Abstract
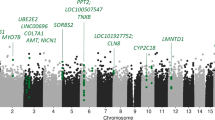
Association between response to antidepressant treatment and genetic polymorphisms was examined in two independent Japanese samples of patients with major depressive disorder (MDD). Genome-wide approach using the Illumina Human CNV370-quad Bead Chip was utilized in the analysis of the 92 MDD patients in the first sample. In all, 11 non-intergenic single-nucleotide polymorphisms with uncorrected allelic P-value <0.0001 were selected for the subsequent association analyses in the second sample of 136 MDD patients. Difference in allele distribution between responders and nonresponders were found in the second-stage sample for rs365836 and rs201522 of the CUX1 gene (P=0.005 and 0.004, respectively). The allelic P-values for rs365836 and rs201522 in both samples combined were 0.0000023 and 0.0000040, respectively. Our results provide the first evidence that polymorphisms of the CUX1 gene may be associated with response to antidepressant treatment in Japanese patients with MDD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garriock HA, Kraft JB, Shyn SI, Peters EJ, Yokoyama JS, Jenkins GD et al. A genomewide association study of citalopram response in major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2010; 67: 133–138.
Ising M, Lucae S, Binder EB, Bettecken T, Uhr M, Ripke S et al. A genomewide association study points to multiple loci that predict antidepressant drug treatment outcome in depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2009; 66: 966–975.
Uher R, Perroud N, Ng MY, Hauser J, Henigsberg N, Maier W et al. Genome-wide pharmacogenetics of antidepressant response in the GENDEP project. Am J Psychiatry 2010; 167: 555–564.
Franchini L, Serretti A, Gasperini M, Smeraldi E . Familial concordance of fluvoxamine response as a tool for differentiating mood disorder pedigrees. J Psychiatr Res 1998; 32: 255–259.
American Psychiatric Association. DSM-IV: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Press: Washington, DC, 1994.
Hamilton M . Development of a rating scale for primary depressive illness. Br J Soc Clin Psychol 1967; 6: 278–296.
Tabuse H, Kalali A, Azuma H, Ozaki N, Iwata N, Naitoh H et al. The new GRID Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression demonstrates excellent inter-rater reliability for inexperienced and experienced raters before and after training. Psychiatry Res 2007; 153: 61–67.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Nepveu A . Role of the multifunctional CDP/Cut/Cux homeodomain transcription factor in regulating differentiation, cell growth and development. Gene 2001; 270: 1–15.
Sansregret L, Nepveu A . The multiple roles of CUX1: insights from mouse models and cell-based assays. Gene 2008; 412: 84–94.
Hulea L, Nepveu A . CUX1 transcription factors: from biochemical activities and cell-based assays to mouse models and human diseases. Gene 2012; 497: 18–26.
Cubelos B, Sebastian-Serrano A, Beccari L, Calcagnotto ME, Cisneros E, Kim S et al. Cux1 and Cux2 regulate dendritic branching, spine morphology, and synapses of the upper layer neurons of the cortex. Neuron 2010; 66: 523–535.
Cubelos B, Nieto M . Intrinsic programs regulating dendrites and synapses in the upper layer neurons of the cortex. Commun Integr Biol 2010; 3: 483–486.
Neufeld EJ, Skalnik DG, Lievens PM, Orkin SH . Human CCAAT displacement protein is homologous to the Drosophila homeoprotein, cut. Nat Genet 1992; 1: 50–55.
Jacobsen NJ, Elvidge G, Franks EK, O’Donovan MC, Craddock N, Owen MJ . CUX2, a potential regulator of NCAM expression: genomic characterization and analysis as a positional candidate susceptibility gene for bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet 2001; 105: 295–300.
Vanden Heuvel GB, Quaggin SE, Igarashi P . A unique variant of a homeobox gene related to Drosophila cut is expressed in mouse testis. Biol Reprod 1996; 55: 731–739.
Quaggin SE, Heuvel GB, Golden K, Bodmer R, Igarashi P . Primary structure, neural-specific expression, and chromosomal localization of Cux-2, a second murine homeobox gene related to Drosophila cut. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 22624–22634.
Ferrere A, Vitalis T, Gingras H, Gaspar P, Cases O . Expression of Cux-1 and Cux-2 in the developing somatosensory cortex of normal and barrel-defective mice. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 2006; 288: 158–165.
Nieto M, Monuki ES, Tang H, Imitola J, Haubst N, Khoury SJ et al. Expression of Cux-1 and Cux-2 in the subventricular zone and upper layers II–IV of the cerebral cortex. J Comp Neurol 2004; 479: 168–180.
Gingras H, Cases O, Krasilnikova M, Berube G, Nepveu A . Biochemical characterization of the mammalian Cux2 protein. Gene 2005; 344: 273–285.
Zimmer C, Tiveron MC, Bodmer R, Cremer H . Dynamics of Cux2 expression suggests that an early pool of SVZ precursors is fated to become upper cortical layer neurons. Cereb Cortex 2004; 14: 1408–1420.
Cubelos B, Sebastian-Serrano A, Kim S, Moreno-Ortiz C, Redondo JM, Walsh CA et al. Cux-2 controls the proliferation of neuronal intermediate precursors of the cortical subventricular zone. Cereb Cortex 2008; 18: 1758–1770.
Glaser B, Kirov G, Green E, Craddock N, Owen MJ . Linkage disequilibrium mapping of bipolar affective disorder at 12q23–q24 provides evidence for association at CUX2 and FLJ32356. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2005; 132B: 38–45.
Correa R, Akiskal H, Gilmer W, Nierenberg AA, Trivedi M, Zisook S . Is unrecognized bipolar disorder a frequent contributor to apparent treatment resistant depression? J Affect Disord 2010; 127: 10–18.
Li N, Zhao CT, Wang Y, Yuan XB . The transcription factor Cux1 regulates dendritic morphology of cortical pyramidal neurons. PLoS One 2010; 5: e10596.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Intramural Research Grant (21-9) for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders of NCNP, CREST by JST (Creation of a Novel Technology towards Diagnosis and Treatment based on Understanding of Molecular Pathogenesis of Psychiatric and Neurological Disorders), and the Strategic Research Program (Understanding of molecular and environmental bases for brain health) for Brain Sciences by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasayama, D., Hiraishi, A., Tatsumi, M. et al. Possible association of CUX1 gene polymorphisms with antidepressant response in major depressive disorder. Pharmacogenomics J 13, 354–358 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2012.18
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2012.18