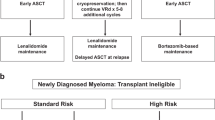
Abstract
Multiple myeloma (MM) is more recently being recognized as a heterogeneous group of disease with variability in outcomes based on specific clinical and biologic predictors. MM patients can be broadly categorized into standard, intermediate and high risk for disease relapse, morbidity and mortality. The high-risk features include patient-specific factors such as old age, poor performance status and comorbidities; clinical features such as primary plasma cell leukemia and extramedullary disease; disease-specific biologic features such as deletion 17p, t(4;14) and high-risk gene expression profiling signatures. The current paper reviews the available data on best therapeutic approaches for high-risk MM.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ludwig H, Durie BG, Bolejack V, Turesson I, Kyle RA, Blade J et al. Myeloma in patients younger than age 50 years presents with more favorable features and shows better survival: an analysis of 10 549 patients from the International Myeloma Working Group. Blood 2008; 111: 4039–4047.
Reece DE, Bredeson C, Perez WS, Jagannath S, Zhang MJ, Ballen KK et al. Autologous stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma patients <60 vs >/=60 years of age. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 32: 1135–1143.
Siegel DS, Desikan KR, Mehta J, Singhal S, Fassas A, Munshi N et al. Age is not a prognostic variable with autotransplants for multiple myeloma. Blood 1999; 93: 51–54.
Bringhen S, Mateos MV, Zweegman S, Larocca A, Falcone AP, Oriol A et al. Age and organ damage correlate with poor survival in myeloma patients: meta-analysis of 1435 individual patient data from 4 randomized trials. Haematologica 2013; 98: 980–987.
Palumbo A, Bringhen S, Mateos MV, Larocca A, Facon T, Kumar SK et al. Geriatric assessment predicts survival and toxicities in elderly myeloma: an International Myeloma Working Group report. Blood 2015; 125: 2068–2074.
Fonseca R, Bergsagel PL, Drach J, Shaughnessy J, Gutierrez N, Stewart AK et al. International Myeloma Working Group molecular classification of multiple myeloma: spotlight review. Leukemia 2009; 23: 2210–2221.
Boyd KD, Ross FM, Chiecchio L, Dagrada GP, Konn ZJ, Tapper WJ et al. A novel prognostic model in myeloma based on co-segregating adverse FISH lesions and the ISS: analysis of patients treated in the MRC Myeloma IX trial. Leukemia 2012; 26: 349–355.
Gutierrez NC, Castellanos MV, Martin ML, Mateos MV, Hernandez JM, Fernandez M et al. Prognostic and biological implications of genetic abnormalities in multiple myeloma undergoing autologous stem cell transplantation: t(4;14) is the most relevant adverse prognostic factor, whereas RB deletion as a unique abnormality is not associated with adverse prognosis. Leukemia 2007; 21: 143–150.
Gertz MA, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A, Greipp PR, Litzow MR, Henderson KJ et al. Clinical implications of t(11;14)(q13;q32), t(4;14)(p16.3;q32), and -17p13 in myeloma patients treated with high-dose therapy. Blood 2005; 106: 2837–2840.
Avet-Loiseau H, Attal M, Moreau P, Charbonnel C, Garban F, Hulin C et al. Genetic abnormalities and survival in multiple myeloma: the experience of the Intergroupe Francophone du Myelome. Blood 2007; 109: 3489–3495.
Kumar S, Fonseca R, Ketterling RP, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Gertz MA et al. Trisomies in multiple myeloma: impact on survival in patients with high-risk cytogenetics. Blood 2012; 119: 2100–2105.
Hebraud B, Magrangeas F, Cleynen A, Lauwers-Cances V, Chretien ML, Hulin C et al. Role of additional chromosomal changes in the prognostic value of t(4;14) and del(17p) in multiple myeloma: the IFM experience. Blood 2015; 125: 2095–2100.
Avet-Loiseau H, Attal M, Campion L, Caillot D, Hulin C, Marit G et al. Long-term analysis of the IFM 99 trials for myeloma: cytogenetic abnormalities [t(4;14), del(17p), 1q gains] play a major role in defining long-term survival. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 1949–1952.
Avet-Loiseau H, Malard F, Campion L, Magrangeas F, Sebban C, Lioure B et al. Translocation t(14;16) and multiple myeloma: is it really an independent prognostic factor?. Blood 2011; 117: 2009–2011.
Avet-Loiseau H, Soulier J, Fermand JP, Yakoub-Agha I, Attal M, Hulin C et al. Impact of high-risk cytogenetics and prior therapy on outcomes in patients with advanced relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma treated with lenalidomide plus dexamethasone. Leukemia 2010; 24: 623–628.
Mateo G, Castellanos M, Rasillo A, Gutierrez NC, Montalban MA, Martin ML et al. Genetic abnormalities and patterns of antigenic expression in multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 3661–3667.
Avet-Loiseau H, Li C, Magrangeas F, Gouraud W, Charbonnel C, Harousseau JL et al. Prognostic significance of copy-number alterations in multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 4585–4590.
Smadja NV, Bastard C, Brigaudeau C, Leroux D, Fruchart C . Hypodiploidy is a major prognostic factor in multiple myeloma. Blood 2001; 98: 2229–2238.
Garcia-Sanz R, Orfao A, Gonzalez M, Moro MJ, Hernandez JM, Ortega F et al. Prognostic implications of DNA aneuploidy in 156 untreated multiple myeloma patients. Castelano-Leones (Spain) Cooperative Group for the Study of Monoclonal Gammopathies. Br J Haematol 1995; 90: 106–112.
Chng WJ, Dispenzieri A, Chim CS, Fonseca R, Goldschmidt H, Lentzsch S et al. IMWG consensus on risk stratification in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2014; 28: 269–277.
Durie BG, Salmon SE . A clinical staging system for multiple myeloma. Correlation of measured myeloma cell mass with presenting clinical features, response to treatment, and survival. Cancer 1975; 36: 842–854.
Greipp PR, San Miguel J, Durie BG, Crowley JJ, Barlogie B, Blade J et al. International staging system for multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 3412–3420.
Avet-Loiseau H, Durie BG, Cavo M, Attal M, Gutierrez N, Haessler J et al. Combining fluorescent in situ hybridization data with ISS staging improves risk assessment in myeloma: an International Myeloma Working Group collaborative project. Leukemia 2013; 27: 711–717.
Moreau P, Cavo M, Sonneveld P, Rosinol L, Attal M, Pezzi A et al. Combination of international scoring system 3, high lactate dehydrogenase, and t(4;14) and/or del(17p) identifies patients with multiple myeloma (MM) treated with front-line autologous stem-cell transplantation at high risk of early MM progression-related death. J Clin Oncol 2014; 32: 2173–2180.
Cavo M SH, Rosinol L et al. Double vs single autologous stem cell transplantation after bortezomib-based induction regimens for multiple myeloma: an integrated analysis of patient-level data from Phase European III Studies. Blood 2013; 122: 767.
Shaughnessy JD Jr, Zhan F, Burington BE, Huang Y, Colla S, Hanamura I et al. A validated gene expression model of high-risk multiple myeloma is defined by deregulated expression of genes mapping to chromosome 1. Blood 2007; 109: 2276–2284.
Decaux O, Lode L, Magrangeas F, Charbonnel C, Gouraud W, Jezequel P et al. Prediction of survival in multiple myeloma based on gene expression profiles reveals cell cycle and chromosomal instability signatures in high-risk patients and hyperdiploid signatures in low-risk patients: a study of the Intergroupe Francophone du Myelome. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 4798–4805.
Kuiper R, Broyl A, de Knegt Y, van Vliet MH, van Beers EH, van der Holt B et al. A gene expression signature for high-risk multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2012; 26: 2406–2413.
Gonsalves WI, Rajkumar SV, Gupta V, Morice WG, Timm MM, Singh PP et al. Quantification of clonal circulating plasma cells in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: implications for redefining high-risk myeloma. Leukemia 2014; 28: 2060–2065.
Usmani SZ, Nair B, Qu P, Hansen E, Zhang Q, Petty N et al. Primary plasma cell leukemia: clinical and laboratory presentation, gene-expression profiling and clinical outcome with Total Therapy protocols. Leukemia 2012; 26: 2398–2405.
Bianchi G, Kyle RA, Larson DR, Witzig TE, Kumar S, Dispenzieri A et al. High levels of peripheral blood circulating plasma cells as a specific risk factor for progression of smoldering multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2013; 27: 680–685.
Usmani SZ, Heuck C, Mitchell A, Szymonifka J, Nair B, Hoering A et al. Extramedullary disease portends poor prognosis in multiple myeloma and is over-represented in high-risk disease even in the era of novel agents. Haematologica 2012; 97: 1761–1767.
Zamagni E, Patriarca F, Nanni C, Zannetti B, Englaro E, Pezzi A et al. Prognostic relevance of 18- F FDG PET/CT in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients treated with up-front autologous transplantation. Blood 2011; 118: 5989–5995.
Rosinol L, Oriol A, Teruel AI, Hernandez D, Lopez-Jimenez J, de la Rubia J et al. Superiority of bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone (VTD) as induction pretransplantation therapy in multiple myeloma: a randomized phase 3 PETHEMA/GEM study. Blood 2012; 120: 1589–1596.
Paiva B, Gutierrez NC, Rosinol L, Vidriales MB, Montalban MA, Martinez-Lopez J et al. High-risk cytogenetics and persistent minimal residual disease by multiparameter flow cytometry predict unsustained complete response after autologous stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma. Blood 2012; 119: 687–691.
Fonseca R, Blood E, Rue M, Harrington D, Oken MM, Kyle RA et al. Clinical and biologic implications of recurrent genomic aberrations in myeloma. Blood 2003; 101: 4569–4575.
Avet-Loiseau H, Leleu X, Roussel M, Moreau P, Guerin-Charbonnel C, Caillot D et al. Bortezomib plus dexamethasone induction improves outcome of patients with t(4;14) myeloma but not outcome of patients with del(17p). J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 4630–4634.
Lokhorst HM, van der Holt B, Zweegman S, Vellenga E, Croockewit S, van Oers MH et al. A randomized phase 3 study on the effect of thalidomide combined with adriamycin, dexamethasone, and high-dose melphalan, followed by thalidomide maintenance in patients with multiple myeloma. Blood 2010; 115: 1113–1120.
Morgan GJ, Davies FE, Gregory WM, Bell SE, Szubert AJ, Navarro Coy N et al. Cyclophosphamide, thalidomide, and dexamethasone as induction therapy for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients destined for autologous stem-cell transplantation: MRC Myeloma IX randomized trial results. Haematologica 2012; 97: 442–450.
Morgan GJ, Davies FE, Gregory WM, Russell NH, Bell SE, Szubert AJ et al. Cyclophosphamide, thalidomide, and dexamethasone (CTD) as initial therapy for patients with multiple myeloma unsuitable for autologous transplantation. Blood 2011; 118: 1231–1238.
Morgan GJ, Gregory WM, Davies FE, Bell SE, Szubert AJ, Brown JM et al. The role of maintenance thalidomide therapy in multiple myeloma: MRC Myeloma IX results and meta-analysis. Blood 2012; 119: 7–15.
Kapoor P, Kumar S, Fonseca R, Lacy MQ, Witzig TE, Hayman SR et al. Impact of risk stratification on outcome among patients with multiple myeloma receiving initial therapy with lenalidomide and dexamethasone. Blood 2009; 114: 518–521.
Attal M, Lauwers-Cances V, Marit G, Caillot D, Moreau P, Facon T et al. Lenalidomide maintenance after stem-cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: 1782–1791.
Neben K, Lokhorst HM, Jauch A, Bertsch U, Hielscher T, van der Holt B et al. Administration of bortezomib before and after autologous stem cell transplantation improves outcome in multiple myeloma patients with deletion 17p. Blood 2012; 119: 940–948.
Cavo M, Moreau P, Sonneveld P, Blade J, Goldshmidt H, San Miguel J et al. Impact of bortezomib incorporated into autotransplantation on outcomes of myeloma patients with high-risk cytogenetics: an integrated analysis of 1894 patients enrolled in four European Phase 3 Studies. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2012; 2012: 749.
San Miguel JF, Schlag R, Khuageva NK, Dimopoulos MA, Shpilberg O, Kropff M et al. Bortezomib plus melphalan and prednisone for initial treatment of multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 906–917.
Mateos MV, Gutierrez NC, Martin-Ramos ML, Paiva B, Montalban MA, Oriol A et al. Outcome according to cytogenetic abnormalities and DNA ploidy in myeloma patients receiving short induction with weekly bortezomib followed by maintenance. Blood 2011; 118: 4547–4553.
Rajkumar SV, Jacobus S, Callander NS, Fonseca R, Vesole DH, Williams ME et al. Lenalidomide plus high-dose dexamethasone versus lenalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone as initial therapy for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: an open-label randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2010; 11: 29–37.
Avet-Loiseau H, Hulin C, Campion L, Rodon P, Marit G, Attal M et al. Chromosomal abnormalities are major prognostic factors in elderly patients with multiple myeloma: the intergroupe francophone du myelome experience. J Clin Oncol 2013; 31: 2806–2809.
Usmani SZ SR, Ailawadhi S et al. SWOG 1211: initial report on phase I trial of RVD-elotuzumab for newly diagnosed high risk multiple myeloma (HRMM). Blood 2014; 124: 4762.
Usmani SZ, Hoering A . Heterogeneity of outcome with single-agent carfilzomib: all relapsed/refractory myelomas are not created equal. Leukemia 2013; 27: 2269–2271.
Shaughnessy JD, Zhou Y, Haessler J, van Rhee F, Anaissie E, Nair B et al. TP53 deletion is not an adverse feature in multiple myeloma treated with total therapy 3. Br J Haematol 2009; 147: 347–351.
Schilling G, Hansen T, Shimoni A, Zabelina T, Perez-Simon JA, Gutierrez NC et al. Impact of genetic abnormalities on survival after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2008; 22: 1250–1255.
Krishnan A, Pasquini MC, Logan B, Stadtmauer EA, Vesole DH, Alyea E 3rd et al. Autologous haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation followed by allogeneic or autologous haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma (BMT CTN 0102): a phase 3 biological assignment trial. Lancet Oncol 2011; 12: 1195–1203.
Roos-Weil D, Moreau P, Avet-Loiseau H, Golmard JL, Kuentz M, Vigouroux S et al. Impact of genetic abnormalities after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma: a report of the Societe Francaise de Greffe de Moelle et de Therapie Cellulaire. Haematologica 2011; 96: 1504–1511.
Kroger N, Badbaran A, Zabelina T, Ayuk F, Wolschke C, Alchalby H et al. Impact of high-risk cytogenetics and achievement of molecular remission on long-term freedom from disease after autologous-allogeneic tandem transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 398–404.
Jakubowiak AJ, Siegel DS, Martin T, Wang M, Vij R, Lonial S et al. Treatment outcomes in patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma and high-risk cytogenetics receiving single-agent carfilzomib in the PX-171-003-A1 study. Leukemia 2013; 27: 2351–2356.
Dimopoulos MA, Weisel K, Song KW, Delforge M, Karlin L, Goldshmidt H et al. Final analysis, cytogenetics, long-term treatment, and long-term survival in MM-003, a phase 3 study comparing pomalidomide+low-dose dexamethasone (POM+LoDEX) vs high-dose dexamethasone (HiDEX) in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). Blood 2013; 122: 408.
Leleu X, Karlin L, Marco M, Hulin C, Garderet L, Roussel M et al. Pomalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) with deletion (del)17p and/or translocation t(4;14). Blood 2013; 122: 689.
Shah JJ, Stadtmauer E, Abonour R, Cohen AD, Bensinger WI, Gasparetto C et al. A multi-center phase I/II trial of carfilzomib and pomalidomide with dexamethasone (CAR-POM-D) in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2013; 122: 690.
Mikhael JR, Dingli D, Roy V, Reeder CB, Buadi FK, Hayman SR et al. Management of newly diagnosed symptomatic multiple myeloma: updated Mayo Stratification of Myeloma and Risk-Adapted Therapy (mSMART) consensus guidelines 2013. Mayo Clin Proc 2013; 88: 360–376.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
SZU is a consultant to Celgene, Millennium, Onyx and Sanofi, received research funding from ArrayBioPharma, Celgene, Onyx, Janssen and Pharmacyclics, and speaking honoraria from Celgene, Millennium and Onyx. M-VM has received honoraria of lectures and advisory boards from Janssen, Celgene, Onyx, Millennium and Novartis. JSM participates in advisory boards for Celgene, Millennium, Janssen, Novartis, BMS, Onyx and Sanofi. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Usmani, S., Rodriguez-Otero, P., Bhutani, M. et al. Defining and treating high-risk multiple myeloma. Leukemia 29, 2119–2125 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.209
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.209
This article is cited by
-
Impact of chromosomal abnormalities on the efficacy of lenalidomide plus dexamethasone treatment in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma
International Journal of Hematology (2019)
-
Response and progression-free survival according to planned treatment duration in patients with relapsed multiple myeloma treated with carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd) versus lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) in the phase III ASPIRE study
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2018)
-
Clinical predictors of long-term survival in newly diagnosed transplant eligible multiple myeloma — an IMWG Research Project
Blood Cancer Journal (2018)
-
Flavopiridol enhances ABT-199 sensitivity in unfavourable-risk multiple myeloma cells in vitro and in vivo
British Journal of Cancer (2018)
-
Real-world data on prognosis and outcome of primary plasma cell leukemia in the era of novel agents: a multicenter national study by the Greek Myeloma Study Group
Blood Cancer Journal (2018)