Abstract
Constitutive activation of STAT5 is critical for the maintenance of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) characterized by the BCR-ABL oncoprotein. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) for the STAT5-activating kinase JAK2 have been discussed as a treatment option for CML patients. Using murine leukemia models combined with inducible ablation of JAK2, we show JAK2 dependence for initial lymphoid transformation, which is lost once leukemia is established. In contrast, initial myeloid transformation and leukemia maintenance were independent of JAK2. Nevertheless, several JAK2 TKIs induced apoptosis in BCR-ABL+ cells irrespective of the presence of JAK2. This is caused by the previously unknown direct 'off-target' inhibition of BCR-ABL. Cellular and enzymatic analyses suggest that BCR-ABL phosphorylates STAT5 directly. Our findings suggest uncoupling of the canonical JAK2-STAT5 module upon BCR-ABL expression, thereby making JAK2 targeting dispensable. Thus, attempts to pharmacologically target STAT5 in BCR-ABL+ diseases need to focus on STAT5 itself.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wong, S. & Witte, O.N. The BCR-ABL story: bench to bedside and back. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22, 247–306 (2004).
Goldman, J.M. & Melo, J.V. Chronic myeloid leukemia–advances in biology and new approaches to treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 349, 1451–1464 (2003).
Lugo, T.G., Pendergast, A.M., Muller, A.J. & Witte, O.N. Tyrosine kinase activity and transformation potency of bcr-abl oncogene products. Science 247, 1079–1082 (1990).
Capdeville, R., Buchdunger, E., Zimmermann, J. & Matter, A. Glivec (STI571, imatinib), a rationally developed, targeted anticancer drug. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 1, 493–502 (2002).
Weisberg, E., Manley, P.W., Cowan-Jacob, S.W., Hochhaus, A. & Griffin, J.D. Second generation inhibitors of BCR-ABL for the treatment of imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 7, 345–356 (2007).
Druker, B.J. et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 355, 2408–2417 (2006).
Hochhaus, A. et al. Six-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for the first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 23, 1054–1061 (2009).
Shah, N.P. & Sawyers, C.L. Mechanisms of resistance to STI571 in Philadelphia chromosome-associated leukemias. Oncogene 22, 7389–7395 (2003).
Druker, B.J. Translation of the Philadelphia chromosome into therapy for CML. Blood 112, 4808–4817 (2008).
Nicolini, F.E. et al. Epidemiological study on survival of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) patients with BCR-ABL T315I mutation. Blood 114, 5271–5278 (2009).
Carlesso, N., Frank, D.A. & Griffin, J.D. Tyrosyl phosphorylation and DNA binding activity of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins in hematopoietic cell lines transformed by Bcr/Abl. J. Exp. Med. 183, 811–820 (1996).
Ilaria, R.L. Jr. & Van Etten, R.A. P210 and P190(BCR/ABL) induce the tyrosine phosphorylation and DNA binding activity of multiple specific STAT family members. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 31704–31710 (1996).
Shuai, K., Halpern, J., ten Hoeve, J., Rao, X. & Sawyers, C.L. Constitutive activation of STAT5 by the BCR-ABL oncogene in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Oncogene 13, 247–254 (1996).
Nieborowska-Skorska, M. et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)5 activation by BCR/ABL is dependent on intact Src homology (SH)3 and SH2 domains of BCR/ABL and is required for leukemogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 189, 1229–1242 (1999).
Scherr, M. et al. Enhanced sensitivity to inhibition of SHP2, STAT5, and Gab2 expression in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Blood 107, 3279–3287 (2006).
Ye, D., Wolff, N., Li, L., Zhang, S. & Ilaria, R.L. Jr. STAT5 signaling is required for the efficient induction and maintenance of CML in mice. Blood 107, 4917–4925 (2006).
Hoelbl, A. et al. Clarifying the role of Stat5 in lymphoid development and Abelson-induced transformation. Blood 107, 4898–4906 (2006).
Hoelbl, A. et al. Stat5 is indispensable for the maintenance of bcr/abl-positive leukaemia. EMBO Mol. Med. 2, 98–110 (2010).
Warsch, W. et al. High STAT5 levels mediate imatinib resistance and indicate disease progression in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 117, 3409–3420 (2011).
Shuai, K. et al. Interferon activation of the transcription factor Stat91 involves dimerization through SH2-phosphotyrosyl peptide interactions. Cell 76, 821–828 (1994).
Kisseleva, T., Bhattacharya, S., Braunstein, J. & Schindler, C.W. Signaling through the JAK/STAT pathway, recent advances and future challenges. Gene 285, 1–24 (2002).
Ihle, J.N. & Gilliland, D.G. Jak2: normal function and role in hematopoietic disorders. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 17, 8–14 (2007).
Kralovics, R. Genetic complexity of myeloproliferative neoplasms. Leukemia 22, 1841–1848 (2008).
Hedvat, M. et al. The JAK2 inhibitor AZD1480 potently blocks Stat3 signaling and oncogenesis in solid tumors. Cancer Cell 16, 487–497 (2009).
Miyamoto, N. et al. The JAK2 inhibitor AG490 predominantly abrogates the growth of human B-precursor leukemic cells with 11q23 translocation or Philadelphia chromosome. Leukemia 15, 1758–1768 (2001).
Xie, S. et al. Involvement of Jak2 tyrosine phosphorylation in Bcr-Abl transformation. Oncogene 20, 6188–6195 (2001).
Samanta, A. et al. Janus kinase 2 regulates Bcr-Abl signaling in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 25, 463–472 (2011).
Samanta, A.K., Lin, H., Sun, T., Kantarjian, H. & Arlinghaus, R.B. Janus kinase 2: a critical target in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res. 66, 6468–6472 (2006).
Pardanani, A. et al. JAK inhibitor therapy for myelofibrosis: critical assessment of value and limitations. Leukemia 25, 218–225 (2011).
Pardanani, A. et al. TG101209, a small molecule JAK2-selective kinase inhibitor potently inhibits myeloproliferative disorder-associated JAK2V617F and MPLW515L/K mutations. Leukemia 21, 1658–1668 (2007).
Wernig, G. et al. Efficacy of TG101348, a selective JAK2 inhibitor, in treatment of a murine model of JAK2V617F-induced polycythemia vera. Cancer Cell 13, 311–320 (2008).
Geron, I. et al. Selective inhibition of JAK2-driven erythroid differentiation of polycythemia vera progenitors. Cancer Cell 13, 321–330 (2008).
Wagner, K.-U. et al. Impaired alveologenesis and maintenance of secretory mammary epithelial cells in Jak2 conditional knockout mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24, 5510–5520 (2004).
Neubauer, H. et al. Jak2 deficiency defines an essential developmental checkpoint in definitive hematopoiesis. Cell 93, 397–409 (1998).
Samanta, A.K. et al. Jak2 inhibition deactivates Lyn kinase through the SET-PP2A–SHP1 pathway, causing apoptosis in drug-resistant cells from chronic myelogenous leukemia patients. Oncogene 28, 1669–1681 (2009).
Baker, S.J., Rane, S.G. & Reddy, E.P. Hematopoietic cytokine receptor signaling. Oncogene 26, 6724–6737 (2007).
Blake, R.A. et al. SU6656, a selective src family kinase inhibitor, used to probe growth factor signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 9018–9027 (2000).
Rix, U. et al. Chemical proteomic profiles of the BCR-ABL inhibitors imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib reveal novel kinase and non-kinase targets. Blood 110, 4055–4063 (2007).
Remsing Rix, L.L. et al. Global target profile of the kinase inhibitor bosutinib in primary chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia 23, 477–485 (2009).
Gouilleux, F., Wakao, H., Mundt, M. & Groner, B. Prolactin induces phosphorylation of Tyr694 of Stat5 (MGF), a prerequisite for DNA binding and induction of transcription. EMBO J. 13, 4361–4369 (1994).
de Jong, R., ten Hoeve, J., Heisterkamp, N. & Groffen, J. Tyrosine 207 in CRKL is the BCR/ABL phosphorylation site. Oncogene 14, 507–513 (1997).
Songyang, Z. et al. Catalytic specificity of protein-tyrosine kinases is critical for selective signalling. Nature 373, 536–539 (1995).
Pardanani, A. JAK2 inhibitor therapy in myeloproliferative disorders: rationale, preclinical studies and ongoing clinical trials. Leukemia 22, 23–30 (2008).
Quintás-Cardama, A. et al. Preclinical characterization of the selective JAK1/2 inhibitor INCB018424: therapeutic implications for the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 115, 3109–3117 (2010).
Lasho, T.L. et al. TG101348, a JAK2-selective antagonist, inhibits primary hematopoietic cells derived from myeloproliferative disorder patients with JAK2V617F, MPLW515K or JAK2 exon 12 mutations as well as mutation negative patients. Leukemia 22, 1790–1792 (2008).
Lim, W.A. & Pawson, T. Phosphotyrosine signaling: evolving a new cellular communication system. Cell 142, 661–667 (2010).
Brehme, M. et al. Charting the molecular network of the drug target Bcr-Abl. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 7414–7419 (2009).
Titz, B. et al. The proximal signaling network of the BCR-ABL1 oncogene shows a modular organization. Oncogene 29, 5895–5910 (2010).
Nelson, E.A. et al. The STAT5 inhibitor pimozide decreases survival of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells resistant to kinase inhibitors. Blood 117, 3421–3429 (2011).
Hantschel, O. et al. A myristoyl/phosphotyrosine switch regulates c-Abl. Cell 112, 845–857 (2003).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants WWTF-LS037 and SFB-28-10 to V.S. and GenAU-PLACEBO to G.S.-F. and V.S. We thank S. Georgeon for expert technical assistance. We thank all members of participating laboratories and R. Moriggl and T. Decker for continuous support and discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
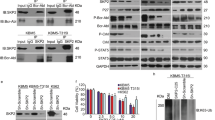
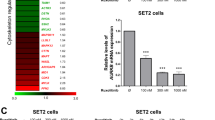
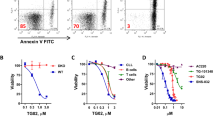
O.H. did the experiments in Figures 5d,e, 6b–f and 7. W.W. did the experiments in Figures 1, 2d,e, 3b–e, 4b–e, 5a–c,g and 6a. E.E. did the experiments in Figures 2a,b, 3a and 4a. I.K. provided technical assistance and vital tools for experiments in Figures 5d,e, 6b–f and 7. F.G. did the experiments in Figure 2c. K.-U.W. provided the conditional Jak2 knockout mice. G.S.-F. and V.S. designed the experiments and interpreted the data. O.H., W.W., G.S.-F. and V.S. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Results (PDF 2523 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hantschel, O., Warsch, W., Eckelhart, E. et al. BCR-ABL uncouples canonical JAK2-STAT5 signaling in chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat Chem Biol 8, 285–293 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.775
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.775