Abstract
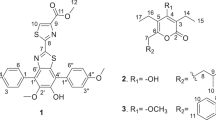
A new diketopiperazine-like compound, designated protuboxepin K (1), was isolated together with the known structurally related protuboxepin A (2) from culture broth of the marine-derived fungal strain Aspergillus sp. BFM-0085 isolated from a sediment sample of Tokyo Bay. The structure of protuboxepin K was elucidated by spectroscopic data, including 1D and 2D NMR. Compounds 1 and 2 inhibited bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-induced alkaline phosphatase activity with IC50 values of 4.7 and 25.2 μM, respectively, in mutant BMP receptor-carrying C2C12(R206H) cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaplan FS, Chakkalakal SA, Shore EM. Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: mechanisms and models of skeletal metamorphosis. Dis Model Mech. 2012;5:756–62.
Katagiri T, Tsukamoto S, Nakachi Y, Kuratani M. Recenttopics in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33:331–8.
Yu PB, et al. BMP type I receptor inhibition reduces heterotopic [corrected] ossification. Nat Med. 2008;14:1363–9.
Shimono K, et al. Potent inhibition of heterotopic ossification by nuclear retinoic acid receptor-γ agonists. Nat Med. 2011;17:454–60.
Hatsell SJ, et al. ACVR1R206H receptor mutation causes fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva by imparting responsiveness to activin A. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7:303ra137.
Chakkalakal SA, et al. Palovarotene inhibits heterotopic ossification and maintains limb mobility and growth in mice with the human ACVR1(R206H) fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) mutation. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31:1666–75.
Hino K, et al. Activin-A enhances mTOR signaling to promote aberrant chondrogenesis in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. J Clin Investig. 2017;127:3339–52.
Shore EM, et al. A recurrent mutation in the BMP type I receptor ACVR1 causes inherited and sporadic fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Nat Genet. 2006;38:525–7.
Fukuda T, et al. Constitutively activated ALK2 and increased SMAD1/5 cooperatively induce bone morphogenetic protein signaling in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:7149–56.
Fukuda T, et al. Fungal pyrrolidine-containing metabolites inhibit alkaline phosphatase activity in bone morphogenetic protein-stimulated myoblastoma cells. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2012;2:23–7.
Fukuda T, et al. Trichocyalides A and B, new inhibitors of alkaline phosphatase activity in bone morphogenetic protein-stimulated myoblasts, produced by Trichoderma sp. FKI-5513. J Antibiot. 2012;65:565–9.
Uchida R, et al. 5-Prenyltryptophol, a new inhibitor of bone morphogenetic protein-induced alkaline phosphatase expression in myoblasts, produced by Streptomyces colinus subsp. albescens HEK608. J Antibiot. 2014;67:589–91.
Uchida R, et al. Scopranones with two atypical scooplike moieties produced by Streptomyces sp. BYK-11038. Org Lett. 2017;19:5980–3.
Lee SU, et al. Protuboxepins A and B and protubonines A and B from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SF-5044. J Nat Prod. 2011;74:1284–7.
Luo X, et al. Structurally diverse diketopiperazine alkaloids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor SCSIO 41016. Org Chem Front. 2019;6:736–40.
Tian YQ, et al. Protuboxepin C and protuboxepin D from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp SCSIO XWS02F40. Nat Prod Res. 2018;32:2510–5.
Fan YQ, et al. Alkaloids with Cardiovascular Effects from the marine-derived Fungus Penicillium expansum Y32. Mar Drugs. 2015;13:6489–504.
Asami Y, et al. Protuboxepin A, a marine fungal metabolite, inducing metaphase arrest and chromosomal misalignment in tumor cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012;20:3799–806.
Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983;65:55–63.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Noriko Sato and Dr. Kenichiro Nagai (School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kitasato University) for measurements of NMR spectra and MS data, and Mr. Seiji Taki (Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology) for collecting sediment samples of Tokyo Bay. This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant number JP26253009 (HT), the Takeda Science Foundation (HT), and a Kitasato University Research Grant for Young Researchers (SO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This article is dedicated to Professor William Fenical in recognition of his contributions to marine-derived secondary metabolites.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
41429_2020_316_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
A new diketopiperazine-like inhibitor of bone morphogenetic protein-induced osteoblastic differentiation produced by marine-derived <i>Aspergillus</i> sp. BFM-0085
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohte, S., Shiokawa, T., Koyama, N. et al. A new diketopiperazine-like inhibitor of bone morphogenetic protein-induced osteoblastic differentiation produced by marine-derived Aspergillus sp. BFM-0085. J Antibiot 73, 554–558 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-020-0316-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-020-0316-3
This article is cited by
-
Screening of marine sediment-derived microorganisms and their bioactive metabolites: a review
World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology (2023)
-
Oxepinamide F biosynthesis involves enzymatic d-aminoacyl epimerization, 3H-oxepin formation, and hydroxylation induced double bond migration
Nature Communications (2020)