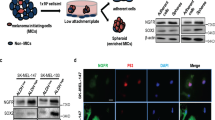
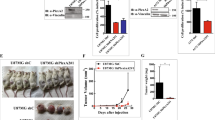
Abstract
Plexin C1 is a type I transmembrane receptor with intrinsic R-Ras GTPase activity, which regulates cytoskeletal remodeling and adhesion in normal human melanocytes. Melanocytes are pigment-producing cells of the epidermis, precursors for melanoma, and express high levels of Plexin C1, which is lost in melanoma in vitro and in vivo. To determine if Plexin C1 is a tumor suppressor for melanoma, we introduced Plexin C1 into a primary human melanoma cell line, and phenotypes including migration, apoptosis, proliferation and tumor growth in mice were analyzed. Complimentary studies in which Plexin C1 was silenced in human melanocytes were performed. Plexin C1 significantly inhibited migration and proliferation in melanoma, whereas in melanocytes, loss of Plexin C1 increased migration and proliferation. In mouse xenografts, Plexin C1 delayed tumor growth of melanoma at early time points, but tumors eventually escaped the suppressive effects of Plexin C1, due to Plexin C1-dependent activation of the pro-survival protein Akt. R-Ras activation stimulates melanoma migration. Plexin C1 lowered R-Ras activity in melanoma and melanocytes, consistent with inhibitory effects of Plexin C1 on migration of melanocytes and melanoma. To determine if R-Ras is expressed in melanocytic lesions in vivo, staining of tissue microarrays of nevi and melanoma were performed. R-Ras expression was highly limited in melanocytic lesions, being essentially confined to primary melanoma, and almost completely absent in nevi and metastatic melanoma. These data suggest that loss of Plexin C1 in melanoma may promote early steps in melanoma progression through suppression of migration and proliferation, but pro-survival effects of Plexin C1 ultimately abrogate the tumor suppressive effects of Plexin C1. In primary melanoma, loss of Plexin C1 may function in early steps of melanoma progression by releasing inhibition of R-Ras activation, and stimulating migration.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SD:
-
standard deviation
- Sema7A:
-
Semaphorin 7A
- SEM:
-
standard error of the mean
References
Artigiani S, Comoglio PM, Tamagnone L . Plexins semaphorins, and scatter factor receptors: a common root for cell guidance signals? IUBMB Life 1999; 48: 477–482.
Yazdani U, Terman JR . The semaphorins. Genome Biol 2006; 7: 211.
Perala N, Sariola H, Immonen T . More than nervous: the emerging roles of plexins. Differentiation 2012; 83: 77–91.
Barton WA, Himanen JP, Antipenko A, Nikolov DB . Structures of axon guidance molecules and their neuronal receptors. Adv Protein Chem 2004; 68: 65–106.
Uesugi K, Oinuma I, Katoh H, Negishi M . Different requirement for Rnd GTPases of R-Ras GAP activity of Plexin-C1 and Plexin-D1. J. Biol Chem 2009; 284: 6743–6751.
Puschel AW . GTPases in semaphorin signaling. Adv Exp Med Biol 2007; 600: 12–23.
Negishi M, Oinuma I, Katoh H . R-ras as a key player for signaling pathway of plexins. Mol Neurobiol 2005; 32: 217–222.
Oinuma I, Katoh H, Negishi M . Semaphorin 4D/Plexin-B1-mediated R-Ras GAP activity inhibits cell migration by regulating beta(1) integrin activity. J Cell Biol 2006; 173: 601–613.
Wang Y, He H, Srivastava N, Vikarunnessa S, Chen Y-b, Jiang J et al. Plexins are GTPase-activating proteins for Rap and are activated by induced dimerization. Sci Signal 2012; 5: ra6.
Aurandt J, Vikis HG, Gutkind JS, Ahn N, Guan KL . The semaphorin receptor plexin-B1 signals through a direct interaction with the Rho-specific nucleotide exchange factor, LARG. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 12085–12090.
Barberis D, Casazza A, Sordella R, Corso S, Artigiani S, Settleman J et al. p190 Rho-GTPase activating protein associates with plexins and it is required for semaphorin signalling. J Cell Sci 2005; 118 (Part 20): 4689–4700.
Giger RJ, Hollis ER, Tuszynski MH . Guidance molecules in axon regeneration. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol 2010; 2: a001867.
Walzer T, Galibert L, De Smedt T . Dendritic cell function in mice lacking Plexin C1. Int Immunol 2005; 17: 943–950.
Lallier TE . Semaphorin profiling of periodontal fibroblasts and osteoblasts. J Dent Res 2004; 83: 677–682.
Messina A, Ferraris N, Wray S, Cagnoni G, Donohue DE, Casoni F et al. Dysregulation of Semaphorin7A/beta1-integrin signaling leads to defective GnRH-1 cell migration, abnormal gonadal development and altered fertility. Hum Mol Genet 2011; 20: 4759–4774.
Scott GA, McClelland LA, Fricke AF . Semaphorin 7a promotes spreading and dendricity in human melanocytes through beta1-integrins. J Invest Dermatol 2008; 128: 151–161.
Comeau MR, Johnson R, DuBose RF, Petersen M, Gearing P, VandenBos T et al. A poxvirus-encoded semaphorin induces cytokine production from monocytes and binds to a novel cellular semaphorin receptor. VESPR Immunity 1998; 8: 473–482.
Xu C, Fan CM . Allocation of paraventricular and supraoptic neurons requires Sim1 function: a role for a Sim1 downstream gene PlexinC1. Mol Endocrinol 2007; 21: 1234–1245.
Pasterkamp RJ, Kolk SM, Hellemons AJ, Kolodkin AL . Expression patterns of semaphorin7A and plexinC1 during rat neural development suggest roles in axon guidance and neuronal migration BMC. Devl Biol 2007; 7: 98.
Liu H, Juo ZS, Shim AH, Focia PJ, Chen X, Garcia KC et al. Structural basis of semaphorin-plexin recognition and viral mimicry from Sema7A and A39R complexes with PlexinC1. Cell 2010; 142: 749–761.
Pasterkamp RJ, Peschon JJ, Spriggs MK, Kolodkin AL . Semaphorin 7A promotes axon outgrowth through integrins and MAPKs. Nature 2003 424, 398–405.
Suzuki K, Okuno T, Yamamoto M, Pasterkamp RJ, Takegahara N, Takamatsu H et al. Semaphorin 7A initiates T-cell-mediated inflammatory responses through alpha1beta1 integrin. Nature 2007; 446: 680–684.
Scott GA, McClelland LA, Fricke AF, Fender A . Plexin C1, a receptor for semaphorin 7a, inactivates cofilin and is a potential tumor suppressor for melanoma progression. J Invest Dermatol 2009; 129: 954–963.
Maddodi N, Setaluri V . Role of UV in cutaneous melanoma. Photochem Photobiol 2008; 84: 528–536.
Lazova R, Gould Rothberg BE, Rimm D, Scott G . The semaphorin 7A receptor Plexin C1 is lost during melanoma metastasis. Am J Dermatopathol 2009; 31: 177–181.
Balakrishnan A, Penachioni JY, Lamba S, Bleeker FE, Zanon C, Rodolfo M et al. Molecular profiling of the "plexinome" in melanoma and pancreatic cancer. Hum Mutat 2009; 30: 1167–1174.
Gao L, Feng Y, Bowers R, Becker-Hapak M, Gardner J, Council L et al. Ras-associated protein-1 regulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation and migration in melanoma cells: two processes important to melanoma tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 7880–7888.
Gawecka JE, Griffiths GS, Ek-Rylander B, Ramos JW, Matter ML . R-Ras regulates migration through an interaction with filamin A in melanoma cells. PLoS One 2010; 5: e11269.
Yang D, Tao J, Li L, Kedei N, Tóth ZE, Czap A et al. RasGRP3, a Ras activator, contributes to signaling and the tumorigenic phenotype in human melanoma. Oncogene 2011; 30: 4590–4600.
Stevens L, McClelland L, Fricke A, Williamson M, Kuo I, Scott G . Plexin B1 suppresses c-Met in melanoma: a role for Plexin B1 as a tumor-suppressor protein through regulation of c-Met. J Invest Dermatol 2010; 130: 1636–1645.
Abi-Habib RJ, Urieto JO, Liu A, Leppla SH, Duesbery N, Frankel A . BRAF status and mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1/2 activity indicate sensitivity of melanoma cells to anthrax lethal toxin. Mol Can Ther 2005; 4: 1303–1310.
Keely PJ, Rusyn EV, Cox AD, Parise LV . R-Ras signals through specific integrin alpha cytoplasmic domains to promote migration and invasion of breast epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 1999; 145: 1077–1088.
Zhang Z, Vuori K, Wang H, Reed JC, Ruoslahti E . Integrin activation by R-ras. Cell 1996; 85: 61–69.
Holly SP, Larson MK, Parise LV . The unique N-terminus of R-ras is required for Rac activation and precise regulation of cell migration. Mol Biol Cell 2005; 16: 2458–2469.
Wozniak MA, Kwong L, Chodniewicz D, Klemke RL, Keely PJ . R-Ras controls membrane protrusion and cell migration through the spatial regulation of Rac and Rho. Mol Biol Cell 2005; 16: 84–96.
Iwashita S, Kobayashi M, Kubo Y, Hinohara Y, Sezaki M, Nakamura K et al. Versatile roles of R-Ras GAP in neurite formation of PC12 cells and embryonic vascular development. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 3413–3417.
Iwasawa N, Negishi M, Oinuma I . R-Ras controls axon branching through Afadin in cortical neurons. Mol Biol Cell 2012; 23: 2793–2804.
Hara M, Yaar M, Tang A, Eller MS, Reenstra W, Gilchrest BA . Role of integrins in melanocyte attachment and dendricity. J Cell Sci 1994; 107 (Part 10): 2739–2748.
Scott G, Leopardi S . The cAMP-PKA signaling pathway has opposing effects on Rac and Rho in B16F10 cells: implications for dendrite formation in melanocytic cells. Pigment Cell Res 2003; 16: 139–148.
Scott G . Rac and Rho: the story of melanocyte dendrite formation (Review). Pigm Cell Res 2002; 5: 322–330.
Argast GM, Croy CH, Couts KL, Zhang Z, Litman E, Chan DC et al. Plexin B1 is repressed by oncogenic B-Raf signaling and functions as a tumor suppressor in melanoma cells. Oncogene 2009; 28: 2697–2709.
Winograd-Katz SE, Levitzk A . Cisplatin induces PKB/Akt activation and p38MAPK phosphorylation of the EGF receptor. Oncogene 2006; 25: 7381–7390.
Itahana K, Campisi J, Dimri GP . Methods to detect biomarkers of cellular senescence: the senescence-associated beta-galactosidase assay. Methods Mol Biol 2007; 371: 21–31.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by R01CA136499 (GS), by NIH training Grant 5T32AR007472 (JS), and by the Department of Biogenetics, University of Rochester (LX). We also thank Lori Moll (Oncogene Inc.,) for assistance with subcloning of Plexin C1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Soong, J., Mohanty, S. et al. The neural guidance receptor Plexin C1 delays melanoma progression. Oncogene 32, 4941–4949 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.511
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.511
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
SEMAPHORINS and their receptors: focus on the crosstalk between melanoma and hypoxia
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)
-
Oxysterol binding protein-like 3 (OSBPL3) is a novel driver gene that promotes tumor growth in part through R-Ras/Akt signaling in gastric cancer
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
MiR-4500 Regulates PLXNC1 and Inhibits Papillary Thyroid Cancer Progression
Hormones and Cancer (2019)
-
Stage-specific functions of Semaphorin7A during adult hippocampal neurogenesis rely on distinct receptors
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Gas5 Exerts Tumor-suppressive Functions in Human Glioma Cells by Targeting miR-222
Molecular Therapy (2015)