Featured
-
-
Article |
 HER kinase inhibition in patients with HER2- and HER3-mutant cancers
HER kinase inhibition in patients with HER2- and HER3-mutant cancers
In a basket trial design, the efficacy of the pan-HER kinase inhibitor neratinib is tested in patients with 21 different tumour types, and responses are determined by mutation and tissue type, and are restricted to HER2-mutant cancers.
- David M. Hyman
- , Sarina A. Piha-Paul
- & David B. Solit
-
Letter |
 Pharmacological activation of REV-ERBs is lethal in cancer and oncogene-induced senescence
Pharmacological activation of REV-ERBs is lethal in cancer and oncogene-induced senescence
REV-ERBs, nuclear hormone receptors that regulate transcription as part of the circadian clock cell machinery, inhibit autophagy and lipogenesis in premalignant and malignant cells and impair tumour growth in vivo.
- Gabriele Sulli
- , Amy Rommel
- & Satchidananda Panda
-
Letter |
 Drug-tolerant persister cancer cells are vulnerable to GPX4 inhibition
Drug-tolerant persister cancer cells are vulnerable to GPX4 inhibition
Cancer persister cells, which survive cytotoxic treatments, are shown to be sensitive to inhibition of the lipid hydroperoxidase GPX4.
- Matthew J. Hangauer
- , Vasanthi S. Viswanathan
- & Michael T. McManus
-
Article |
 Visualization of chemical modifications in the human 80S ribosome structure
Visualization of chemical modifications in the human 80S ribosome structure
A high-resolution structure of the human ribosome determined by cryo-electron microscopy visualizes numerous RNA modifications that are concentrated at functional sites with an extended shell, and suggests the possibility of designing more specific ribosome-targeting drugs.
- S. Kundhavai Natchiar
- , Alexander G. Myasnikov
- & Bruno P. Klaholz
-
Letter |
 A neoantigen fitness model predicts tumour response to checkpoint blockade immunotherapy
A neoantigen fitness model predicts tumour response to checkpoint blockade immunotherapy
An immune fitness model for tumours under checkpoint blockade immunotherapy is proposed, through which the authors show that the presentation and recognition properties of dominant neoantigens distributed over tumour subclones are predictive of response in melanoma and lung cancer cohorts.
- Marta Łuksza
- , Nadeem Riaz
- & Benjamin D. Greenbaum
-
Letter |
 Cancer drug addiction is relayed by an ERK2-dependent phenotype switch
Cancer drug addiction is relayed by an ERK2-dependent phenotype switch
The identification of an ERK2–JUNB–FRA1 signalling pathway that drives addiction to therapeutic drugs in cancer cells, and an ERK2-dependent phenotype switch that precedes cell death after drug withdrawal, may help to guide therapies that exploit the addiction phenotype.
- Xiangjun Kong
- , Thomas Kuilman
- & Daniel S. Peeper
-
Letter |
 Discovery of a selective catalytic p300/CBP inhibitor that targets lineage-specific tumours
Discovery of a selective catalytic p300/CBP inhibitor that targets lineage-specific tumours
A potent and selective catalytic inhibitor of p300/CBP histone acetyltransferases suppresses tumour proliferation across multiple cell lineages, illustrating the therapeutic potential of drug-like small molecules that target histone acetyltransferases.
- Loren M. Lasko
- , Clarissa G. Jakob
- & Kenneth D. Bromberg
-
Letter |
 PAK signalling drives acquired drug resistance to MAPK inhibitors in BRAF-mutant melanomas
PAK signalling drives acquired drug resistance to MAPK inhibitors in BRAF-mutant melanomas
BRAF-inhibition resistance in metastatic melanoma occurs through p21-activated kinase-mediated reactivation of ERK, whereas resistance to combined BRAF and MEK inhibition occurs through p21-activated kinase-mediated regulation of JNK and β-catenin phosphorylation, mTOR pathway activation and apoptosis inhibition in many patients.
- Hezhe Lu
- , Shujing Liu
- & Wei Guo
-
Letter |
 CDK4/6 inhibition triggers anti-tumour immunity
CDK4/6 inhibition triggers anti-tumour immunity
Mouse models of breast carcinoma and other solid tumours show that selective cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) inhibitors not only induce tumour cell cycle arrest but also promote anti-tumour immunity.
- Shom Goel
- , Molly J. DeCristo
- & Jean J. Zhao
-
Letter |
 Tumours with class 3 BRAF mutants are sensitive to the inhibition of activated RAS
Tumours with class 3 BRAF mutants are sensitive to the inhibition of activated RAS
Hypoactive BRAF mutants bind more tightly than wild type to the upstream regulator RAS, thus amplifying to amplify ERK signalling; tumours expressing these mutants require coexistent mechanisms for RAS activation to grow and are sensitive to their inhibition.
- Zhan Yao
- , Rona Yaeger
- & Neal Rosen
-
Letter |
 Cysteine protease cathepsin B mediates radiation-induced bystander effects
Cysteine protease cathepsin B mediates radiation-induced bystander effects
The cysteine protease CPR-4, a cathepsin B homologue, is identified as a radiation-induced bystander effect (RIBE) factor in nematodes in response to ultraviolet or ionizing radiation, and causes inhibition of cell death and increased embryonic lethality.
- Yu Peng
- , Man Zhang
- & Ding Xue
-
Letter |
 Personalized RNA mutanome vaccines mobilize poly-specific therapeutic immunity against cancer
Personalized RNA mutanome vaccines mobilize poly-specific therapeutic immunity against cancer
The authors report the first-in-human application of personalized neo-antigen RNA vaccines in patients with melanoma.
- Ugur Sahin
- , Evelyna Derhovanessian
- & Özlem Türeci
-
Letter |
 Dependency of a therapy-resistant state of cancer cells on a lipid peroxidase pathway
Dependency of a therapy-resistant state of cancer cells on a lipid peroxidase pathway
Therapy-resistant cancer cell states identified across diverse contexts are selectively vulnerable to ferroptotic cell death induced by inhibition of lipid peroxidase pathways converging on GPX4.
- Vasanthi S. Viswanathan
- , Matthew J. Ryan
- & Stuart L. Schreiber
-
Letter |
 Rare cell variability and drug-induced reprogramming as a mode of cancer drug resistance
Rare cell variability and drug-induced reprogramming as a mode of cancer drug resistance
Through drug exposure, a rare, transient transcriptional program characterized by high levels of expression of known resistance drivers can get ‘burned in’, leading to the selection of cells endowed with a transcriptional drug resistance and thus more chemoresistant cancers.
- Sydney M. Shaffer
- , Margaret C. Dunagin
- & Arjun Raj
-
Letter |
 A Wnt-producing niche drives proliferative potential and progression in lung adenocarcinoma
A Wnt-producing niche drives proliferative potential and progression in lung adenocarcinoma
A subset of Kras and p53 mutant cancer cells acts as a Wnt-producing niche for another cancer cell subset, and porcupine inhibition disrupts Wnt secretion in this niche, thereby suppressing proliferative potential and leading to therapeutic benefit.
- Tuomas Tammela
- , Francisco J. Sanchez-Rivera
- & Tyler Jacks
-
Letter |
 Modulating the therapeutic response of tumours to dietary serine and glycine starvation
Modulating the therapeutic response of tumours to dietary serine and glycine starvation
Dependence on exogenous serine means that tumour growth is restricted in mice on a low-serine diet; this effect on tumour growth can be amplified by antagonizing the antioxidant response.
- Oliver D. K. Maddocks
- , Dimitris Athineos
- & Karen H. Vousden
-
Article |
 Visualization and targeting of LGR5+ human colon cancer stem cells
Visualization and targeting of LGR5+ human colon cancer stem cells
LGR5+ cells in human colorectal cancer tissue xenografted into mice act as cancer stem cells, and differentiated cancer cells can revert to cancer stem cells and express LGR5 after ablation of existing LGR5+ cells.
- Mariko Shimokawa
- , Yuki Ohta
- & Toshiro Sato
-
Letter |
 The allosteric inhibitor ABL001 enables dual targeting of BCR–ABL1
The allosteric inhibitor ABL001 enables dual targeting of BCR–ABL1
The selective allosteric ABL1 inhibitor ABL001 (asciminib) represents a new inhibitory mechanism for BCR–ABL1-driven malignancies, and its efficacy and evolving mechanisms of resistance do not overlap with those of other BCR–ABL1 kinase inhibitors.
- Andrew A. Wylie
- , Joseph Schoepfer
- & William R. Sellers
-
Letter |
 Effective combinatorial immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer
Effective combinatorial immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer
A new chimaeric mouse model of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer to efficiently test combination therapies in an autochthonous setting.
- Xin Lu
- , James W. Horner
- & Ronald A. DePinho
-
Article |
 TIRR regulates 53BP1 by masking its histone methyl-lysine binding function
TIRR regulates 53BP1 by masking its histone methyl-lysine binding function
A new protein, Tudor interacting repair regulator (TIRR), affects DNA repair by masking the chromatin interaction domain of 53BP1, thereby preventing its recruitment to double-strand breaks.
- Pascal Drané
- , Marie-Eve Brault
- & Dipanjan Chowdhury
-
Letter |
 Targeting a CAR to the TRAC locus with CRISPR/Cas9 enhances tumour rejection
Targeting a CAR to the TRAC locus with CRISPR/Cas9 enhances tumour rejection
Introducing chimeric antigen receptors into the endogenous T-cell receptor locus reduces tonic signalling, averts accelerated T-cell differentiation and delays T-cell exhaustion, leading to enhanced function and anti-tumour efficacy compared to random integrations.
- Justin Eyquem
- , Jorge Mansilla-Soto
- & Michel Sadelain
-
Letter |
 Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase δ blockade increases genomic instability in B cells
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase δ blockade increases genomic instability in B cells
PI3Kδ controls the expression of the recombinogenic enzyme AID; excessive AID activity caused by PI3Kδ inhibition can induce genomic instability in leukaemia and lymphoma cells, as well as in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia treated with PI3Kδ inhibitors.
- Mara Compagno
- , Qi Wang
- & Roberto Chiarle
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Consistency in drug response profiling
Consistency in drug response profiling
- John Patrick Mpindi
- , Bhagwan Yadav
- & Tero Aittokallio
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Drug response consistency in CCLE and CGP
Drug response consistency in CCLE and CGP
- Mehdi Bouhaddou
- , Matthew S. DiStefano
- & Marc R. Birtwistle
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Safikhani et al. reply
Safikhani et al. reply
- Zhaleh Safikhani
- , Nehme El-Hachem
- & Benjamin Haibe-Kains
-
Brief Communications Arising |
Safikhani et al. reply
- Zhaleh Safikhani
- , Nehme El-Hachem
- & Benjamin Haibe-Kains
-
Article |
 The MCL1 inhibitor S63845 is tolerable and effective in diverse cancer models
The MCL1 inhibitor S63845 is tolerable and effective in diverse cancer models
S63845 specifically inhibits MCL1 and induces tumour cell death in vitro and in vivo in diverse cancer-derived cell lines with an acceptable safety margin.
- András Kotschy
- , Zoltán Szlavik
- & Olivier Geneste
-
Letter |
 The epichaperome is an integrated chaperome network that facilitates tumour survival
The epichaperome is an integrated chaperome network that facilitates tumour survival
Chaperomes are dynamic assemblies of proteins that regulate cellular homeostasis but specific cellular stresses remodel chaperome components into a stable chaperome network called the epichaperome, which might offer a new cancer target.
- Anna Rodina
- , Tai Wang
- & Gabriela Chiosis
-
Letter |
 HER2 expression identifies dynamic functional states within circulating breast cancer cells
HER2 expression identifies dynamic functional states within circulating breast cancer cells
Patient-derived circulating tumour cells are used to characterize the dynamics and underlying plasticity of HER2 expression in non-HER2-amplified breast tumours.
- Nicole Vincent Jordan
- , Aditya Bardia
- & Daniel A. Haber
-
Letter |
 Small molecule stabilization of the KSR inactive state antagonizes oncogenic Ras signalling
Small molecule stabilization of the KSR inactive state antagonizes oncogenic Ras signalling
A class of small molecules that stabilize a previously unrecognized inactive state of KSR is reported; the agonists synergize with MEK inhibitors to prevent growth of Ras mutant cell lines.
- Neil S. Dhawan
- , Alex P. Scopton
- & Arvin C. Dar
-
Article |
 Replication fork stability confers chemoresistance in BRCA-deficient cells
Replication fork stability confers chemoresistance in BRCA-deficient cells
Protection of nascent DNA from degradation provides a mechanism that can promote synthetic viability and drug resistance in Brca-deficient cells without restoring homologous recombination at double-strand breaks.
- Arnab Ray Chaudhuri
- , Elsa Callen
- & André Nussenzweig
-
Letter |
 Allosteric inhibition of SHP2 phosphatase inhibits cancers driven by receptor tyrosine kinases
Allosteric inhibition of SHP2 phosphatase inhibits cancers driven by receptor tyrosine kinases
SHP099, a selective inhibitor of signalling meditator SHP2 with drug-like properties, has an allosteric mechanism of action whereby it stabilizes SHP2 in an auto-inhibited conformation, and suppresses RAS–ERK signalling and proliferation in receptor-tyrosine-kinase-driven cancer cell lines and mouse tumour xenograft models.
- Ying-Nan P. Chen
- , Matthew J. LaMarche
- & Pascal D. Fortin
-
Article |
 A combinatorial strategy for treating KRAS-mutant lung cancer
A combinatorial strategy for treating KRAS-mutant lung cancer
A systematic screen identifies FGFR1 signalling reactivation as an adaptive resistance mechanism after MEK inhibition specific for KRAS tumours, which can be targeted by combined inhibition with the clinically approved drugs trametinib and ponatinib.
- Eusebio Manchado
- , Susann Weissmueller
- & Scott W. Lowe
-
Letter |
 Rocaglates convert DEAD-box protein eIF4A into a sequence-selective translational repressor
Rocaglates convert DEAD-box protein eIF4A into a sequence-selective translational repressor
The cancer drug rocaglamide A cements the RNA helicase eIF4A on polypurine sequences and thereby prevents scanning of the 43S subunit along the messenger RNA, highlighting how a drug can act by stabilizing sequence-selective RNA–protein interactions.
- Shintaro Iwasaki
- , Stephen N. Floor
- & Nicholas T. Ingolia
-
Letter |
 Image-based detection and targeting of therapy resistance in pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Image-based detection and targeting of therapy resistance in pancreatic adenocarcinoma
The stem cell determinant Musashi (Msi) is a key mediator of pancreatic cancer progression and therapy resistance.
- Raymond G. Fox
- , Nikki K. Lytle
- & Tannishtha Reya
-
Letter |
 Systemic RNA delivery to dendritic cells exploits antiviral defence for cancer immunotherapy
Systemic RNA delivery to dendritic cells exploits antiviral defence for cancer immunotherapy
The development of a nanoparticle RNA vaccine is reported that preferentially targets dendritic cells after systemic administration, and is shown to provide durable interferon-α-dependent antigen-specific immunity in mouse tumour models; initial results in advanced melanoma patients indicate potential efficacy in humans.
- Lena M. Kranz
- , Mustafa Diken
- & Ugur Sahin
-
Letter |
 Overcoming mTOR resistance mutations with a new-generation mTOR inhibitor
Overcoming mTOR resistance mutations with a new-generation mTOR inhibitor
Inhibitors of the mTOR kinase are in clinical trials for the treatment of cancer; here, mutations in mTOR that can lead to drug resistance are investigated and the results are used to design a new class of mTOR inhibitors that can overcome this resistance.
- Vanessa S. Rodrik-Outmezguine
- , Masanori Okaniwa
- & Kevan M. Shokat
-
Letter |
 Melanoma addiction to the long non-coding RNA SAMMSON
Melanoma addiction to the long non-coding RNA SAMMSON
A known oncogene, MITF, resides in a region of chromosome 3 that is amplified in melanomas and associated with poor prognosis; now, a long non-coding RNA gene, SAMMSON, is shown to also lie in this region, to also act as a melanoma-specific survival oncogene, and to be a promising therapeutic target for anti-melanoma therapy.
- Eleonora Leucci
- , Roberto Vendramin
- & Jean-Christophe Marine
-
Letter |
 Targeting PTPRK-RSPO3 colon tumours promotes differentiation and loss of stem-cell function
Targeting PTPRK-RSPO3 colon tumours promotes differentiation and loss of stem-cell function
Antibody-mediated inhibition of R-spondin-3 in colorectal tumours decreases tumour growth and promotes differentiation—these effects are associated with a decrease in expression of genes associated with stem-cell function.
- Elaine E. Storm
- , Steffen Durinck
- & Frederic J. de Sauvage
-
Article |
 Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) lineage-tracing system in a mouse model of breast-to-lung metastasis reveals that although some cells undergo EMT in a primary epithelial tumour, the lung metastases mainly arise from cells that have not undergone EMT; in addition, cells that have undergone EMT appear more resistant to chemotherapy.
- Kari R. Fischer
- , Anna Durrans
- & Dingcheng Gao
-
Letter |
 Microenvironment-induced PTEN loss by exosomal microRNA primes brain metastasis outgrowth
Microenvironment-induced PTEN loss by exosomal microRNA primes brain metastasis outgrowth
Expression of the tumour suppressor PTEN in disseminated primary tumour cells is lost after tumour cells metastasize to the brain, with downregulation instigated by microRNAs from astrocytes, which are transferred from cell to cell by exosomes; these findings reveal the dynamic nature of metastatic cancer cells when adapting to a new tissue environment.
- Lin Zhang
- , Siyuan Zhang
- & Dihua Yu
-
Letter |
 RAF inhibitors that evade paradoxical MAPK pathway activation
RAF inhibitors that evade paradoxical MAPK pathway activation
Next-generation RAF inhibitors that inhibit oncogenic BRAF without inducing paradoxical pathway activation in cells with mutant RAS might yield improved safety and more durable efficacy.
- Chao Zhang
- , Wayne Spevak
- & Gideon Bollag
-
Letter |
 BET inhibitor resistance emerges from leukaemia stem cells
BET inhibitor resistance emerges from leukaemia stem cells
BET inhibitors that target bromodomain chromatin readers such as BRD4 are being explored as potential therapeutics in cancer; here, in a MLL–AF9 mouse leukaemia model, resistance to BET inhibitors is shown to emerge from leukaemia stem cells, and be partly due to increased Wnt/β-catenin signalling.
- Chun Yew Fong
- , Omer Gilan
- & Mark A. Dawson
-
Letter |
 Transcriptional plasticity promotes primary and acquired resistance to BET inhibition
Transcriptional plasticity promotes primary and acquired resistance to BET inhibition
BET bromodomain inhibitors are being explored as potential therapeutics in cancer; here, AML cells are shown to evade sensitivity to BET inhibition through rewiring the transcriptional regulation of BRD4 target genes such as MYC in a process that is facilitated by suppression of PRC2 and WNT signalling activation.
- Philipp Rathert
- , Mareike Roth
- & Johannes Zuber
-
Article |
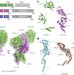 Structural integration in hypoxia-inducible factors
Structural integration in hypoxia-inducible factors
This study describes the long-awaited crystal structures for hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) heterodimers, including complexes bound to small molecules and DNA; the HIF–ARNT architecture is distinct from the bHLH-PAS-containing CLOCK–BMAL1 heterodimer, and HIF mutations linked to cancer can be mapped to important structural regions, with the structures providing future reference for small-molecule drug discovery efforts.
- Dalei Wu
- , Nalini Potluri
- & Fraydoon Rastinejad
-
Letter |
 Improving survival by exploiting tumour dependence on stabilized mutant p53 for treatment
Improving survival by exploiting tumour dependence on stabilized mutant p53 for treatment
Novel hotspot mutant p53 gain-of-function mouse model shows that tumours depend on its sustained expression, and genetic and pharmacological approaches reveal mutant p53 as an actionable cancer drug target.
- E. M. Alexandrova
- , A. R. Yallowitz
- & U. M. Moll
-
Letter |
 Mutant MHC class II epitopes drive therapeutic immune responses to cancer
Mutant MHC class II epitopes drive therapeutic immune responses to cancer
The authors show that a large fraction of tumour mutations is immunogenic and predominantly recognized by CD4+ T cells; they use these data to design synthetic messenger-RNA-based vaccines specific against tumour mutations, and show that these can reject tumours in mice.
- Sebastian Kreiter
- , Mathias Vormehr
- & Ugur Sahin
-
Letter |
 Therapy-induced tumour secretomes promote resistance and tumour progression
Therapy-induced tumour secretomes promote resistance and tumour progression
Tumour cells respond to an effective, targeted drug treatment with BRAF, ALK or EGFR kinase inhibitors by inducing a complex network of secreted signals that promote tumour growth, dissemination and metastasis of drug-resistant cancer cell clones, and increase the survival of drug-sensitive tumour cells, potentially contributing to incomplete tumour regression.
- Anna C. Obenauf
- , Yilong Zou
- & Joan Massagué
-
Letter |
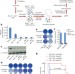 REV7 counteracts DNA double-strand break resection and affects PARP inhibition
REV7 counteracts DNA double-strand break resection and affects PARP inhibition
Loss of REV7 is shown to regulate end resection of double-stranded DNA breaks in BRCA1-deficient cells, leading to PARP inhibitor resistance and restoration of homologous recombination; REV7 dictates pathway choice in BRCA1-deficient cells and during immunoglobulin class switching.
- Guotai Xu
- , J. Ross Chapman
- & Sven Rottenberg

 Intra-tumour diversification in colorectal cancer at the single-cell level
Intra-tumour diversification in colorectal cancer at the single-cell level