Abstract
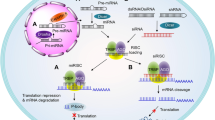
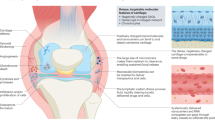
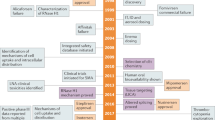
RNA interference (RNAi) is one of the most exciting and important discoveries of the past few decades. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can silence gene activity and be used to interfere with pathophysiological processes. Substantial research has focused on introducing 'drug-like' properties—stability, selectivity and potency—to RNAi molecules, and clinical trials have been initiated. Despite initial success, the current challenge that remains is to develop optimized vehicles that avoid off-target effects whilst efficiently delivering the therapeutic siRNA to specific cell types. As for many other diseases, siRNA-based therapy is emerging as a promising approach for the treatment of rheumatic disorders. Although the pathogenesis of rheumatic diseases is complex, identification of candidate genes able to influence either inflammation or structural damage has been successful. Here, we will discuss advances in the field and potential applications of siRNA therapeutics in clinical trials for rheumatic conditions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carthew, R. W. & Sontheimer, E. J. Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 136, 642–655 (2009).
Mello, G. C. & Conte, D. Revealing the world of RNA interference. Nature 431, 338–342 (2004).
De Paula, D., Bentley, M. V. & Mahato, R. I. Hydrophobization and bioconjugation for enhanced siRNA delivery and targeting. RNA 13, 431–456 (2007).
Li, C. X. et al. Delivery of RNA interference. Cell Cycle 5, 2103–2109 (2006).
Jackson, A. L. & Linsley, P. S. Recognizing and avoiding siRNA off-target effects for target identification and therapeutic application. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 9, 57–67 (2010).
Grimm, D. et al. Fatality in mice due to oversaturation of cellular microRNA/short hairpin RNA pathways. Nature 441, 537–541 (2006).
McBride, J. L. et al. Artificial miRNAs mitigate shRNA-mediated toxicity in the brain: implications for the therapeutic development of RNAi. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 5868–5873 (2008).
Sioud, M. RNA interference and innate immunity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59, 153–163 (2007).
Schiffelers, R. M., Xu, J., Storm, G., Woodle, M. C. & Scaria, P. V. Effects of treatment with small interfering RNA on joint inflammation in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 52, 1314–1318 (2005).
Inoue, A. et al. Electro-transfer of small interfering RNA ameliorated arthritis in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 336, 903–908 (2005).
Inoue, A. et al. Comparison of anti-rheumatic effects of local RNAi-based therapy in collagen induced arthritis rats using various cytokine genes as molecular targets. Mod. Rheumatol. 19, 125–133 (2009).
Nakagawa, S. et al. Small interfering RNA targeting CD81 ameliorated arthritis in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 388, 467–472 (2009).
Takanashi, M. et al. Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by siRNA cream in an arthritis model mouse. Gene Ther. 16, 982–989 (2009).
Xu, G. et al. Role of osteopontin in amplification and perpetuation of rheumatoid synovitis. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 1060–1067 (2005).
Boumans, M. J. et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and efficacy of the monoclonal antibody ASK8007 blocking osteopontin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised, placebo controlled, proof-of-concept study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 71, 180–185 (2012).
Mountziaris, P. M., Sing, D. C., Mikos, A. G. & Kramer, P. R. Intra-articular microparticles for drug delivery to the TMJ. J. Dent. Res. 89, 1039–1044 (2010).
Présumey, J. et al. PLGA microspheres encapsulating siRNA anti-TNFα: efficient RNAi-mediated treatment of arthritic joints. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2012.07.021.
Lai Kwan Lam, Q., King Hung Ko, O., Zheng, B. J. & Lu, L. Local BAFF gene silencing suppresses TH17-cell generation and ameliorates autoimmune arthritis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 14993–14998 (2008).
Wang, C. R. et al. Intra-articular lentivirus-mediated delivery of galectin-3 shRNA and galectin-1 gene ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis. Gene Ther. 17, 1225–1233 (2010).
Khoury, M. et al. Adeno-associated virus type 5-mediated intraarticular administration of tumor necrosis factor small interfering RNA improves collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 62, 765–770 (2010).
Fabre, S. & Apparailly, F. Gene therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: current status and future prospects. BioDrugs 25, 381–391 (2011).
Andrianaivo, F., Lecocq, M., Wattiaux-De Coninck, S., Wattiaux, R. & Jadot, M. Hydrodynamics-based transfection of the liver: entrance into hepatocytes of DNA that causes expression takes place very early after injection. J. Gene Med. 6, 877–883 (2004).
Brunetti-Pierri, N. et al. Increased hepatic transduction with reduced systemic dissemination and proinflammatory cytokines following hydrodynamic injection of helper-dependent adenoviral vectors. Mol. Ther. 12, 99–106 (2005).
Zheng, X. et al. RNAi-mediated CD40–CD154 interruption promotes tolerance in autoimmune arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 12, R13 (2010).
Zheng, X. et al. Treatment of autoimmune arthritis using RNA interference-modulated dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 184, 6457–6464 (2010).
Charbonnier, L. M. et al. Immature dendritic cells suppress collagen-induced arthritis by in vivo expansion of CD49b+ regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 177, 3806–3813 (2006).
Stoop, J. N. et al. Therapeutic effect of tolerogenic dendritic cells in established collagen-induced arthritis is associated with a reduction in Th17 responses. Arthritis Rheum 62, 3656–3665 (2010).
Howard, K. A. et al. Influence of hydrophilicity of cationic polymers on the biophysical properties of polyelectrolyte complexes formed by self-assembly with DNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1475, 245–255 (2000).
Howard, K. A. et al. Chitosan/siRNA nanoparticle-mediated TNF-α knockdown in peritoneal macrophages for anti-inflammatory treatment in a murine arthritis model. Mol. Ther. 17, 162–168 (2009).
Whitehead, K. A., Langer, R., Anderson, D. G. Knocking down barriers: advances in siRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 8, 129–138 (2009).
Komano, Y. et al. Arthritic joint-targeting small interfering RNA-encapsulated liposome: implication for treatment strategy for rheumatoid arthritis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 340, 109–113 (2012).
Schlegel, A. et al. Anionic polymers for decreased toxicity and enhanced in vivo delivery of siRNA complexed with cationic liposomes. J. Control Release 152, 393–401 (2011).
Khoury, M. et al. Efficient new cationic liposome formulation for systemic delivery of small interfering RNA silencing tumor necrosis factor alpha in experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 1867–1877 (2006).
Khoury, M. et al. Efficient suppression of murine arthritis by combined anticytokine small interfering RNA lipoplexes. Arthritis Rheum. 58, 2356–2367 (2008).
Courties, G. et al. Cytosolic phospholipase A2α gene silencing in the myeloid lineage alters development of TH1 responses and reduces disease severity in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 63, 681–690 (2011).
Courties, G. et al. In vivo RNAi-mediated silencing of TAK1 decreases inflammatory TH1 and TH17 cells through targeting of myeloid cells. Blood 116, 3505–3516 (2010).
Schett, G. Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoclasts. Arthritis Res. Ther. 9, 203 (2007).
Gerwin, N., Hops, C. & Lucke, A. Intraarticular drug delivery in osteoarthritis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 58, 226–242 (2006).
Ulrich-Vinther, M. et al. In vivo gene delivery to articular chondrocytes mediated by an adeno-associated virus vector. J. Orthop. Res. 22, 726–734 (2004).
Santangelo, K. S. & Bertone, A. L. Effective reduction of the interleukin-1β transcript in osteoarthritis-prone guinea pig chondrocytes via short hairpin RNA mediated RNA interference influences gene expression of mediators implicated in disease pathogenesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 19, 1449–1457 (2011).
Chen, L. X. et al. Suppression of early experimental osteoarthritis by in vivo delivery of the adenoviral vector-mediated NF-κBp65-specific siRNA. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 16, 174–184 (2008).
Kinne, R. W., Stuhlmüller, B. & Burmester, G. R. Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Macrophages. Arthritis Res. Ther. 9, 224 (2007).
Thurlings, R. M. et al. Monocyte scintigraphy in rheumatoid arthritis: the dynamics of monocyte migration in immune-mediated inflammatory disease. PLoS ONE 4, e7865 (2009).
Breedveld, F. C. et al. Association between baseline radiographic damage and improvement in physical function after treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64, 52–55 (2005).
Acknowledgements
The authors of this article are supported by grants from INSERM and the IMI EU funded project BeTheCure (contract n° 115142-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors contributed equally to all aspects of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Apparailly, F., Jorgensen, C. siRNA-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 9, 56–62 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2012.176
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2012.176
This article is cited by
-
Unlocking the potential of RNAi as a therapeutic strategy against infectious viruses: an in-silico study
Chemical Papers (2024)
-
A novel Anti-ROS osteoblast-specific delivery system for ankylosing spondylitis treatment via suppression of both inflammation and pathological new bone formation
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2023)
-
Induction of apoptosis and autosis in cardiomyocytes by the combination of homocysteine and copper via NOX-mediated p62 expression
Cell Death Discovery (2022)
-
Dynamic profiles, biodistribution and integration evaluation after intramuscular/intravenous delivery of a novel therapeutic DNA vaccine encoding chicken type II collagen for rheumatoid arthritis in vaccinated normal rodent
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2019)
-
Breaking Prometheus's curse for cartilage regeneration
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2017)