Abstract
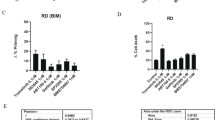
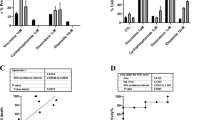
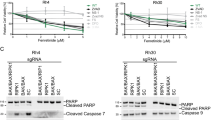
Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and their receptor, IGF-1 receptor (IGF1R), have important roles in growth, development, stress response, aging and cancer. There are many agents that inhibit IGF1R in oncology clinical development, and in some cases, they have been associated with rapid tumor regression. However, it is not clear by which process these targeted agents induce cancer cell death and how to predict such tumor responses. Here, we showed that IGF1R antibody led to rapid cell death and tumor regression in some rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) cells. Mechanistic analysis revealed a rapid onset of mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis, including mitochondrial depolarization, cytochrome C release and the activation of specific caspases. The antibody sensitive cells had greater dependence on AKT for maintaining downstream signaling and the expression of a constitutively active AKT, which restored AKT-signaling in these cells, inhibited anti-IGF1R induced cell death. Further analysis showed IGF1R antibody-induced hypophosphorylation of BAD and activation of downstream BAX. Interestingly, the examination of RMS cell lines and tumors revealed an inverse correlation between elevated IGF1R and Bcl-2 level (P=0.033), with the sensitive cells lacking Bcl-2 expression. The overexpression of BAD specific target, Bcl-xL, conferred resistance, whereas Bcl-xL knockdown sensitized cells lacking Bcl-2 to anti-IGF1R-induced cell death. We propose that RMS pathogenesis involves increased IGF1R expression that enhances AKT and Bcl-xL-mediated cell survival, and the blockage of IGF1R results in inhibition of survival signal from Bcl-xL and cell death in the sensitive Bcl-2 negative cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JM, Cory S . (2007). The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 26: 1324–1337.
Barcia RN, Dana MR, Kazlauskas A . (2007). Corneal graft rejection is accompanied by apoptosis of the endothelium and is prevented by gene therapy with bcl-xL. Am J Transplant 7: 2082–2089.
Burtrum D, Zhu Z, Lu D, Anderson DM, Prewett M, Pereira DS et al. (2003). A fully human monoclonal antibody to the insulin-like growth factor I receptor blocks ligand-dependent signaling and inhibits human tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res 63: 8912–8921.
Cao L, Yu Y, Darko I, Currier D, Mayeenuddin LH, Wan X et al. (2008). Addiction to elevated insulin-like growth factor I receptor and initial modulation of the AKT pathway define the responsiveness of rhabdomyosarcoma to the targeting antibody. Cancer Res 68: 8039–8048.
Clemmons DR . (2007). Modifying IGF1 activity: an approach to treat endocrine disorders, atherosclerosis and cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6: 821–833.
Cohen BD, Baker DA, Soderstrom C, Tkalcevic G, Rossi AM, Miller PE et al. (2005). Combination therapy enhances the inhibition of tumor growth with the fully human anti-type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody CP-751,871. Clin Cancer Res 11: 2063–2073.
Datta SR, Ranger AM, Lin MZ, Sturgill JF, Ma YC, Cowan CW et al. (2002). Survival factor-mediated BAD phosphorylation raises the mitochondrial threshold for apoptosis. Dev Cell 3: 631–643.
Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman J, van Bree C . (2006). Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc 1: 2315–2319.
Goetsch L, Gonzalez A, Leger O, Beck A, Pauwels PJ, Haeuw JF et al. (2005). A recombinant humanized anti-insulin-like growth factor receptor type I antibody (h7C10) enhances the antitumor activity of vinorelbine and anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapy against human cancer xenografts. Int J Cancer 113: 316–328.
Gualberto A, Pollak M . (2009). Emerging role of insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibitors in oncology: early clinical trial results and future directions. Oncogene 28: 3009–3021.
Haluska P, Shaw HM, Batzel GN, Yin D, Molina JR, Molife LR et al. (2007). Phase I dose escalation study of the anti insulin-like growth factor-I receptor monoclonal antibody CP-751,871 in patients with refractory solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 13: 5834–5840.
Hennessy BT, Smith DL, Ram PT, Lu Y, Mills GB . (2005). Exploiting the PI3K/AKT pathway for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4: 988–1004.
Jiang X, Wang X . (2004). Cytochrome C-mediated apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem 73: 87–106.
Kooijman R . (2006). Regulation of apoptosis by insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17: 305–323.
Kurmasheva RT, Houghton PJ . (2006). IGF-I mediated survival pathways in normal and malignant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1766: 1–22.
Manning BD, Cantley LC . (2007). AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129: 1261–1274.
Minshall C, Arkins S, Straza J, Conners J, Dantzer R, Freund GG et al. (1997). IL-4 and insulin-like growth factor-I inhibit the decline in Bcl-2 and promote the survival of IL-3-deprived myeloid progenitors. J Immunol 159: 1225–1232.
Muslin AJ, Tanner JW, Allen PM, Shaw AS . (1996). Interaction of 14-3-3 with signaling proteins is mediated by the recognition of phosphoserine. Cell 84: 889–897.
Parrizas M, LeRoith D . (1997). Insulin-like growth factor-1 inhibition of apoptosis is associated with increased expression of the bcl-xL gene product. Endocrinology 138: 1355–1358.
Peruzzi F, Prisco M, Dews M, Salomoni P, Grassilli E, Romano G et al. (1999). Multiple signaling pathways of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in protection from apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 19: 7203–7215.
Phillips DC, Martin S, Doyle BT, Houghton JA . (2007). Sphingosine-induced apoptosis in rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines is dependent on pre-mitochondrial Bax activation and post-mitochondrial caspases. Cancer Res 67: 756–764.
Rathmell JC, Vander Heiden MG, Harris MH, Frauwirth KA, Thompson CB . (2000). In the absence of extrinsic signals, nutrient utilization by lymphocytes is insufficient to maintain either cell size or viability. Mol Cell 6: 683–692.
Rodriguez-Tarduchy G, Collins MK, Garcia I, Lopez-Rivas A . (1992). Insulin-like growth factor-I inhibits apoptosis in IL-3-dependent hemopoietic cells. J Immunol 149: 535–540.
Sachdev D, Li SL, Hartell JS, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, Miller JS, Yee D . (2003). A chimeric humanized single-chain antibody against the type I insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor renders breast cancer cells refractory to the mitogenic effects of IGF-I. Cancer Res 63: 627–635.
Shimizu S, Narita M, Tsujimoto Y . (1999). Bcl-2 family proteins regulate the release of apoptogenic cytochrome c by the mitochondrial channel VDAC. Nature 399: 483–487.
Tolcher AW, Sarantopoulos J, Patnaik A, Papadopoulos K, Lin CC, Rodon J et al. (2009). Phase I, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of AMG 479, a fully human monoclonal antibody to insulin-like growth factor receptor 1. J Clin Oncol 27: 5800–5807.
Troiano L, Ferraresi R, Lugli E, Nemes E, Roat E, Nasi M et al. (2007). Multiparametric analysis of cells with different mitochondrial membrane potential during apoptosis by polychromatic flow cytometry. Nat Protoc 2: 2719–2727.
Wang Y, Hailey J, Williams D, Wang Y, Lipari P, Malkowski M et al. (2005). Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF1R) signaling and tumor cell growth by a fully human neutralizing anti-IGF1R antibody. Mol Cancer Ther 4: 1214–1221.
Wu JD, Odman A, Higgins LM, Haugk K, Vessella R, Ludwig DL et al. (2005). In vivo effects of the human type I insulin-like growth factor receptor antibody A12 on androgen-dependent and androgen-independent xenograft human prostate tumors. Clin Cancer Res 11: 3065–3074.
Yaffe MB, Rittinger K, Volinia S, Caron PR, Aitken A, Leffers H et al. (1997). The structural basis for 14-3-3:phosphopeptide binding specificity. Cell 91: 961–971.
Yang E, Zha J, Jockel J, Boise LH, Thompson CB, Korsmeyer SJ . (1995). Bad, a heterodimeric partner for Bcl-XL and Bcl-2, displaces Bax and promotes cell death. Cell 80: 285–291.
Zha J, Harada H, Yang E, Jockel J, Korsmeyer SJ . (1996). Serine phosphorylation of death agonist BAD in response to survival factor results in binding to 14-3-3 not BCL-X(L). Cell 87: 619–628.
Zhang J, D'Ercole AJ . (2004). Expression of Mcl-1 in cerebellar granule neurons is regulated by IGF-I in a developmentally specific fashion. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 152: 255–263.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Andrius Kazlauskas for providing the lentivirus expressing Bcl-xL, and Arnulfo Mendoza, Vanessa Moore, Susan Garfield and Barbara Taylor for excellent technical assistance. This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the US National Cancer Institute (NCI). This project was also funded in part with federal funds from the NCI, NIH, under contract N01-CO-12400.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mayeenuddin, L., Yu, Y., Kang, Z. et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor antibody induces rhabdomyosarcoma cell death via a process involving AKT and Bcl-xL. Oncogene 29, 6367–6377 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.364
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.364
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Small GTPase Arl6 controls RH30 rhabdomyosarcoma cell growth through ciliogenesis and Hedgehog signaling
Cell & Bioscience (2016)
-
Antibody-coupled siRNA as an efficient method for in vivo mRNA knockdown
Nature Protocols (2016)
-
Downregulation of IGFBP2 is associated with resistance to IGF1R therapy in rhabdomyosarcoma
Oncogene (2014)
-
Proof-of-concept rare cancers in drug development: the case for rhabdomyosarcoma
Oncogene (2014)
-
Pediatric sarcomas: translating molecular pathogenesis of disease to novel therapeutic possibilities
Pediatric Research (2012)