Abstract
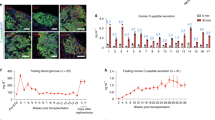
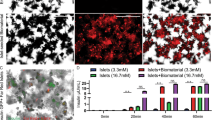
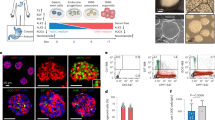
Advances in islet transplantation have encouraged efforts to create alternative insulin-secreting cells that overcome limitations associated with current therapies. We have recently demonstrated durable correction of murine and porcine diabetes by syngeneic and autologous implantation, respectively, of primary hepatocytes non-virally modified with a glucose-responsive promoter-regulated insulin transgene. As surgical procurement of hepatocytes may be clinically unappealing, we here describe primary bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (BMMSC) as alternative insulin-secreting bioimplants. BMMSC are abundant and less invasively procured for clinical autologous transplantation. Electroporation achieved high transgene transfection efficiencies in human BMMSC (HBMMSC) and porcine BMMSC (PBMMSC). We transcriptomically identified an HBMMSC glucose-responsive promoter, EGR1. This endogenously active promoter drove rapid glucose-induced transgene secretions in BMMSC with near-physiological characteristics during static and kinetic induction assays simulating normal human islets. Preparatory to preclinical transplantation, PBMMSC transfected with the circular insulin transgene vector or stably integrated with the linearized vector were evaluated by intrahepatic or intraperitoneal xenotransplantation in streptozotocin-diabetic and non-diabetic NOD-SCID mice. Hyperglycemia, glucose tolerance and body weight were corrected in a dose–responsive manner. Hypoglycemia was not observed even in identically implanted non-diabetic mice. These results establish human EGR1 promoter-insulin construct-modified BMMSC as safe and efficient insulin-secreting bioimplants for diabetes treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Shapiro AMJ, Ricordi C, Hering BJ, Auchincloss H, Lindblad R, Robertson RP et al. International trial of the Edmonton protocol for islet transplantation. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 1318–1330.
Huurman VAL, Hilbrands R, Pinkse GGM, Gillard P, Duinkerken G, van de Linde P et al. Cellular islet autoimmunity associates with clinical outcome of islet cell transplantation. PLoS ONE 2008; 3: e2435.
Kobayashi N . The current status of islet transplantation and its perspectives. Rev Diabet Stud 2008; 5: 136–143.
Chen NKF, Sivalingam J, Tan SY, Kon OL . Plasmid-electroporated primary hepatocytes acquire quasi-physiological secretion of human insulin and restore euglycemia in diabetic mice. Gene Ther 2005; 12: 655–667.
Chen NKF, Wong JS, Kee IHC, Lai SH, Thng CH, Ng WH et al. Nonvirally modified autologous primary hepatocytes correct diabetes and prevent target organ injury in a large preclinical model. PLoS One 2008; 3: e1734.
Keating A . Mesenchymal stromal cells. Curr Opin Hematol 2006; 13: 419–425.
Haleem-Smith H, Derfoul A, Okafor C, Tuli R, Olsen D, Hall DJ et al. Optimization of high-efficiency transfection of adult human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Mol Biotech 2005; 30: 9–19.
Wang Z, Troilo PJ, Wang X, Griffiths II TG, Pacchione SJ, Barnum AB et al. Detection of integration of plasmid DNA into host genomic DNA following intramuscular injection and electroporation. Gene Ther 2004; 11: 711–721.
Josefsen K, Sørensen LR, Buschard K, Birkenbach M . Glucose induces early growth response gene (Egr-1) expression in pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 1999; 42: 195–203.
Hasan RN, Phukan S, Harada S . Differential regulation of early growth response gene-1 expression by insulin and glucose in vascular endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003; 23: 988–993.
Ferrannini E, Haffner SM, Mitchell BD, Stern MP . Hyperinsulinaemia: the key feature of cardiovascular and metabolic syndrome. Diabetologia 1991; 34: 416–422.
Carrasco-Serrano C, Criado M . Glucocorticoid activation of the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α7 subunit gene: involvement of transcription factor Egr-1. FEBS Lett 2004; 566: 247–250.
Barsoum J . Introduction of stable high-copy-number DNA into Chinese hamster ovary cells by electroporation. DNA Cell Biol 1990; 9: 293–300.
Kong Q, Wu M, Huan Y, Zhang L, Liu H, Bou G et al. Transgene expression is associated with copy number and cytomegalovirus promoter methylation in transgenic pigs. PLoS One 2009; 4: e6679.
Berry C, Hannenhalli S, Leipzig J, Bushman FD . Selection of target sites for mobile DNA integration in the human genome. PLoS Comput Biol 2006; 11: e157.
Fox A, Mountford J, Braakhuis A, Harrison LC . Innate and adaptive immune response to nonvascular xenografts: evidence that macrophages are direct effectors of xenograft rejection. J Immunol 2001; 166: 2133–2140.
Gabr MM, Sobh MM, Zakaria MM, Refaie AF, Ghoneim MA . Transplantation of insulin-producing clusters derived from adult bone marrow stem cells to treat diabetes in rats. Exp Clin Transplant 2008; 6: 236–243.
Kumar S, Chanda D, Ponnazhagan S . Therapeutic potential of genetically modified mesenchymal stem cells. Gene Ther 2008; 15: 711–715.
Wang N, Fallavollita L, Nguyen L, Burnier J, Rafei M, Galipeau J et al. Autologous bone marrow stromal cells genetically engineered to secrete an IGF-I receptor decoy prevent the growth of liver metastases. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 1241–1249.
Campeau PM, Rafei M, François M, Birman E, Forner K-A, Galipeau J . Mesenchymal stromal cells engineered to express erythropoietin induce anti-erythropoietin antibodies and anemia in allorecipients. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 369–372.
Xu R, Li H, Tse L-Y, Kung H-F, Lu H, Lam KS . Diabetes gene therapy: potential and challenges. Curr Gene Ther 2003; 3: 65–82.
Gill DR, Pringle IA, Hyde SC . Progress and Prospects: the design and production of plasmid vectors. Gene Ther 2009; 16: 165–171.
Kachi S, Esumi N, Zack DJ, Campochiaro PA . Sustained expression after nonviral ocular gene transfer using mammalian promoters. Gene Ther 2006; 13: 798–804.
Gros L, Montoliu L, Riu E, Lebrigard L, Bosch F . Regulated production of mature insulin by non-β-cells. Hum Gene Ther 1997; 8: 2249–2259.
Leibiger B, Moede T, Schwarz T, Brown GR, Köhler M, Leibiger IB et al. Short-term regulation of insulin gene transcription by glucose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 9307–9312.
Herdegen T, Leah JD . Inducible and constitutive transcription factors in the mammalian nervous system: control of gene expression by Jun, Fos and Krox, and CREB/ATF proteins. Brain Res Rev 1998; 28: 370–490.
Schwachtgen J-L, Campbell CJ, Braddock M . Full promoter sequence of human early growth response factor-1 (Egr-1): demonstration of a fifth functional serum response element. DNA Seq 2000; 10: 429–432.
Thiel G, Cibelli G . Regulation of life and death by the zinc finger transcription factor Egr-1. J Cell Physiol 2002; 193: 287–292.
Berasi SP, Huard C, Li D, Shih HH, Sun Y, Zhong W et al. Inhibition of gluconeogenesis through transcriptional activation of EGR1 and DUSP4 by AMP-activated kinase. J Biol Chem 2006; 37: 27167–27177.
Eto K, Kaur V, Thomas M . Regulation of pancreas duodenum homeobox-1 expression by early growth response-1. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 5973–5983.
Rhodes CJ . Processing of the insulin molecule. In: LeRoith D, Taylor SI, Olefsky JM (eds). Diabetes Mellitus: A Fundamental and Clinical Text, 3rd edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, USA, 2004, pp 27–50.
Pratley RE, Weyer C . The role of impaired early insulin secretion in the pathogenesis of type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2001; 44: 929–945.
Polonsky KS, Given BD, Hirsch LJ, Tillil H, Shapiro ET, Beebe C et al. Abnormal patterns of insulin secretion in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1998; 318: 1231–1239.
Blackman JD, Polonsky KS, Jaspan JB, Sturis J, Cauter EV, Thistlethwaite JR et al. Insulin secretory profiles and C-peptide clearance kinetics at 6 months and 2 years after kidney-pancreas transplantation. Diabetes 1992; 41: 1346–1354.
Luzi L, Hering BJ, Socci C, Raptis G, Battezzati A, Terruzzi I et al. Metabolic effects of successful intraportal islet transplantation in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest 1996; 97: 2611–2618.
Alejandro R, Barton FB, Hering BJ, Wease S . 2008 update from the collaborative islet transplant registry. Transplantation 2008; 86: 1783–1788.
Roach P, Woodworth JR . Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of insulin lispro mixtures. Clin Pharmacokinet 2002; 41: 1043–1057.
Jones TW, Davis EA . Hypoglycemia in children with type 1 diabetes: current issues and controversies. Pediatr Diabetes 2003; 4: 143–150.
Xia Z, Taylor PR, Locklin RM, Gordon S, Cui Z, Triffitt JT . Innate immune response to human bone marrow fibroblastic cell implantation in CB17 Scid/Beige mice. J Cell Biochem 2006; 98: 966–980.
Fox A, Mountford J, Braakhuis A, Harrison LC . Innate and adaptive immune response to nonvascular xenografts: evidence that macrophages are direct effectors of xenograft rejection. J Immunol 2001; 166: 2133–2140.
Nasef A, Ashammakhi N, Fouillard L . Immunomodulatory effect of mesenchymal stromal cells: possible mechanisms. Regen Med 2008; 3: 531–546.
Prigozhina TB, Khitrin S, Elkin G, Eizik O, Morecki S, Slavin S . Mesenchymal stromal cells lose their immunosuppressive potential after allotransplantation. Exp Hematol 2008; 36: 1370–1376.
Medvinsky A, Smith A . Fusion brings down barriers. Science 2003; 422: 823–825.
Karp JM, Teo GSL . Mesenchymal stem cell homing: the devil is in the details. Cell Stem Cell 2009; 4: 206–216.
Lufino MMP, Edser PAH, Wade-Martins R . Advances in high-capacity extrachromosomal vector technology: episomal maintenance, vector delivery, and transgene expression. Mol Ther 2008; 16: 1525–1538.
Li S-D, Huang L . Non-viral is superior to viral gene delivery. J Control Release 2007; 123: 181–183.
Manzini S, Vargiolu A, Stehle IM, Bacci ML, Cerrito MG, Giovannoni R et al. Genetically modified pigs produced with a nonviral episomal vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 17672–17677.
Seaquist ER, Robertson RP . Effects of hemipancreatectomy on pancreatic alpha and beta cell function in healthy human donors. J Clin Invest 1992; 89: 1761–1766.
Bosch P, Pratt SL, Stice SL . Isolation, characterization, gene modification, and nuclear reprogramming of porcine mesenchymal stem cells. Biol Reprod 2006; 74: 46–57.
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R . e potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 1999; 284: 143–147.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation, USA and the Biomedical Research Council, Singapore. We thank Irene Kee and In Chin Song for procuring porcine bone marrow aspirates, Cheryl Lee and Sze Sing Lee for assistance with FACS analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Gene Therapy website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, N., Tan, S., Udolph, G. et al. Insulin expressed from endogenously active glucose-responsive EGR1 promoter in bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells as diabetes therapy. Gene Ther 17, 592–605 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2010.12
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2010.12
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells for diabetes therapy: touch, fuse, and fix?
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2022)
-
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells as a delivery platform in cell and gene therapies
BMC Medicine (2015)
-
Non-hematopoietic stem cells as factories for in vivo therapeutic protein production
Gene Therapy (2012)