Abstract
Magnetic attapulgite-Fe3O4 nanocomposites (ATP-Fe3O4) were prepared by coprecipitation of Fe3O4 on ATP. The composites were characterized by scanning electron microscopey, X-ray diffractometry, Brunauer-Emmett-Teller analysis, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, energy dispersive spectrometer and transmission electron microscopy. Surface characterization showed that Fe3O4 particles with an average size of approximately 15 nm were successfully embedded in matrix of ATP. The capacity of the Fe3O4-activated ATP (A-ATP@Fe3O4) composites for catalytic degradation of ethidium bromide (EtBr, 80 mg/L) at different pH values, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) concentrations, temperatures, and catalyst dosages was investigated. EtBr degradation kinetics studies indicated that the pseudo-first-order kinetic constant was 2.445 min−1 at T = 323 K and pH 2.0 with 30 mM H2O2, and 1.5 g/L of A-ATP@Fe3O4. Moreover, a regeneration study suggested that A-ATP@Fe3O4 maintained over 80% of its maximal EtBr degradation ability after five successive cycles. The effects of the iron concentrations and free radical scavengers on EtBr degradation were studied to reveal possible catalytic mechanisms of the A-ATP@Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance revealed both hydroxyl (∙OH) and superoxide anion (∙O2 −) radicals were involved in EtBr degradation. Radical scavenging experiment suggested EtBr degradation was mainly ascribed to ∙OH radicals, which was generated by reaction between Fe2+ and H2O2 on the surface of A-ATP@Fe3O4.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Ethidium bromide (EtBr) is widely employed for rapid visualization of nucleic acids in electrophoretic gels and is commonly used in the life sciences1. However, due to its strong toxicity and powerful mutagenicity2, EtBr is detrimental to human health and could cause hepatocellular carcinoma and some infectious diseases. To remediate EtBr contamination, sorption3 and degradation techniques4, 5 are commonly adopted for EtBr removal. Although sorption has been proven for its reasonable EtBr removal efficiency, the sorbed EtBr requires further treatment.
Advanced oxidation technologies for wastewater treatment have attracted attention due to the generation of strongly oxidizing hydroxyl radical (∙OH)6,7,8,9. Hydroxyl radicals, a very active and efficient non-selective oxidant, are capable of degrading organic pollutants into such harmless endproducts as carbon dioxide (CO2) and H2O10. Heterogeneous Fenton technology has gained popularity recently, especially that employing nano-sized magnetite (Fe3O4) as a catalyst11, 12. Nano-sized Fe3O4 has a similar catalytic activity with horseradish peroxidase, which can effectively decompose hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into ∙OH13. Fe3O4 nanoparticles can initiate Fenton reaction through the following mechanisms, eg. (i) Fe2+ can act as an electron donor to initiate the Fenton reaction according to the classical Haber–Weiss mechanism, (ii) Fe2+ and Fe3+ can be easily accommodated on the octahedral site in the magnetite structure, where Fe2+ can be oxidized and thereafter reduced back to the same structure14, and (iii) the presence of multiple oxidation states of iron (Fe2+ and Fe3+) in magnetite enhances decomposition of hydrogen peroxide15. However, the Fe3O4 nanoparticles with high surface energies and intrinsic magnetic inter-action tend to aggregate that would reduce surface/volume ratio and dispersion stability in aqueous solution, and thus compromise the catalytic activity16. Therefore, to improve degradation catalytic ability, Fe3O4 nanoparticles are commonly supported by clay minerals such as bentonite17, carbon nano-material18, 19, and fly ash20, etc. The supported nanoparticles are characterized with enhanced activities.
Attapulgite (ATP) is a crystalline hydrated magnesium silicate mineral. It has an unusual layer-chain crystal structure with a large number of microporous channels and a relatively high surface area, which assign it remarkable adsorption ability. ATP has good sorptive removal capacity for metallic21, 22 and organic contaminants23, 24 in aqueous solutions. However, ATP could not degrade organic contaminants. Besides, colloidal ATPs are hard to be separated from aqueous solutions25. Instead, Fe3O4 nanoparticles can not only degrade organic contamiants by generating free radicals, but are paramagnetic which facilitate easy separation, from aqueous solution26. Thus, ATP supported Fe3O4 nanoparticles is not only capable of degradation of organic contaminants, but easy to be seperated from solutions. Further, ATP has a good cation exchange capacity and thus can attract Fe2+ and Fe3+ to its surfaces. The sorbed Fe2+ and Fe3+ can react with -OH to generate Fe(OH)2 and Fe(OH)3, respectively. Although Fe3O4-ATP nanomaterials have been reported by a few researchers for removal of hazardous metal ions from water27, 28, their use as a catalyst in the heterogeneous Fenton reaction has rarely been reported. In this study, the catalytic properties of Fe3O4-ATP nanomaterials for degradation of EtBr and the relevant mechanisms were investigated.
Since Fe3O4-ATP nanoparticles simultaneously exhibit adsorptive and catalytic, we anticipate that Fe3O4-ATP nanoparticles are a powerful candidate for catalytic activation of H2O2. This paper presents our research on the catalytic properties of superparamagnetic nanoscaled Fe3O4-ATP composite, which was used to promote Fenton oxidation of EtBr by H2O2. Thereby, Fe3O4-ATP nanoparticles were prepared and their physical and chemical characteristics were determined. The applicability of this composite in heterogeneous Fenton reaction was evaluated in view of the effect of the main variables (pH, temperature and H2O2 concentration, and catalyst dosage), reaction kinetics, and material stability, as well as the degradation mechanism.
Results and Discussion
Characterization of catalysts
The powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) characteristic peaks of purified ATP (P-ATP) and activated ATP (A-ATP) (Fig. 1(a)) at 2θ = 13.7° and 19.8° are consistent with (200) and (040) planes of ATP29. The peaks at 2θ = 20.9° and 26.6° correspond to quartz (SiO2) in P-ATP and A-ATP28, but the intensity of diffraction peaks of quartz SiO2 was weakened in A-ATP. The XRD patterns of Fe3O4 in the ATP@Fe3O4 composites all exhibited cubic spinel structure (JCPDS 65–3170), as evidenced by the weak diffraction peaks from the (220), (311), (400), (511) and (440) planes at 30.1°, 35.5°, 43.1°, 56.9° and 62.6°, respectively30, 31. The intensities of the ATP peak at 2θ = 19.8° and the quartz peaks at 2θ = 20.9° and 26.6° were weaker for the Fe3O4-purified ATP (P-ATP@Fe3O4) and Fe3O4-activated ATP (A-ATP@Fe3O4), indicating that Fe3O4 nano-particles were embedded in the ATP. But the characteristic reflections for ATP were observed in all of ATP@Fe3O4 composites, suggesting that modification process did not destroy the characteristic structure of ATP.
The average crystallite size (D) of Fe3O4 particles on the surface of A-ATP was 12.8 nm, as estimated with Scherrer equation30. The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images (Fig. 1(b,IV)) show that Fe3O4 particles were distributed regularly on the rod-like structure of ATP. The SEM images indicate that the average size of the Fe3O4 particles was about 15 nm, which matches well with XRD results.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images show that the materials exhibited rod like structure with highly uniform rotundness and void sizes (Fig. 2(a)), in agreement with the results of SEM analysis. The particles size ranged from 10–15 nm, which is consistent with the XRD result. Elemental mapping images (Fig. 2(c–g)) of A-ATP@Fe3O4 confirmed that the presence of Fe and O atoms in nanocomposites with a content of above 30% and 50% (Table 1). All of these results demonstrated that the Fe3O4 nanoparticles were loaded on the ATP.
The nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms of Fe3O4, P-ATP@Fe3O4, and A-ATP@Fe3O4 (Supplementary information Fig. S1(a)) all illustrated a typical type IV pattern with a bend of volume adsorption of nitrogen at a P/P 0 value of approximately 0.5 with a H3-type hysteresis loop. This pattern indicates the presence of mesoporous structure. In addition, the presence of mesoporous structure is also confirmed by the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) corresponding pore size distribution curve (see Supplementary Fig. S1(b)). Furthermore, the typical type IV pattern with a H3-type hysteresis loop also illustrated that the nanomaterials comprised of aggregates (loose assemblages) of platelike (rod-like) particles forming slitlike pores32. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area, pore size, and pore volume of A-ATP@Fe3O4 were 125.2745 m2/g, 11.80 nm, and 0.3695 cm3/g, respectively (Table 2). In particular, the specific surface area was about 1.5 times larger than that of other reported catalysts33.
The surface elemental composition of A-ATP@Fe3O4 was obtained (Fig. 3(a)) by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis, and the binding energy (BE) for Mg 1s, Fe 2p, O 1s, Si 2p and Al 2p were 1304.08, 712.08, 532.08, 103.08 and 87.08 eV, respectively.
(a) XPS spectra of A-ATP@Fe3O4, high-resolution XPS spectra of (b) Fe2p, (c)O1s. (d) Magnetization curves of P-ATP@Fe3O4 and A-ATP@Fe3O4 nanocomposites and Fe3O4 serves as control. The inset pattern is a photograph of the magnetic separation, which shows that the nanoparticles can be separated easily with a magnet.
Four peaks were observed in the Fe 2p spectrum of A-ATP@Fe3O4 (Fig. 3(b)). The Fe 2p3/2 peak with a BE of 710.7 eV was indicative of Fe3+ octahedral species34. The BE of 724.8 eV for Fe 2p1/2 indicated the presence of octahedrally coordinated Fe2+ 34, or ferric iron oxides (Fe3O4)35. The relative lower BE peak at 712.5 eV is attributed to Fe3+, with a corresponding Fe3+ satellite at 719.1 eV, which furthermore confirmed that both Fe2+ and Fe3+ were present in the nanocomposites.
Figure 3(c) showed the O 1s XPS spectrum of A-ATP@Fe3O4. The spectrum can be fitted to four peaks with BEs of 530.6, 531.8, 532.6, and 533.5 eV. The peak at 530.6 eV resulted from the lattice oxygen in Fe3O4 36. The two peaks at 531.8 and 532.6 eV were attributed to the monodentate oxygen atoms (H–O) and monodentate and bidentate oxygen species (Si–O–Si), respectively36, 37. The intensity ratios of the monodentate to bidentate oxygen atoms showed that surface of A-ATP@Fe3O4 was primarily bidentate. The remaining peak at 533.5 eV could be assigned to the chemically equivalent oxygen in the bidentate bond (O–C=O)38. For A-ATP@Fe3O4 catalyst, chemisorbed oxygen is the most active oxygen species which plays an important role in the oxidation reaction.
The Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra of the P-ATP, A-ATP, P-ATP@Fe3O4 and A-ATP@Fe3O4 samples are shown in Supplementary Fig. S2. In the spectrum of P-ATP and A-ATP, the absorbance bands at 3357 cm−1 and 3617 cm−1 were ascribed to the O–H stretching vibration of structural water and other water molecules in ATP39. The characteristic bands of stretching vibration of Si–O–Si for P-ATP and A-ATP was observed around 1033 cm−1, as well as the bending vibration of H–O–H located at 1652 cm−1. These three typical adsorption bands were also observed for P-ATP@Fe3O4 and A-ATP@Fe3O4, but the absorption peaks were all weaker than those of the samples not loaded with Fe3O4, which implies that crystallization was essentially completely40. In addition, the peak at 582 cm−1 was owing to Fe–O bond for Fe3O4 was observed in both P-ATP@Fe3O4 and A-ATP@Fe3O4 41. All the results confirmed that the Fe3O4 nanoparticles were loaded on the ATP.
The hysteresis loops of Fe3O4, P-ATP@Fe3O4, and A-ATP@Fe3O4 were investigated to observe their magnetization property. Figure 3(d) clearly showed that the three curves all exhibit almost zero remanence and coercivity, indicating that three types of nanoparticles were superparamagnetic42. The saturation magnetization (M s ) values were found to be 62.61, 44.78 and 41.78 emu/g for Fe3O4, P-ATP@Fe3O4, and A-ATP@Fe3O4, respectively. However, the “dilution effects” of ATP result in lower, M s values of the P-ATP@Fe3O4 and A-ATP@Fe3O4 particles relative to Fe3O4 particles43. Superparamagnetism is shown in Fig. 3(d) (pattern in inset) and demonstrated that the synthesized particles could be easily separated from solution by applying an external magnetic field. This phenomenon suggests an especially important advantage of our catalyst because it could be used for recycling.
Catalytic activity of ATP-Fe3O4 composite
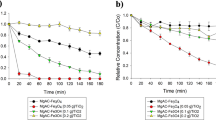
To compare the efficiency of EtBr removal by various processes, the control experiments with Fe3O4 only were investigated at pH 2.0 with initial EtBr concentration of 80 mg/L. After 30 min of dark adsorption, P-ATP@Fe3O4 and A-ATP@Fe3O4 showed better EtBr removal rates (51% and 64% respectively) than Fe3O4 alone (15%) (Table 1). The EtBr removal was ascribed mainly to the surface adsorption by ATP and Fe3O4 minerals. The enhanced EtBr sorption by A-ATP was due to the increased surface area. The degradation reaction results (Fig. 4) showed that H2O2 yielded only negligible removal of EtBr within 60 min. In the presence of H2O2, the degradation rate of EtBr using the Fe3O4-ATP composite was notably higher than that for Fe3O4, implying that the catalytic activity was enhanced by the introduction of ATP. After a 60 min heterogeneous Fenton reaction, Fe3O4-ATP composites exhibited a removal rate of 94%. In addition, the catalytic activity of A-ATP@Fe3O4 composite was higher than those of P-ATP@Fe3O4 or Fe3O4. The degradation rates within 20 min reached 90% for A-ATP@Fe3O4 composite but only 50% for Fe3O4, suggesting a synergetic effect in the A-ATP@Fe3O4 composite. The enhanced degradation rate of A-ATP@Fe3O4 nanoparticles may be ascribed to increased surface area of Fe3O4 nanoparticles which were well dispersed on the surface of A-ATP. The relative rates of mass transfer to reactive sites and chemical reaction at reactive sites would thus be enhanced.
Removal of EtBr under different conditions: (a) 30 mM H2O2. (b) 1.5 g/L Fe3O4 without H2O2. (c) 1.5 g/L P-ATP@Fe3O4 without H2O2. (d) 1.5 g/L A-ATP@Fe3O4 without H2O2. (e) 1.5 g/L Fe3O4 with 30 mM H2O2. (f) 1.5 g/L P-ATP@Fe3O4 with 30 mM H2O2. (g) 1.5 g/L A-ATP@Fe3O4 with 30 mM H2O2. Other reaction conditions were initial EtBr concentration 80 mg/L, pH 2.0, and T = 323 K, C 0 and C are initial EtBr concentration after 30 min adsorption and its concentration at any time during the reaction, respectively.
The pH effects on EtBr degradation by A-ATP@Fe3O4 catalyst was determined (Fig. 5 (a)). About 78% of EtBr was removed after 180 min of reaction at pH 5. EtBr degradation increased as pH decreased, suggesting that the production of ∙OH on the surface of A-ATP@Fe3O4 was limited at higher pHs. Although EtBr removal rates decreased between pH 3 and 9, the nanocomposites still exhibited good EtBr degradation capacity. This implied that A-ATP@Fe3O4 exhibited strong catalytic activity in a wide range of pH values. Under acidic, neutral, and alkaline conditions, the EtBr degradation was content with a pseudo first order reaction in kinetics, which might be expressed as ln(C t /C 0 ) = kt + m, where m is a constant, k is the apparent rate constant (min−1), C 0 is the residual concentration of EtBr (mmol/L) after 30 min absorption and C t is EtBr concentration at different sampling times. The highest k values of 2.445 min−1 for EtBr degradation was observed at pH 2.0, and thus pH 2.0 was selected for subsequent experiments.
Factorial effects of heterogeneous Fenton reaction on EtBr (80 mg/L) degradation by A-ATP@Fe3O4: (a) initial pH value, and (b) Arrhenius plot based on the effect of temperature. (c) H2O2 dosage, (e) A-ATP@Fe3O4 composite addition, (d) and (f) Pseudo-first-order kinetics corresponding to (c) and (e) (where the slope of the plot of −ln(C/C 0 ) versus reaction time is the apparent degradation rate constant k). Except for the investigated parameter, other parameters were fixed: catalysts load 1.5 g/L, initial H2O2 concentration 30 mmol/L and the temperature of the system 323 K of (a), catalysts load 1 g/L, pH 2.0, initial H2O2 concentration 15 mmol/L of (b). And catalysts load 1 g/L, pH 2.0, the temperature of the system 323 K of (c) and (e), pH 2.0, initial H2O2 concentration 30 mmol/L and the temperature of the system 323 K of (d) and (f).
The kinetics of EtBr degradation was also investigated at different temperatures (293, 303, 313, and 323 K). The activation energy (E a ) of the reaction was evaluated by plotting lnk against 1/T (Fig. 5(b)) according to the Arrhenius equation. The activation energy was determined to be 78.39 kJ/mol for A-ATP@Fe3O4. This E a value falls within a reasonable range from the literature of 60 to 250 kJ/mol44. Dependence on the temperature in a heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction was previously reported through a carbon-Fe structured catalyst for the degradation of orange II with an activation energy of 56.1 kJ/mol (in a similar temperature range)45. Thus, the heterogeneous catalytic reaction of A-ATP@Fe3O4/H2O2 is geared to a general chemical reaction. This result indicated that the heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction of A-ATP@Fe3O4/H2O2 does not require a very high energy. The effects of H2O2 concentration and A-ATP@Fe3O4 dosage at pH 2.0 and T = 323 K on the catalytic activity of A-ATP@Fe3O4. As shown in Fig. 5(d), the apparent rate constant k increased from 0.0361 to 0.844 min−1 as the increase of H2O2 dosage from 10 to 30 mmol/L, being about 2 folds of nanoscaled Fe3O4/CeO2 composite reported by Xu et al.46 According to the classical Haber–Weiss mechanism47, Fe2+ induces hydrogen peroxide to generate hydroxyl radicals (∙OH), and the ∙OH can then react with Fe3+ to regenerate Fe2+ that can circularly produce ∙OH radicals in the Fenton reaction. However, k value declined to 0.446 min−1 at a higher H2O2 concentrations of 40 mmol/L. It is possibly related to the scavenging effect of ∙OH radicals when excessive H2O2 inhibits the production of ∙OH radicals48. To shorten reaction time, a higher concentration of H2O2 (30 mmol/L) was applied for EtBr removal. In this case, it is necessary to investigate the loading of A-ATP@Fe3O4 (Fig. 5(f)). In our study, as the amount of A-ATP@Fe3O4 increased from 0.2 to 2.0 g/L, the rate constant k of EtBr degradation first increased and then decreased sharply. The increased removal rate may be due to the production of more reactive oxidants resulting from more active sites at higher rates of A-ATP@Fe3O4. The severe depression of EtBr removal is possibly ascribed to the scavenging of ∙OH radicals by excess Fe2+ 49. To conclude, better removal of EtBr with a shorter reaction time can be achieved under the following conditions: the 1.5 g/L of A-ATP@Fe3O4, pH = 2.0, T = 323 K, and 30 mmol/L H2O2 (standard reaction condition).
Effect of Fe ion release
To investigate the effects of the concentrations of dissolved Fe on the degradation of EtBr, the heterogeneous Fenton reaction was performed under the standard reaction condition. As shown in Fig. 6(a), in the adsorption stage, the concentration of ferrous ion increased gradually and reached a peak value of 2.48 mg/L, at which about 60% of EtBr was absorbed. After H2O2 was added, the concentration of Fe2+ decreased to about 0.26 mg/L where the removal rate of EtBr was 90% after 20 min. The reason is that the catalyst can release ferrous ions to the acid solution, and H2O2 can oxidize the ferrous ions to generate ∙OH50. Different from other heterogeneous Fenton reaction, a small amount of ferrous ion was released from the catalyst in the catalytic degradation stage. However, the fast degradation rate at 2 min implies that H2O2 exhibited an excellent ability to oxidize ferrous ions to produce ∙OH quickly, leading to a fast decreasing of ferrous ions. Further, the variation of ferrous ions also caused the increase of the dissolved iron from the A-ATP@Fe3O4 composite and the oxidation of ferrous ions in solution. The dissolved iron amounted to 5 mg/L, which is equivalent to about 0.62% of total iron in the catalyst (1.5 g/L).
Reusability of A-ATP@Fe3O4
The spent A-ATP@Fe3O4 was recycled and reused for EtBr degradation under standard reaction condition. As shown in Fig. 6(b), A-ATP@Fe3O4 maintained more than 80% of its catalytic capacity after five successive runs in 150 min of reaction. The reduced EtBr degradation efficiency probably resulted from the reduction of released iron ions from the catalyst in each successive runs. Therefore, to maintain an adequate quantity of the catalyst in the aqueous solutions and thus maintain the degradation efficiency, a prolonged degradation time may be needed.
Possible degradation mechanisms
The EtBr degradation process was indicated by mineralization (reduction of TOC) (Fig. 7(a)) and the UV–visible absorption spectrum. The results indicated that the maximum TOC removal rate was approximately 45% after 20 min, suggesting that 45% of EtBr was oxidized by active species(∙OH, ∙O2 −, etc.) to CO2 and H2O. This result is confirmed by the UV–vis absorption spectra of EtBr (Fig. 7(b)), which showed that the characteristic peak at λ = 285 nm became smaller and almost disappeared as the degradation proceeded. In addition, we observed that the absorption peak at λ = 241 nm weakened sharply after the addition of H2O2, indicating that the attack by the highly reactive hydroxyl radicals led to rapid opening of the benzene ring51. In addition, a new absorption peak at λ = 210 nm was recorded after 2 min of treatment and decreased gradually with reaction time. This may suggest that EtBr was attacked by hydroxyl radicals to produce a large number of intermediate products52, although further confirmation is needed.
(a) Temporal change in EtBr and TOC removal. (b) UV-vis absorption spectra of the EtBr solution during the reaction in the systems of A-ATP@Fe3O4 (c) Effect of radical scavengers on the degradation of EtBr, and Reactions were conducted under the standard conditions. (d) The EPR spectra for the DMPO−∙OH (I) and DMPO−∙O2 − (II) of the A-ATP@Fe3O4 catalytic system with H2O2.
To confirm reactive species in the degradation process, t-butyl alcohol and benzoquinone (BQ) were selected as radical scavengers during EtBr degradation, respectively. Excess t-butyl alcohol could scavenger all of the ∙OH produced by the system in the solution53. As shown in the Fig. 7(c), the degradation reaction rate of EtBr decreased evidently after the addition of t-butyl alcohol, which indicated the existence of ∙OH. However, about 20% of EtBr was not affected by the presence of t-butyl alcohol, which suggests the existence of other reactive species. After that, BQ was added to the system as a scavenger of ∙O2 − 54. From Fig. 7(c), with the addition of excess BQ, the EtBr degradation decreased from 68%, 77%, 86%, and 90% (in the absence of BQ) to 56%, 69%, 70%, and 72% at 2, 5, 10, and 15 min, respectively, suggesting that EtBr was also oxidized by the attack of ∙O2 − in the solution. Further, the electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) technique was used to further confirm the direct involvement of ∙OH and ∙O2 − in the degradation process. As shown in Fig. 7(d,I), the characteristic 1:2:2:1 quartet signal was detected using 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO) as a spin trapping agent, indicating the existence of ∙OH during the heterogeneous Fenton reaction. Besides, because ∙O2 − was extremely unstable in aqueous solution, methanol was used as a solvent for detection of ∙O2 −. Figure 7(d,II) clearly shows that the six characteristic peaks of DMPO-∙O2 − existed in the degraded system.
Combining the results from the reactive oxygen species assay and the EPR analysis, we determined that ∙OH and ∙O2 − were present in the catalytic system. Thus, the possible reaction mechanism of H2O2 activation by A-ATP@Fe3O4 under acidic condition is illustrated in Fig. 8. According to our observations, it is possible that Fe2+ and Fe3+ from partial dissolution of iron oxides under acidic conditions initiate the decomposition of H2O2 through a homogeneous Fenton chain reaction. Initially, the dissolved Fe2+ can react with H2O2 to generate Fe3+ and ∙OH (equation (1)), which yield HO2∙/∙O2 − and simultaneously produce Fe2+ (equation (2)). The generated ∙OH (equation (1)) may further react with H2O2 to generate HO2∙/∙O2 − (equation (3)). Then partial Fe2+ is converted to Fe3+ through oxidation of the produced ∙OH (equation (4)). Thus, all of these reactions lead to cycling of iron ions in the solution system. In our work, a large number of H+ ions in solution facilitate that the reactions in equations (1) and (4), leading to decreased Fe2+ along with increased Fe3+ during the catalytic reactions.
Moreover, the amount of EtBr degradation declined from 68%, 77%, 86%, and 90% to 51%, 59%, 64%, and 66% at 2, 5, 10, and 15 min in the presence of excess KI (10 mM), suggesting that ∙OH originating from the surface of the catalyst played a dominant role in EtBr degradation (Fig. 7(c)). And the total amount of iron dissolved remained constant (Fig. 6(a)), implying that not much Fe2+ was released in EtBr degradation. Therefore, we conjecture that similar chain reactions occurred on the surface of the catalyst, which is different from the that in solution. Moreover, the hydroxyl radicals generated on the catalyst surface by the chain reaction are also involved in the degradation of EtBr. This may explain the reduction of catalytic performance in the process of reusing, which is similar with the result reported by Luo et al.55.
Conclusion
In this study, a heterogeneous Fenton catalyst ATP@Fe3O4 was successfully synthesized by introducing nanoscaled Fe3O4 particles onto the treated ATP surface via co-precipitation. The obtained nanocomposites were carefully characterized which confirmed Fe3O4 nanoparticles with an average size of 15 nm was spread on the surface of ATP samples after different treatments. The as-prepared ATP@Fe3O4 nanocomposites all exhibited good sorptive removal ability for EtBr. Compared to P-ATP@Fe3O4, A-ATP@Fe3O4 has greater sorptive and catalytic capacity for EtBr. The higher sorptive capacity of A-ATP@Fe3O4 nanocomposites was attributed to larger specific surface area, while degradation of EtBr was mainly ascribed to more abundant hydroxyl radicals (∙OH). The highest degradation rate of EtBr and TOC removal were 92% and 45% within 60 min under optimal operation conditions: T = 323 K, 30 mmol/L H2O2, 1.5 g/L A-ATP@Fe3O4, and pH 2.0. Moreover, A-ATP@Fe3O4 composites have good regeneration ability and could be separated by external magnet. Thus, A-ATP@Fe3O4 nanocomposites can be safely used to remediate organic contaminants from aqueous solution.
Materials and Methods
Chemicals and materials
All the reagents used in the experiment were of analytical reagent grade and used without further purification. ATP was provided by Xuyu Clay Technology Co., Jiangsu China. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 30% (w/w)), ethanol, t-butyl alcohol, potassium iodide (KI), hydrochloric acid (HCl), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), ferric chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O), ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO4·7H2O), and high-purity compressed nitrogen (N2) gases were obtained from Yangzhou Chemicals Corporation (Yangzhou, China). EtBr and BQ were purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Bio-Chem Technology Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China).
Preparation and characterization of catalyst
The pristine ATP powder was purified as follows. Briefly, 20 g of ATP were dispersed in 300 mL of deionized water and stirred for 2 h. The resulting slurry was then settled for 2 h, and the supernatant was decanted to remove impurities. Next, the prepared ATP was immersed in 300 mL of deionized water with 200 mL of H2O2 (30%, w/w). The suspension was magnetically stirred for 5 h, and sonicated for 30 min (40 kHz). The suspension was centrifuged at 5000 rpm, and the resulting precipitate was vacuum dried for 24 h at 70 °C and stored for subsequent use.
P-ATP was then activated in 150 mL of 1 M HCl with constant magnetic stirring for 5 h followed by sonication for 30 min. A-ATP was vacuum filtered, washed with deionized water and ethanol to a pH value of 6–7, and then dried for 24 h at 70 °C under vacuum.The prepared ATP was stored in a desiccator at room temperature for further use.
A-ATP@Fe3O4 were synthesized by co-precipitation method56. A-ATP (2.0 g) were added to 240 mL of deionized water in a 500 mL flask and stirred for 6 h. Then, the pH of the suspension was adjusted to 8 using 5 M NaOH solution. The stable suspension was bubbled with a constant N2 flow for 30 min to remove the dissolved oxygen57. Next, a 0.6 mol/L FeSO4 solution (20 m L) was added to the flask and sonicated for 30 min, followed by addition of 0.8 mol/L FeCl3 solution (20 ml). The mixture was then sonicated for 15 min. NaOH solution (5 M) was added to the flask drop wisely. Black precipitate appeared immediately after NaOH addition, and the reaction was terminated at a pH of 10. The nanocomposites were aged at 60 °C for another 1.5 h. The suspension was centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 5 min; the as-prepared Fe3O4 loaded ATP was washed with deionized water and ethanol several times to remove free ions and dried in a vacuum oven at 70 °C for 24 h. Finally, A-ATP@Fe3O4 nanoparticles with an Fe3O4-to-ATP mass ratio of 1:1 were obtained. In addition, P-ATP@Fe3O4 was prepared following the above procedure without HCl activation and Fe3O4 alone was synthesized without adding ATP. All the products were stored in a desiccator under room temperature before use.
Characterization of catalyst
The morphology of the catalyst was observed on a scanning electron microscope (S-4800II, Japan) operated at an acceleration voltage of 15 kV. The surface groups of the nanocomposites were recorded by a micro infrared spectrometer (Cary 610/670, USA). The phase structure of the nanocomposites was obtained by XRD analysis (D8 Advance Bruker AXS, Germany). EDS were measured using a X-ray energy dispersive spectrometer (Thermo Electron Corporation) with Al Kα radiation as the excitation source. XPS (ESCALAB 250 Xi, USA) was used to identify the metal oxidation states of the nanocomposites. The magnetization of ATP-Fe3O4 and Fe3O4 was measured at room temperature using vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM-EV7, ADE) with a maximum applied field of 1.7 T. The specific surface area of the catalysts was determined by N2-BET analysis using an accelerated surface area and a porosimetry analyzer (ASAP 2460).
Degradation experiment
Batch degradation experiments of EtBr were conducted in a conical flask (250 mL) incubated in a water bath with a constant temperature oscillator (TZ-2EH, Beijing Wode Co.) and shaken at 150 rpm in darkness. The reaction suspension was prepared by adding the required amount of catalyst (0.2–2.0 g/L) to 200 mL of an 80 mg/L EtBr solution at different pH values (2.0–9.0). The suspension was vibrated for 30 min to achieve the adsorption/desorption equilibrium. The EtBr concentration after equilibrium was measured and considered as the initial concentration (C 0 ). Then, a known concentration of H2O2 was added to initiate the degradation reaction. Subsamples were taken at set intervals during the reaction using a 3 mL centrifuge tube and immediately centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 5 min using an H1650-W centrifuge (HuNan) to remove the catalyst. The EtBr concentration of the supernatant was determined at λ = 285 nm by using a UV–visible spectrophotometer. Each experiment was run in triplicate.
To test the regeneration ability of Fe3O4-ATP, spent nanoparticles were separated from the suspension when the EtBr was almost completely degraded. The regenerated sorbents were then used again for EtBr degradation. The regeneration process was repeated five times.
Analytical methods
Total organic carbon (TOC) was analyzed using a TOC-LCPN analyzer (Shimadzu, Japan). The component and content of different elements were measured by an energy dispersive X-ray Spectrometer. The concentration of EtBr was analyzed using an intelligent UV-2501PC/2550 detector (ShangHai) at λ = 285 nm.
The presence of hydroxyl radicals and superoxide radical were determined using t-butyl alcohol, KI and BQ, respectively, as scavengers. The effective radicals that appeared in the degradation process were further detected by electron spin resonance (A300–10/12, Bruker, Germany).The concentration of ferrous ions was measured colorimetrically with 1,10-phenanthroline at λ = 510 nm on a UV–vis spectrophotometer58. The total dissolved iron was analyzed by atomic absorption spectroscopy (G8433A).
References
Fiust, A., Rapacz, M. & Wójcik-Jagła, M. Development of DArT-based PCR markers for selecting drought-tolerant spring barley. Journal of Applied Genetics. 56, 299–309, doi:10.1007/s13353-015-0273-x (2015).
Macgregor, J. T. & Johnson, I. J. In vitro metabolic activation of ethidium bromide and other phenanthridinium compounds: Mutagenic activity in Salmonella typhimurium. Mutation Research/fundamental & Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis. 48, 103–107, doi:10.1016/0027-5107(77)90194-4 (1977).
Moradi, O., Norouzi, M., Fakhri, A. & Naddafi, K. Interaction of removal Ethidium Bromide with Carbon Nanotube: Equationuilibrium and Isotherm studies. Journal of Environmental Health Science & Engineering. 12, 1–9, doi:10.1186/2052-336X-12-17 (2014).
Zhang, C., Liu, L., Wang, J., Rong, F. & Fu, D. Electrochemical degradation of ethidium bromide using boron-doped diamond electrode. Separation & Purification Technology. 107, 91–101, doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2013.01.033 (2013).
Adán, C., Martínez-Arias, A., Fernández-García, M. & Bahamonde, A. Photocatalytic degradation of ethidium bromide over titania in aqueous solutions. Applied Catalysis B Environmental. 76, 395–402, doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.06.013 (2007).
Guo, J., Dong, C., Zhang, J. & Lan, Y. Biogenic synthetic schwertmannite photocatalytic degradation of acid orange 7 (AO7) assisted by citric acid. Separation & Purification Technology. 143, 27–31, doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2015.01.018 (2015).
Sun, S. P., Zeng, X. & Lemley, A. T. Nano-magnetite catalyzed heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation of emerging contaminants carbamazepine and ibuprofen in aqueous suspensions and montmorillonite clay slurries at neutral pH. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A Chemical. 371, 94–103, doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2013.01.027 (2013).
Zhang, Y., Zhang, K., Dai, C., Zhou, X. & Si, H. An enhanced Fenton reaction catalyzed by natural heterogeneous pyrite for nitrobenzene degradation in an aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal. 244, 438–445, doi:10.1016/j.cej.2014.01.088 (2014).
Xue, X., Hanna, K., Despas, C., Feng, W. & Deng, N. Effect of chelating agent on the oxidation rate of PCP in the magnetite/H2O2 system at neutral pH. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A Chemical. 311, 29–35, doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2009.06.016 (2009).
Sun, J. H. et al. A kinetic study on the degradation of p-nitroaniline by Fenton oxidation process. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 148, 172–177, doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.02.022 (2007).
Huan-Yan, X. U. et al. Heterogeneous Fenton-like discoloration of methyl orange using Fe3O4/MWCNTs as catalyst: process optimization by response surface methodology. Frontiers of Materials Science. 10, 45–55, doi:10.1007/s11706-016-0326-z (2016).
Wang, N., Zhu, L., Wang, M., Wang, D. & Tang, H. Sono-enhanced degradation of dye pollutants with the use of H2O2 activated by Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as peroxidase mimetic. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry. 17, 78–83, doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2009.06.014 (2010).
Gao, L. & Zhuang, J. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles and its application in immunoassay and environment treatment. Journal of Biological Physics. 304–305 (2009).
Xue, X., Hanna, K. & Deng, N. Fenton-like oxidation of rhodamine B in the presence of two types of iron (II, III) oxide. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 166, 407–414, doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.11.089 (2009).
Zhang, S. et al. Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanopartic/les as catalysts for the catalytic oxidation of phenolic and aniline compounds. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 167, 560–566, doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.01.024 (2009).
Fan, W. et al. Hybridization of graphene sheets and carbon-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a synergistic adsorbent of organic dyes. Journal of Materials Chemistry. 22, 25108–25115, doi:10.1039/C2JM35609K (2012).
Wan, D. et al. Adsorption and heterogeneous degradation of rhodamine B on the surface of magnetic bentonite material. Applied Surface Science. 349, 988–996, doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.05.004 (2015).
Shen, J., Li, Y., Zhu, Y., Hu, Y. & Li, C. Aerosol synthesis of Graphene-Fe3O4 hollow hybrid microspheres for heterogeneous Fenton and electro-Fenton reaction. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. 4, 2469–2476, doi:10.1016/j.jece.2016.04.027 (2016).
Song, S., Yang, H., Rao, R., Liu, H. & Zhang, A. High catalytic activity and selectivity for hydroxylation of benzene to phenol over multi-walled carbon nanotubes supported Fe3O4 catalyst. Applied Catalysis A: General. 375, 265–271, doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2010.01.008 (2010).
Li, Y. & Zhang, F. S. Catalytic oxidation of Methyl Orange by an amorphous FeOOH catalyst developed from a high iron-containing fly ash. Chemical Engineering Journal. 158, 148–153, doi:10.1016/j.cej.2009.12.021 (2010).
Wang, W., Tian, G., Zhang, Z. & Wang, A. A simple hydrothermal approach to modify palygorskite for high-efficient adsorption of Methylene blue and Cu(II) ions. Chemical Engineering Journal. 265, 228–238, doi:10.1016/j.cej.2014.11.135 (2015).
Cui, H., Yan, Q., Li, Q., Zhang, Q. & Zhai, J. Adsorption of aqueous Hg (II) by a polyaniline/attapulgite composite. Chemical Engineering Journal. 211-212, 216–223, doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.09.057 (2012).
Mu, B., Kang, Y., Zheng, M. & Wang, A. One-pot preparation of superparamagnetic attapulgite/Fe3O4/polydopamine nanocomposites for adsorption of methylene blue. 1736, 2402–2410, doi:10.1063/1.4949722 (2016).
Huang, J., Wang, X., Jin, Q., Liu, Y. & Wang, Y. Removal of phenol from aqueous solution by adsorption onto OTMAC-modified attapulgite. Journal of Environmental Management. 84, 229–236, doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.05.007 (2007).
Ouellet, C. Comparison between granular pillared, organo- and inorgano-organo-bentonites for hydrocarbon and metal ion adsorption. Applied Clay Science. 67–68, 91–98, doi:10.1016/j.clay.2012.08.003 (2012).
Mu, B. & Wang, A. One-pot fabrication of multifunctional superparamagnetic attapulgite/Fe3O4/polyaniline nanocomposites served as an adsorbent and catalyst support. J.mater.chem.a. 3, 281–289, doi:10.1039/C4TA05367B (2014).
Huang, Z. N., Dou, S. M. & Du, J. Study on Adsorption of Cr (VI) in Wastewater by Magnetic-modified Palygorskite lays and Its Application. Science Technology and Engineering. 15, 108–113, doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815 (2015).
Fan, Q. H., Li, P., Chen, Y. F. & Wu, W. S. Preparation and application of attapulgite/iron oxide magnetic composites for the removal of U (VI) from aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 192, 1851–1859, doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.07.022 (2011).
Xu, J. et al. Direct electron transfer and bioelectrocatalysis of hemoglobin on nano-structural attapulgite clay-modified glassy carbon electrode. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science. 315, 170–176, doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2007.06.059 (2007).
Mirmohseni, A., Dorraji, M. S. S. & Hosseini, M. G. Influence of metal oxide nanoparticles on pseudocapacitive behavior of wet-spun polyaniline-multiwall carbon nanotube fibers. Electrochimica Acta. 70, 182–192, doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2012.03.100 (2012).
Meng, J. H., Yang, G. Q., Yan, L. M. & Wang, X. Y. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanometer pigment Fe3O4. Dyes & Pigments. 66, 109–113, doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2004.08.016 (2005).
And, M. K. & Jaroniec, M. Gas Adsorption Characterization of Ordered Organic-Inorganic Nanocomposite Materials. Chemistry of Materials. 13, 3169–3183, doi:10.1021/cm0101069 (2001).
Wang, N. et al. Sono-assisted preparation of highly-efficient peroxidase-like Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for catalytic removal of organic pollutants with H2O2. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry. 17, 526–533 (2010).
Wilson, D. & Langell, M. A. XPS analysis of oleylamine/oleic acid capped Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a function of temperature. Applied Surface Science. 303, 6–13, doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.02.006 (2014).
Zhu, Y. et al. Heteroepitaxial growth of gold on flowerlike magnetite: An efficacious and magnetically recyclable catalyst for chemoselective hydrogenation of crotonaldehyde to crotyl alcohol. Journal of Catalysis. 281, 106–118, doi:10.1016/j.jcat.2011.04.007 (2011).
Palimi, M. J., Rostami, M., Mahdavian, M. & Ramezanzadeh, B. Surface modification of Fe2O3 nanoparticles with 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (APTMS): An attempt to investigate surface treatment on surface chemistry and mechanical properties of polyurethane/Fe2O3 nanocomposites. 60–72, doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.09.026 (Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, 2001).
Reitz, C. et al. Morphology, microstructure, and magnetic properties of ordered large-pore mesoporous cadmium ferrite thin film spin glasses. Inorganic Chemistry. 52, 3744–3754, doi:10.1021/ic302283q (2013).
Briggs, D. & Beamson, G. XPS studies of the oxygen 1s and 2s levels in a wide range of functional polymers. Analytical Chemistry. 65, 1517–1523, doi:10.1021/ac00059a006 (1993).
Suárez, M. & Garcia, E. FTIR spectroscopic study of palygorskite: Influence of the composition of the octahedral sheet. Applied Clay Science. 31, 154–163, doi:10.1016/j.clay.2005.10.005 (2006).
Liu, Y., Liu, P., Su, Z., Li, F. & Wen, F. Attapulgite-Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles via co-precipitation technique. Applied Surface Science. 255, 2020–2025, doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.06.193 (2008).
Starodoubtsev, S. G. et al. Composite Gels of Poly (acrylamide) with Incorporated Bentonite. Interaction with Cationic Surfactants, ESR and SAXS Study. Macromolecules. 35, 6362–6369, doi:10.1021/ma012021z (2002).
Wang, X., Wang, L., He, X., Zhang, Y. & Chen, L. A molecularly imprinted polymer-coated nanocomposite of magnetic nanoparticles for estrone recognition. Talanta. 78, 327–332, doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2008.11.024 (2009).
Mikhaylova, M. et al. Superparamagnetism of magnetite nanoparticles: dependence on surface modification. Langmuir. 20, 2472–2477, doi:10.1021/la035648e (2004).
Hu, Y. Physical Chemistry Reference (ed. Hu, Y.) (Higher Education Press: China, 2003).
Ramirez, J. H. et al. Azo-dye Orange II degradation by heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction using carbon-Fe catalysts. Applied Catalysis B Environmental. 75, 312–323, doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.05.003 (2007).
Xu, L. & Wang, J. Magnetic nanoscaled Fe3O4/CeO2 composite as an efficient Fenton-like heterogeneous catalyst for degradation of 4-chlorophenol. Environmental Science Technology. 46, 10145–10153, doi:10.1021/es300303f (2012).
Haber, F. & Weiss, J. The Catalytic Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide by Iron Salts. Proceedings of the Royal Society A Mathematical Physical & Engineering Sciences. 147, 332–351, doi:10.1098/rspa.1934.0221 (1934).
Xu, L. & Wang, J. A heterogeneous Fenton-like system with nanoparticulate zero-valent iron for removal of 4-chloro-3-methyl phenol. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 186, 256–264, doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.116 (2011).
Daud, N. K. & Hameed, B. H. Decolorization of Acid Red 1 by Fenton-like process using rice husk ash-based catalyst. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 176, 938–944, doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.130 (2010).
Luo, M., Bowden, D. & Brimblecombe, P. Catalytic property of Fe-Al pillared clay for Fenton oxidation of phenol by H2O2. Applied Catalysis B Environmental. 85, 201–206, doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.07.013 (2009).
Zhao,Y. X. Spectral Identification of Organic Molecular Structure (ed. Zhao, Y. X.) (Science Press: China, 2003).
Zhang, L. & Ma, H. R. Reaction mechanism and degradation course of azo dyes by catalytic wet peroxide oxidation (CWPO). Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering. 05, 2032–2038 (2011).
Rush, J. D. & Koppenol, W. H. Oxidizing intermediates in the reaction of ferrous EDTA with hydrogen peroxide. Reactions with organic molecules and ferrocytochrome c. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 261, 6730–6733 (1986).
Patel, K. B. & Willson, R. L. Semiquinone free radicals and oxygen. Pulse radiolysis study of one electron transfer equationuilibria. Journal of the Chemical Society Faraday Transactions. 69, 814–825, doi:10.1039/f19736900814 (1973).
Luo, W. et al. Efficient Removal of Organic Pollutants with Magnetic Nanoscaled BiFeO3 as a Reusable Heterogeneous Fenton-Like Catalyst. Environmental Science & Technology. 44, 1786–1791, doi:10.1021/es903390g (2010).
Yin, H., Chen, H. & Chen, D. Hydrogen bond interaction in poly(acrylonitrile-co-methylacrylate)/attapulgite nanocomposites. Polymer Engineering & Science. 50, 312–319, doi:10.1002/pen.21550 (2010).
Hu, X. et al. Adsorption and heterogeneous Fenton degradation of 17α-methyltestosterone on nano Fe3O4/MWCNTs in aqueous solution. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 107, 274–283, doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.07.025 (2011).
Tamura, H., Goto, K., Yotsuyanagi, T. & Nagayama, M. Spectrophotometric determination of iron (II) with 1,10-phenanthroline in the presence of large amounts of iron (III). Talanta. 21, 314–318, doi:10.1016/0039-9140(74)80012-3 (1974).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (41371294), State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse (PCRRF1102), Social development project of Jiangsu Province (BE2015661), Six talent peaks project in Jiangsu Province (2013-NY-017) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions. We thank the Testing Center of Yangzhou University for Sample Characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript. X.W. and S.W. designed the project. S.H. and H.Y. synthesized the samples. S.W. supervised the synthesis of the samples. S.H. and T.Y. performed the structural characterizations. S.H. and S.W. performed the chemical characterizations. S.H., X.W. and S.W. coperformed and coanalyzed the catalytic experiments. S.H. and X.W. co-wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, S., Yu, H., Yang, T. et al. Magnetic Activated-ATP@Fe3O4 Nanocomposite as an Efficient Fenton-Like Heterogeneous Catalyst for Degradation of Ethidium Bromide. Sci Rep 7, 6070 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06398-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06398-3
This article is cited by
-
Magnetic attapulgite synthesized via Sonochemistry: an innovative strategy for efficient solid phase extraction of As3+ from simulated and unrefined crude oil samples
Journal of Porous Materials (2024)
-
Adsorption and removal of ethidium bromide from aqueous solution using optimized biogenic catalytically active antibacterial palladium nanoparticles
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2023)
-
Efficient removal of ethidium bromide from aqueous solutions using chromatin-loaded chitosan polyvinyl alcohol composites
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2023)
-
Efficient removal of ethidium bromide from aqueous solution by using DNA-loaded Fe3O4 nanoparticles
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.