Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access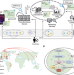 A scalable, secure, and interoperable platform for deep data-driven health management
A scalable, secure, and interoperable platform for deep data-driven health management
The increasing scale and scope of biomedical data is generating tremendous opportunities for improving health outcomes, but also raises new challenges ranging from data acquisition and storage to data analysis and utilization. To meet these challenges, the authors develop the Personal Health Dashboard, which provides an end-to-end solution for deep biomedical data analytics.
- Amir Bahmani
- , Arash Alavi
- & Michael P. Snyder
-
Article
| Open Access Geographical drivers and climate-linked dynamics of Lassa fever in Nigeria
Geographical drivers and climate-linked dynamics of Lassa fever in Nigeria
Lassa Fever is a rodent-borne viral haemorrhagic fever that is a public health problem in West Africa. Here, the authors develop a spatiotemporal model of the socioecological drivers of disease using surveillance data from Nigeria, and find evidence of climate sensitivity.
- David W. Redding
- , Rory Gibb
- & Chikwe Ihekweazu
-
Article
| Open Access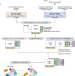 Spatiotemporal proteomic profiling of the pro-inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide in the THP-1 human leukaemia cell line
Spatiotemporal proteomic profiling of the pro-inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide in the THP-1 human leukaemia cell line
“Protein relocalisation plays a major role in the innate immune response but remains incompletely characterised. Here, the authors combine temporal proteomics with LOPIT, a spatial proteomic workflow, in a fully Bayesian framework to elucidate spatiotemporal proteomic changes during the LPS-induced immune response in THP-1 cells.
- Claire M. Mulvey
- , Lisa M. Breckels
- & Kathryn S. Lilley
-
Article
| Open Access A rational blueprint for the design of chemically-controlled protein switches
A rational blueprint for the design of chemically-controlled protein switches
Small-molecule responsive protein switches are crucial components to control synthetic cellular activities. Here, we present a computational protein design strategy to repurpose drug-inhibited protein-protein interactions into OFF- and ON-switches active in cells.
- Sailan Shui
- , Pablo Gainza
- & Bruno E. Correia
-
Article
| Open Access Possible future waves of SARS-CoV-2 infection generated by variants of concern with a range of characteristics
Possible future waves of SARS-CoV-2 infection generated by variants of concern with a range of characteristics
Understanding the potential impacts of new variants of SARS-CoV-2 is important for pandemic planning. Here, the authors develop a model incorporating hypothetical new variants with varying transmissibility and immune evasion properties, and use it to project possible future epidemic waves in the UK.
- Louise Dyson
- , Edward M. Hill
- & Matt J. Keeling
-
Article
| Open Access Chromatin accessibility associates with protein-RNA correlation in human cancer
Chromatin accessibility associates with protein-RNA correlation in human cancer
Studies show the cancer transcriptome correlates poorly with the cancer proteome, questioning the role of chromatin regulation. Here the authors demonstrate proximal-gene-body chromatin elements and transcription predict abundances of differentially expressed proteins in thyroid and breast cancers.
- Akshay Sanghi
- , Joshua J. Gruber
- & Michael P. Snyder
-
Article
| Open Access ECNet is an evolutionary context-integrated deep learning framework for protein engineering
ECNet is an evolutionary context-integrated deep learning framework for protein engineering
Protein engineering is an active area of research in which machine learning has proven quite powerful. Here, the authors present a deep learning method that integrates both general and protein-specific sequence representations to improve the engineering of one’s protein of interest.
- Yunan Luo
- , Guangde Jiang
- & Jian Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Bayesian inference with incomplete knowledge explains perceptual confidence and its deviations from accuracy
Bayesian inference with incomplete knowledge explains perceptual confidence and its deviations from accuracy
A Bayesian framework based on partially observable Markov decision processes (POMDPs) not only predicts subjects’ confidence in a perceptual decision making task but also explains well-known discrepancies between confidence and choice accuracy as arising from incomplete knowledge of the environment.
- Koosha Khalvati
- , Roozbeh Kiani
- & Rajesh P. N. Rao
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic memory to alleviate catastrophic forgetting in continual learning with medical imaging
Dynamic memory to alleviate catastrophic forgetting in continual learning with medical imaging
In clinical practice, the continuous progress of image acquisition technology or diagnostic procedures and evolving imaging protocols hamper the utility of machine learning, as prediction accuracy on new data deteriorates. Here, the authors propose a continual learning approach to deal with such domain shifts occurring at unknown time points.
- Matthias Perkonigg
- , Johannes Hofmanninger
- & Georg Langs
-
Article
| Open Access VEGA is an interpretable generative model for inferring biological network activity in single-cell transcriptomics
VEGA is an interpretable generative model for inferring biological network activity in single-cell transcriptomics
Developing interpretable models is a major challenge in single cell deep learning. Here we show that the VEGA variational autoencoder model, whose decoder wiring mirrors gene modules, can provide direct interpretability to the latent space further enabling the inference of biological module activity.
- Lucas Seninge
- , Ioannis Anastopoulos
- & Joshua Stuart
-
Article
| Open Access Confronting false discoveries in single-cell differential expression
Confronting false discoveries in single-cell differential expression
Differential expression analysis of single-cell transcriptomics allows scientists to dissect cell-type-specific responses to biological perturbations. Here, the authors show that many commonly used methods are biased and can produce false discoveries.
- Jordan W. Squair
- , Matthieu Gautier
- & Grégoire Courtine
-
Article
| Open Access Conserved and species-specific chromatin remodeling and regulatory dynamics during mouse and chicken limb bud development
Conserved and species-specific chromatin remodeling and regulatory dynamics during mouse and chicken limb bud development
The vertebrate limb bud is a paradigm to uncover the fundamental mechanisms that govern embryogenesis and evolutionary diversification. Here the authors compare mouse and chicken limb bud development to study the impact of genome evolution on conserved and divergent gene regulatory interactions.
- Shalu Jhanwar
- , Jonas Malkmus
- & Rolf Zeller
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the glycosyltransferase fold landscape using interpretable deep learning
Mapping the glycosyltransferase fold landscape using interpretable deep learning
Glycosyltransferases (GT) are proteins that display extensive sequence and functional variation on a subset of 3D folds. Here, the authors use interpretable deep learning to predict 3D folds from sequence without the need for sequence alignment, which also enables the prediction of GTs with new folds.
- Rahil Taujale
- , Zhongliang Zhou
- & Natarajan Kannan
-
Article
| Open Access An immune response characterizes early Alzheimer’s disease pathology and subjective cognitive impairment in hydrocephalus biopsies
An immune response characterizes early Alzheimer’s disease pathology and subjective cognitive impairment in hydrocephalus biopsies
Specific transcriptional changes in microglia associated with Alzheimer’s disease have been reported. Here, the authors show that transcriptional analysis of human hydrocephalus biopsies identifies changes in immune response genes associated with early AD pathology, including cognitive decline.
- Wenrui Huang
- , Anne Marie Bartosch
- & Andrew F. Teich
-
Article
| Open Access Robust whole slide image analysis for cervical cancer screening using deep learning
Robust whole slide image analysis for cervical cancer screening using deep learning
Computer-assisted diagnosis is key for scaling up cervical cancer screening, but current algorithms perform poorly on whole slide image analysis and generalization. Here, the authors present a WSI classification and top lesion cell recommendation system using deep learning, and achieve comparable results with cytologists.
- Shenghua Cheng
- , Sibo Liu
- & Xiuli Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Differentially expressed genes reflect disease-induced rather than disease-causing changes in the transcriptome
Differentially expressed genes reflect disease-induced rather than disease-causing changes in the transcriptome
Identification of gene expression changes between healthy and diseased individuals can reveal mechanistic insights and biomarkers. Here, the authors propose a bi-directional transcriptome-wide Mendelian Randomization approach to assess causal effects between gene expression and complex traits.
- Eleonora Porcu
- , Marie C. Sadler
- & Zoltán Kutalik
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionarily informed machine learning enhances the power of predictive gene-to-phenotype relationships
Evolutionarily informed machine learning enhances the power of predictive gene-to-phenotype relationships
Predicting complex phenotypes from genomic information is still a challenge. Here, the authors use an evolutionarily informed machine learning approach within and across species to predict genes affecting nitrogen utilization in crops, and show their approach is also useful in mammalian systems.
- Chia-Yi Cheng
- , Ying Li
- & Gloria M. Coruzzi
-
Article
| Open Access Dissecting transition cells from single-cell transcriptome data through multiscale stochastic dynamics
Dissecting transition cells from single-cell transcriptome data through multiscale stochastic dynamics
How to infer transient cells and cell-fate transitions from snap-shot single cell transcriptome dataset remains a major challenge. Here the authors present a multiscale approach to construct single-cell dynamical manifold, quantify cell stability, and compute transition trajectory and probability between cell states.
- Peijie Zhou
- , Shuxiong Wang
- & Qing Nie
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-diffraction error mapping for localisation microscopy images
Sub-diffraction error mapping for localisation microscopy images
Determining the quality of localisation microscopy images is currently challenging. Here the authors report use of the Haar wavelet kernel analysis (HAWK) Method for the Assessment of Nanoscopy, termed HAWKMAN, to assess the reliability of localisation information.
- Richard J. Marsh
- , Ishan Costello
- & Susan Cox
-
Article
| Open Access Coevolutionary methods enable robust design of modular repressors by reestablishing intra-protein interactions
Coevolutionary methods enable robust design of modular repressors by reestablishing intra-protein interactions
Genetic sensors can be created by mix and matching DNA-binding modules with ligand-binding modules. Here the authors use a computational model to overcome module incompatibilities and restore function by rescuing key interactions.
- Xian-Li Jiang
- , Rey P. Dimas
- & Faruck Morcos
-
Article
| Open Access Development of a model-inference system for estimating epidemiological characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern
Development of a model-inference system for estimating epidemiological characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern
Quantification of the transmissibility and immune escape properties of SARS-CoV-2 variants is necessary to support pandemic planning. Here, the authors develop a model inference system to estimate these properties using incidence and mortality data for three variants of concern.
- Wan Yang
- & Jeffrey Shaman
-
Article
| Open Access Modelling the persistence and control of Rift Valley fever virus in a spatially heterogeneous landscape
Modelling the persistence and control of Rift Valley fever virus in a spatially heterogeneous landscape
Rift Valley fever is a zoonotic haemorrhagic fever with complex transmission dynamics influenced by environmental variables and animal movements. Here, the authors develop a metapopulation model incorporating these factors and use it to identify the main drivers of transmission in the Comoros archipelago.
- Warren S. D. Tennant
- , Eric Cardinale
- & Raphaëlle Métras
-
Article
| Open Access A high-risk retinoblastoma subtype with stemness features, dedifferentiated cone states and neuronal/ganglion cell gene expression
A high-risk retinoblastoma subtype with stemness features, dedifferentiated cone states and neuronal/ganglion cell gene expression
Retinoblastoma is the most frequent intraocular paediatric malignancy whose molecular basis remains poorly understood. Here, the authors perform multi-omic analysis and identify two subtypes; one in a cone differentiated state and one more aggressive showing cone dedifferentiation and expressing neuronal markers.
- Jing Liu
- , Daniela Ottaviani
- & François Radvanyi
-
Article
| Open Access Leveraging the Cell Ontology to classify unseen cell types
Leveraging the Cell Ontology to classify unseen cell types
Classifying cells into unseen cell types remains challenging in scRNA-seq analysis. Here we show that Cell Ontology enables an accurate classification of unseen cell types through considering the cell type relationships in the Cell Ontology graph.
- Sheng Wang
- , Angela Oliveira Pisco
- & Russ B. Altman
-
Article
| Open Access Peak learning of mass spectrometry imaging data using artificial neural networks
Peak learning of mass spectrometry imaging data using artificial neural networks
The high dimensional and complex nature of mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) data poses challenges to downstream analyses. Here the authors show an application of artificial intelligence in mining MSI data revealing biologically relevant metabolomic and proteomic information from data acquired on different mass spectrometry platforms.
- Walid M. Abdelmoula
- , Begona Gimenez-Cassina Lopez
- & Nathalie Y. R. Agar
-
Article
| Open Access Generalized and scalable trajectory inference in single-cell omics data with VIA
Generalized and scalable trajectory inference in single-cell omics data with VIA
Scalable trajectory inference for multi-omic single cell datasets is challenging in terms of capturing non-tree complex topologies. Here the authors present a method, VIA, that scales to millions of cells across multiple omic modalities using lazy-teleporting random walks.
- Shobana V. Stassen
- , Gwinky G. K. Yip
- & Kevin K. Tsia
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-species behavior analysis with attention-based domain-adversarial deep neural networks
Cross-species behavior analysis with attention-based domain-adversarial deep neural networks
Comparing changes in behaviour across various species is not always trivial, especial across significantly divergent species. Here, the authors develop a deep learning framework that allows them to map changes in locomotion demonstrated on dopamine-deficient humans, mice and worms.
- Takuya Maekawa
- , Daiki Higashide
- & Susumu Takahashi
-
Article
| Open Access A human liver cell-based system modeling a clinical prognostic liver signature for therapeutic discovery
A human liver cell-based system modeling a clinical prognostic liver signature for therapeutic discovery
Drug and target discovery for advanced liver disease are hampered by a lack of suitable models for clinical translation. Here the authors present a human liver cell-based system modeling a clinical prognostic signature allowing to propose nizatidine for treatment of advanced liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma prevention.
- Emilie Crouchet
- , Simonetta Bandiera
- & Thomas F. Baumert
-
Article
| Open Access Automated bone mineral density prediction and fracture risk assessment using plain radiographs via deep learning
Automated bone mineral density prediction and fracture risk assessment using plain radiographs via deep learning
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool are recommended tools for osteoporotic fracture risk evaluation, but are underutilized. Here, the authors present an opportunistic tool to identify fractures, predict bone mineral density and evaluate fracture risk using plain pelvis and lumbar spine radiographs.
- Chen-I Hsieh
- , Kang Zheng
- & Chang-Fu Kuo
-
Article
| Open Access A deep-learning framework for multi-level peptide–protein interaction prediction
A deep-learning framework for multi-level peptide–protein interaction prediction
Peptide-protein interactions play fundamental roles in cellular processes and are crucial for designing peptide therapeutics. Here, the authors present a deep learning framework for simultaneously predicting peptide-protein interactions and identifying peptide binding residues involved in the interactions.
- Yipin Lei
- , Shuya Li
- & Jianyang Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying the unknown impact of segmentation uncertainty on image-based simulations
Quantifying the unknown impact of segmentation uncertainty on image-based simulations
Image-based simulation for obtaining physical quantities is limited by the uncertainty in the underlying image segmentation. Here, the authors introduce a workflow for efficiently quantifying segmentation uncertainty and creating uncertainty distributions of the resulting physics quantities.
- Michael C. Krygier
- , Tyler LaBonte
- & Scott A. Roberts
-
Article
| Open Access Parental relatedness through time revealed by runs of homozygosity in ancient DNA
Parental relatedness through time revealed by runs of homozygosity in ancient DNA
Little is known about how human parental relatedness varied across ancient populations. Runs of homozygosity (ROH) in the offspring’s genome can give clues. Here, the authors present a method to identify ROH in ancient genomes and infer low rates of close kin unions across most ancient populations.
- Harald Ringbauer
- , John Novembre
- & Matthias Steinrücken
-
Article
| Open Access Chromatin-based, in cis and in trans regulatory rewiring underpins distinct oncogenic transcriptomes in multiple myeloma
Chromatin-based, in cis and in trans regulatory rewiring underpins distinct oncogenic transcriptomes in multiple myeloma
Despite extensive genetic heterogeneity, nearly half of all multiple myeloma (MM) cases are driven by cyclin D2 (CCND2) over-expression. Here the authors dissect the chromatin landscape of MM to provide insights into the transcriptional regulatory landscape driving MM and divergent transcriptomes corresponding to different MM genetic subtypes.
- Jaime Alvarez-Benayas
- , Nikolaos Trasanidis
- & Anastasios Karadimitris
-
Article
| Open Access Contact tracing is an imperfect tool for controlling COVID-19 transmission and relies on population adherence
Contact tracing is an imperfect tool for controlling COVID-19 transmission and relies on population adherence
Evaluations of the UK’s contact tracing programme have shown that it has had limited impact on COVID-19 control. Here, the authors show that with high levels of reporting and adherence, contact tracing could reduce transmission, but it should not be used as the sole control measure.
- Emma L. Davis
- , Tim C. D. Lucas
- & Petra Klepac
-
Article
| Open Access Unified AI framework to uncover deep interrelationships between gene expression and Alzheimer’s disease neuropathologies
Unified AI framework to uncover deep interrelationships between gene expression and Alzheimer’s disease neuropathologies
The molecular basis of Alzheimer’s Disease has been obscured by heterogeneity and scarcity of brain gene expression data, which limit effectiveness in complex models. Here, the authors introduce a multi-task deep learning framework to learn generalizable and nuanced relationships between gene expression and neuropathology.
- Nicasia Beebe-Wang
- , Safiye Celik
- & Su-In Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Trade-offs between individual and ensemble forecasts of an emerging infectious disease
Trade-offs between individual and ensemble forecasts of an emerging infectious disease
Newly emerged pathogens are inherently difficult to forecast, due to many unknowns about their biology early in an epidemic. Here, the authors assess forecasts of a suite of models during the Zika epidemic in Colombia, finding that the models that performed best changed over the course of the epidemic.
- Rachel J. Oidtman
- , Elisa Omodei
- & T. Alex Perkins
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial localisation meets biomolecular networks
Spatial localisation meets biomolecular networks
Complex biomolecular networks are fundamental to the functioning of living systems, both at the cellular level and beyond. In this paper, the authors develop a systems framework to elucidate the interplay of networks and the spatial localisation of network components.
- Govind Menon
- & J. Krishnan
-
Article
| Open Access CloneSig can jointly infer intra-tumor heterogeneity and mutational signature activity in bulk tumor sequencing data
CloneSig can jointly infer intra-tumor heterogeneity and mutational signature activity in bulk tumor sequencing data
Intratumour heterogeneity (ITH) and mutational signatures are typically analysed separately, even though they are not necessarily independent. Here, the authors present CloneSig, a tool for the joint estimation of ITH and mutational signatures, with which they analyse the TCGA and PCAWG datasets.
- Judith Abécassis
- , Fabien Reyal
- & Jean-Philippe Vert
-
Article
| Open Access Automatically disambiguating medical acronyms with ontology-aware deep learning
Automatically disambiguating medical acronyms with ontology-aware deep learning
Disambiguating abbreviations is important for automated clinical note processing; however, deploying machine learning for this task is restricted by lack of good training data. Here, the authors show novel data augmentation methods that use biomedical ontologies to improve abbreviation disambiguation in many datasets.
- Marta Skreta
- , Aryan Arbabi
- & Michael Brudno
-
Article
| Open Access Different historical generation intervals in human populations inferred from Neanderthal fragment lengths and mutation signatures
Different historical generation intervals in human populations inferred from Neanderthal fragment lengths and mutation signatures
Historical interbreeding between Neanderthals and humans should leave signatures of historical demographics in modern human genomes. Analysing the size distribution of Neanderthal fragments in non-African genomes suggests consistent differences in the generation interval across Eurasia, and that this could explain mutational spectrum variation.
- Moisès Coll Macià
- , Laurits Skov
- & Mikkel Heide Schierup
-
Comment
| Open Access Computational challenges and opportunities in spatially resolved transcriptomic data analysis
Computational challenges and opportunities in spatially resolved transcriptomic data analysis
Spatially resolved transcriptomic data demand new computational analysis methods to derive biological insights. Here, we comment on these associated computational challenges as well as highlight the opportunities for standardized benchmarking metrics and data-sharing infrastructure in spurring innovation moving forward.
- Lyla Atta
- & Jean Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Learning interpretable cellular and gene signature embeddings from single-cell transcriptomic data
Learning interpretable cellular and gene signature embeddings from single-cell transcriptomic data
Computational single-cell RNA-seq analyses often face challenges in scalability, model interpretability, and confounders. Here, we show a new model to address these challenges by learning meaningful embeddings from the data that simultaneously refine gene signatures and cell functions in diverse conditions.
- Yifan Zhao
- , Huiyu Cai
- & Yue Li
-
Article
| Open Access Inferring multilayer interactome networks shaping phenotypic plasticity and evolution
Inferring multilayer interactome networks shaping phenotypic plasticity and evolution
Genetic plasticity drives phenotypic differences. Here, the authors develop a framework to quantify the individual and combinatorial contributions of SNPs on a phenotype of interest and use it to identify SNP-SNP interactions associated with variations in bacteria’s response to external changes.
- Dengcheng Yang
- , Yi Jin
- & Rongling Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of bloodstream Trypanosoma brucei reconstructs cell cycle progression and developmental quorum sensing
Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of bloodstream Trypanosoma brucei reconstructs cell cycle progression and developmental quorum sensing
Trypanosoma brucei undergoes developmental steps during host infection. Here, using oligopeptide-induced differentiation in vitro, authors model replicative ‘slender’ to transmissible ‘stumpy’ bloodstream forms and identify developmental and cell cycle regulators by single cell transcriptomics.
- Emma M. Briggs
- , Federico Rojas
- & Thomas D. Otto
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell ATAC and RNA sequencing reveal pre-existing and persistent cells associated with prostate cancer relapse
Single-cell ATAC and RNA sequencing reveal pre-existing and persistent cells associated with prostate cancer relapse
Identifying the molecular mechanisms of response to systemic therapy in prostate cancer remains crucial. Here, the authors apply single cell-ATAC and RNAseq to models of early treatment response and resistance to enzalutamide and identify chromatin and gene expression patterns that can predict treatment response.
- S. Taavitsainen
- , N. Engedal
- & A. Urbanucci
-
Article
| Open Access Binding of regulatory proteins to nucleosomes is modulated by dynamic histone tails
Binding of regulatory proteins to nucleosomes is modulated by dynamic histone tails
The intrinsic disorder of histone tails poses challenges in their characterization. Here the authors apply extensive molecular dynamics simulations of the full nucleosome to show reversible binding to DNA with specific binding modes of different types of histone tails, where charge-altering modifications suppress tail-DNA interactions and may boost interactions between nucleosomes and nucleosome-binding proteins.
- Yunhui Peng
- , Shuxiang Li
- & Anna R. Panchenko
-
Article
| Open Access Translating polygenic risk scores for clinical use by estimating the confidence bounds of risk prediction
Translating polygenic risk scores for clinical use by estimating the confidence bounds of risk prediction
The application of polygenic risk scores to individual-level disease susceptibility is challenging, as risk is evaluated at a group-level. Here, the authors describe a machine learning method, Mondrian Cross-Conformal Prediction, that reports disease status conditional probability value at the individual level.
- Jiangming Sun
- , Yunpeng Wang
- & Kasper Lage
-
Article
| Open Access The concurrence of DNA methylation and demethylation is associated with transcription regulation
The concurrence of DNA methylation and demethylation is associated with transcription regulation
The global pattern of the mammalian methylome is formed by changes in methylation and demethylation. Here the authors describe a metric methylation concurrence that measures the ratio of unmethylated CpGs inside the partially methylated reads and show that methylation concurrence is associated with epigenetically regulated tumour suppressor genes.
- Jiejun Shi
- , Jianfeng Xu
- & Wei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Epistatic Net allows the sparse spectral regularization of deep neural networks for inferring fitness functions
Epistatic Net allows the sparse spectral regularization of deep neural networks for inferring fitness functions
Finding a biologically-relevant inductive bias for training DNNs on large fitness landscapes is challenging. Here, the authors propose a method called Epistatic Net that improves DNN prediction accuracy and interpretation speed by integrating the knowledge that higher-order epistatic interactions are usually sparse.
- Amirali Aghazadeh
- , Hunter Nisonoff
- & Kannan Ramchandran
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Biochemical reaction networks
- Cellular signalling networks
- Classification and taxonomy
- Communication and replication
- Computational models
- Computational neuroscience
- Computational platforms and environments
- Data acquisition
- Data integration
- Data mining
- Data processing
- Data publication and archiving
- Databases
- Functional clustering
- Gene ontology
- Gene regulatory networks
- Genome informatics
- Hardware and infrastructure
- High-throughput screening
- Image processing
- Literature mining
- Machine learning
- Microarrays
- Network topology
- Phylogeny
- Power law
- Predictive medicine
- Probabilistic data networks
- Programming language
- Protein analysis
- Protein design
- Protein folding
- Protein function predictions
- Protein structure predictions
- Proteome informatics
- Quality control
- Scale invariance
- Sequence annotation
- Software
- Standards
- Statistical methods
- Virtual drug screening
