Abstract
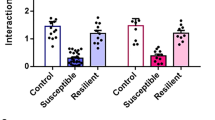
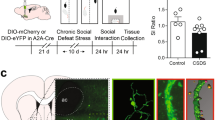
Molecular and cellular adaptations in nucleus accumbens (NAc) medium spiny neurons (MSNs) underlie stress-induced depression-like behavior, but the molecular substrates mediating cellular plasticity and activity in MSN subtypes in stress susceptibility are poorly understood. We find the transcription factor early growth response 3 (EGR3) is increased in D1 receptor containing MSNs of mice susceptible to social defeat stress. Genetic reduction of Egr3 levels in D1-MSNs prevented depression-like outcomes in stress susceptible mice by preventing D1-MSN dendritic atrophy, reduced frequency of excitatory input and altered in vivo activity. Overall, we identify NAc neuronal-subtype molecular control of dendritic morphology and related functional adaptations, which underlie susceptibility to stress.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrari AJ, Charlson FJ, Norman RE, Patten SB, Freedman G, Murray CJ et al. Burden of depressive disorders by country, sex, age, and year: Findings from the global burden of disease study 2010. PLoS Med 2013; 10: e1001547.
Krishnan V, Nestler EJ . The molecular neurobiology of depression. Nature 2008; 455: 894–902.
Russo SJ, Nestler EJ . The brain reward circuitry in mood disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 2013; 14: 609–625.
Floresco SB . The nucleus accumbens: an interface between cognition, emotion, and action. Annu Rev Psychol 2015; 66: 25–52.
Francis TC, Chandra R, Friend DM, Finkel E, Dayrit G, Miranda J et al. Nucleus accumbens medium spiny neuron subtypes mediate depression-related outcomes to social defeat stress. Biol Psychiatry 2015; 77: 212–222.
Lim BK, Huang KW, Grueter BA, Rothwell PE, Malenka RC . Anhedonia requires MC4R-mediated synaptic adaptations in nucleus accumbens. Nature 2012; 487: 183–189.
Dias C, Feng J, Sun H, Shao NY, Mazei-Robison MS, Damez-Werno D et al. Beta-catenin mediates stress resilience through Dicer1/microRNA regulation. Nature 2014; 516: 51–55.
Francis TC, Lobo MK . Emerging role for nucleus accumbens medium spiny neuron subtypes in depression. Biol Psychiatry 2016; 81: 645–653.
Smith RJ, Lobo MK, Spencer S, Kalivas PW . Cocaine-induced adaptations in D1 and D2 accumbens projection neurons (a dichotomy not necessarily synonymous with direct and indirect pathways). Curr Opin Neurobiol 2013; 23: 546–552.
Kupchik YM, Brown RM, Heinsbroek JA, Lobo MK, Schwartz DJ, Kalivas PW . Coding the direct/indirect pathways by D1 and D2 receptors is not valid for accumbens projections. Nat Neurosci 2015; 18: 1230–1232.
Golden SA, Christoffel DJ, Heshmati M, Hodes GE, Magida J, Davis K et al. Epigenetic regulation of RAC1 induces synaptic remodeling in stress disorders and depression. Nat Med 2013; 19: 337–344.
Christoffel DJ, Golden SA, Dumitriu D, Robison AJ, Janssen WG, Ahn HF et al. IkappaB kinase regulates social defeat stress-induced synaptic and behavioral plasticity. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 314–321.
Kim JH, Roberts DS, Hu Y, Lau GC, Brooks-Kayal AR, Farb DH et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor uses CREB and Egr3 to regulate NMDA receptor levels in cortical neurons. J Neurochem 2012; 120: 210–219.
Roberts DS, Hu Y, Lund IV, Brooks-Kayal AR, Russek SJ . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-induced synthesis of early growth response factor 3 (Egr3) controls the levels of type A GABA receptor alpha 4 subunits in hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 29431–29435.
Li L, Carter J, Gao X, Whitehead J, Tourtellotte WG . The neuroplasticity-associated arc gene is a direct transcriptional target of early growth response (egr) transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 10286–10300.
Li L, Yun SH, Keblesh J, Trommer BL, Xiong H, Radulovic J et al. Egr3, a synaptic activity regulated transcription factor that is essential for learning and memory. Mol Cell Neurosci 2007; 35: 76–88.
Thiel G, Mayer SI, Muller I, Stefano L, Rossler OG . Egr-1- A ca(2+)-regulated transcription factor. Cell Calcium 2010; 47: 397–403.
Milbrandt J . A nerve growth factor-induced gene encodes a possible transcriptional regulatory factor. Science 1987; 238: 797–799.
Malkani S, Rosen JB . Specific induction of early growth response gene 1 in the lateral nucleus of the amygdala following contextual fear conditioning in rats. Neuroscience 2000; 97: 693–702.
Bhat RV, Worley PF, Cole AJ, Baraban JM . Activation of the zinc finger encoding gene krox-20 in adult rat brain: Comparison with zif268. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1992; 13: 263–266.
Gallitano-Mendel A, Izumi Y, Tokuda K, Zorumski CF, Howell MP, Muglia LJ et al. The immediate early gene early growth response gene 3 mediates adaptation to stress and novelty. Neuroscience 2007; 148: 633–643.
Chandra R, Francis TC, Konkalmatt P, Amgalan A, Gancarz AM, Dietz DM et al. Opposing role for Egr3 in nucleus accumbens cell subtypes in cocaine action. J Neurosci 2015; 35: 7927–7937.
O'Donovan KJ, Tourtellotte WG, Millbrandt J, Baraban JM . The EGR family of transcription-regulatory factors: Progress at the interface of molecular and systems neuroscience. Trends Neurosci 1999; 22: 167–173.
Jones MW, Errington ML, French PJ, Fine A, Bliss TV, Garel S et al. A requirement for the immediate early gene Zif268 in the expression of late LTP and long-term memories. Nat Neurosci 2001; 4: 289–296.
Quach DH, Oliveira-Fernandes M, Gruner KA, Tourtellotte WG . A sympathetic neuron autonomous role for Egr3-mediated gene regulation in dendrite morphogenesis and target tissue innervation. J Neurosci 2013; 33: 4570–4583.
McEwen BS . Physiology and neurobiology of stress and adaptation: Central role of the brain. Physiol Rev 2007; 87: 873–904.
McEwen BS, Bowles NP, Gray JD, Hill MN, Hunter RG, Karatsoreos IN et al. Mechanisms of stress in the brain. Nat Neurosci 2015; 18: 1353–1363.
Herman JP, Ostrander MM, Mueller NK, Figueiredo H . Limbic system mechanisms of stress regulation: Hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2005; 29: 1201–1213.
Gong S, Doughty M, Harbaugh CR, Cummins A, Hatten ME, Heintz N et al. Targeting cre recombinase to specific neuron populations with bacterial artificial chromosome constructs. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 9817–9823.
Sanz E, Yang L, Su T, Morris DR, McKnight GS, Amieux PS . Cell-type-specific isolation of ribosome-associated mRNA from complex tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 13939–13944.
Berton O, McClung CA, Dileone RJ, Krishnan V, Renthal W, Russo SJ et al. Essential role of BDNF in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway in social defeat stress. Science 2006; 311: 864–868.
Krishnan V, Han MH, Graham DL, Berton O, Renthal W, Russo SJ et al. Molecular adaptations underlying susceptibility and resistance to social defeat in brain reward regions. Cell 2007; 131: 391–404.
Longair MH, Baker DA, Armstrong JD . Simple neurite tracer: Open source software for reconstruction, visualization and analysis of neuronal processes. Bioinformatics 2011; 27: 2453–2454.
Prasad KM, Smith RS, Xu Y, French BA . A single direct injection into the left ventricular wall of an adeno-associated virus 9 (AAV9) vector expressing extracellular superoxide dismutase from the cardiac troponin-T promoter protects mice against myocardial infarction. J Gene Med 2011; 13: 333–341.
Pnevmatikakis EA, Soudry D, Gao Y, Machado TA, Merel J, Pfau D et al. Simultaneous denoising, deconvolution, and demixing of calcium imaging data. Neuron 2016; 89: 285–299.
Lobo MK, Covington HE 3rd, Chaudhury D, Friedman AK, Sun H, Damez-Werno D et al. Cell type-specific loss of BDNF signaling mimics optogenetic control of cocaine reward. Science 2010; 330: 385–390.
Chen H, Firestein BL . RhoA regulates dendrite branching in hippocampal neurons by decreasing cypin protein levels. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 8378–8386.
Berkel S, Tang W, Trevino M, Vogt M, Obenhaus HA, Gass P et al. Inherited and de novo SHANK2 variants associated with autism spectrum disorder impair neuronal morphogenesis and physiology. Hum Mol Genet 2012; 21: 344–357.
Cai DJ, Aharoni D, Shuman T, Shobe J, Biane J, Song W et al. A shared neural ensemble links distinct contextual memories encoded close in time. Nature 2016; 534: 115–118.
Ghosh KK, Burns LD, Cocker ED, Nimmerjahn A, Ziv Y, Gamal AE et al. Miniaturized integration of a fluorescence microscope. Nat Methods 2011; 8: 871–878.
Resendez SL, Jennings JH, Ung RL, Namboodiri VM, Zhou ZC, Otis JM et al. Visualization of cortical, subcortical and deep brain neural circuit dynamics during naturalistic mammalian behavior with head-mounted microscopes and chronically implanted lenses. Nat Protoc 2016; 11: 566–597.
Bolam JP, Hanley JJ, Booth PA, Bevan MD . Synaptic organisation of the basal ganglia. J Anat 2000; 196 (Pt 4): 527–542.
Vialou V, Bagot RC, Cahill ME, Ferguson D, Robison AJ, Dietz DM et al. Prefrontal cortical circuit for depression- and anxiety-related behaviors mediated by cholecystokinin: Role of DeltaFosB. J Neurosci 2014; 34: 3878–3887.
Schlaepfer TE, Cohen MX, Frick C, Kosel M, Brodesser D, Axmacher N et al. Deep brain stimulation to reward circuitry alleviates anhedonia in refractory major depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008; 33: 368–377.
George MS, Wassermann EM, Williams WA, Callahan A, Ketter TA, Basser P et al. Daily repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) improves mood in depression. Neuroreport 1995; 6: 1853–1856.
Calipari ES, Bagot RC, Purushothaman I, Davidson TJ, Yorgason JT, Pena CJ et al. In vivo imaging identifies temporal signature of D1 and D2 medium spiny neurons in cocaine reward. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2016; 113: 2726–2731.
Gunaydin LA, Grosenick L, Finkelstein JC, Kauvar IV, Fenno LE, Adhikari A et al. Natural neural projection dynamics underlying social behavior. Cell 2014; 157: 1535–1551.
Kravitz AV, Tye LD, Kreitzer AC . Distinct roles for direct and indirect pathway striatal neurons in reinforcement. Nat Neurosci 2012; 15: 816–818.
Turrigiano GG . The self-tuning neuron: synaptic scaling of excitatory synapses. Cell 2008; 135: 422–435.
Pratt KG, Aizenman CD . Homeostatic regulation of intrinsic excitability and synaptic transmission in a developing visual circuit. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 8268–8277.
Acknowledgements
We thank Brian N. Mathur and Scott M. Thompson (UMSOM) for input on electrophysiology experiments. This work was supported by NIMH R01MH106500, NIDA R01DA038613 and The One Mind / Janssen Rising Star Translational Research Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Francis, T., Chandra, R., Gaynor, A. et al. Molecular basis of dendritic atrophy and activity in stress susceptibility. Mol Psychiatry 22, 1512–1519 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.178
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.178
This article is cited by
-
α-MSH-catabolic enzyme prolylcarboxypeptidase in nucleus accumbens shell ameliorates stress susceptibility in mice through regulating synaptic plasticity
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2023)
-
Plasticity of synapses and reward circuit function in the genesis and treatment of depression
Neuropsychopharmacology (2023)
-
Transcriptome profiling of the ventral pallidum reveals a role for pallido-thalamic neurons in cocaine reward
Molecular Psychiatry (2022)
-
SWI/SNF chromatin remodeler complex within the reward pathway is required for behavioral adaptations to stress
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Cocaine-induced neuron subtype mitochondrial dynamics through Egr3 transcriptional regulation
Molecular Brain (2021)