size distributions of intracellular condensates reflect competition between coalescence and nucleation
Size distributions of intracellular condensates reflect competition between coalescence and nucleation
Biomolecular condensates play a role in cellular processes and their size affects reaction pathways. The size distribution is connected to varying contributions of nucleation and coalescence.
- Daniel S. W. Lee
- , Chang-Hyun Choi
- & Ned S. Wingreen
-
Article |
 Quantum simulation of an exotic quantum critical point in a two-site charge Kondo circuit
Quantum simulation of an exotic quantum critical point in a two-site charge Kondo circuit
The quantum critical behaviour of a two-impurity Kondo model variant is observed in a system of hybrid-semiconductor islands that could provide a scalable platform for solid-state quantum simulation
- Winston Pouse
- , Lucas Peeters
- & David Goldhaber-Gordon
-
Article
| Open Access Coupling of terahertz light with nanometre-wavelength magnon modes via spin–orbit torque
Coupling of terahertz light with nanometre-wavelength magnon modes via spin–orbit torque
Engineering of the spin–orbit interactions in a magnetic multilayered structure makes it possible to coherently generate coherent spin waves using terahertz radiation, which could benefit the development of spintronic devices.
- Ruslan Salikhov
- , Igor Ilyakov
- & Sergey Kovalev
-
Article |
 Antiferromagnetic metal phase in an electron-doped rare-earth nickelate
Antiferromagnetic metal phase in an electron-doped rare-earth nickelate
Films of the correlated oxide NdNiO3 form a metallic antiferromagnetic phase that can be identified using electrical currents, raising the prospect of applications in spintronics.
- Qi Song
- , Spencer Doyle
- & Julia A. Mundy
-
Article |
 Liquid-like VASP condensates drive actin polymerization and dynamic bundling
Liquid-like VASP condensates drive actin polymerization and dynamic bundling
The protein VASP can undergo liquid–liquid phase separation. The interplay between the surface tension of the VASP droplet and actin polymerization controls the bundling of actin filaments, a necessary step for many cellular processes.
- Kristin Graham
- , Aravind Chandrasekaran
- & Jeanne C. Stachowiak
-
Article |
 Ultrafast relaxation of lattice distortion in two-dimensional perovskites
Ultrafast relaxation of lattice distortion in two-dimensional perovskites
The ultrafast structural dynamics in 2D perovskites are an important part of their non-equilibrium properties. Now, their visualization reveals a light-induced reduction in the antiferro-distortion initiated by the electron–hole plasma.
- Hao Zhang
- , Wenbin Li
- & Aditya D. Mohite
-
Article |
 Quasiparticles, flat bands and the melting of hydrodynamic matter
Quasiparticles, flat bands and the melting of hydrodynamic matter
The concept of quasiparticles helps to describe various quantum phenomena in solids. It is now shown that certain properties of a classical system of hydrodynamically interacting particles can also be described by means of quasiparticles.
- Imran Saeed
- , Hyuk Kyu Pak
- & Tsvi Tlusty
-
Article |
 Visualization of bulk and edge photocurrent flow in anisotropic Weyl semimetals
Visualization of bulk and edge photocurrent flow in anisotropic Weyl semimetals
Understanding the fundamental mechanisms of photocurrent generation is important for photodetector design. Now, the anisotropy of the thermal properties of Weyl semimetals is shown to generate circulating photocurrents.
- Yu-Xuan Wang
- , Xin-Yue Zhang
- & Brian B. Zhou
-
Letter |
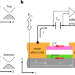 Laughlin charge pumping in a quantum anomalous Hall insulator
Laughlin charge pumping in a quantum anomalous Hall insulator
Quantized charge pumping is a hallmark of topological phases. Now, this effect is observed in the quantum anomalous Hall regime.
- Minoru Kawamura
- , Masataka Mogi
- & Yoshinori Tokura
-
-
-
Article |
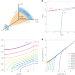 Interplay between superconductivity and the strange-metal state in FeSe
Interplay between superconductivity and the strange-metal state in FeSe
Superconductivity can emerge from a strange-metal state, but the exact relationship between them is unknown. Now, quantitative measurements reveal the dependence of resistivity in the strange metal on the superconducting transition temperature.
- Xingyu Jiang
- , Mingyang Qin
- & Zhongxian Zhao
-
Article |
 Anomalous enhancement of the Nernst effect at the crossover between a Fermi liquid and a strange metal
Anomalous enhancement of the Nernst effect at the crossover between a Fermi liquid and a strange metal
The transport behaviour of strange metals is distinct from weakly interacting Fermi liquids. Now, a large thermoelectric response has been shown at the transition between those two states.
- Yusen Yang
- , Qian Tao
- & Zhu-An Xu
-
News & Views |
 Topological defects with a half twist
Topological defects with a half twist
Liquid crystal defect structures with topology similar to a Möbius strip can rotate, translate and transform into one another under an applied electric field.
- Lisa Tran
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid crystal defect structures with Möbius strip topology
Liquid crystal defect structures with Möbius strip topology
Topological defect structures that swim have been realized in liquid crystals. Now, a range of structures with topology reminiscent of a Möbius strip swim and transform into one another.
- Hanqing Zhao
- , Jung-Shen B. Tai
- & Ivan I. Smalyukh
-
Article |
 Josephson–Coulomb drag effect between graphene and a LaAlO3/SrTiO3 superconductor
Josephson–Coulomb drag effect between graphene and a LaAlO3/SrTiO3 superconductor
Transport measurements between a normal conductor and superconductor show that in this case, the Coulomb drag response can be much larger than that between two normal conductors.
- Ran Tao
- , Lin Li
- & Changgan Zeng
-
Letter |
 Floquet engineering of strongly driven excitons in monolayer tungsten disulfide
Floquet engineering of strongly driven excitons in monolayer tungsten disulfide
The interaction of strong laser fields with tungsten disulfide leads to light-dressed Floquet replica of excitonic states, which manifest as new features in the transient absorption spectrum.
- Yuki Kobayashi
- , Christian Heide
- & Shambhu Ghimire
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast X-ray imaging of the light-induced phase transition in VO2
Ultrafast X-ray imaging of the light-induced phase transition in VO2
The intermediate states in photo-excited phase transitions are expected to be inhomogeneous. However, ultrafast X-ray imaging shows the early part of the metal–insulator transition in VO2 is homogeneous but then becomes heterogeneous.
- Allan S. Johnson
- , Daniel Perez-Salinas
- & Simon E. Wall
-
-
Article |
 Spin–orbital liquid state and liquid–gas metamagnetic transition on a pyrochlore lattice
Spin–orbital liquid state and liquid–gas metamagnetic transition on a pyrochlore lattice
At low temperatures, the orbital degrees of freedom in insulating magnets normally do not fluctuate, leaving only magnetic behaviour. Measurements now suggest that in Pr2Zr2O7, it is possible to reach a quantum regime of coupled spin–orbital dynamics.
- Nan Tang
- , Yulia Gritsenko
- & Satoru Nakatsuji
-
Letter |
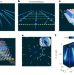 Crossed Luttinger liquid hidden in a quasi-two-dimensional material
Crossed Luttinger liquid hidden in a quasi-two-dimensional material
The Luttinger liquid is a theoretical concept used to describe interacting fermions in a 1D system. Now it is shown that the model also describes electron physics in η-Mo4O11, a quasi-2D material in which 1D chains cross each other.
- X. Du
- , L. Kang
- & L. X. Yang
-
Letter |
 Autonomous waves and global motion modes in living active solids
Autonomous waves and global motion modes in living active solids
A continuum active solid system is realized in a bacterial biofilm. Self-sustained elastic waves are observed, and two modes of collective motion with a sharp transition between them are identified.
- Haoran Xu
- , Yulu Huang
- & Yilin Wu
-
News & Views |
 A highly anisotropic polymorph
A highly anisotropic polymorph
Superconductivity with an anisotropy is revealed in a layered material. This result points towards a version of superconductivity where spin–orbit interactions produce a material that is resilient to external magnetic fields.
- Joseph Falson
-
Article |
 Spin–orbit–parity coupled superconductivity in atomically thin 2M-WS2
Spin–orbit–parity coupled superconductivity in atomically thin 2M-WS2
A form of superconductivity where strong spin–orbit coupling combines with topological band inversions to produce strong robustness against magnetic fields is shown in a few-layer transition metal dichalcogenide.
- Enze Zhang
- , Ying-Ming Xie
- & Shaoming Dong
-
News & Views |
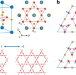 Waves break the symmetry
Waves break the symmetry
Optical experiments reveal nematicity and broken time-reversal symmetry in the charge density waves in kagome metals.
- Luyi Yang
-
Article |
 Three-state nematicity and magneto-optical Kerr effect in the charge density waves in kagome superconductors
Three-state nematicity and magneto-optical Kerr effect in the charge density waves in kagome superconductors
The interplay between superconductivity that might break time-reversal symmetry and charge order is a key issue in kagome materials. Now, optical measurements show that spatial and time-reversal symmetries are broken at the onset of charge order.
- Yishuai Xu
- , Zhuoliang Ni
- & Liang Wu
-
Article |
 Quantum microscopy with van der Waals heterostructures
Quantum microscopy with van der Waals heterostructures
Hexagonal boron nitride is a common component of 2D heterostructures. Defects implanted in boron nitride crystals can be used to perform spatially resolved sensing of properties, including temperature, magnetism and current.
- A. J. Healey
- , S. C. Scholten
- & J.-P. Tetienne
-
Letter
| Open Access Truly chiral phonons in α-HgS
Truly chiral phonons in α-HgS
The notion of chirality in dynamical systems with broken spatial symmetry but preserved time inversion symmetry has led to the concept of truly chiral phonons. These have now been observed in bulk HgS using circularly polarized Raman spectroscopy.
- Kyosuke Ishito
- , Huiling Mao
- & Takuya Satoh
-
Article |
 Emergence of equilibrated liquid regions within the glass
Emergence of equilibrated liquid regions within the glass
The transition from a glassy to a liquid phase is normally assumed to take place cooperatively across the whole material. But now, experiments show that, under certain conditions, isolated regions of liquid can form in the glassy matrix first.
- Ana Vila-Costa
- , Marta Gonzalez-Silveira
- & Javier Rodriguez-Viejo
-
Letter |
 Tailored Ising superconductivity in intercalated bulk NbSe2
Tailored Ising superconductivity in intercalated bulk NbSe2
The superconducting critical temperature of monolayer materials is often lower than their bulk counterparts. Now, intercalation is shown to induce two-dimensional superconducting properties while maintaining the bulk critical temperature.
- Haoxiong Zhang
- , Awabaikeli Rousuli
- & Shuyun Zhou

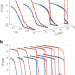 A multilayer superconductor acts as an interdependent network
A multilayer superconductor acts as an interdependent network Metallic mashups
Metallic mashups Ultracold atoms visit curved universes
Ultracold atoms visit curved universes One spin at a time
One spin at a time