Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Biohybrid nanoparticles for treating arthritis
Biohybrid nanoparticles for treating arthritis
A biohybrid nanoparticle formulation effectively treats rheumatoid arthritis by concurrently providing symptom relief and restoring proper immune function.
- Ronnie H. Fang
- & Liangfang Zhang
-
Article |
 Ceria-vesicle nanohybrid therapeutic for modulation of innate and adaptive immunity in a collagen-induced arthritis model
Ceria-vesicle nanohybrid therapeutic for modulation of innate and adaptive immunity in a collagen-induced arthritis model
Rheumatoid arthritis involves both inflammation and immune dysfunction, yet most therapies only target one aspect. Here, the authors report on ceria nanoparticle vesicle hybrids producing anti-inflammatory action and immunomodulation to relieve symptoms and restore normal function.
- Sagang Koo
- , Hee Su Sohn
- & Taeghwan Hyeon
-
Article |
 Honeybee comb-inspired stiffness gradient-amplified catapult for solid particle repellency
Honeybee comb-inspired stiffness gradient-amplified catapult for solid particle repellency
Nanoindentation of the microscale honeybee comb reveals a stiffness gradient that spans two orders of magnitude, which amplifies the catapult effect and facilitates solid particle repellency. By leveraging this, the study presents the fabrication of scaled-up, bioinspired stiffness-gradient elastomeric catapult-like soft actuators.
- Wei Zhang
- , Wei Jiang
- & Zuankai Wang
-
News & Views |
 Breaking the bottleneck of synthetic cells
Breaking the bottleneck of synthetic cells
In a major advancement for synthetic biology, dynamin A has been identified as a minimal component enabling cell division in synthetic cells, moving us one step nearer to realizing the ambition of creating synthetic life forms.
- Oskar Staufer
-
Article
| Open Access Multivalent insulin receptor activation using insulin–DNA origami nanostructures
Multivalent insulin receptor activation using insulin–DNA origami nanostructures
DNA-origami-based insulin assembly into well-defined nanoclusters reveals that insulin valency and spatial organization modulate insulin receptor activation and downstream responses independent of ligand concentration.
- Joel Spratt
- , José M. Dias
- & Ana I. Teixeira
-
Article |
 Dynamin A as a one-component division machinery for synthetic cells
Dynamin A as a one-component division machinery for synthetic cells
Bacterial protein dynamin A is shown to self-assemble at the membrane neck of dumbbell-shaped liposomes, triggering membrane hemi-scission and full scission, establishing dynamin-based single protein as a minimal synthetic divisome for synthetic cells.
- Nicola De Franceschi
- , Roman Barth
- & Cees Dekker
-
Article |
 A wearable aptamer nanobiosensor for non-invasive female hormone monitoring
A wearable aptamer nanobiosensor for non-invasive female hormone monitoring
A reagentless, wireless, wearable aptamer nanobiosensor interfaced with a gold nanoparticle-MXene-based electrode enables the selective, automatic and non-invasive analysis of the female hormone oestradiol in sweat during menstrual cycles with subpicomolar sensitivity.
- Cui Ye
- , Minqiang Wang
- & Wei Gao
-
News & Views |
 Barcoding biomarkers with nanopore sequencing
Barcoding biomarkers with nanopore sequencing
Nanopore sequencing combined with DNA-barcoded probes enables multiplexed detection of diverse biomarkers in blood serum.
- Ashley Stephenson
- & Jeff Nivala
-
Article
| Open Access Nanopore sequencing of DNA-barcoded probes for highly multiplexed detection of microRNA, proteins and small biomarkers
Nanopore sequencing of DNA-barcoded probes for highly multiplexed detection of microRNA, proteins and small biomarkers
This study establishes a method for multiplexed detection of up to 40 different biomarkers in a single assay by combining nanopore sequencing with analyte-selective barcoded probes, including cardiac disease-associated microRNA directly from blood serum.
- Caroline Koch
- , Benedict Reilly-O’Donnell
- & Joshua B. Edel
-
Article |
 Exploring the host range for genetic transfer of magnetic organelle biosynthesis
Exploring the host range for genetic transfer of magnetic organelle biosynthesis
Biosynthesis of magnetosomes is of interest for a range of applications. Here, factors needed for magnetosome biosynthesis are evaluated and new diverse bacteria are engineered to biofabricate magnetic nanoparticles, facilitating translation to biotechnology and nanomedicine.
- Marina V. Dziuba
- , Frank-Dietrich Müller
- & Dirk Schüler
-
Article |
 Age-associated disparity in phagocytic clearance affects the efficacy of cancer nanotherapeutics
Age-associated disparity in phagocytic clearance affects the efficacy of cancer nanotherapeutics
Here, the authors find a decrease in hepatic phagocytic uptake of nanoparticles in old mice due to age-associated downregulation of the scavenger receptor MARCO, which led to improved tumour delivery and antitumour efficacy of cancer nanomedicine, showing the need to consider age as a factor in therapeutics.
- Yifan Wang
- , Weiye Deng
- & Wen Jiang
-
Article |
 Breaking through the basement membrane barrier to improve nanotherapeutic delivery to tumours
Breaking through the basement membrane barrier to improve nanotherapeutic delivery to tumours
Nanoparticle penetration into tumours is an obstacle to cancer therapeutics. Here the authors show that the tumour vascular basement membrane constitutes a barrier that reduces nanoparticle delivery and demonstrate an immune-driven strategy to overcome the barrier, increasing nanoparticle movement into tumours.
- Qin Wang
- , Qirui Liang
- & Yucai Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Wireless electrical–molecular quantum signalling for cancer cell apoptosis
Wireless electrical–molecular quantum signalling for cancer cell apoptosis
Quantum biological electron transfer has potential in diagnostic and therapeutic settings. Here the authors report the triggered apoptosis of cancer cells using electricical input to wirelessly induce redox interactions at bio-nanoantennae in proximity to cancer cells.
- Akhil Jain
- , Jonathan Gosling
- & Frankie J. Rawson
-
Comment |
The Cancer Moonshot, the role of in vitro models, model accuracy, and the need for validation
Reducing cancer-related deaths can only happen with a better understanding of cancer biology and the development of improved, new therapeutics and delivery mechanisms. Nearly all cancer research is dependent upon the models being used, the model’s accuracy, and appropriate validation and benchmarking. Here the need for such considerations is discussed in line with the goal of the Cancer Moonshot.
- Peter C. Searson
-
News & Views |
 Unfolding the path to nanopore protein sequencing
Unfolding the path to nanopore protein sequencing
A modified nanopore enables enzyme-free threading of single polypeptides to detect post-translational modifications
- Adam Dorey
- & Stefan Howorka
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable multispecific DNA-origami-based T-cell engagers
Programmable multispecific DNA-origami-based T-cell engagers
A synthetic nanocarrier based on DNA origami chassis offers control over valency, orientation and spatial arrangement of antibodies for simultaneously engaging immune signalling pathways, checkpoint inhibition and targeted co-stimulation in anticancer immunotherapy in vivo.
- Klaus F. Wagenbauer
- , Nhi Pham
- & Hendrik Dietz
-
Article
| Open Access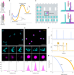 Single-molecule analysis of DNA base-stacking energetics using patterned DNA nanostructures
Single-molecule analysis of DNA base-stacking energetics using patterned DNA nanostructures
DNA-based point accumulation in nanoscale topography (DNA-PAINT) super-resolution imaging reveals the kinetics of the free energy of base-stacking interactions of all 16 dinucleotide combinations at the single-molecule level in patterned DNA-origami nanostructures.
- Abhinav Banerjee
- , Micky Anand
- & Mahipal Ganji
-
News & Views |
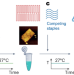 Shaken, not heated: DNA self-assembly at room temperature
Shaken, not heated: DNA self-assembly at room temperature
DNA-origami nanostructures self-assembled at milder physicochemical parameters in magnesium-free conditions achieve structural complexities akin to those formed by thermal annealing at elevated temperatures, and open a route to assembling DNA nanomachines in physiological conditions.
- Elisa Franco
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic matrices with DNA-encoded viscoelasticity for cell and organoid culture
Dynamic matrices with DNA-encoded viscoelasticity for cell and organoid culture
DNA nanotechnology is used to develop fully synthetic, programmable and printable 3D cell-culture matrices with stress-relaxation crosslinkers that encode (nano)mechanical stability. The hydrogel performs on par with solubilized animal-basement-membrane-derived cell-culture matrices.
- Yu-Hsuan Peng
- , Syuan-Ku Hsiao
- & Elisha Krieg
-
News & Views |
 Effects of cholesterol on biomolecular corona
Effects of cholesterol on biomolecular corona
Cholesterol levels in biological fluids are shown to change the composition of the protein corona affecting the biological fate of nanoparticles.
- Negar Mahmoudi
- & Morteza Mahmoudi
-
Article |
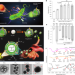 Electroactive membrane fusion-liposome for increased electron transfer to enhance radiodynamic therapy
Electroactive membrane fusion-liposome for increased electron transfer to enhance radiodynamic therapy
Here the authors report on exoelectrogenic bacteria-derived membrane fusion-liposome-coated titanium dioxide nanoparticles to mimic extracellular electron transfer to enhance superoxide anion production under low-dose X-ray irradiation for radiodynamic therapy.
- Ying-Chi Chen
- , Yi-Ting Li
- & Chen-Sheng Yeh
-
Article |
 Development of epistatic YES and AND protein logic gates and their assembly into signalling cascades
Development of epistatic YES and AND protein logic gates and their assembly into signalling cascades
Protein-based nanobiosensors with two epistatically interacting synthetic allosteric regulatory systems result in YES gate protein switches with large dynamic ranges and fast response times. These biosensors enable construction of rapid diagnostic tests compatible with clinical chemistry analysers.
- Zhong Guo
- , Oleh Smutok
- & Kirill Alexandrov
-
Article |
 Close the cancer–immunity cycle by integrating lipid nanoparticle–mRNA formulations and dendritic cell therapy
Close the cancer–immunity cycle by integrating lipid nanoparticle–mRNA formulations and dendritic cell therapy
Overcoming the immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment is a challenge. A strategy to close the cancer–immunity cycle has been reported by integrating lipid nanoparticle–mRNA formulations and dendritic cell therapy to promote tumour elimination and develop antitumour immunity.
- Yuebao Zhang
- , Xucheng Hou
- & Yizhou Dong
-
Article |
 Universal, label-free, single-molecule visualization of DNA origami nanodevices across biological samples using origamiFISH
Universal, label-free, single-molecule visualization of DNA origami nanodevices across biological samples using origamiFISH
Signal amplification through hybridization chain reaction by targeting conserved regions of the M13mp18 bacteriophage-based scaffold sequences is used for in situ imaging of unlabelled DNA origami nanostructures.
- Wendy Xueyi Wang
- , Travis R. Douglas
- & Leo Y. T. Chou
-
Article
| Open Access Enzyme-less nanopore detection of post-translational modifications within long polypeptides
Enzyme-less nanopore detection of post-translational modifications within long polypeptides
Electro-osmosis in an anion-selective α-hemolysin nanopore is used to capture, unfold and transport polypeptides of over 1,200 residues, which allows the mapping of post-translational modifications in polypeptide chains by monitoring the ionic current at a single-molecule resolution.
- Pablo Martin-Baniandres
- , Wei-Hsuan Lan
- & Hagan Bayley
-
Article
| Open Access DNA-origami-directed virus capsid polymorphism
DNA-origami-directed virus capsid polymorphism
DNA and RNA origami nanostructures direct the size, shape and topology of different virus capsids in a user-defined manner while shielding encapsulated origamis from degradation.
- Iris Seitz
- , Sharon Saarinen
- & Mauri A. Kostiainen
-
Article |
 Investigation of the enhanced antitumour potency of STING agonist after conjugation to polymer nanoparticles
Investigation of the enhanced antitumour potency of STING agonist after conjugation to polymer nanoparticles
STING agonists are often limited by low circulation time and cellular uptake. The conjugation of STING agonists with polymer nanoparticles is shown to enhance stability, circulation time and cellular uptake, increasing the immunotherapeutic activity.
- Pere Dosta
- , Alexander M. Cryer
- & Natalie Artzi
-
Article
| Open Access Adeno-associated viral vectors for functional intravenous gene transfer throughout the non-human primate brain
Adeno-associated viral vectors for functional intravenous gene transfer throughout the non-human primate brain
Crossing the blood–brain barrier in primates is a major obstacle to gene delivery in the brain. Here an adeno-associated virus variant (AAV.CAP-Mac) is identified and demonstrated for crossing the blood–brain barrier and delivering gene sequences to the brain of different non-human primates species.
- Miguel R. Chuapoco
- , Nicholas C. Flytzanis
- & Viviana Gradinaru
-
Article |
 Molecular machines stimulate intercellular calcium waves and cause muscle contraction
Molecular machines stimulate intercellular calcium waves and cause muscle contraction
Intercellular calcium waves drive numerous biological processes. Here light-activated molecular machines that—via nanomechanical action—stimulate ICW are reported, opening up avenues for the modulation of downstream biological processes using molecular-scale devices.
- Jacob L. Beckham
- , Alexis R. van Venrooy
- & James M. Tour
-
Article |
 Transport by circulating myeloid cells drives liposomal accumulation in inflamed synovium
Transport by circulating myeloid cells drives liposomal accumulation in inflamed synovium
PEGylated liposomal accumulation in inflamed regions has mainly been attributed to the enhanced permeation and retention effect. An arthritis model that chemotactically attracted myeloid cells shows that monocytes and neutrophils play an essential role in liposome delivery towards inflamed joints.
- Joke Deprez
- , Rein Verbeke
- & Ine Lentacker
-
Research Briefing |
 A shock-absorbing material made from a mechanosensitive protein
A shock-absorbing material made from a mechanosensitive protein
Certain proteins have been optimized over millennia to exhibit shock-absorbing capabilities. To harness these capabilities, synthetic biology was used to incorporate the mechanosensitive protein talin into a hydrogel. The resulting talin shock-absorbing material (TSAM) retains the mechanical properties of talin and can absorb the impact of, as well as capture, supersonic projectiles.
-
Article
| Open Access Next-generation protein-based materials capture and preserve projectiles from supersonic impacts
Next-generation protein-based materials capture and preserve projectiles from supersonic impacts
An engineered version of the mechanosensitive protein talin was used as a monomer in combination with a synthetic chemical crosslinker to form a hydrogel. This shock-absorbing material is shown to capture and preserve projectiles fired at 1.5 km s−1.
- Jack A. Doolan
- , Luke S. Alesbrook
- & Benjamin T. Goult
-
Article |
 Adjuvant lipidoid-substituted lipid nanoparticles augment the immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines
Adjuvant lipidoid-substituted lipid nanoparticles augment the immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines
A lipid nanoparticle (LNP) component—an adjuvant lipidoid—is developed to enhance the adjuvanticity of LNPs, which significantly increases the innate and adaptive responses of the COVID-19 mRNA vaccines with good tolerability in mice.
- Xuexiang Han
- , Mohamad-Gabriel Alameh
- & Michael J. Mitchell
-
Article |
 Spatially multiplexed single-molecule translocations through a nanopore at controlled speeds
Spatially multiplexed single-molecule translocations through a nanopore at controlled speeds
In single-molecule characterization, the near-infinite re-read capability on the same region of interest has the potential to unlock greater sensing capacity. A nanopore-based method, named scanning ion conductance spectroscopy, provides complete control over the translocation speed and nanopore position along a selected region and can detect a single 3 Å gap in a long strand of DNA.
- S. M. Leitao
- , V. Navikas
- & A. Radenovic
-
News & Views |
 Carbon nanotubes activate inflammatory signalling through binding to Siglec-14
Carbon nanotubes activate inflammatory signalling through binding to Siglec-14
Discovery of a novel axis through which multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) elicit toxicity in human macrophages, involving the propagation of inflammatory signalling via the Siglec-14-DAP12-Syk pathway, and how it may be controlled pharmacologically.
- Michelle K. Greene
- & Christopher J. Scott
-
Article |
 Controlled delivery of a neurotransmitter–agonist conjugate for functional recovery after severe spinal cord injury
Controlled delivery of a neurotransmitter–agonist conjugate for functional recovery after severe spinal cord injury
Here the authors report the delivery of neurotransmitter-conjugated KCC2 agonist using a reactive oxygen species–responsive polymer nanoparticle that can cross the damaged blood–spinal cord barrier and significantly increase recovery after spinal cord injury in vivo.
- Yanming Zuo
- , Jingjia Ye
- & Xuhua Wang
-
Article |
 A universal reagent for detection of emerging diseases using bioengineered multifunctional yeast nanofragments
A universal reagent for detection of emerging diseases using bioengineered multifunctional yeast nanofragments
Yeast cells are engineered to prepare multifunctional synthetic biofragments as nanoprobes, which allow multivalent interactions and optimal molecular orientation on material surfaces for the detection of emerging biomarkers in a range of sensor platforms.
- Junrong Li
- , Christopher B. Howard
- & Matt Trau
-
Comment |
 Nanotechnology for coral reef conservation, restoration and rehabilitation
Nanotechnology for coral reef conservation, restoration and rehabilitation
The mounting environmental pressure on coral reefs calls for a rapid push towards innovative actions. Nanotechnology could help understand and protect present-day reefs to ensure their survival.
- Liza Roger
- , Nastassja Lewinski
- & Daniel Wangpraseurt
-
Article |
 Cell spheroid creation by transcytotic intercellular gelation
Cell spheroid creation by transcytotic intercellular gelation
Creation of cell spheroids by using triggered d-peptide self-assembly is reported. Peptides are dephosphorylated by transcytosis in cells and intercellularly assembled to facilitate fibronectin fibrillogenesis and subsequent spheroid formation.
- Jiaqi Guo
- , Fengbin Wang
- & Bing Xu
-
Article |
 Non-invasive activation of intratumoural gene editing for improved adoptive T-cell therapy in solid tumours
Non-invasive activation of intratumoural gene editing for improved adoptive T-cell therapy in solid tumours
Cancer resistance to apoptosis can hinder T-cell-based therapies. Here, the authors develop a temperature-sensitive system for the controlled delivery of a Cas9 gene-editing sequence targeting resistance mechanisms HSP70 and BAG3, which with a mild thermal effect increases T-cell delivery and therapeutic outcomes.
- Xiaohong Chen
- , Shuang Wang
- & Yuan Ping
-
Comment |
 Nano-enabled strategies to enhance biological nitrogen fixation
Nano-enabled strategies to enhance biological nitrogen fixation
Increasing the capacity of biological nitrogen fixation (BNF) is an effective strategy to enhance food security while simultaneously reducing the carbon and nitrogen footprint of agriculture. Nanotechnology offers several pathways to enhance BNF successfully.
- Mingshu Li
- , Li Gao
- & Peng Zhang
-
Analysis
| Open Access An ancestral molecular response to nanomaterial particulates
An ancestral molecular response to nanomaterial particulates
While engineered nanomaterials are relatively new, organisms have been exposed to natural nanoparticles over vast periods of time. Here the authors explore the possibility that common mechanisms of response to nanomaterials may have resulted from a long evolutionary exposure history to natural nano-sized matter.
- G. del Giudice
- , A. Serra
- & D. Greco
-
Article
| Open Access DNA storage in thermoresponsive microcapsules for repeated random multiplexed data access
DNA storage in thermoresponsive microcapsules for repeated random multiplexed data access
Microcompartments with a temperature-responsive membrane are used to stably localize DNA-encoded files, which enables parallel, repeated polymerase-chain-reaction-based random access and DNA file sorting using fluorescent barcodes.
- Bas W. A. Bögels
- , Bichlien H. Nguyen
- & Tom F. A. de Greef
-
Comment |
 Active ingredient vs excipient debate for nanomedicines
Active ingredient vs excipient debate for nanomedicines
Nanomedicines are complex drugs where components that have typically been regarded as excipients may now be considered part of the active ingredient. The distinction between the active ingredient and excipients for nanomedicines has important consequences for regulatory review and product development. The dissimilarity in the review of the recent ribonucleic acid (RNA)-based lipid nanoparticles highlights the need for further regulatory alignment on this topic.
- Eva Hemmrich
- & Scott McNeil
-
Article |
 Tailoring renal-clearable zwitterionic cyclodextrin for colorectal cancer-selective drug delivery
Tailoring renal-clearable zwitterionic cyclodextrin for colorectal cancer-selective drug delivery
Optimizing the retention of drug delivery nanocarriers for improved cancer therapy has the potential to improve clinical outcomes. Here the authors screen 20 renal-clearable zwitterionic cyclodextrin-based nanocarriers for optimized biodistribution and tumour retention, demonstrating application in colorectal cancer models.
- Min-Jun Baek
- , Duy-Thuc Nguyen
- & Dae-Duk Kim
-
Article |
 Hierarchically resistive skins as specific and multimetric on-throat wearable biosensors
Hierarchically resistive skins as specific and multimetric on-throat wearable biosensors
Wearable resistive sensors for biometrics and machine interfacing are often non-specific. Here the authors report on the creation of hierarchically resistive skins for monitoring physical or physiological activities around the throat which, with the use of neural networking, can be used to distinguish different activities.
- Shu Gong
- , Xin Zhang
- & Wenlong Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR-Cas-amplified urinary biomarkers for multiplexed and portable cancer diagnostics
CRISPR-Cas-amplified urinary biomarkers for multiplexed and portable cancer diagnostics
Protease profiling of the tumour microenvironment using DNA-barcoded nanosensors and CRISPR amplification enables portable cancer diagnosis in preclinical models.
- Liangliang Hao
- , Renee T. Zhao
- & Sangeeta N. Bhatia
-
News & Views |
 Rerouting nanoparticles to bone marrow via neutrophil hitchhiking
Rerouting nanoparticles to bone marrow via neutrophil hitchhiking
Drug delivery to the bone marrow has limited efficiency, hitchhiking on bone marrow homing neutrophils offers a solution.
- Ningqiang Gong
- & Michael J. Mitchell
-
News & Views |
 Artificial intelligence assists nanoparticles to enter solid tumours
Artificial intelligence assists nanoparticles to enter solid tumours
Single blood vessel analysis by artificial intelligence (AI) reveals heterogeneous vascular permeability among different tumour types, which is leveraged in rationally designing protein nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems to achieve active trans-endothelial permeability in tumours.
- Lutz Nuhn
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Animal biotechnology
- Applied immunology
- Assay systems
- Biologics
- Biomaterials
- Biomimetics
- Cell delivery
- Environmental biotechnology
- Expression systems
- Functional genomics
- Gene delivery
- Gene therapy
- Genomics
- Industrial microbiology
- Metabolic engineering
- Metabolomics
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Nucleic-acid therapeutics
- Oligo delivery
- Peptide delivery
- Plant biotechnology
- Protein delivery
- Proteomics
- Regenerative medicine
- Sequencing
- Stem-cell biotechnology
- Tissue engineering

 A modular approach to enhancing cell membrane-coated nanoparticle functionality using genetic engineering
A modular approach to enhancing cell membrane-coated nanoparticle functionality using genetic engineering