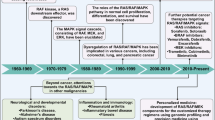
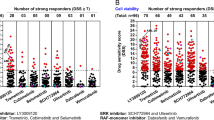
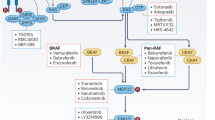
Abstract
The Ras/Raf/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway is often implicated in sensitivity and resistance to leukemia therapy. Dysregulated signaling through the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway is often the result of genetic alterations in critical components in this pathway as well as mutations at upstream growth factor receptors. Unrestricted leukemia proliferation and decreased sensitivity to apoptotic-inducing agents and chemoresistance are typically associated with activation of pro-survival pathways. Mutations in this pathway and upstream signaling molecules can alter sensitivity to small molecule inhibitors targeting components of this cascade as well as to inhibitors targeting other key pathways (for example, phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K)/phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN)/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)) activated in leukemia. Similarly, PI3K mutations can result in resistance to inhibitors targeting the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway, indicating important interaction points between the pathways (cross-talk). Furthermore, the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway can be activated by chemotherapeutic drugs commonly used in leukemia therapy. This review discusses the mechanisms by which abnormal expression of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway can contribute to drug resistance as well as resistance to targeted leukemia therapy. Controlling the expression of this pathway could improve leukemia therapy and ameliorate human health.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCubrey J, LaHair M, Franklin RA . Reactive oxygen species-induced activation of the MAP kinase signaling pathway. Antioxidants Redox Signal 2006; 8: 1745–1748.
Franklin R, Rodriquez-Mora O, La Hair M, McCubrey JA . Activation of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases as a consequence of oxidative stress. Antioxidants Redox Signal 2006; 8: 1807–1817.
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Kempf CR, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Stivala F et al. Therapeutic resistance resulting from mutations in Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. J Cell Physiol 2011; e-pub ahead of print 1 February 2011; doi:10.1002jcp22647.
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F et al. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 2007; 1773: 1263–1284.
Steelman LS, Abrams SL, Whelan J, Bertrand FE, Ludwig DE, Basecke J et al. Contributions of the Raf/MEK/ERK, PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR and JAK/STAT pathways to leukemia. Leukemia 2008; 22: 686–707.
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Abrams SL, Bertrand FE, Lugwig DE, Basecke J et al. Targeting survival vascades induced by activation of Raf/Raf/MEK/ERK, PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR and Jak/STAT pathways for effective leukemia therapy. Leukemia 2008; 22: 708–722.
Misaghian N, Ligresti G, Steelman LS, Bertand FE, Basecke J, Libra M et al. Targeting the leukemic stem cell—the holy grail of leukemia therapy. Leukemia 2009; 23: 25–42.
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Abrams SL, Chappell WH, Russo S, Ove R et al. Emerging Raf inhibitors. Exp Opin Emerging Drugs 2009; 14: 633–648.
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Abrams SL, Chappell WH, Russo S, Ove R et al. Emerging MEK inhibitors. Exp Opin Emerging Drugs 2010; 15: 203–223.
McCubrey JA, Abrams SL, Ligresti G, Misaghian N, Wong ET, Basecke J et al. Involvement of p53 and Raf/MEK/ERK pathways in hematopoietic drug resistance. Leukemia 2008; 22: 2080–2090.
Steelman LS, Abrams SL, Shelton JG, Chappell WH, Bäsecke J, Stivala F et al. Dominant roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell cycle progression, prevention of apoptosis and sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 1629–1638.
Abrams SL, Steelman LS, Shelton JG, Wong ET, Chappell WH, Bäsecke J et al. The Raf/MEK/ERK pathway can govern drug resistance, apoptosis and sensitivity to targeted therapy. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 1781–1791.
Kornblau SM, Womble M, Qiu YH, Jackson CE, Chen W, Konopleva M et al. Simultaneous activation of multiple signal transduction pathways confers poor prognosis in acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood 2006; 108: 2358–2365.
Casar B, Arozarena I, Sanz-Moreno V, Pinto A, Agudo-Ibáñez L, Marais R et al. Ras subcellular localization defines extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 substrate specificity through distinct utilization of scaffold proteins. Mol Cell Biol 2009; 29: 1338–1353.
Downward J . Targeting Ras signaling pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 11–22.
Hayashi K, Shibata K, Morita T, Iwasaki K, Watanabe M, Sobue K . Insulin receptor substrate-1/SHP-2 interaction, a phenotype-dependent switching machinery of insulin-like growth factor-I signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 40807–40818.
Marais R, Light Y, Paterson HF, Marshall CJ . Ras recruits Raf-1 to the plasma membrane for activation by tyrosine phosphorylation. EMBO J 1995; 14: 3136–3145.
Marais R, Light Y, Paterson HF, Mason CS, Marshall CJ . Differential regulation of Raf-1, A-Raf, and B-Raf by oncogenic ras and tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 4378–4383.
Mason CS, Springer CJ, Cooper RG, Superti-Furga G, Marshall CJ, Marais R . Serine and tyrosine phosphorylations cooperate in Raf-1, but not B-Raf activation. EMBO J 1999; 18: 2137–2148.
XU S, Robbins D, Frost J, Dang A, Lange-Carter C, Cobb MH . MEKK1 phosphorylates MEK1 and MEK2 but does not cause activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 6808–6812.
Derijard B, Raingeaud J, Barrett T, Wu IH, Han J, Ulevitch RJ et al. Independent human MAP kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms. Science 1995; 267: 682–685.
Xing J, Ginty DD, Greenberg ME . Coupling of the Ras-MAPK pathway to gene activation by Rsk2, a growth factor regulated CREB kinase. Science 1996; 273: 959–963.
Davis RJ . Transcriptional regulation by MAP kinases. Mol Reprod Dev 1995; 42: 459–467.
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Hoyle PE, Blalock WL, Weinstein-Oppenheimer C, Franklin RA et al. Differential abilities of activated Raf oncoproteins to abrogate cytokine-dependency, prevent apoptosis and induce autocrine growth factor synthesis in human hematopoietic cells. Leukemia 1998; 12: 1903–1929.
Hoyle PE, Moye PW, Steelman LS, Blalock WL, Franklin RA, Pearce M et al. Differential abilities of the Raf family of protein kinases to abrogate cytokine-dependency and prevent apoptosis in murine hematopoietic cells by a MEK1-dependent mechanism. Leukemia 2000; 14: 642–656.
Blalock WL, Pearce M, Steelman LS, Franklin RA, McCarthy SA, Cherwinski H et al. A conditionally-active form of MEK1 results in autocrine transformation of human and mouse hematopoeitic cells. Oncogene 2000; 19: 526–536.
Blalock WL, Moye PW, Chang F, Pearce M, Steelman LS, McMahon M et al. Combined effects of aberrant MEK1 activity and BCL2 overexpression on relieving the cytokine-dependency of human and murine hematopoietic cells. Leukemia 2000; 14: 1080–1096.
Moye PW, Blalock WL, Hoyle PE, Chang F, Franklin RA, Weinstein-Oppenheimer C et al. Between Raf and BCL2 in abrogating the cytokine-dependency of hematopoietic cells. Leukemia 2000; 14: 1060–1079.
Blalock WL, Pearce M, Chang F, Lee J, Pohnert S, Burrows C et al. Effects of inducible MEK1 activation on the cytokine-dependency of lymphoid cells. Leukemia 2001; 15: 794–807.
Weinstein-Oppenheimer CR, Henríquez-Roldán CF, Davis J, Navolanic PM, Saleh OA, Steelman LS et al. Role of the Raf signal transduction cascade in the in vitro resistance to the anticancer drug doxorubicin. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 2892–2907.
Davis JM, Weinstein-Oppenheimer CR, Steelman LS, Navolanic PN, Hu W, Konopleva M et al. Raf-1 and Bcl-2 induce distinct and common pathways which contribute to breast cancer drug resistance. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 1161–1170.
Balan V, Leicht DT, Zhu J, Balan K, Kaplun A, Singh-Gupta V et al. Identification of novel in vivo Raf-1 phosphorylation sites mediating positive feedback Raf-1 regulation by extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Mol Biol Cell 2006; 17: 1141–1153.
Dougherty MK, Muller J, Ritt DA, Zhou M, Zhou XZ, Copeland TD et al. Regulation of Raf-1 by direct feedback phosphorylation. Mol Cell 2005; 17: 215–224.
Brummer T, Naegele H, Reth M, Misawa Y . Identification of novel ERK-mediated feedback phosphorylation sites at the C-terminus of B-Raf. Oncogene 2003; 22: 8823–8834.
Catalanotti F, Reyes G, Jesenberger V, Galabova-Kovacs G, de Matos Simoes R, Carugo O et al. A Mek1-Mek2 heterodimer determines the strength and duration of the Erk signal. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2009; 16: 294–303.
Dong C, Waters SB, Holt KH, Pessin JE . SOS phosphorylation and disassociation of the Grb2-SOS complex by the ERK and JNK signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 6328–6332.
Dhillon AS, von Kriegsheim A, Grindlay J, Kolch W . Phosphatase and feedback regulation of Raf-1 signaling. Cell Cycle 2007; 6: 3–7.
von Kriegsheim A, Pitt A, Grindlay GJ, Kolch W, Dhillon AS . Regulation of the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway by protein phosphatase 5. Nat Cell Biol 2006; 8: 1011–1016.
Kim D, Rath O, Kolch W, Cho KH . A hidden oncogenic positive feedback loop caused by crosstalk between Wnt and ERK pathways. Oncogene 2007; 26: 4571–4579.
Schaeffer HJ, Catling AD, Eblen ST, Collier LS, Krauss A, Weber MJ . MP1: a MEK binding partner that enhances enzymatic activation of the MAP kinase cascade. Science 1998; 281: 1668–1671.
O’Neill E, Kolch W . Conferring specificity on the ubiquitous Raf/MEK signallingpathway. Br J Cancer 2004; 90: 283–288.
Kolch W . Coordinating ERK/MAPK signalling through scaffolds and inhibitors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005; 6: 827–837.
Hagan S, Garcia R, Dhillon A, Kolch W . Raf kinase inhibitor protein regulation of raf and MAPK signaling. Methods Enzymol 2006; 407: 248–259.
LaHair MM, Howe CJ, Rodriguez-Mora O, McCubrey JA, Franklin RA . Molecular pathways leading to oxidative stress-induced phosphorylation of Akt. Antioxidants Redox Signal 2006; 8: 1749–1756.
Rodriguez-Mora O, LaHair MM, Howe CJ, McCubrey JA, Franklin RA . The calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases as potential targets in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Tar 2005; 9: 791–808.
Weisberg E, Barrett R, Liu Q, Stone R, Gray N, Griffin JD . FLT3 inhibition and mechanisms of drug resistance in mutant FLT3-positive AML. Drug Resist Updat 2009; 12: 81–89.
von Bubnoff N, Gorantla SP, Engh RA, Oliveira TM, Thöne S, Aberg E et al. The low frequency of clinical resistance to PDGFR inhibitors in myeloid neoplasms with abnormalities of PDGFRA might be related to the limited repertoire of possible PDGFRA kinase domain mutations in vitro. Oncogene 2010; 30: 933–943.
Haslam K, Chadwick N, Kelly J, Browne P, Vandenberghe E, Flynn C et al. Incidence and significance of FLT3-ITD and NPM1 mutations in patients with normal karyotype acute myeloid leukaemia. Ir J Med Sci 2010; 179: 507–510.
Shih LY, Huang CF, Wang PN, Wu JH, Lin TL, Dunn P et al. Acquisition of FLT3 or N-ras mutations is frequently associated with progression of myelodysplastic syndrome to acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2004; 18: 466–475.
Bacher U, Haferlach T, Kern W, Haferlach C, Schnittger S . A comparative study of molecular mutations in 381 patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and in 4130 patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2007; 92: 744–752.
Shih LY, Lin TL, Wang PN, Wu JH, Dunn P, Kuo MC et al. Internal tandem duplication of fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 is associated with poor outcome in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Cancer 2004; 101: 989–998.
Armstrong SA, Mabon ME, Silverman LB, Li A, Gribben JG, Fox EA et al. FLT3 mutations in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2004; 103: 3544–3546.
Perentesis JP, Bhatia S, Boyle E, Shao Y, Shu XO, Steinbuch M et al. RAS oncogene mutations and outcome of therapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2004; 18: 685–692.
Hou P, Liu D, Xing M . The T1790A BRAF mutation (L597Q) in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia is a functional oncogene. Leukemia 2007; 21: 2216–2218.
Tartaglia M, Martinelli S, Cazzaniga G, Cordeddu V, Iavarone I, Spinelli M et al. Genetic evidence for lineage-related and differentiation stage-related contribution of somatic PTPN11 mutations to leukemogenesis in childhood acute leukemia. Blood 2004; 104: 307–313.
Case M, Matheson E, Minto L, Hassan R, Harrison CJ, Bown N et al. Mutation of genes affecting the RAS pathway is common in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 6803–6809.
Davidsson J, Lilljebjörn H, Panagopoulos I, Fioretos T, Johansson B . BRAF mutations are very rare in B- and T-cell pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Leukemia 2008; 22: 1619–1621.
Gustafsson B, Angelini S, Sander B, Christensson B, Hemminki K, Kumar R . Mutations in the BRAF and N-ras genes in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Leukemia 2005; 19: 310–312.
Christiansen DH, Andersen MK, Desta F, Pedersen-Bjergaard J . Mutations of genes in the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)/RAS-BRAF signal transduction pathway in therapy-related myelodysplasia and acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2005; 19: 2232–2240.
Pedersen-Bjergaard J, Andersen MK, Andersen MT, Christiansen DH . Genetics of therapy-related myelodysplasia and acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2008; 22: 240–248.
Christiansen DH, Desta F, Andersen MK, Pedersen-Bjergaard J . Mutations of the PTPN11 gene in therapy-related MDS and AML with rare balanced chromosome translocations. Genes Chromosomes Canc 2007; 46: 517–521.
Zebisch A, Staber PB, Delavar A, Bodner C, Hiden K, Fischereder K et al. Two transforming C-RAF germ-line mutations identified in patients with therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res 2006; 166: 3401–3408.
Makita Y, Narumi Y, Yoshida M, Niihori T, Kure S, Fujieda K et al. Leukemia in cardio-facio-cutaneous (CFC) syndrome: a patient with a germline mutation in BRAF proto-oncogene. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2007; 29: 287–290.
McMahon M . RAF translocations expand cancer targets. Nat Med 2010; 16: 749–750.
Palanisamy N, Ateeq B, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Pflueger D, Ramnarayanan K, Shankar S et al. Rearrangements of the RAF kinase pathway in prostate cancer, gastric cancer and melanoma. Nat Med 2010; 16: 793–798.
Borthakur G, Kantarjian H, Ravandi F, Zhang W, Konopleva M, Wright JJ et al. Phase 1 study of sorafenib in patients with refractory or relapsed acute leukemias. Haematologica 2010; 96: 62–68.
Crump M, Hedley D, Kamel-Reid S, Leber B, Wells R, Brandwein J et al. A randomized phase I clinical and biologic study of two schedules of sorafenib in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid leukemia: a NCIC (National Cancer Institute of Canada) Clinical Trials Group Study. Leuk Lymphoma 2011; 51: 252–260.
Zhang W, Konopleva M, Ruvolo VR, McQueen T, Evans RL, Bornmann WG et al. Sorafenib induces apoptosis of AML cells via Bim-mediated activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Leukemia 2008; 22: 808–818.
Yeung K, Seitz T, Li S, Janosch P, McFerran B, Kaiser C et al. Suppression of Raf-1 kinase activity and MAP kinase signalling by RKIP. Nature 1999; 401: 173–177.
Yeung K, Janosch P, McFerran B, Rose DW, Mischak H, Sedivy JM et al. Mechanism of suppression of the Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway by the Raf kinase inhibitor protein. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 3079–3085.
Corbit KC, Trakul N, Eves EM, Diaz B, Marshall M, Rosner MR . Activation of Raf-1 signaling by protein kinase C through a mechanism involving Raf kinase inhibitory protein. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 13061–13068.
Cho KH, Shin SY, Kim HW, Wolkenbauer O, McFerran B, Kolch W . Mathematical modeling of the influence of RKIP on the ERK signaling pathway. Comput Methods Syst Biol 2003, 127–141.
Park S, Rath O, Beach S, Xiang X, Kelly SM, Luo Z et al. Regulation of RKIP binding to the N-region of the Raf-1 kinase. FEBS Lett 2006; 580: 6405–6412.
Rath O, Park S, Tang HH, Banfield MJ, Brady RL, Lee YC et al. The RKIP (Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein) conserved pocket binds to the phosphorylated N-region of Raf-1 and inhibits the Raf-1-mediated activated phosphorylation of MEK. Cell Signal 2008; 20: 935–941.
Shin SY, Rath O, Choo SM, Fee F, McFerran B, Kolch W et al. Positive- and negative-feedback regulations coordinate the dynamic behavior of the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signal transduction pathway. J Cell Sci 2009; 122: 425–435.
Beach S, Tang H, Park S, Dhillon AS, Keller ET, Kolch W et al. Snail is a repressor of RKIP transcription in metastatic prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 2008; 27: 2243–2248.
Yeung KC, Rose DW, Dhillon AS, Yaros D, Gustafsson M, Chatterjee D et al. Raf kinase inhibitor protein interacts with NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and TAK1 and inhibits NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 7207–7217.
Odabaei G, Chatterjee D, Jazirehi AR, Goodglick L, Yeung K, Bonavida B . Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein: structure, function, regulation of cell signaling, and pivotal role in apoptosis. Adv Cancer Res 2004; 91: 169–200.
Keller ET, Fu Z, Brennan M . The role of Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) in health and disease. Biochem Pharmacol 2004; 68: 1049–1053.
Hagan S, Al-Mulla F, Mallon E, Oien K, Ferrier R, Gusterson B et al. Reduction of Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein expression correlates with breast cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 7392–7397.
Baritaki S, Katsman A, Chatterjee D, Yeung KC, Spandidos DA, Bonavida B . Regulation of tumor cell sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by the metastatic suppressor Raf kinase inhibitor protein via Yin Yang 1 inhibition and death receptor 5 up-regulation. J Immunol 2007; 179: 5441–5453.
Chatterjee D, Bai Y, Wang Z, Beach S, Mott S, Roy R et al. RKIP sensitizes prostate and breast cancer cells to drug-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 17515–17523.
Baritaki S, Yeung K, Palladino M, Berenson J, Bonavida B . Pivotal roles of snail inhibition and RKIP induction by the proteasome inhibitor NPI-0052 in tumor cell chemoimmunosensitization. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 8376–8385.
Zebisch A, Haller M, Hiden K, Goebel T, Hoefler G, Troppmair J et al. Loss of Raf kinase inhibitor protein is a somatic event in the pathogenesis of therapy-related acute myeloid leukemias with c-RAF germline mutations. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1049–1053.
Wilson BE, Mochon E, Boxer LM . Induction of bcl-2 expression by phosphorylated CREB proteins during B-cell activation and rescue from apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 1996; 16: 5546–5556.
Thomas A, El Rouby S, Reed JC, Krajewski S, Silber R, Potmesil M et al. Drug-induced apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: relationship between p53 gene mutation and bcl-2/bax proteins in drug resistance. Oncogene 1996; 12: 1055–1062.
Nuessler V, Stötzer O, Gullis E, Pelka-Fleischer R, Pogrebniak A, Gieseler F et al. Bcl-2, bax and bcl-xL expression in human sensitive and resistant leukemia cell lines. Leukemia 1999; 13: 1864–1872.
Buggins AG, Pepper CJ . The role of Bcl-2 family proteins in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Leuk Res 2010; 34: 837–842.
Capitani N, Baldari CT . The Bcl-2 family as a rational target for the treatment of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Curr Med Chem 2010; 17: 801–811.
McCubrey JA, May WS, Duronio V, Mufson A . Serine/threonine phosphorylation in cytokine signal transduction. Leukemia 2000; 14: 9–21.
Deng X, Kornblau SM, Ruvolo PP, Way Jr WS . Regulation of Bcl2 phosphorylation and potential significance for leukemic cell chemoresistance. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 2001; 28: 30–37.
Harada H, Quearry B, Ruiz-Vela A, Korsmeyer SJ . Survival factor-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylates BIM, inhibiting its association with BAX and proapoptotic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 15313–15317.
Domina AM, Vrana JA, Gregory MA, Hann SR, Craig RW . MCL1 is phosphorylated in the PEST region and stabilized upon ERK activation in viable cells, and at additional sites with cytotoxic okadaic acid or taxol. Oncogene 2004; 23: 5301–5315.
High LM, Szymanska B, Wilczynska-Kalak U, Barber N, O’Brien R, Khaw SL et al. The Bcl-2 homology domain 3 mimetic ABT-737 targets the apoptotic machinery in acute lymphoblastic leukemia resulting in synergistic in vitro and in vivo interactions with established drugs. Mol Pharmacol 2010; 77: 483–494.
Kuroda J, Kimura S, Andreeff M, Ashihara E, Kamitsuji Y, Yokota A et al. ABT-737 is a useful component of combinatory chemotherapies for chronic myeloid leukaemias with diverse drug-resistance mechanisms. Br J Haematol 2008; 140: 181–190.
Stolz C, Hess G, Hähnel PS, Grabellus F, Hoffarth S, Schmid KW et al. Targeting Bcl-2 family proteins modulates the sensitivity of B-cell lymphoma to rituximab-induced apoptosis. Blood 2008; 112: 3312–3321.
Paoluzzi L, Gonen M, Bhagat G, Furman RR, Gardner JR, Scotto L et al. The BH3-only mimetic ABT-737 synergizes the antineoplastic activity of proteasome inhibitors in lymphoid malignancies. Blood 2008; 112: 2906–2916.
Pepper C, Lin TT, Pratt G, Hewamana S, Brennan P, Hiller L et al. Mcl-1 expression has in vitro and in vivo significance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is associated with other poor prognostic markers. Blood 2008; 112: 3807–3817.
Zimmerman EI, Dollins CM, Crawford M, Grant S, Nana-Sinkam SP, Richards KL et al. Lyn kinase-dependent regulation of miR181 and myeloid cell leukemia-1 expression: implications for drug resistance in myelogenous leukemia. Mol Pharmacol 2010; 78: 811–817.
Stewart ML, Fire E, Keating AE, Walensky LD . MCL-1 BH3 helix is an exclusive MCL-1 inhibitor and apoptosis sensitizer. Nat Chem Biol 2010; 6: 595–601.
Balakrishnan K, Burger JA, Wierda WG, Gandhi V . AT-101 induces apoptosis in CLL B cells and overcomes stromal cell-mediated Mcl-1 induction and drug resistance. Blood 2009; 113: 149–153.
Brunelle JK, Ryan J, Yecies D, Opferman JT, Letai A . MCL-1-dependent leukemia cells are more sensitive to chemotherapy than BCL-2-dependent counterparts. J Cell Biol 2009; 187: 429–442.
Ley R, Ewings KE, Hadfield K, Cook SJ . Regulatory phosphorylation of Bim: sorting out the ERK from JNK. Cell Death Differ 2005; 12: 1008–1014.
Qi XJ, Wildey GM, Howe PH . Evidence that Ser87 of BimEL is phosphorylated by Akt and regulates BimEL apoptotic function.J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 813–823.
Gillings AS, Balmanno K, Wiggins CM, Johnson M, Cook SJ . Apoptosis and autophagy: BIM as a mediator of tumour cell death in response to oncogene-targeted therapeutics. FEBS J 2009; 276: 6050–6062.
Lei K, Davis RJ . JNK phosphorylation of Bim-related members of the Bcl2 family induces Bax-dependent apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 2432–2437.
Myatt SS, Lam EWF . The emerging roles of forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 847–859.
Bachmann PS, Piazza RG, Janes ME, Wong NC, Davies C, Mogavero A et al. Epigenetic silencing of BIM in glucocorticoid poor-responsive pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and its reversal by histone deacetylase inhibition. Blood 2010; 116: 3013–3022.
Hazlehurst LA, Argilagos RF, Dalton WS . Beta1 integrin mediated adhesion increases Bim protein degradation and contributes to drug resistance in leukaemia cells. Br J Haematol 2007; 136: 269–275.
Meads MB, Hazlehurst LA, Dalton WS . The bone marrow microenvironment as a tumor sanctuary and contributor to drug resistance. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 2519–2526.
Nair RR, Tolentino J, Hazlehurst LA . The bone marrow microenvironment as a sanctuary for minimal residual disease in CML. Biochem Pharmacol 2010; 80: 602–612.
Podar K, Chauhan D, Anderson KC . Bone marrow microenvironment and the identification of new targets for myeloma therapy. Leukemia 2009; 23: 10–24.
Kuribara R, Honda H, Matsui H, Shinjyo T, Inukai T, Sugita K et al. Roles of Bim in apoptosis of normal and Bcr-Abl-expressing hematopoietic progenitors. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 6172–6183.
Shinjyo T, Kuribara R, Inukai T, Hosoi H, Kinoshita T, Miyajima A et al. Downregulation of Bim, a proapoptotic relative of Bcl-2, is a pivotal step in cytokine-initiated survival signaling in murine hematopoietic progenitors. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 854–864.
Kuroda J, Puthalakath H, Cragg MS, Kelly PN, Bouillet P, Huang DC et al. Bim and Bad mediate imatinib-induced killing of Bcr/Abl+ leukemic cells, and resistance due to their loss is overcome by a BH3 mimetic. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 14907–14912.
Essafi A, Fernández de Mattos S, Hassen YA, Soeiro I, Mufti GJ, Thomas NS et al. Direct transcriptional regulation of Bim by FoxO3a mediates STI571-induced apoptosis in Bcr-Abl-expressing cells. Oncogene 2005; 24: 2317–2329.
Scheijen B, Ngo HT, Kang H, Griffin JD . FLT3 receptors with internal tandem duplications promote cell viability and proliferation by signaling through Foxo proteins. Oncogene 2004; 23: 3338–3349.
Weisberg E, Sattler M, Ray A, Griffin JD . Drug resistance in mutant FLT3-positive AML. Oncogene 2010; 29: 5120–5134.
Chapuis N, Park S, Leotoing L, Tamburini J, Verdier F, Bardet V et al. IκB kinase overcomes PI3K/Akt and ERK/MAPK to control FOXO3a activity in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2010; 116: 4240–4250.
Graff JR, Konicek BW, Carter JH, Marcusson EG . Targeting the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E for cancer therapy. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 631–664.
Chapuis N, Tamburini J, Green AS, Willems L, Bardet V, Park S et al. Perspectives on inhibiting mTOR as a future treatment strategy for hematological malignancies. Leukemia 2010; 24: 1686–1699.
Sonenberg N, Hinnebusch AG . New modes of translational control in development, behavior and disease. Mol Cell 2007; 28: 721–729.
Wendel HG, De Stanchina E, Friedman JS, Malina A, Ray S, Kogan S et al. Survival signalling by Akt and eIF4E in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Nature 2004; 428: 332–337.
Roux PP, Shahbazian D, Vu H, Holz MK, Cohen MS, Taunton J et al. RAS/ERK signaling promotes site-specific ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation via RSK and stimulates Cap-dependent translation. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 14056–14064.
Shahbazian D, Roux PP, Mieulet V, Cohen MS, Raught B, Tauton J et al. The mTOR/PI3K and MAPK pathways converge on eIF4B to control its phosphorylation and activity. EMBO J 2006; 25: 2781–2791.
Bordeleau ME, Robert F, Gerard B, Lindqvist L, Chen SM, Wendel HG et al. Therapeutic suppression of translation initiation modulates chemosensitivity in a mouse lymphoma model. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 2651–2660.
Malina A, Mills JR, Zhu H, Ueda T, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Fukunaga R et al. Dissecting eIF4E action in tumorigenesis. Genes Dev 2007; 21: 3232–3237.
Waskiewicz AJ, Flynn A, Proud CG, Cooper JA . Mitogen-activated protein kinases activate the serine/threonine kinases Mnk1 and Mnk2. EMBO J 1997; 16: 1909–1920.
Waskiewicz AI, Hohnson JC, Penn B, Mahalingam M, Kimball SR, Cooper JA . Phosphoryaltion of the cap-binding protein eukaryotic translation initation factor 4E by protein kinase Mnk in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 1871–1880.
Wendel HG, Silva RL, Malina A, Mills JR, Zhu H, Ueda T et al. Dissecting eIF4E action in tumorigenesis. Genes Dev 2007; 21: 3232–3237.
Silva RL, Wendel HG . MNK, EIF4E and targeting translation for therapy. Cell Cycle 2008; 7: 553–555.
Ueda T, Watanabe Fukunga R, Fujuyama H, Nagata S, Fukunga R . Mnk2 and Mnk1 are essential for constitutive and inducible phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E but not for cell growth or development. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 6539–6549.
Ueda T, Sasaki M, Elia AJ, Chio II, Hamada K, Fukunaga R et al. Combined deficiency for MAP kinase-interacting kinase 1 and 2 (Mnk1 and Mnk2) delays tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 13984–13990.
Nardella C, Chen Z, Salmena L, Carracedo A, Alimonti A, Egia A et al. Aberrant Rheb-mediated mTORC1 activation and Pten haploinsufficiency are cooperative oncogenic events. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 2172–2177.
Lassman AB, Rossi MR, Raizer JJ, Abrey LE, Lieberman FS, Grefe CN et al. Molecular study of malignant gliomas treated with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors: tissue analysis from North American Brain Tumor Consortium Trials 01-03 and 00-01. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 7841–7850.
Leseux L, Hamdi SM, Al Saati T, Capilla F, Recher C, Laurent G et al. Syk-dependent mTOR activation in follicular lymphoma cells. Blood 2006; 108: 4156–4162.
Peponi E, Drakos E, Reyes G, Leventaki V, Rassidakis GZ, Medeiros LJ . Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling promotes cell cycle progression and protects cells from apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma. Am J Pathol 2006; 169: 2171–2180.
Lu ZH, Shvartsman MB, Lee AY, Shao JM, Murray MM, Kladney RD et al. Mammalian target of rapamycin activator RHEB Is frequently overexpressed in human carcinomas and is critical and sufficient for skin epithelial carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 3287–3298.
Lin AW, Barradas M, Stone JC, van Aelst L, Serrano M, Lowe SW . Premature senescence involving p53 and p16 is activated in response to constitutive MEK/MAPK mitogenic signaling. Genes Dev 1998; 12: 3008–3019.
Mavrakis KJ, Zhu H, Silva RL, Mills JR, Teruya-Feldstein J, Lowe SW et al. Tumorigenic activity and therapeutic inhibition of Rheb GTPase. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 2178–2288.
Moerke NJ, Aktas H, Chen H, Cantel S, Reibarkh MY, Fahmy A et al. Small-molecule inhibition of the interaction between the translation initiation factors eIF4E and eIF4G. Cell 2007; 128: 257–267.
Tamburini J, Green AS, Bardet V, Chapuis N, Park S, Willems L et al. Protein synthesis is resistant to rapamycin and constitutes a promising therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2009; 114: 1618–1627.
Kentsis A, Topisirovic I, Culjkovic B, Shao L, Borden KL . Ribavirin suppresses eIF4E-mediated oncogenic transformation by physical mimicry of the 7-methyl guanosine mRNA cap. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 18105–18110.
Kentsis A, Volpon L, Topisirovic I, Soll CE, Culjkovic B, Shao L et al. Further evidence that ribavirin interacts with eIF4E. RNA 2005; 11: 1762–1766.
Assouline S, Culjkovic B, Cocolakis E, Rousseau C, Beslu N, Amri A et al. Molecular targeting of the oncogene eIF4E in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): a proof-of-principle clinical trial with ribavirin. Blood 2009; 114: 257–260.
Hall-Jackson CA, Eyers PA, Cohen P, Goedert M, Boyle FT, Hewitt N et al. Paradoxical activation of Raf by a novel Raf inhibitor. Chem Biol 1999; 6: 559–568.
Lee Jr JT, McCubrey JA . Targeting the Raf kinase cascade in cancer therapy—novel molecular targets and therapeutic strategies. Expert Opin Ther Tar 2002; 6: 659–678.
Shelton JG, Moye PW, Steelman LS, Blalock WL, Lee JT, Franklin RA et al. Differential effects of kinase cascade inhibitors on neoplastic and cytokine-mediated cell proliferation. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1765–1782.
Heidorn SJ, Milagre C, Whittaker S, Nourry A, Niculescu-Duvas I, Dhomen N et al. Kinase-dead BRAF and oncogenic RAS cooperate to drive tumor progression through CRAF. Cell 2010; 140: 209–221.
Hatzivassiliou G, Song K, Yen I, Brandhuber BJ, Anderson DJ, Alvarado R et al. RAF inhibitors prime wild-type RAF to activate the MAPK pathway and enhance growth. Nature 2010; 464: 431–435.
Poulikakos PI, Zhang C, Bollag G, Shokat KM, Rosen N . RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signalling in cells with wild-type BRAF. Nature 2010; 464: 427–430.
Sebolt-Leopold JS, English JM . Mechanisms of drug inhibition of signaling molecules. Nature 2006; 441: 457–462.
Pratilas CA, Hanrahan AJ, Halilovic E, Persaud Y, Soh J, Chitale D et al. Genetic predictors of MEK dependence in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 9375–9383.
Dry JR, Pavey S, Pratilas CA, Harbron C, Runswick S, Hodgson D et al. Transcriptional pathway signatures predict MEK addiction and response to selumetinib (AZD6244). Cancer Res 2010; 70: 2264–2273.
Pratilas CA, Taylor BS, Ye Q, Viale A, Sander C, Solit DB et al. V600E)BRAF is associated with disabled feedback inhibition of RAF-MEK signaling and elevated transcriptional output of the pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 4519–4524.
Emery CM, Vijayendran KG, Zipser MC, Sawyer AM, Niu L, Kim JJ et al. MEK1 mutations confer resistance to MEK and B-RAF inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 20411–20416.
Ohren JF, Chen H, Pavlovsky A, Whitehead C, Zhang E, Kuffa P et al. Structures of human MAP kinase kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2 describe novel noncompetitive kinase inhibition. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2004; 11: 1192–1197.
Halilovic E, She QB, Ye Q, Pagliarini R, Sellers WR, Solit DB et al. PIK3CA mutation uncouples tumor growth and cyclin D1 regulation from MEK/ERK and mutant KRAS signaling. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 6804–6814.
Joseph EW, Pratilas CA, Poulikakos PI, Tadi M, Wang W, Taylor BS et al. The RAF inhibitor PLX4032 inhibits ERK signaling and tumor cell proliferation in a V600E BRAF-selective manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 14903–14908.
She QB, Halilovic E, Ye Q, Zhen W, Shirasawa S, Sasazuki T et al. 4E-BP1 is a key effector of the oncogenic activation of the AKT and ERK signaling pathways that integrates their function in tumors. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 39–51.
Pratilas CA, Solit DB . Targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway: physiological feedback and drug response. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 3329–3334.
Marks JL, Gong Y, Chitale D, Golas B, McLellan MD, Kasai Y et al. Novel MEK1 mutation identified by mutational analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway genes in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 5524–5528.
Smalley KS, Lioni M, Dalla Palma M, Xiao M, Desai B, Egyhazi S et al. Increased cyclin D1 expression can mediate BRAF inhibitor resistance in BRAF V600E-mutated melanomas. Mol Cancer Ther 2008; 7: 2876–2883.
Di Nicolantonio F, Arena S, Tabernero J, Grosso S, Molinari F, Macarulla T et al. Deregulation of the PI3K and KRAS signaling pathways in human cancer cells determines their response to everolimus. J Clin Invest 2010; 120: 2858–2866.
Lauchle JO, Kim D, Le DT, Akagi K, Crone M, Krisman K et al. Response and resistance to MEK inhibition in leukaemias initiated by hyperactive Ras. Nature 2009; 461: 411–414.
Lauchle JO, Braun BS, Loh ML, Shannon K . Inherited predispositions and hyperactive Ras in myeloid leukemogenesis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2006; 46: 579–585.
Le DT, Kong N, Zhu Y, Lauchle JO, Aiyigari A, Braun BS et al. Somatic inactivation of Nf1 in hematopoietic cells results in a progressive myeloproliferative disorder. Blood 2004; 103: 4243–4250.
Shah NP, Nicoll JM, Nagar B, Gorre ME, Paquette RL, Kuriyan J et al. Multiple BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations confer polyclonal resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib (STI571) in chronic phase and blast crisis chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2002; 2: 117–125.
Choi S, Henderson MJ, Kwan E, Beesley AH, Sutton R, Bahar AY et al. Relapse in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia involving selection of a preexisting drug-resistant subclone. Blood 2007; 110: 632–639.
Montagut C, Sharma SV, Shioda T, McDermott U, Ullman M, Ulkus LE et al. Elevated CRAF as a potential mechanism of acquired resistance to BRAF inhibition in melanoma. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 4853–4861.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from Fondazione del Monte di Bologna e Ravenna, MinSan 2008, ‘Molecular therapy in pediatric sarcomas and leukemias against IGF-1 receptor system’ (PRIN 2008 and FIRB 2010 (RBAP10447J)) to AMM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steelman, L., Franklin, R., Abrams, S. et al. Roles of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in leukemia therapy. Leukemia 25, 1080–1094 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.66
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.66
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mast cell deficiency prevents BCR::ABL1 induced splenomegaly and cytokine elevation in a CML mouse model
Leukemia (2023)
-
Combination of RSK inhibitor LJH-685 and FLT3 inhibitor FF-10101 promoted apoptosis and proliferation inhibition of AML cell lines
Cellular Oncology (2022)
-
Temporal multiomic modeling reveals a B-cell receptor proliferative program in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Leukemia (2021)
-
Small-molecule inhibitor targeting the Hsp70-Bim protein–protein interaction in CML cells overcomes BCR-ABL-independent TKI resistance
Leukemia (2021)
-
Pan-RAF inhibition induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells and synergizes with BCL2 inhibition
Leukemia (2020)