Featured
-
-
-
-
Article |
 Diffusive topological transport in spatiotemporal thermal lattices
Diffusive topological transport in spatiotemporal thermal lattices
Topological effects have been found in a range of classical-wave systems, but it was unclear if the concept could be extended to diffusion. An approach using spatiotemporal modulations has now implemented them in a diffusive system
- Guoqiang Xu
- , Yihao Yang
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Letter |
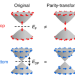 Experimental signature of the parity anomaly in a semi-magnetic topological insulator
Experimental signature of the parity anomaly in a semi-magnetic topological insulator
An electron with a linear dispersion relation should contribute half of a quantum of Hall conductance and thereby manifest the parity anomaly. This is demonstrated in a heterostructure of topological insulator materials.
- M. Mogi
- , Y. Okamura
- & Y. Tokura
-
Letter |
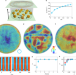 Polar state reversal in active fluids
Polar state reversal in active fluids
Active matter exhibits a plethora of collective phenomena in both biological and artificial systems. In a model system of colloidal rollers, polar states in active liquids can be controlled.
- Bo Zhang
- , Hang Yuan
- & Alexey Snezhko
-
Article |
 Evidence for a monolayer excitonic insulator
Evidence for a monolayer excitonic insulator
Insulating states that are formed because of pairing between electrons and holes are known to exist in engineered bilayer structures in high magnetic fields. Now evidence suggests they can occur in a monolayer crystal at zero field.
- Yanyu Jia
- , Pengjie Wang
- & Sanfeng Wu
-
Article
| Open Access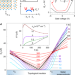 Evidence for equilibrium exciton condensation in monolayer WTe2
Evidence for equilibrium exciton condensation in monolayer WTe2
Exciton condensation has been observed in various three-dimensional (3D) materials. Now, monolayer WTe2—a 2D topological insulator—also shows the phenomenon. Strong electronic interactions allow the excitons to form and condense at high temperature.
- Bosong Sun
- , Wenjin Zhao
- & David H. Cobden
-
News & Views |
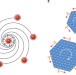 Crystals break up with a twist
Crystals break up with a twist
When crystal defects are present in an ensemble of spinning colloids that induce transverse forces on each other, the defects assemble into grain boundaries that can break the system apart into a set of crystal whorls.
- Cynthia J. O. Reichhardt
- & Charles Reichhardt
-
Article |
 Motile dislocations knead odd crystals into whorls
Motile dislocations knead odd crystals into whorls
The addition of transverse forces to an ensemble of colloidal spinners induces the appearance of odd elastic crystals, featuring self-propelled defects that organize the system into a ‘self-kneading’ crystal whorl state.
- Ephraim S. Bililign
- , Florencio Balboa Usabiaga
- & William T. M. Irvine
-
Perspective |
 Charge order and superconductivity in kagome materials
Charge order and superconductivity in kagome materials
Superconductivity and ordered states formed by interactions—both of which could be unconventional—have recently been observed in a family of kagome materials.
- Titus Neupert
- , M. Michael Denner
- & M. Zahid Hasan
-
Letter |
 Twist engineering of the two-dimensional magnetism in double bilayer chromium triiodide homostructures
Twist engineering of the two-dimensional magnetism in double bilayer chromium triiodide homostructures
Stacking and twisting two-dimensional materials has led to the observation of a variety of electronic phenomena. Now, magnetic behaviour that is distinct from anything seen in individual layers is induced by a moiré pattern in double bilayer chromium triiodide.
- Hongchao Xie
- , Xiangpeng Luo
- & Liuyan Zhao
-
News & Views |
 Double charge wave
Double charge wave
Charge density waves are the periodic spatial modulation of electrons in a solid. A new experiment reveals that they can originate from two different electronic bands in a prototypical transition metal dichalcogenide, NbSe2.
- Young-Woo Son
-
-
Measure for Measure |
 From books to batteries
From books to batteries
The laws governing electrolysis developed by Michael Faraday, who originally trained as a bookbinder, led to the determination of the Faraday constant, as Daren Caruana recounts.
- Daren Caruana
-
News & Views |
 The oddity of active matter
The oddity of active matter
Active matter can have macroscopic properties that defy the usual laws of hydrodynamics. Now these tell-tale properties have been traced down to the non-equilibrium character and handedness of interactions between individual particles.
- Patrick Pietzonka
-
Article |
 Fluctuating hydrodynamics of chiral active fluids
Fluctuating hydrodynamics of chiral active fluids
Active fluids exhibit properties reminiscent of equilibrium systems when their degrees of freedom are statistically decoupled. A theory for the fluctuating hydrodynamics of these fluids offers a probe of their anomalous transport coefficients.
- Ming Han
- , Michel Fruchart
- & Vincenzo Vitelli
-
Letter |
 Interaction-driven band flattening and correlated phases in twisted bilayer graphene
Interaction-driven band flattening and correlated phases in twisted bilayer graphene
Twisted bilayer graphene hosts flat electronic bands, but their relationship to the observed correlated phases is still debated. Here, it is shown that electron–electron interactions can help to flatten the bands and generate the correlated phases.
- Youngjoon Choi
- , Hyunjin Kim
- & Stevan Nadj-Perge
-
Article |
 Intracellular softening and increased viscoelastic fluidity during division
Intracellular softening and increased viscoelastic fluidity during division
The cell cortex stiffens during cell division, facilitating the necessary shape changes. Microrheology measurements now reveal that the rest of the cell interior actually softens, in a process that probably involves two key biomolecules trading roles.
- Sebastian Hurst
- , Bart E. Vos
- & Timo Betz
-
-
Letter |
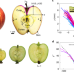 The cusp of an apple
The cusp of an apple
A study of growing apples shows that the singular cusp at the stalk has a universal form that arises due to the differential growth of a soft solid. Although the cusps are usually symmetric, they can lose stability to form lobes that depend on the geometry of the fruit.
- Aditi Chakrabarti
- , Thomas C. T. Michaels
- & L. Mahadevan
-
Article |
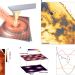 Observation of interband collective excitations in twisted bilayer graphene
Observation of interband collective excitations in twisted bilayer graphene
Moiré potentials substantially alter the electronic properties of twisted bilayer graphene at a magic twist angle. A propagating plasmon mode, which can be observed with optical nano-imaging, is associated with transitions between the moiré minibands.
- Niels C. H. Hesp
- , Iacopo Torre
- & Frank H. L. Koppens
-
-
News & Views |
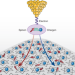 A tell-tale wiggle
A tell-tale wiggle
Scanning tunnelling microscopy reveals an unexpected periodicity in the local density of states of a transition metal dichalcogenide — with a puzzling wavelength that casts the material as a quantum spin liquid.
- Carmen Rubio-Verdú
- & Abhay N. Pasupathy
-
Letter |
 Imaging local discharge cascades for correlated electrons in WS2/WSe2 moiré superlattices
Imaging local discharge cascades for correlated electrons in WS2/WSe2 moiré superlattices
The Hubbard model describes many fascinating phenomena, but relating it to complicated quantum materials is difficult. Now, atomic-resolution measurements can estimate the interaction parameters that appear in the model for real materials.
- Hongyuan Li
- , Shaowei Li
- & Feng Wang
-
News & Views |
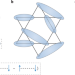 Singlets singled out
Singlets singled out
The state that forms at low temperatures in a quantum antiferromagnet on a kagome lattice has been debated for decades. Nuclear magnetic resonance has now shown the gradual emergence of entangled spin singlets in a disordered kagome antiferromagnet.
- Martin Klanjšek
-
News & Views |
 The onset of a slip
The onset of a slip
Frictional sliding starts with a crack front propagating across an interface — a process that is well described by fracture mechanics. Experiments now show that the onset of crack formation is governed by physics that is yet to be fully understood.
- Anders Malthe-Sørenssen
-
Article |
 Nucleation fronts ignite the interface rupture that initiates frictional motion
Nucleation fronts ignite the interface rupture that initiates frictional motion
Frictional motion between two surfaces in contact starts with the formation of nucleating rupture fronts. It is now shown that these emerge from nucleation fronts, which develop from a certain stress level onwards and with a characteristic velocity.
- Shahar Gvirtzman
- & Jay Fineberg
-
Letter |
 Coherent spin-wave transport in an antiferromagnet
Coherent spin-wave transport in an antiferromagnet
Ultrashort light pulses generate nanometre-scale wavepackets of magnons that propagate coherently and at high speed in an antiferromagnet. This pushes antiferromagnetic magnonics forward as a future platform for information processing.
- J. R. Hortensius
- , D. Afanasiev
- & A. D. Caviglia
-
News & Views |
 Competition under pressure
Competition under pressure
Using pressure to tune the balance of interactions in a new class of kagome superconductor results in a surprising competition between states — and hints at an unusual, electronically intertwined order.
- Stephen D. Wilson
-
News & Views |
 Have tail, will travel
Have tail, will travel
The flagella of microorganisms have provided inspiration for many synthetic devices, but they’re typically not easy to produce. A new class of swimmer makes it look simple by spontaneously growing a tail that it can whip to self-propel.
- Sophie Ramananarivo
-
Article |
 Rechargeable self-assembled droplet microswimmers driven by surface phase transitions
Rechargeable self-assembled droplet microswimmers driven by surface phase transitions
A class of synthetic microswimmers self-assembled from alkane oil drops in a surfactant solution offers a rechargeable platform for studying how microorganisms exploit flagellar elasticity to move around.
- Diana Cholakova
- , Maciej Lisicki
- & Nikolai Denkov
-
Article |
 Detecting photoelectrons from spontaneously formed excitons
Detecting photoelectrons from spontaneously formed excitons
Excitons have been predicted to form spontaneously—without external excitation—in some materials. Low-temperature ARPES measurements on Ta2NiSe5 now provide evidence for such an excitonic insulator and for so-called preformed excitons.
- Keisuke Fukutani
- , Roland Stania
- & Han Woong Yeom
-
-
Article |
 Nanoscale Turing patterns in a bismuth monolayer
Nanoscale Turing patterns in a bismuth monolayer
Macroscale patterns seen in biological systems such as animal coats or skin can be described by Turing’s reaction–diffusion theory. Now Turing patterns are shown to also exist in bismuth monolayers, an exemplary nanoscale atomic system.
- Yuki Fuseya
- , Hiroyasu Katsuno
- & Aharon Kapitulnik
-
News & Views |
Hidden in plain light
Light pulses transiently change a metal to an insulator by unveiling a hidden ordered state.
- Chong-Yu Ruan
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Non-local oddities
Non-local oddities
Introducing non-local effects to metamaterials increases the complexity of their dispersion relation, which allows carefully designed elastic structures to mimic the peculiar roton behaviour of correlated quantum superfluids.
- Romain Fleury
-
News & Views |
 Turn towards the crowd
Turn towards the crowd
A type of polar self-propelled particle generates a torque that makes it naturally drawn to higher-density areas. The collective behaviour this induces in assemblies of particles constitutes a new form of phase separation in active fluids.
- Olivier Dauchot
-
Article |
 Two-fold symmetric superconductivity in few-layer NbSe2
Two-fold symmetric superconductivity in few-layer NbSe2
A two-fold rotational symmetry is observed in the superconducting state of NbSe2. This is strikingly different from the three-fold symmetry of the lattice, and suggests that a mixed conventional and unconventional order parameter exists in this material.
- Alex Hamill
- , Brett Heischmidt
- & Vlad S. Pribiag
-
Letter |
 Unusual high-field metal in a Kondo insulator
Unusual high-field metal in a Kondo insulator
Transport and thermodynamic measurements on strongly correlated Kondo metal YbB12 reveal the coexistence of charged and charge-neutral fermions in the material and the crucial role played by the latter in the quantum oscillations of resistivity.
- Ziji Xiang
- , Lu Chen
- & Lu Li
-
News & Views |
 Endless forms fabricated
Endless forms fabricated
The patterning dynamics of confined immiscible fluids has inspired an elegant and versatile approach to building periodic three-dimensional multi-material architectures. The technique extends to triphasic composites, three-dimensional droplet networks and even biological tissues.
- Séverine Le Gac
-
Letter |
 Fluid interfacial energy drives the emergence of three-dimensional periodic structures in micropillar scaffolds
Fluid interfacial energy drives the emergence of three-dimensional periodic structures in micropillar scaffolds
The revelation that fluid–fluid interfacial energy can drive structure formation in micropillar scaffolds offers a scalable way of synthesizing soft composites, which may have applications in building materials that mimic biological tissue.
- Hiroki Yasuga
- , Emre Iseri
- & Wouter van der Wijngaart
-
-
-
Comment |
 Topology and superconductivity on the edge
Topology and superconductivity on the edge
Passing a supercurrent through a topological material can highlight the existence of higher-order boundary states, and may lead to applications in topological superconductivity.
- Yaojia Wang
- , Gil-Ho Lee
- & Mazhar N. Ali
-
Article |
 Optical polarization analogue in free electron beams
Optical polarization analogue in free electron beams
The functionality of electron energy loss spectroscopy can be extended to include a polarization analogue constructed via the dipole transition vector between two electronic states, bringing it closer to its optical counterpart.
- Hugo Lourenço-Martins
- , Davy Gérard
- & Mathieu Kociak
-
Article |
 Split superconducting and time-reversal symmetry-breaking transitions in Sr2RuO4 under stress
Split superconducting and time-reversal symmetry-breaking transitions in Sr2RuO4 under stress
When strain is applied to strontium ruthenate, superconductivity emerges at a different temperature to the breaking of time-reversal symmetry. This indicates that the superconductivity could have a chiral d-wave order parameter.
- Vadim Grinenko
- , Shreenanda Ghosh
- & Hans-Henning Klauss
-
Letter |
 Gain-induced topological response via tailored long-range interactions
Gain-induced topological response via tailored long-range interactions
Non-Hermitian concepts together with optical gain allow the tailoring of short- and long-range exchange interactions in integrated topological photonics, and an exact Haldane model can be realized in this way.
- Yuzhou G. N. Liu
- , Pawel S. Jung
- & Mercedeh Khajavikhan

 Quantum phase transition from superconducting to insulating-like state in a pressurized cuprate superconductor
Quantum phase transition from superconducting to insulating-like state in a pressurized cuprate superconductor A twirling crystal
A twirling crystal Wavy worms
Wavy worms All the colours of the rainbow
All the colours of the rainbow The measure of a cell
The measure of a cell One mode at a time
One mode at a time Hot emission by design
Hot emission by design Shear coincidence
Shear coincidence Prosperous gold
Prosperous gold Slippy nitty-gritty
Slippy nitty-gritty Food for thought
Food for thought