Abstract
Objective:
To estimate the presence and sources of inter-center variation (ICV) in the risk of death or tracheostomy placement (D/T) among infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia (sBPD)
Study design:
We analyzed the Children's Hospitals Neonatal Database between 2010 and 2013 to identify referred infants born <32 weeks' gestation with sBPD. The association between center and the primary outcome of D/T was analyzed by multivariable modeling. Hypothesized diagnoses/practices were included to determine if these explained any observed ICV in D/T.
Results:
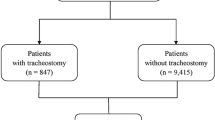
D/T occurred in 280 (20%) of 1383 eligible infants from 21 centers. ICV was significant for D/T (range 2–46% by center, P<0.001) and tracheostomy placement (n=187, range 2–37%, P<0.001), but not death (n=93, range 0–19%, P=0.08). This association persisted in multivariable analysis (adjusted center-specific odds ratios for D/T varied 5.5-fold, P=0.009).
Conclusions:
ICV in D/T is apparent among infants with sBPD. These results highlight that the indications for tracheostomy (and subsequent chronic ventilation) remain uncertain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Natarajan G, Pappas A, Shankaran S, Kendrick DE, Das A, Higgins RD et al. Outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: impact of the physiologic definition. Early Hum Dev 2012; 88 (7): 509–515.
DeMauro SB, D'Agostino JA, Bann C, Bernbaum J, Gerdes M, Bell EF et al. Developmental outcomes of very preterm infants with tracheostomies. J Pediatr 2014; 164 (6): 1303 e2–1310 e2.
Murthy K, Savani RC, Lagatta JM, Zaniletti I, Wadhawan R, Truog W et al. Predicting death or tracheostomy placement in infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Perinatol 2014; 20: 1–6.
Slaughter JL, Stenger MR, Reagan PB . Variation in the use of diuretic therapy for infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics 2013; 131 (4): 716–723.
Truog WE, Nelin LD, Das A, Kendrick DE, Bell EF, Carlo WA et al. Inhaled nitric oxide usage in preterm infants in the NICHD neonatal research network: inter-site variation and propensity evaluation. J Perinatol 2014; 34 (11): 842–846.
Lagatta JM, Clark RH, Brousseau DC, Hoffmann RG, Spitzer AR . Varying patterns of home oxygen use in infants at 23-43 weeks' gestation discharged from United States neonatal intensive care units. J Pediatr 2013; 163 (4): 976 e2–982 e2.
Walsh MC, Yao Q, Horbar JD, Carpenter JH, Lee SK, Ohlsson A . Changes in the use of postnatal steroids for bronchopulmonary dysplasia in 3 large neonatal networks. Pediatrics 2006; 118 (5): e1328–e1335.
Ambalavanan N, Walsh M, Bobashev G, Das A, Levine B, Carlo WA et al. Intercenter differences in bronchopulmonary dysplasia or death among very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2011; 127 (1): e106–e116.
Murthy K, Dykes FD, Padula MA, Pallotto EK, Reber KM, Durand DJ et al. The Children's Hospitals Neonatal Database: an overview of patient complexity, outcomes and variation in care. J Perinatol 2014; 6: 1–5.
Engle WA . American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Age terminology during the perinatal period. Pediatrics 2004; 114 (5): 1362–1364.
Ehrenkranz RA, Walsh MC, Vohr BR, Jobe AH, Wright LL, Fanaroff AA et al. Validation of the National Institutes of Health consensus definition of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics 2004; 116 (6): 1353–1360.
Stark AR . American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Levels of neonatal care. Pediatrics 2004; 114 (5): 1341–1347.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Levels of neonatal care. Ped Pediatrics 2012; 130 (3): 587–597.
Patel AL, Engstrom JL, Meier PP, Jegier BJ, Kimura RE . Calculating postnatal growth velocity in very low birth weight (VLBW) premature infants. J Perinatol 2009; 29 (9): 618–622.
Patel AL, Engstrom JL, Meier PP, Kimura RE . Accuracy of methods for calculating postnatal growth velocity for extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2005; 116 (6): 1466–1473.
Padula MA, Grover TR, Brozanski B, Zaniletti I, Nelin LD, Asselin JM et al. Therapeutic interventions and short-term outcomes for infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia born <32 weeks' gestation. J Perinatol 2013; 4: 1–5.
Overman AE, Liu M, Kurachek SC, Shreve MR, Maynard RC, Mammel MC et al. Tracheostomy for infants requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation: 10 Years' experience. Pediatrics 2013; 131 (5): E1491–E1496.
Com G, Kuo DZ, Bauer ML, Lenker CV, Melguizo-Castro MM, Nick TG et al. Outcomes of children treated with tracheostomy and positive-pressure ventilation at home. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 2013; 52 (1): 54–61.
Malkar MB, Gardner WP, Mandy GT, Stenger MR, Nelin LD, Shepherd EG et al. Respiratory severity score on day of life 30 is predictive of mortality and the length of mechanical ventilation in premature infants with protracted ventilation. Pediatr Pulmonol 2015; 50 (4): 363–369.
Lodha A, Ediger K, Rabi Y, Lodha S, Tang S, Bhandari A et al. Does chronic oxygen dependency in preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia at NICU discharge predict respiratory outcomes at 3 years of age? J Perinatol 2015; 35 (7): 530–536.
Acknowledgements
The CHNC has partnered with Children’s Hospital Association (Overland Park, KS) in order to design, launch and maintain the CHND. For more information, please contact: support@thechnc.org. The Friends of Prentice Foundation (Chicago, IL, USA) sponsored a portion of this work.
We are indebted to the following institutions that serve the infants and their families, and these institutions also have invested in and continue to participate in the Children’s Hospital’s Neonatal Database (CHND). The site sponsors/contributors for the CHND are also included:
1. Children's Healthcare of Atlanta, Atlanta, GA, USA (Francine Dykes, Anthony Piazza)
2. Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta at Scottish Rite (Gregory Sysyn)
3. Children's Hospital of Alabama, Birmingham, AL, USA (Carl Coghill)
4. Le Bonheur Children's Hospital, Memphis, TN, USA (Ramasubbareddy Dhanireddy)
5. Children's Hospital Boston, Boston, MA, USA (Anne Hansen, Tanzeema Houssain)
6. Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA (Karna Murthy)
7. Nationwide Children's Hospital, Columbus, OH, USA (Kristina Reber)
8. Children's Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA (Rashmin Savani, Luc Brion)
9. Children's Hospital Colorado, Aurora, CO, USA (Theresa Grover)
10. Children’s Hospital of Michigan, Detroit, MI, USA (Girija Natarajan)
11. Cook Children's Health Care System, Fort Worth, TX, USA (Jonathan Nedrelow, Annie Chi, Yvette Johnson)
12. Texas Children's Hospital, Houston, TX, USA (Steve Welty, Gautham Suresh)
13. Children's Mercy Hospitals & Clinics, Kansas City, MO, USA (Eugenia Pallotto)
14. Arkansas Children's Hospital, Little Rock, AR, USA (Becky Rogers)
15. Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, USA (Lisa Kelly (deceased), Steven Chin)
16. Children's Hospital & Research Center Oakland, Oakland, CA, USA (David Durand, Jeanette Asselin, Art D’Harlingue, Priscilla Joe)
17. The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, USA (Jacquelyn Evans, Michael Padula)
18. Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC, Pittsburgh, PA, USA (Beverly Brozanski)
19. St. Louis Children's Hospital, St Louis, MO, USA (Joan Rosenbaum, Tasmin Najaf, Rakesh Rao, Amit Mathur)
20. All Children's Hospital, St. Petersburg, FL, USA (Victor McKay)
21. Rady Children's Hospital, San Diego, CA, USA (Mark Speziale)
22. Children's National Medical Center, Washington, DC, USA (Billie Short)
23. AI DuPont Hospital for Children, Wilmington, DE, USA (Kevin Sullivan)
24. Primary Children’s Medical Center, Salt Lake City, UT, USA (Robert DiGeronimo)
25. Children’s Hospital of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA (Michael Uhing; Ankur Datta)
26. Children’s Hospital of Omaha (Lynne Willett, John Grebe)
27. Florida Hospital for Children (Rajan Wadhawan)
28. Seattle Children’s Hospital, Seattle, WA, USA (Elizabeth Jacobsen-Misbe, Craig Jackson)
29. American Family Children’s Hospital; Madison, WI, USA (Jamie Limjoco)
30. Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, ON, Canada (Kyong-Soon Lee).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Children’s Hospitals Neonatal Consortium (CHNC)
JR Evans8, FD Dykes9, B Lou Short10, EK Pallotto4, MA Padula8, KM Reber6, JM Asselin11 and DJ Durand11
8Department of Pediatrics; Perelman School of Medicine at The University of Pennsylvania and The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, USA; 9Department of Pediatrics, Emory University School of Medicine and The Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta at Egleston, Atlanta, GA, USA; 10Department of Pediatrics, George Washington University School of Medicine and Children’s National Medical Center, Washington DC, USA and 11Department of Pediatrics, UCSF Benioff Children's Hospital Oakland, Oakland, CA, USA.
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Journal of Perinatology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murthy, K., Porta, N., Lagatta, J. et al. Inter-center variation in death or tracheostomy placement in infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Perinatol 37, 723–727 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2016.277
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2016.277
This article is cited by
-
Transpyloric feeding is associated with adverse in-hospital outcomes in infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Journal of Perinatology (2024)
-
A review and guide to nutritional care of the infant with established bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Journal of Perinatology (2023)
-
The impact of early tracheostomy on neurodevelopmental outcomes of infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia exposed to postnatal corticosteroids
Journal of Perinatology (2023)
-
In-hospital mortality and length of hospital stay in infants requiring tracheostomy with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Journal of Perinatology (2023)
-
A multidisciplinary chronic lung disease team in a neonatal intensive care unit is associated with increased survival to discharge of infants with tracheostomy
Journal of Perinatology (2021)