Featured
-
-
Comment |
Kidney involvement in COVID-19 and rationale for extracorporeal therapies
The prevalence of direct kidney involvement in novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is low, but such involvement is a marker of multiple organ dysfunction and severe disease. Here, we explore potential pathways of kidney damage and discuss the rationale for extracorporeal support with various blood purification strategies in patients who are critically ill with COVID-19.
- Claudio Ronco
- & Thiago Reis
-
Review Article |
 FGF23 at the crossroads of phosphate, iron economy and erythropoiesis
FGF23 at the crossroads of phosphate, iron economy and erythropoiesis
Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) is crucial to phosphate and calcium homeostasis. In this Review, the authors discuss how levels of biologically active FGF23 are controlled by balanced FGF23 transcription and protein cleavage, and how serum iron levels, inflammation and erythropoietin affect that balance.
- Daniel Edmonston
- & Myles Wolf
-
Review Article |
 Mechanisms of hypoxia signalling: new implications for nephrology
Mechanisms of hypoxia signalling: new implications for nephrology
Therapeutic modulation of hypoxia-inducible factors, which transduce adaptive transcriptional responses to hypoxia, is an emerging theme in kidney disease. This Review summarizes the hypoxia signalling mechanisms underpinning these novel treatments and highlights key remaining questions relevant to their clinical use.
- Johannes Schödel
- & Peter J. Ratcliffe
-
-
Review Article |
 Macrophages: versatile players in renal inflammation and fibrosis
Macrophages: versatile players in renal inflammation and fibrosis
Macrophages are versatile immune cells that protect the host against infection but can also promote chronic inflammation and fibrosis. In this Review, the authors discuss the diverse roles of macrophages in acute and chronic renal pathology as well as potential therapeutic targets.
- Patrick Ming-Kuen Tang
- , David J. Nikolic-Paterson
- & Hui-Yao Lan
-
Year in Review |
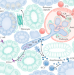 Protecting the kidney against autoimmunity and inflammation
Protecting the kidney against autoimmunity and inflammation
Numerous exciting studies that advanced our understanding of immune-mediated kidney disease were published in 2018. Whereas most of these studies analysed the role of pro-inflammatory mediators, several novel anti-inflammatory mechanisms were discovered that involve immune cells and mediators with previously unrecognized protective roles in renal disease.
- Christian Kurts
- & Catherine Meyer-Schwesinger
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
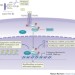 TGF-β: the master regulator of fibrosis
TGF-β: the master regulator of fibrosis
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is a key driver of fibrosis in chronic kidney disease, acting via canonical and non-canonical signalling pathways to activate myofibroblasts and induce the production of extracellular matrix. This Review describes the mechanisms by which TGF-β promotes renal fibrosis, the pathways that modulate TGF-β signalling, and new therapeutic opportunities for the inhibition of TGF-β-driven renal fibrosis
- Xiao-ming Meng
- , David J. Nikolic-Paterson
- & Hui Yao Lan
-
-
Year in Review |
 Updates on immunosuppression in kidney disease
Updates on immunosuppression in kidney disease
Numerous studies in 2015 focused on therapeutic immune modulation and immunosuppression. Trials of budenoside in patients with IgA nephropathy who are unresponsive to supportive therapy, and of low-dose IL-2 to enforce regulatory T-cell-mediated immunosuppression in autoimmune disease all produced promising results.
- Hans-Joachim Anders
-
Review Article |
 HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors for the treatment of renal anaemia and beyond
HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors for the treatment of renal anaemia and beyond
Renal anaemia, resulting from impaired renal production of erythropoietin, is a common occurrence in patients with chronic kidney disease. Conventional erythropoiesis stimulating agents can be used to treat the condition, but small-molecule inhibitors of prolyl hydroxylase domain-containing (PHD) enzymes might provide a more efficient and tolerable approach to anaemia management. Here, Maxwell and Eckardt describe the rationale for targeting PHD enzymes to increase erythropoietin production. They also discuss other potential on-target consequences of HIF activation and possible off-target effects on enzymes that are structurally similar to PHD enzymes.
- Patrick H. Maxwell
- & Kai-Uwe Eckardt
-
-
Research Highlight |
Activation of JAK3/STAT6 contributes to the development of renal fibrosis
- Jessica K. Edwards
-
Review Article |
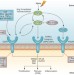 Targeting CTGF, EGF and PDGF pathways to prevent progression of kidney disease
Targeting CTGF, EGF and PDGF pathways to prevent progression of kidney disease
Progression of kidney disease is characterized by the sustained release of proinflammatory and profibrotic cytokines and growth factors, leading to renal fibrosis. TGF-β is considered to be one of the main regulators of fibrosis, but preclinical studies have revealed important synergistic roles for other growth factors, including CTGF, EGF and PDGF, in this process. Here, the authors discuss the roles of these growth factors in kidney fibrosis, as well as the evidence supporting their qualification as additional targets for novel antifibrotic therapies.
- Helena M. Kok
- , Lucas L. Falke
- & Tri Q. Nguyen
-
Research Highlight |
Regulation of fibrotic signalling by TGF-β receptor tyrosine phosphorylation
- Susan J. Allison

 Targeting innate immunity-driven inflammation in CKD and cardiovascular disease
Targeting innate immunity-driven inflammation in CKD and cardiovascular disease IL-1β switches on kidney fibrosis
IL-1β switches on kidney fibrosis PALS1 links polarity, TGF-β and the Hippo pathway
PALS1 links polarity, TGF-β and the Hippo pathway IL-34 promotes persistent ischaemia-induced AKI
IL-34 promotes persistent ischaemia-induced AKI