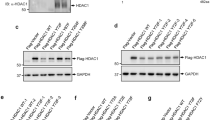
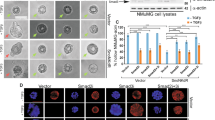
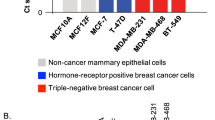
Abstract
Snail1 is a transcriptional factor essential for triggering epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Moreover, Snail1 promotes resistance to apoptosis, an effect associated to PTEN gene repression and Akt stimulation. In this article we demonstrate that Snail1 activates Akt at an additional level, as it directly binds to and activates this protein kinase. The interaction is observed in the nucleus and increases the intrinsic Akt activity. We determined that Akt2 is the isoform interacting with Snail1, an association that requires the pleckstrin homology domain in Akt2 and the C-terminal half in Snail1. Snail1 enhances the binding of Akt2 to the E-cadherin (CDH1) promoter and Akt2 interference prevents Snail1 repression of CDH1 gene. We also show that Snail1 binding increases Akt2 intrinsic activity on histone H3 and have identified Thr45 as a residue modified on this protein. Phosphorylation of Thr45 in histone H3 is sensitive to Snail1 and Akt2 cellular levels; moreover, Snail1 upregulates the binding of phosphoThr45 histone H3 to the CDH1 promoter. These results uncover an unexpected role of Akt2 in transcriptional control and point out to phosphorylation of Thr45 in histone H3 as a new epigenetic mark related to Snail1 and Akt2 action.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed NN, Franke TF, Bellacosa A, Datta K, Gonzalez-Portal ME, Taguchi T et al. (1993). The proteins encoded by c-akt and v-akt differ in post-translational modification, subcellular localization and oncogenic potential. Oncogene 8: 1957–1963.
Ahn JY, Liu X, Liu Z, Pereira L, Cheng D, Peng J et al. (2006). Nuclear Akt associates with PKC-phosphorylated Ebp1, preventing DNA fragmentation by inhibition of caspase-activated DNase. EMBO J 25: 2083–2095.
Alessi DR, Andjelkovic M, Caudwell B, Cron P, Morrice N, Cohen P et al. (1996). Mechanisms of activation of protein kinase B by insulin and IGF-1. EMBO J 15: 6541–6551.
Andjelković M, Alessi DR, Meier R, Fernandez A, Lamb NJ, Frech M et al. (1997). Role of translocation in the activation and function of protein kinase B. J Biol Chem 272: 31515–31524.
Arboleda MJ, Lyons JF, Kabbinavar FF, Bray MR, Snow BE, Ayala R et al. (2003). Overexpression of Akt2/protein kinase B beta leads to upregulation of beta1 integrins, increased invasion, and metastasis of human breast an ovarian cancer cell. Cancer Res 63: 196–206.
Batlle E, Sancho E, Francí C, Domínguez D, Monfar M, Baulida J et al. (2000). The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol 2: 84–89.
Bellacosa A, Testa JR, Moore R, Larue L . (2004). A portrait of Akt kinases: human cancer and animal models depict a family with strong individualities. Cancer Biol Ther 3: 268–275.
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS et al. (1999). Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96: 857–868.
Calleja V, Alcor D, Laguerre M, Park J, Vojnovic B, Hemmings BA et al. (2007). Intramolecular and intermolecular interactions of protein kinase B define its activation in vivo. PLoS Biol 5: e95.
Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I, Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG et al. (2000). The transcription factor Snail controls epithelial–mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol 2: 78–83.
Carver EA, Jiang R, Lan Y, Oram KF, Gridley T . (2001). The mouse snail gene encodes a key regulator of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Mol Cell Biol 21: 8184–8188.
Cha TL, Zhou BP, Xia W, Wu Y, Yang CC, Chen CT et al. (2005). Akt-mediated phosphorylation of EZH2 suppresses methylation of Lysine 27 in histone H3. Science 310: 306–310.
Cheng GZ, Chan J, Wang Q, Zhang W, Sun CD, Wang LH . (2007). Twist transcriptionally upregulates Akt2 in breast cancer cells leading to increased migration, invasion, and resistance to paclitaxel. Cancer Res 67: 1979–1987.
Cho HJ, Baek KE, Saika S, Jeong MJ, Yoo J . (2007). Snail is required for transforming growth factor-β-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition by activating PI3 kinase/Akt signal pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 353: 337–343.
De Craene B, van Roy F, Berx G . (2005). Unraveling signalling cascades from the Snail family of transcription factors. Cell Signal 17: 535–547.
Dillon RL, Marcotte R, Hennessy BT, Woodgett JR, Mills GB, Muller WJ . (2009). Akt1 and Akt2 play distinct roles in the initiation and metastatic phases of tumor progression. Cancer Res 69: 5057–5064.
Domínguez D, Montserrat-Sentís B, Virgós-Soler A, Guaita S, Grueso J, Porta M et al. (2003). Phosphorylation regulates the subcellular location and activity of the snail transcriptional repressor. Mol Cell Biol 23: 5078–5089.
Du K, Tsichlis PN . (2005). Regulation of Akt kinase by interacting proteins. Oncogene 24: 7401–7409.
Ericson K, Gan C, Cheong I, Rago C, Samuels Y, Velculescu VE et al. (2010). Genetic inactivation of AKT1, AKT2, and PDPK1 in human colorectal cancer cells clarifies their roles in tumor growth regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 2598–2603.
Escrivà M, Peiró S, Herranz N, Villagrasa P, Dave N, Montserrat-Sentís B et al. (2008). Repression of PTEN phosphatase by Snail1 transcriptional factor during gamma radiation-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 28: 1528–1540.
Francí C, Takkunen M, Dave N, Alameda F, Gómez S, Rodríguez R et al. (2006). Expression of Snail protein in tumor–stroma interface. Oncogene 25: 5134–5144.
Gao H, Yu Z, Bi D, Jiang L, Cui Y, Sun J et al. (2007). Akt/PKB interacts with the histone methyltransferase SETDB1 and coordinates to silence gene expression. Mol Cell Biochem 305: 35–44.
Gan Y, Shi C, Inge L, Hibner M, Balducci J, Huang Y . (2010). Differential roles of ERK and Akt pathways in regulation of EGFR-mediated signalling and motility in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 29: 4947–4958.
García de Herreros A, Peiró S, Nassour M, Savagner P . (2010). Snail family regulation and epithelial mesenchymal transitions in breast cancer progression. J. Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 15: 135–147.
Grille SJ, Bellacosa A, Upson J, Klein-Szanto AJ, van Roy F, Lee-Kwon W et al. (2003). The protein kinase Akt induces epithelial mesenchymal transition and promotes enhanced motility and invasiveness of squamous cell carcinoma lines. Cancer Res 63: 2172–2178.
He Z, Ma WY, Liu G, Zhang Y, Bode AM, Dong Z . (2003). Arsenite-induced phosphorylation of Histone 3 at Serine 10 is mediated by Akt1, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 and ribosomal S6 kinase 2 but not mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase 1. J Biol Chem 278: 10588–10593.
Herranz N, Pasini D, Díaz VM, Francí C, Gutierrez A, Dave N et al. (2008). Polycomb complex 2 is required for E-cadherin repression by the Snail1 transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol 28: 3198–3207.
Hurd PJ, Bannister AJ, Halls K, Dawson MA, Vermeulen M, Olsen JV et al. (2009). Phosphorylation of histone H3 is linked to apoptosis. J Biol Chem 284: 16575–16583.
Iliopoulos D, Polytarchou C, Hatziapostolou M, Kottakis F, Maroulakou IG, Struhl K et al. (2009). Micro RNAs differentially regulated by Akt isoforms control EMT and stem cell renewal in cancer cells. Sci Signal 92: ra62.
Irie HY, Pearline RV, Grueneberg D, Hsia M, Ravichandran P, Kothari N et al. (2005). Distinct roles of Akt1 and Akt2 in regulating cell migration and epithelial–mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol 171: 1023–1034.
Jahn T, Seipel P, Urschel S, Peschel C, Duyster J. (2002). Role for the adaptor protein Grb10 in the activation of Akt. Mol Cell Biol 22: 979–991.
Jordà M, Olmeda D, Vinyals A, Valero E, Cubillo E, Llorens A et al. (2005). Upregulation of MMP-9 in MDCK epithelial cell line in response to expression of the Snail transcription factor. J Cell Sci 118: 3371–3385.
Jordà M, Vinyals A, Marazuela A, Cubillo E, Olmeda D, Valero E et al. (2007). Id-1 is induced in MDCK epithelial cells by activated ERK/MAPK pathway in response to expression of the Snail and E47 transcription factors. Exp Cell Res 313: 2389–2403.
Julien S, Puig I, Caretti E, Bonaventure J, Nelles L, van Roy F et al. (2007). Activation of NF-κB by Akt upregulates Snail expression and induces epithelium–mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 26: 7445–7456.
Lee SB, Xuan Nguyen TL, Choi JW, Lee KH, Cho SW, Liu Z et al. (2008). Nuclear Akt interacts with B23/NPM and protects it from proteolytic cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 16584–16589.
Masuyama N, Oishi K, Mori Y, Ueno T, Takahama Y, Gotoh Y. (2001). Akt inhibits the orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 and T-cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem 276: 32799–32805.
Ohkubo T, Ozawa M. (2003). The transcription factor Snail downregulates the tight junction components independently of E-cadherin downregulation. J Cell Sci 117: 1675–1685.
Pálmer HG, Larriba MJ, García JM, Ordóñez-Morán P, Peña C, Peiró S et al. (2004). The transcription factor SNAIL represses vitamin D receptor expression and responsiveness in human colon cancer. Nat Med 10: 917–919.
Parsons DW, Wang TL, Samuels Y, Bardelli A, Cummins JM, DeLong L et al. (2005). Colorectal cancer: mutations in a signaling pathway. Nature 436: 792.
Peiró S, Escrivà M, Puig I, Barberà MJ, Dave N, Herranz N et al. (2006). Snail1 transcriptional repressor binds to its own promoter and controls its expression. Nucleic Acids Res 34: 2077–2084.
Pekarsky Y, Hallas C, Palamarchuk A, Koval A, Bullrich F, Hirata Y et al. (2000). Tcl1 enhances Akt kinase activity and mediates its nuclear translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 3028–3033.
Raurell I, Castaño J, Francí C, García de Herreros A, Duñach M . (2006). Presenilin-1 interacts with plakoglobin and enhances plakoglobin–Tcf-4 association: implications for the regulation of β-catenin/Tcf-4-dependent transcription. J Biol Chem 281: 1401–1411.
Rychahou PG, Kang J, Gulhati P, Doan HQ, Chen LA, Xiao SY et al. (2008). Akt2 overexpression plays a critical role in the establishment of colorectal cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 20315–20320.
Sato S, Fujita N, Tsuruo T . (2000). Modulation of Akt kinase activity by binding to Hsp90. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 10832–10837.
Solanas G, Porta-de-la-Riva M, Agustí C, Casagolda D, Sánchez-Aguilera F, Larriba MJ et al. (2008). E-cadherin controls β-catenin and NF-κB transcriptional activity in mesenchymal gene expression. J Cell Sci 121: 2224–2234.
Stemmer V, de Crane B, Berx G, Behrens J . (2008). Snail promotes Wnt target gene expression and interacts with β-catenin. Oncogene 27: 5075–5080.
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA . (2009). Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 139: 871–890.
Vega S, Morales AV, Ocaña OH, Valdés F, Fabregat I, Nieto MA . (2004). Snail blocks the cell cycle and confers resistance to cell death. Genes Dev 18: 1131–1143.
Woodgett JR . (2005). Recent advances in protein kinase B signaling pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17: 150–157.
Zhou BP, Deng J, Xia W, Xu J, Li YM, Gunduz M et al. (2004). Dual regulation of Snail by GSK-3β-mediated phosphorylation in control of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol 6: 931–940.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Neus Ontiveros for technical help; Dr David Casagolda for assistance with confocal microscopy; and Drs Lionel Larue and Alberto Muñoz for reagents. This study was supported by grants awarded by the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (BFU2006-03203 and BFU2009-07578 to MD and SAF2006-00339 and SAF2010-16089 to AGH) and Fundació La Marató de TV3 (to AGH). The partial support from the Instituto Carlos III-Fondos FEDER (RTICCC, C03710, RD06/0020/0040) and the Generalitat de Catalunya (2009SGR867) is also appreciated. PV and RV-C were supported by predoctoral fellowships from the Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología and Instituto Carlos III, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villagrasa, P., Díaz, V., Viñas-Castells, R. et al. Akt2 interacts with Snail1 in the E-cadherin promoter. Oncogene 31, 4022–4033 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.562
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.562
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Snail regulates BMP and TGFβ pathways to control the differentiation status of glioma-initiating cells
Oncogene (2018)
-
Signaling pathways and mesenchymal transition in pediatric high-grade glioma
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2018)
-
Atypical role of sprouty in colorectal cancer: sprouty repression inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition
Oncogene (2016)
-
HRG regulates tumor progression, epithelial to mesenchymal transition and metastasis via platelet-induced signaling in the pre-tumorigenic microenvironment
Angiogenesis (2013)